Create Atomic Metrics
1 Concept
Atomic metrics are metrics that cannot be further decomposed in business definitions. They are the most basic metrics, and subsequent composite metrics and derived metrics can be created based on atomic metrics. Atomic metrics are typically measurements under a specific business event behavior, used to quantitatively统计 products or business performance, usually through aggregation calculations, such as net profit = sum(order net profit), total transaction volume = count(distinct order number).
2 Operation Steps
-
Select "Metrics Center > Metric Topics" in the navigation bar, click the "New Metric" button, and select "Atomic Metric".
-
In the "New Atomic Metric" dialog, set the basic properties, calculation properties, and management properties of the atomic metric.
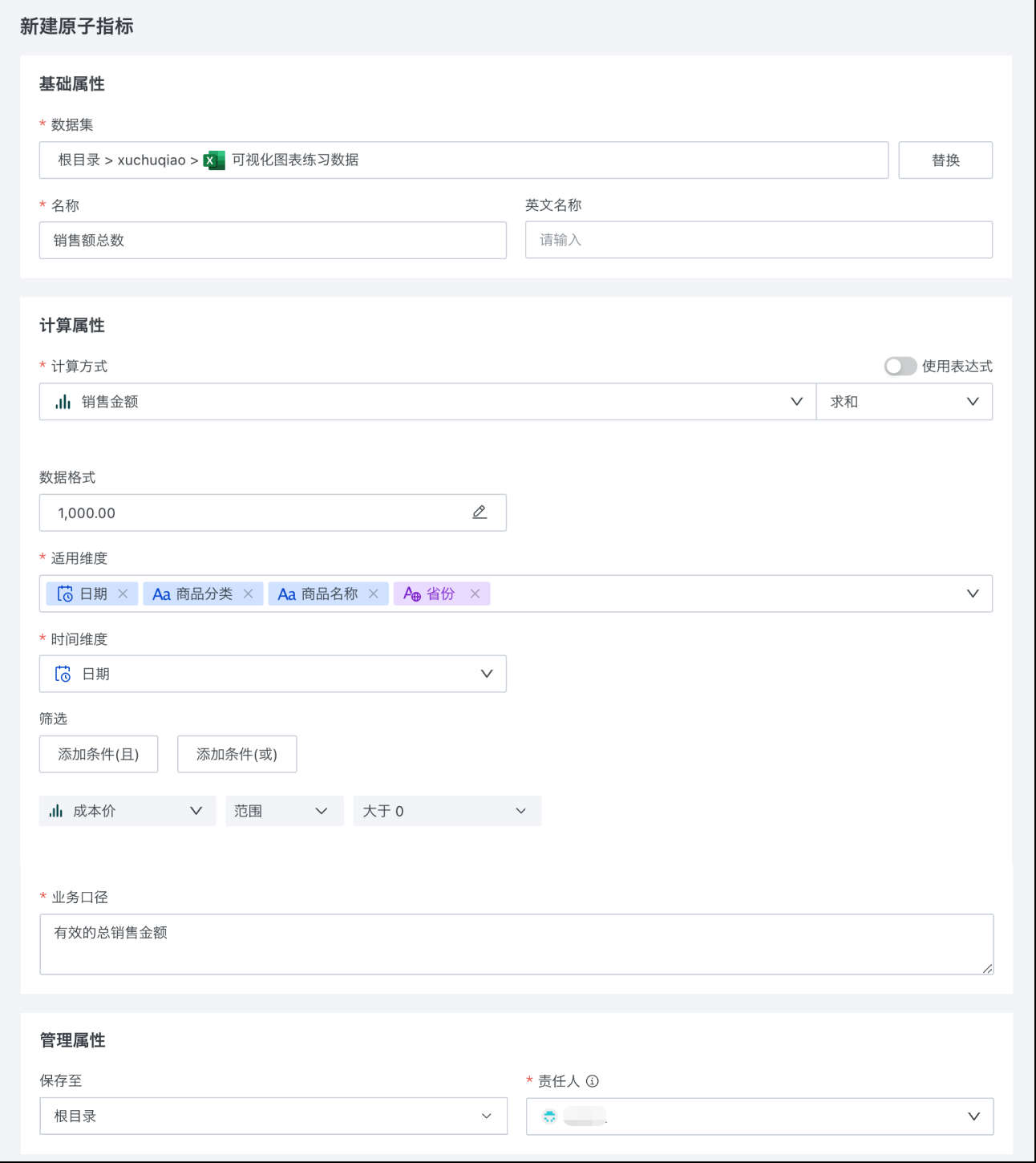
Basic Properties:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Dataset | Select a dataset with usage permissions to create metrics using the content of this dataset. |
| Name | Set the Chinese name of the metric, which cannot be duplicated within a topic. |
| English Name | Set the English name of the metric, which cannot be duplicated within a topic. |
Calculation Properties:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method |  Note: The outermost layer of the expression must be an aggregation function. 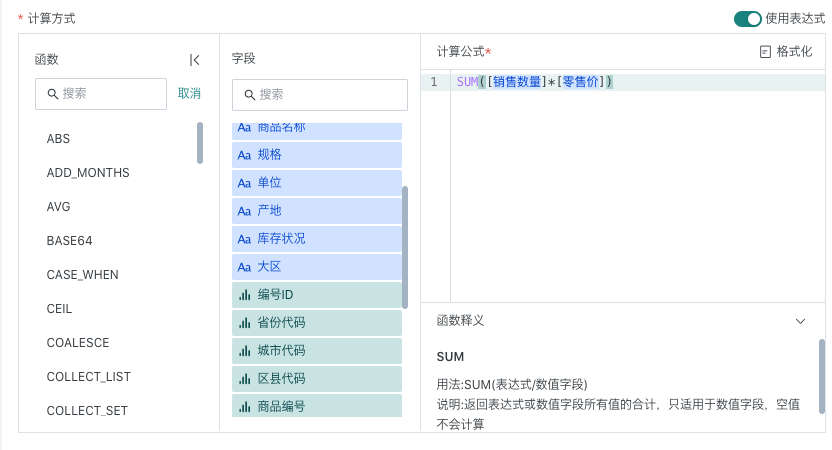 |
| Data Format | Set the display format of the metric result. |
| Applicable Dimensions | Select fields from the dataset as dimensions for subsequent metric analysis under different dimensions. When there are time fields in applicable dimensions, they can be selected as time dimensions for subsequent time-related derivative configurations. 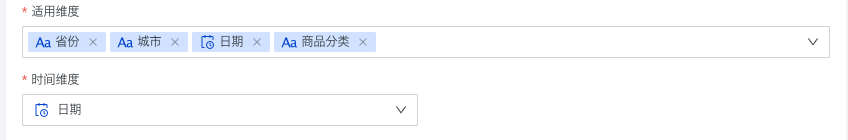 |
| Filter Conditions | Supports adding multiple filter conditions. When calculating metric values, the final result will be calculated according to the filter conditions. 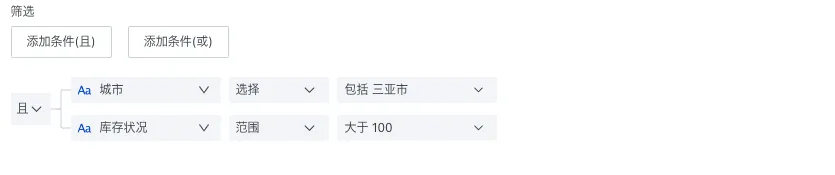 |
| Business Definition | Maintain the business meaning of the metric for subsequent metric applications. |
Management Properties:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Save Location | Set the save location for this metric. |
| Responsible Person | The person responsible for explaining the business definition, responsible for the reasonableness and accuracy of the business definition. |
3 Query Acceleration
Query acceleration configuration is added to the atomic metric details page, supporting configuration of multiple groups of metrics' source datasets, source fields, and aggregation methods (only supports sum and count). It also supports priority sorting. When querying metric data, it will prioritize querying from datasets with higher priority.
In principle, metrics are created on detail tables with sufficiently comprehensive applicable dimensions. The associated query acceleration tables are summary tables/dimension reduction tables of this table.
Example: Atomic metric sum(sales revenue), the source dataset when defining the metric is Table 1, with dimensions of Province, City, District, Store. Associated tables are Table 2 and Table 3. Priority is set as Table 3 > Table 2 > Table 1.
Table 1
| Province | City | District | Store | Sales Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | A | A | a | 1 |
| A | A | A | b | 2 |
| B | B | B | c | 3 |
| C | C | C | d | 4 |
| C | D | D | f | 5 |
Table 2
| Province | City | District | Sales Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | A | A | 1+2 |
| B | B | B | 3 |
| C | C | C | 4 |
| C | D | D | 5 |
Table 3
| Province | Sales Revenue |
|---|---|
| A | 1+2 |
| B | 3 |
| C | 4+5 |
-
When dimension and filter fields all exist in Table 3, query from Table 3;
-
If applicable dimensions don't exist in Table 3, check if they exist in Table 2, query from Table 2;
-
If applicable dimensions don't exist in both Table 3 and Table 2, then directly query from Table 1.
4 Examples
(1)Inventory Market Value
Calculation Logic: Within the statistical date, each store's inventory market value = product tag price * inventory quantity
Table Structure: Date, Store, Category, SKC, Price, Inventory Quantity
- Calculation Definition:
sum(price * inventory_quantity)
- Applicable Dimensions: Store, Category, Date
(2)In-Hand Style Count
Calculation Logic: Count the number of product styles with inventory in the store
Table Structure: Date, Store, SKC, In-Hand Inventory Quantity
- Calculation Definition:
count(distinct concat(`store`, '_', `SKC`)
- Applicable Dimensions: Date, Store
- Filter: In-Hand Inventory Quantity > 0
(3)R&D Person-Day Statistics
Calculation Logic: R&D person-days = total work hours / standard work hours. Before 2025, the standard work hours per day is 7 hours, after 2025, the standard work hours per day is 8 hours. Calculate the average person-days within the statistical date
Table Structure: Date, Total Work Hours
- Calculation Definition:
SUM(CASE
WHEN ([date] < '2025-01-01') THEN ([total_work_hours])/7
ELSE [total_work_hours]/8
END
)
- Applicable Dimensions: Date