Create Derived Metrics
1 Concept
Derived metrics are calculated based on a single metric (atomic metric, derived metric, composite metric) and can be combined with dimensions, statistics, or management properties, such as creating year-over-year net profit based on net profit.
2 Operation Steps
-
In the "Metric Topics" page, click the "New Metric" button and select "Derived Metric".
-
Set basic properties:
- Name/English Name: Set the Chinese and English names of the metric, which cannot be duplicated within a topic.
-
Set calculation properties:
- Derivation Method: Supports year-over-year/period-over-period, recent N days/weeks/months/quarters/years, cumulative calculations, end-of-period values, and combined derivations. For detailed descriptions, see Year-over-Year/Period-over-Period Metrics, Recent N Days/Weeks/Months/Quarters/Years Metrics, Cumulative Calculation Metrics, End-of-Period Value Metrics, Combined Derivation Metrics.
- Derived From: Select a metric that the user has permission to use, and create a derived metric based on this metric. When the derivation method is year-over-year/period-over-period, it can also be derived from metrics with derivation types of recent N days, cumulative calculations, and combined derivations. Other derivation methods only support derivation from atomic metrics and composite metrics.
- Applicable Dimensions: By default inherits the "Applicable Dimensions" from the original metric, cannot be modified/edited, and can be used for metric analysis under different dimensions in the future.
- Time Dimension: By default inherits the "Time Dimension" from atomic metrics and composite metrics, cannot be modified/edited. For year-over-year/period-over-period type derived metrics, it specifies the date dimension used as the basis for year-over-year/period-over-period calculations.
- Data Format: Set the display format of the metric result.
- Business Definition: Maintain the business meaning of the metric for subsequent metric applications.
-
Set management properties:
- Save Location: Supports adding multiple filter conditions. When calculating metric values, the final result will be calculated according to the filter conditions.
- Responsible Person: The person responsible for explaining the business definition, responsible for the reasonableness and accuracy of the business definition.
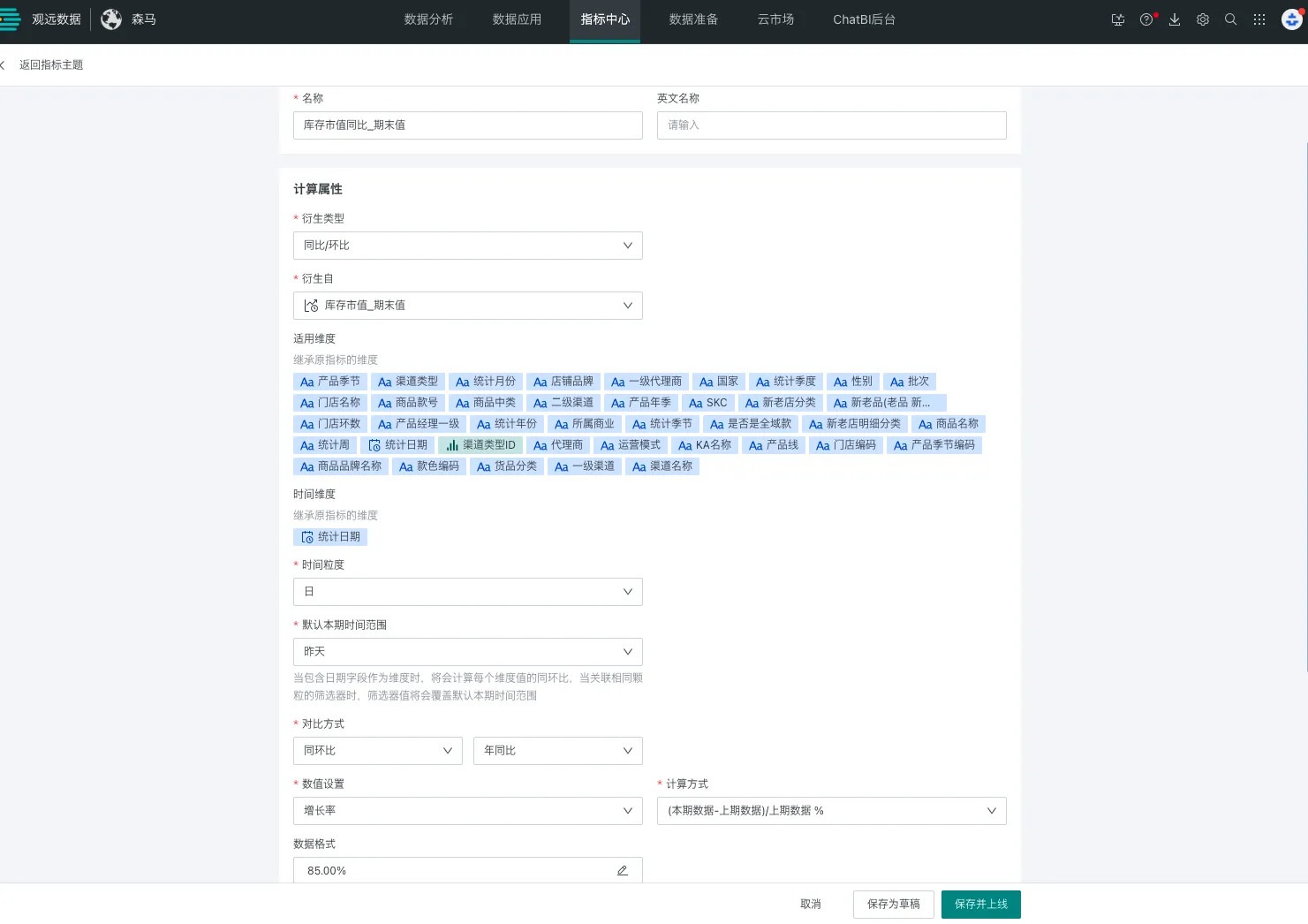
3 Year-over-Year/Period-over-Period Metrics
Year-over-year and period-over-period metrics are two commonly used comparative analysis methods in data analysis that help us evaluate time series changes in data. Year-over-year refers to the growth or decline ratio compared to the same period last year. It is used to measure the trend of data changes over time, especially in annual reports. Period-over-period refers to the growth or decline ratio compared to the previous period (such as the previous month, previous quarter). Period-over-period is usually used for short-term data comparisons, helping us understand recent changes in data.
When "Derivation Method" is configured as year-over-year/period-over-period in calculation properties, the following content needs to be configured:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Granularity | Supports year-over-year/period-over-period calculations under different time granularities: Year, Quarter, Month, Week, Day |
| Default Current Period Time Range | Refers to the data corresponding to the current cycle or period. For year-over-year/period-over-period by day granularity, provides richer configuration: Special Notes: |
| Comparison Method | According to the configuration of time granularity and time range, supports different comparison types. The year-over-year/period-over-period calculations supported by different time granularities are shown in the table below:
|
| Previous Period Time Range | Refers to the data corresponding to the previous cycle or period. When the comparison method is custom time range, specific dates or an interval can be specified. |
| Value Settings | Guandata provides three calculation types: growth value, growth rate, and comparison value. Below are detailed descriptions of the three calculation types:(Current period data - Previous period data) / Previous period data % or (Current period data - Previous period data) / abs(Previous period data) %. |
Year-over-year/period-over-period calculations supported by different time granularities:
| Time Granularity | Supported Year-over-Year/Period-over-Period Calculations |
|---|---|
| Year Granularity | Year-over-Year, Custom Offset |
| Quarter Granularity | Quarter-over-Quarter, Year-over-Year, End-of-Period Value - End of Last Year, Custom Offset |
| Month Granularity | Month-over-Month, Year-over-Year, End-of-Period Value - End of Last Quarter, End-of-Period Value - End of Last Year, Custom Offset |
| Week Granularity | Week-over-Week, Year-over-Year, Custom Offset |
| Day Granularity and Time | Day-over-Day, Week-over-Year, Month-over-Year, Quarter-over-Year, Year-over-Year, Custom Offset End-of-Period Value - End of Last Month, End-of-Period Value - End of Last Quarter, End-of-Period Value - End of Last Year, Custom Offset |
3.1 Specified Time Range Year-over-Year/Period-over-Period Derived Metrics
Users want to perform metric analysis using text fields as dimensions, such as viewing the year-over-year growth of a certain metric's current month data this year by region dimension. You can specify the time range of current period data in the default current period time range configuration item.
Since year-over-year/period-over-period calculations are performed over a time range, the current period time here is equivalent to adding a filter to the current year-over-year/period-over-period reference time field. Taking month granularity as an example, if "This Month" is selected here, it means the current period data is the data of the current month.
3.2 Dynamically Determine Time Range Year-over-Year/Period-over-Period Derived Metrics Based on Dimension Values
When users want to use time dimensions as analysis dimensions for metrics and dynamically calculate derived metric values at different time points, they can drag the time dimension into the analysis dimensions in the metric analysis card.
- The current period time range is determined by the corresponding time dimension value, which will override the default value configured in the metric.
- The previous period time range is calculated by offset according to the comparison type:
- The current period time range is the dimension value of each row of data, such as [July 10, 2024]
- Previous period time range:
- When selecting year-over-year/period-over-period, no configuration is needed. For example, if the comparison type selects month-over-year, the previous period time range is [June 10, 2024]
- When selecting end-of-period value, configuration is needed. Specify end of last month/quarter/year, such as if the comparison type selects end-of-period value - end of last month, the previous period time range is [June 30, 2024]
- When selecting custom offset, configuration is needed. Use corresponding units for offset by day, week, month, year, configuring the interval of X days/weeks/months/years between current period and previous period. For example, if configuring an interval of 3 days between current period and previous period, the previous period time range is [July 7, 2024].
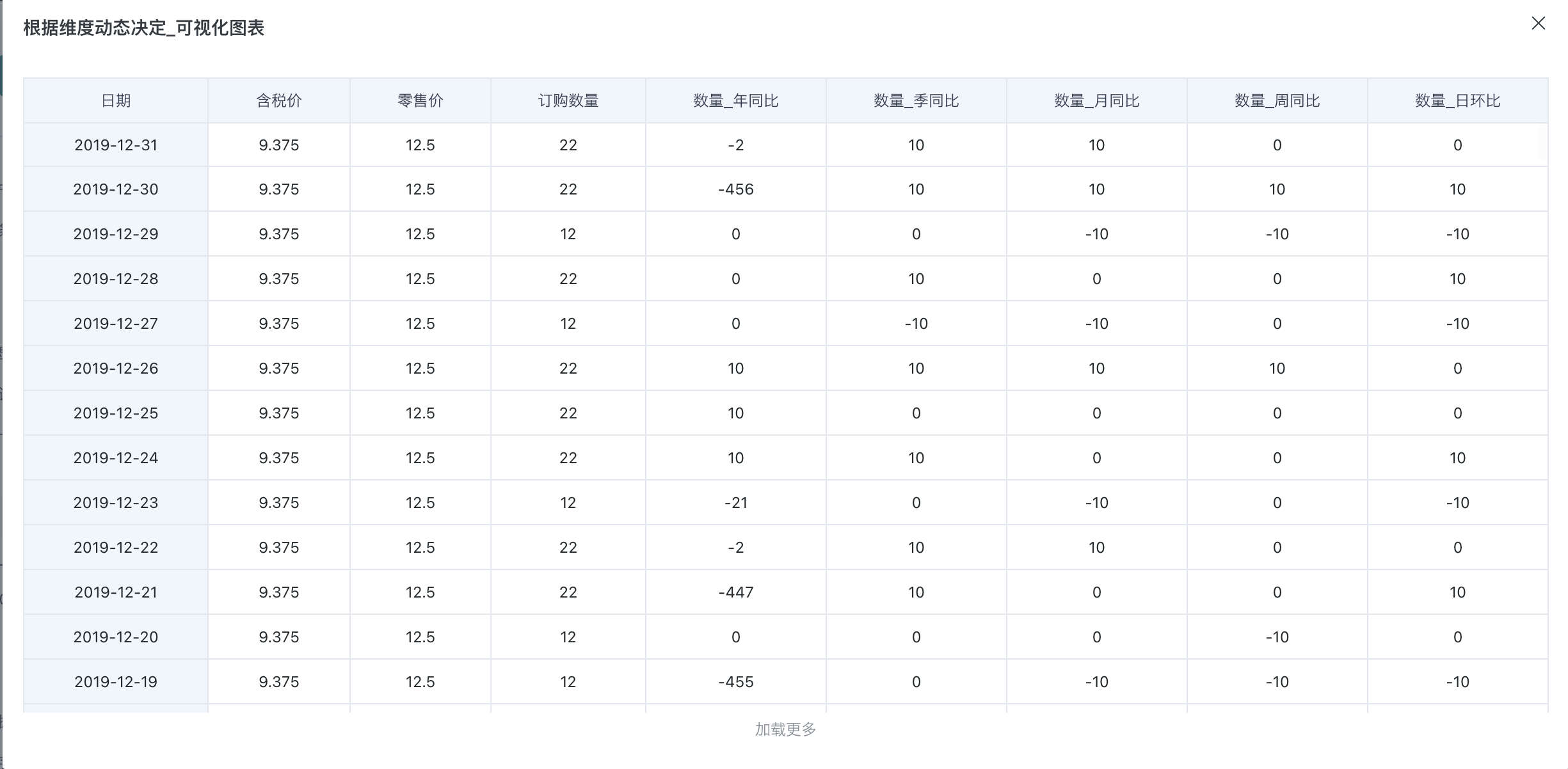
3.3 Dynamically Determine Time Range Year-over-Year/Period-over-Period Derived Metrics Based on Filters
Users want to perform metric analysis using text fields as dimensions and view comparisons between current period data and previous period data through filters. In this scenario, the analysis cannot include date fields as dimensions, and the analysis page needs to have date filters, with the date field in the filter linked to the metric's time dimension field configured for year-over-year/period-over-period.
- The current period time range is passed in by the time filter during analysis, which will override the default value configured in the metric.
- The previous period time range is calculated by offset according to the comparison type. Taking date filter selection [July 10, 2024 - July 31, 2024] as an example:
- The current period time range is [July 10, 2024 - July 31, 2024]
- Previous period time range:
- When selecting year-over-year/period-over-period, no configuration is needed. For example, if the comparison type selects month-over-year, the previous period time range is [June 10, 2024 - June 31, 2024].
- When selecting custom offset, configuration is needed. Use corresponding units for offset by day, week, month, year, configuring the interval of X days/weeks/months/years between current period and previous period. For example, if configuring an interval of 3 days between current period and previous period, the previous period time range is [July 7, 2024 - July 28, 2024].
- When selecting custom date, configuration is needed. Configure custom date/interval, manually setting the specific range of previous period data.
4 Recent N Days/Weeks/Months/Quarters/Years Metrics
"Recent N days/weeks/months/quarters/years" metrics are typically used to capture short-term fluctuations and changes in business to quickly respond to market changes or internal operational issues, used in scenarios requiring quick response and decision-making. For example:
- Sales Revenue: By monitoring changes in sales revenue over the recent N days, sales trends can be quickly identified as rising or falling, allowing for adjustments to sales strategies such as promotional activities and product pricing.
- User Activity: Changes in user activity reflect the level of user interest in products or services. By monitoring user activity over the recent N days, user retention can be understood, and user experience can be optimized to improve user stickiness.
- Conversion Rate: Conversion rate is an important metric for measuring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. By monitoring conversion rates over the recent N days, the effectiveness of marketing campaigns can be evaluated and marketing channels and strategies can be adjusted in a timely manner.
When the metric's derivation method is recent N days/weeks/months/quarters/years, it refers to the continuous N days/weeks/months/quarters/years time range calculated forward from the current date. The recent N days here refers to the recent N days of the natural calendar.
The following content needs to be configured:
| Content | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Granularity | The granularity of the time range, configurable as day/week/month/quarter/year. |
| Calculation Range | The calculation range of data, supports quick setting according to time granularity. When time granularity is day, supports recent 3 days, recent 7 days, recent 14 days, recent 30 days, recent 7 days up to yesterday, recent 14 days to recent 7 days, custom. Except for custom mode, start time and end time are automatically calculated based on selection. Taking today as [2024.12.31] as an example: |
| Base Date | Base date indicates from which day to calculate forward the recent N days/weeks/months/quarters/years. Can select end time of date filter/start time of date filter. When date dimension is used during analysis, base date takes the date corresponding to the date dimension value; when date dimension is not used during analysis, the configuration here takes effect. |
| Start Date | Automatically filled/custom filled according to calculation range, such as recent 3 days, then start date is automatically filled as N=3, end date is automatically filled as N=0, supports custom start time. |
| End Date | Automatically filled/custom filled according to calculation range, such as recent 3 days, end date is automatically filled as N=0. |
| Calculation Method | When date dimension is used during analysis, the metric is first aggregated according to the atomic metric's aggregation logic and then calculated; when date dimension is not used during analysis, the atomic metric calculation method is directly used. Calculation method can choose sum, average, maximum, minimum. Note: When the atomic metric is sum or average, defining secondary calculations here is meaningful. For example: To calculate the average daily sales revenue within 1 month, you can first define the atomic metric sales revenue with aggregation method as sum, configure the derived metric time range as recent 1 month, and set the calculation method here as average, then it will first calculate the sum of daily sales revenue, then add these sums together, and finally divide by 30 (number of days in the month) |
The logic for custom configuration of start and end times is described in the table below:
| Date Granularity | Example Configuration | Rule Description |
|---|---|---|
| Day | 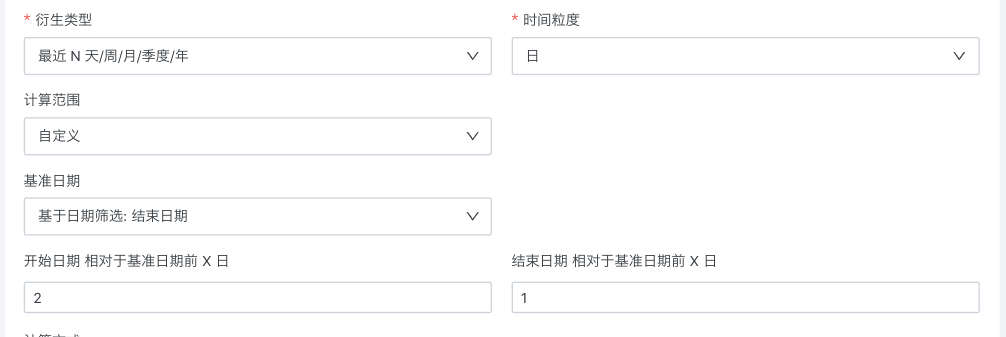 | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example Left closed right closed [2024.12.9, 2024.12.10] |
| Day | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example Left closed right closed [2024.12.9, 2024.12.11] | |
| Week | Taking [2024.12.11 (Wednesday)] as an example 2 weeks ago: Find last Wednesday 2024.11.27, 1 week ago: Find last Wednesday 2024.12.4 Left open right closed (2024.11.27, 2024.12.4] | |
| Week | Taking [2024.12.11 (Wednesday)] as an example Left open right closed (2024.11.27, 2024.12.11] 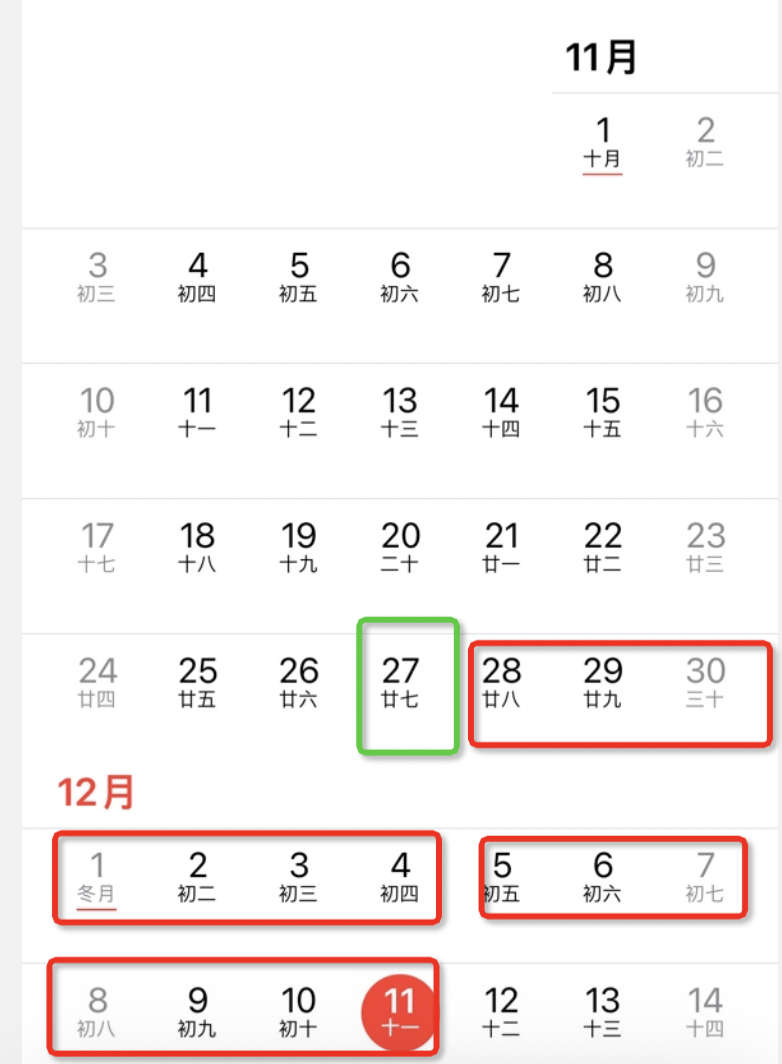 | |
| Month | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example 2 months ago: Find the 11th of the month before last 2024.11.11, 1 month ago: Find the 11th of last month 2024.10.11 Left open right closed (2024.10.11, 2024.11.11] | |
| Month | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example Left open right closed (2024.10.11, 2024.12.11] 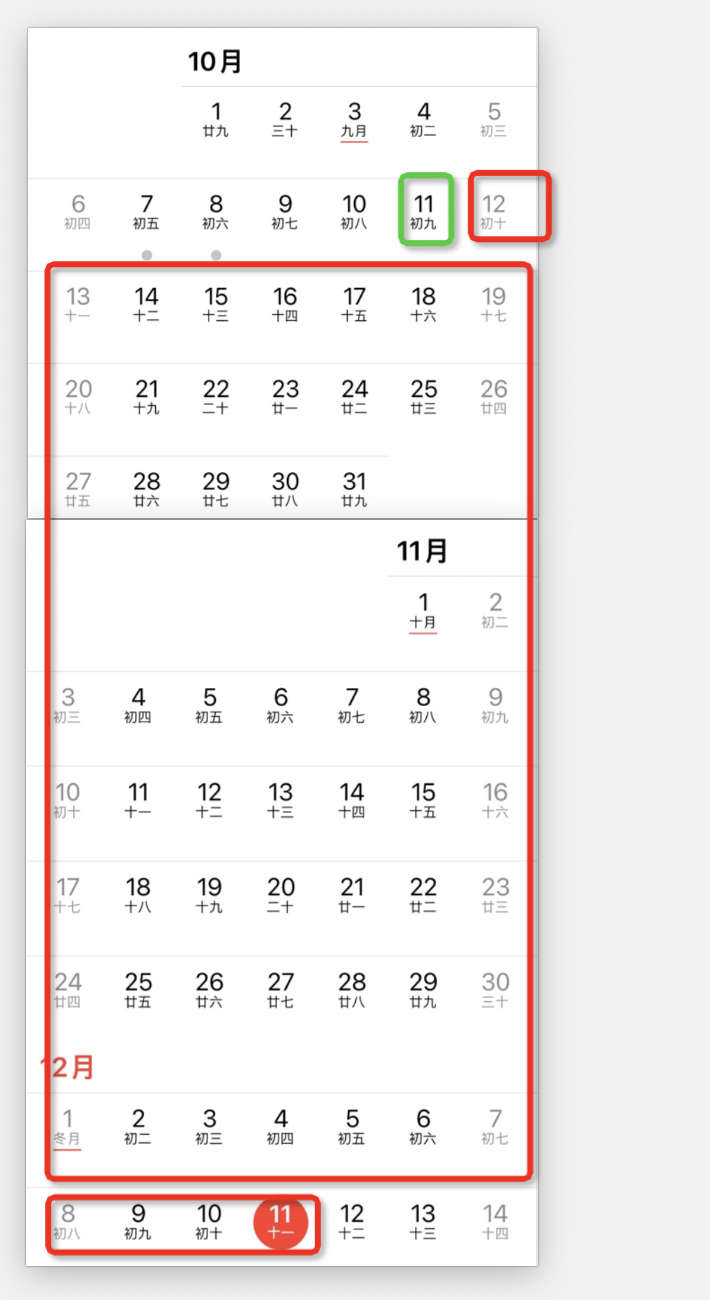 | |
| Quarter | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example 2 quarters ago: Find the 11th 6 months ago 2024.6.11, 1 quarter ago: Find the 11th 3 months ago 2024.9.11 Left open right closed (2024.6.11, 2024.9.11] | |
| Quarter | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example Left open right closed (2024.6.11, 2024.12.11] | |
| Year | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example 2 years ago: Find the 12.11 of the year before last 2022.12.11, 1 year ago: Find the 12.11 of last year 2023.12.11 Left open right closed (2022.12.11, 2024.12.11] | |
| Year | Taking [2024.12.11] as an example Left open right closed (2022.12.11, 2023.12.11] |
Taking the configuration of GMV's recent 7 days metric as an example, you can configure as follows, select recent 7 days for calculation range and sum for calculation method:
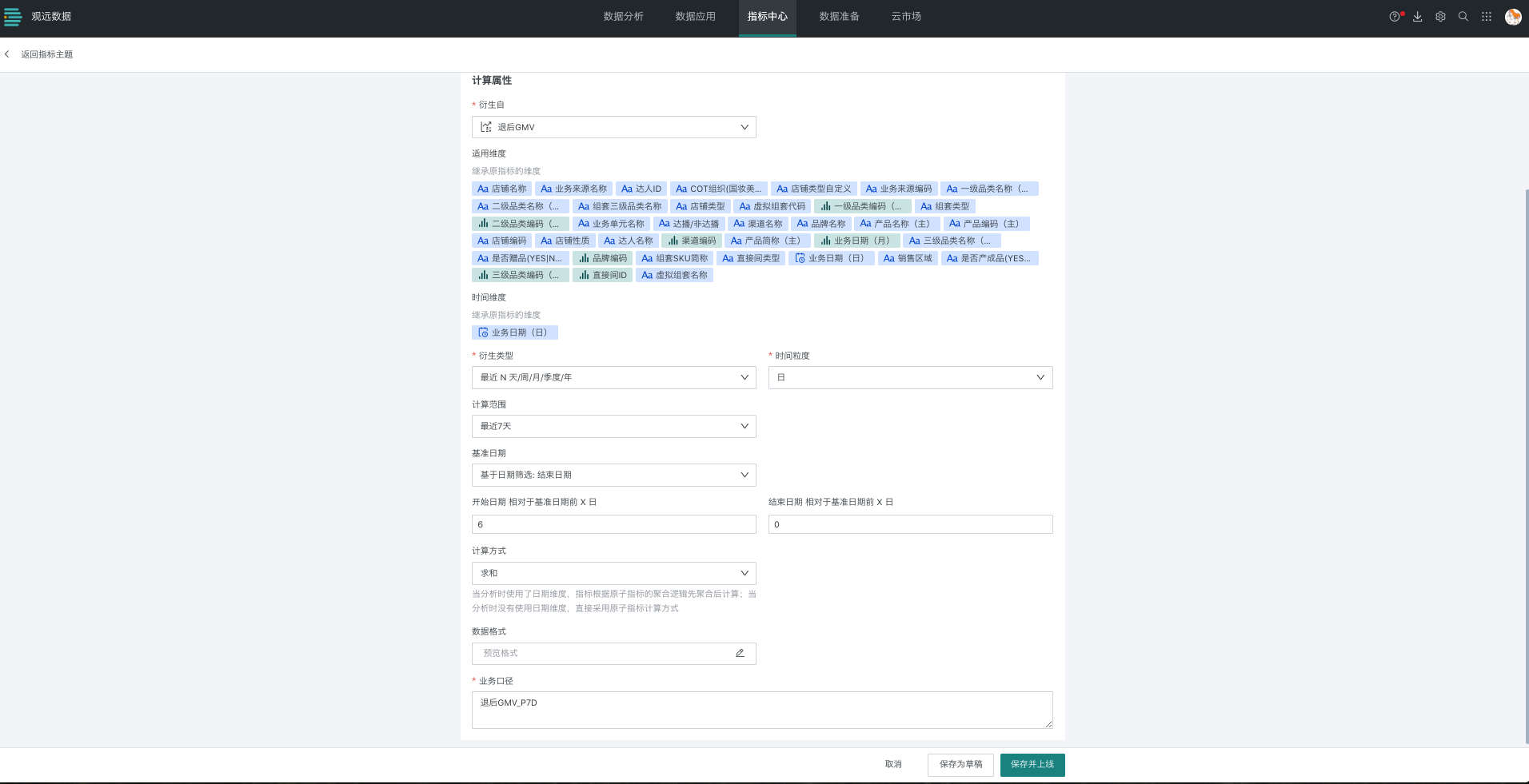
(1) When the time dimension in the analysis card is used as a dimension, the base date for each row is determined by the corresponding time dimension value.
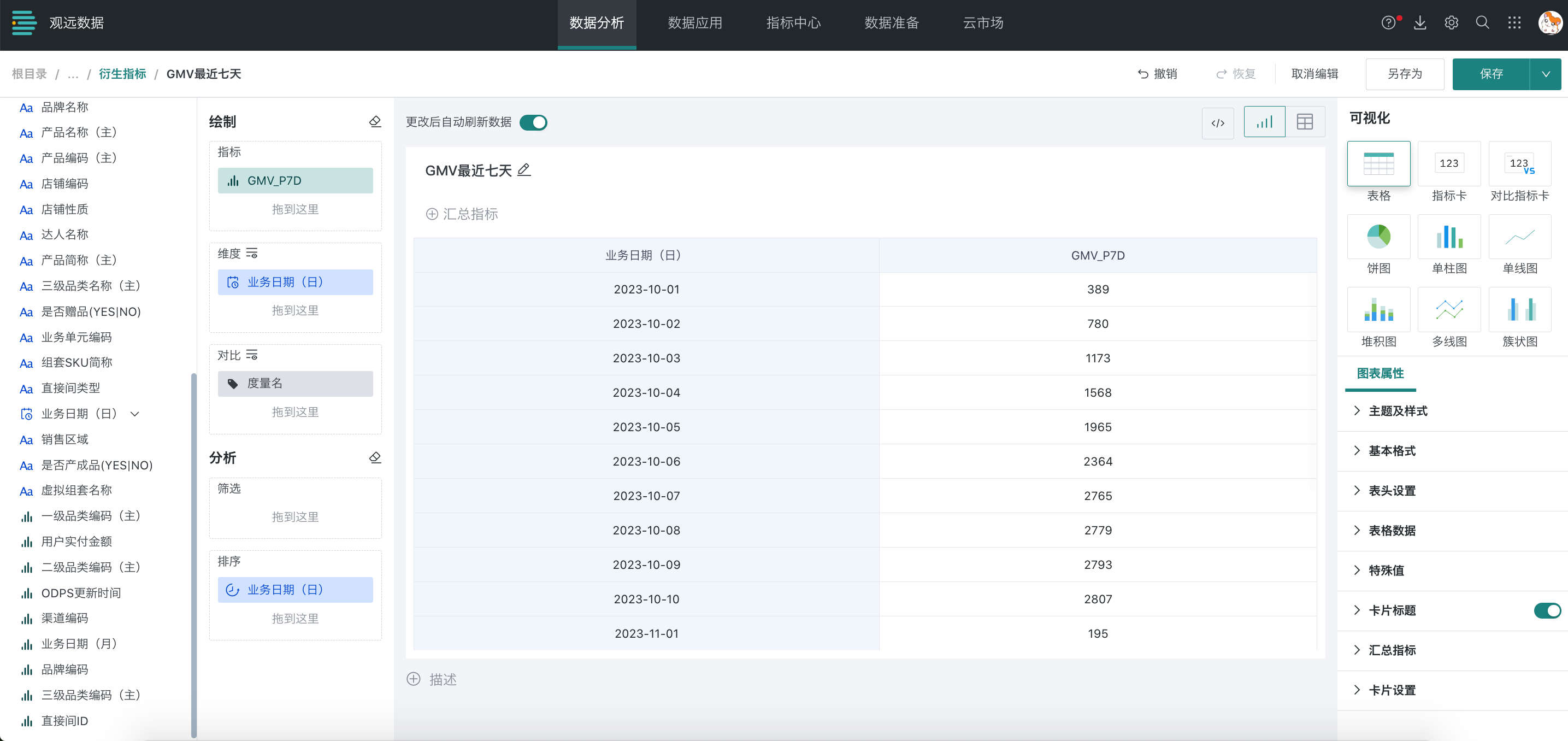
The calculation logic is as follows:
| Business Date (Day) | Recent 7 Days |
|---|---|
| 20231101 | 20231026GMV+20231027GMV+...+20231101GMV |
| 20231102 | 20231027GMV+20231028GMV+...+20231102GMV |
| …… | …… |
(2) When the analysis page has date filters and no time dimension is used as an analysis dimension, the filter is linked to the metric's time dimension field. Taking date filter selection [October 10, 2023 - November 10, 2023] as an example:
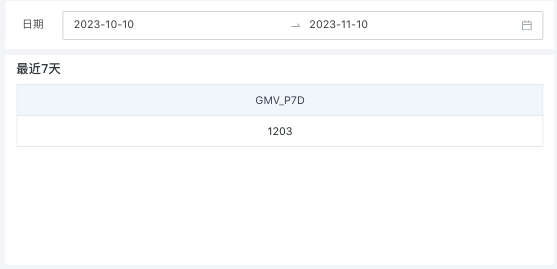
- When the metric base date is configured as "Based on end time of date filter", the calculation logic is as follows:
| GMV_Recent 7 Days |
|---|
| 20231104GMV+20231105GMV+...+20231110GMV |
- When the metric base date is configured as "Based on start time of date filter", the calculation logic is as follows:
| GMV_Recent 7 Days |
|---|
| 20231004GMV+20231005GMV+...+20231010GMV |
5 Cumulative Calculation Metrics
Cumulative calculation metrics focus on reflecting the cumulative performance of business over a longer time period, helping enterprises grasp the overall trend and speed of business growth. The advantage of cumulative metrics lies in their stability and reliability, being able to reflect the overall performance of business over a longer time period. For example:
- Monthly Cumulative: By calculating the cumulative value of a certain business metric within a month, the change trend of this metric within a month can be clearly seen. For example, monthly cumulative sales revenue can reflect the enterprise's sales performance in that month, helping the enterprise understand sales growth and set sales targets for the next month.
- Annual Cumulative: Annual cumulative metrics are used to evaluate the overall business performance of an enterprise for a year. By calculating the cumulative value of a certain metric within a year, the enterprise's business condition in that year can be comprehensively understood, such as annual sales revenue, annual profit, etc. These metrics help enterprises formulate long-term development strategies and plan future development directions.
When the metric's derivation method is cumulative calculation, it supports cumulative summation by time dimension and requires configuration of the following content:
| Content | Description |
|---|---|
| Calculation Range | The calculation range of cumulative data |
| Base Date | Base date indicates the right endpoint of the cumulative time range, i.e., cumulative to which day. Can select end time of date filter/start time of date filter. When date dimension is used during analysis, base date takes the date corresponding to the date dimension value; when date dimension is not used during analysis, the configuration here takes effect. |
| Start Date | Determined by cumulative method to display the first day of month/week/quarter/year/first day of historical data. |
| End Date | Optional whether to include the current value of the base date. If not checked, it will be cumulative to the day before the base date. |
Taking the configuration of GMV's monthly cumulative/quarterly cumulative/year-to-date metrics as an example, you can configure as follows, select monthly cumulative/quarterly cumulative/year-to-date for calculation range respectively:
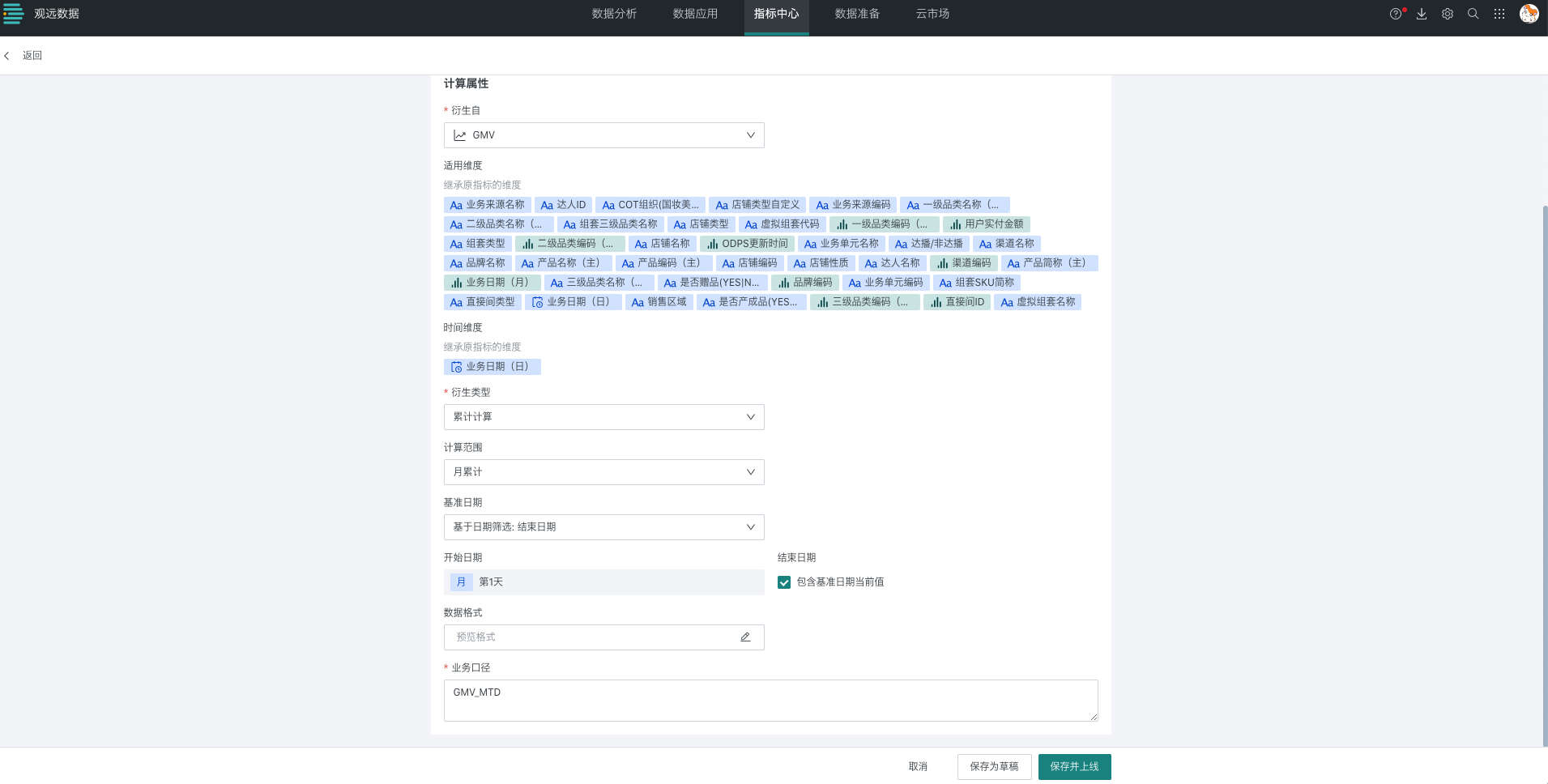
(1) When the time dimension in the analysis card is used as a dimension, the base date for each row is determined by the corresponding time dimension value.
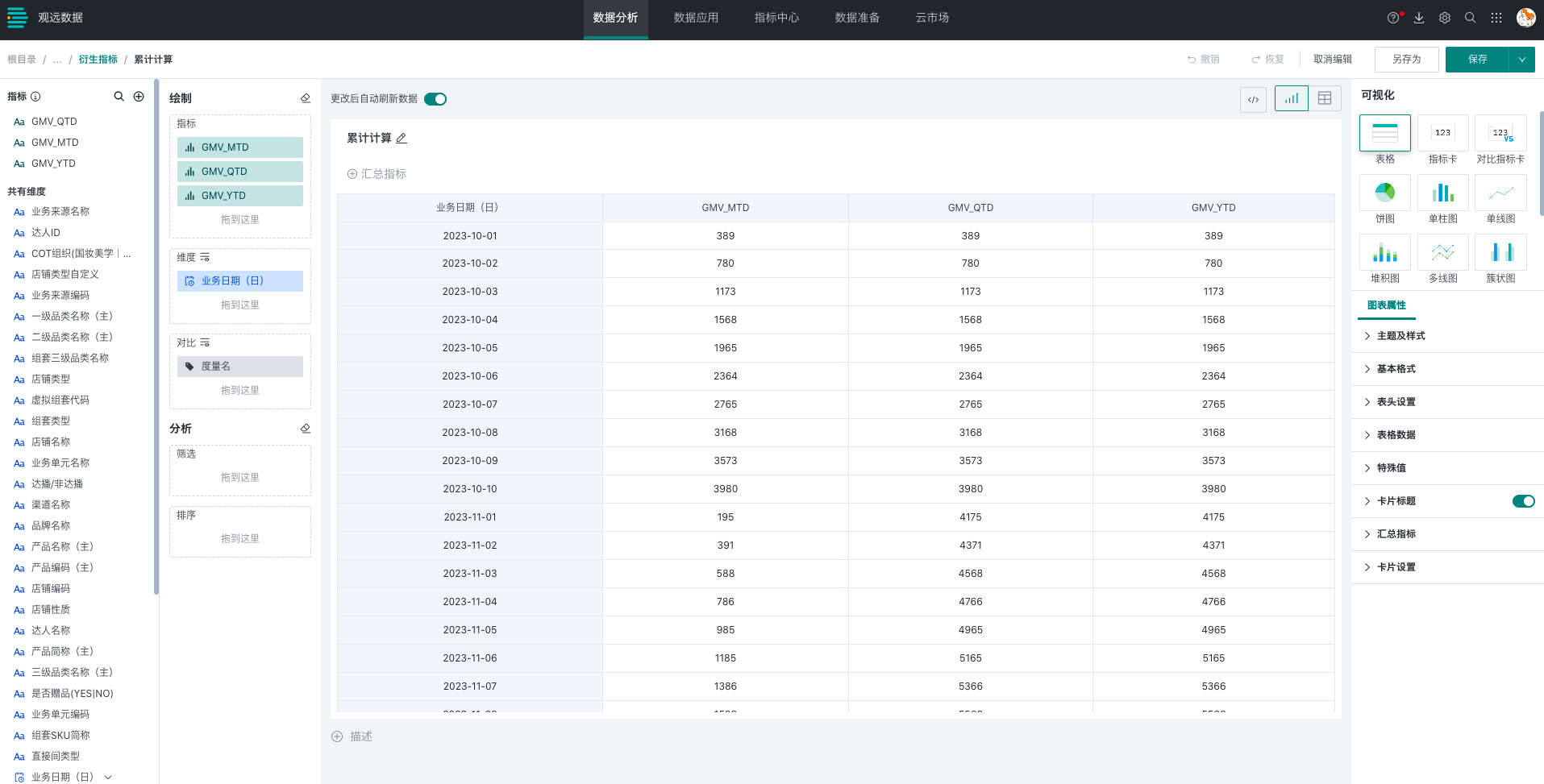
The calculation logic is as follows:
| Business Date (Day) | GMV_MTD | GMV_QTD | GMV_YTD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20231101 | 20231101GMV | 20231001GMV+20231002GMV+...+20231101GMV | 20230101GMV+20230102GMV+...+20231101GMV |
| 20231102 | 20231101GMV+20231102GMV | 20231001GMV+20231002GMV+...+20231101GMV+20231102GMV | 20230101GMV+20230102GMV+...+20231101GMV+20231102GMV |
| …… | …… | …… | …… |
(2) When the analysis page has date filters and no time dimension is used as an analysis dimension, the filter is linked to the cumulative calculation metric's time dimension field. Taking date filter selection [October 10, 2023 - November 10, 2023] as an example:
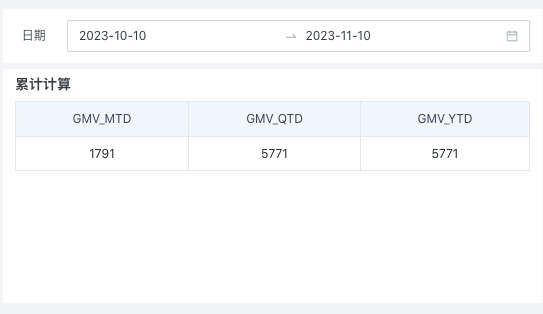
- When the metric base date is configured as "Based on end time of date filter", the calculation logic is as follows:
| GMV_MTD | GMV_QTD | GMV_YTD |
|---|---|---|
| 20231101GMV+20231102GMV+...+20231110GMV | 20231001GMV+20231002GMV+...+20231110GMV | 20230101GMV+20230102GMV+...+20231110GMV |
- When the metric base date is configured as "Based on start time of date filter", the calculation logic is as follows:
| GMV_MTD | GMV_QTD | GMV_YTD |
|---|---|---|
| 20231001GMV+20231002GMV+...+20231010GMV | 20231001GMV+20231002GMV+...+20231010GMV | 20230101GMV+20230102GMV+...+20231010GMV |
6 End-of-Period Value Metrics
End-of-period value refers to the value of assets or liabilities held at the end of a period. It is mainly used to define inventory-type metrics, usually referring to the specific numerical value corresponding to the metric at the end of a specific time point (such as end of month, end of year, etc.). For example:
- Financial Field: In the financial field, end-of-period value usually refers to the value of an investment portfolio or account at the end of a specific period. For example, when calculating investment returns or evaluating investment strategies, end-of-period value needs to be used as a reference.
- Accounting Field: In the accounting field, end-of-period value usually refers to the asset and liability status of a company at the end of a specific accounting period. End-of-period values are usually used to prepare financial statements and evaluate the company's financial condition.
- Inventory Management: In inventory management, end-of-period value refers to the value of inventory items at the end of a specific period. Managers can evaluate inventory liquidity and demand by comparing beginning and end-of-period values, thereby formulating more effective inventory management strategies.
When the metric's derivation method is end-of-period value, it supports taking the end-of-period value of data by time dimension and date filter. When the date filter is an interval, it takes the end date of the interval. For example, inventory end-of-month value, for October's inventory end-of-month value, when the filter selects October, it takes the data of October 31st.
(1) When the time dimension in the analysis card is used as a dimension, it will be calculated based on the date granularity of the time dimension dragged into the dimension column.
For example, if the time hierarchy dragged into the dimension column is year-month, it will take the calculation result of the last day of each month.
| Business Date (Year-Month) | GMV End-of-Period Value |
|---|---|
| 202311 | 20231130GMV |
| 202312 | 20231231GMV |
| …… | …… |
(2) When the analysis page has date filters and no time dimension is used as an analysis dimension, the filter is linked to the end-of-period value metric's time dimension field.
-
When the filter selects data for a specific day, it will take the value of that day as the calculation result.
-
When the filter selects data for a specific month, it will take the value of the last day of that month as the calculation result.
-
When the filter selects data for a specific year, it will take the value of the last day of that year as the calculation result.
-
When the filter selects a date range, it will take the value of the last day of that period as the calculation result. Taking date filter selection [October 10, 2023 - November 10, 2023] as an example, it takes the result of November 10, 2023.
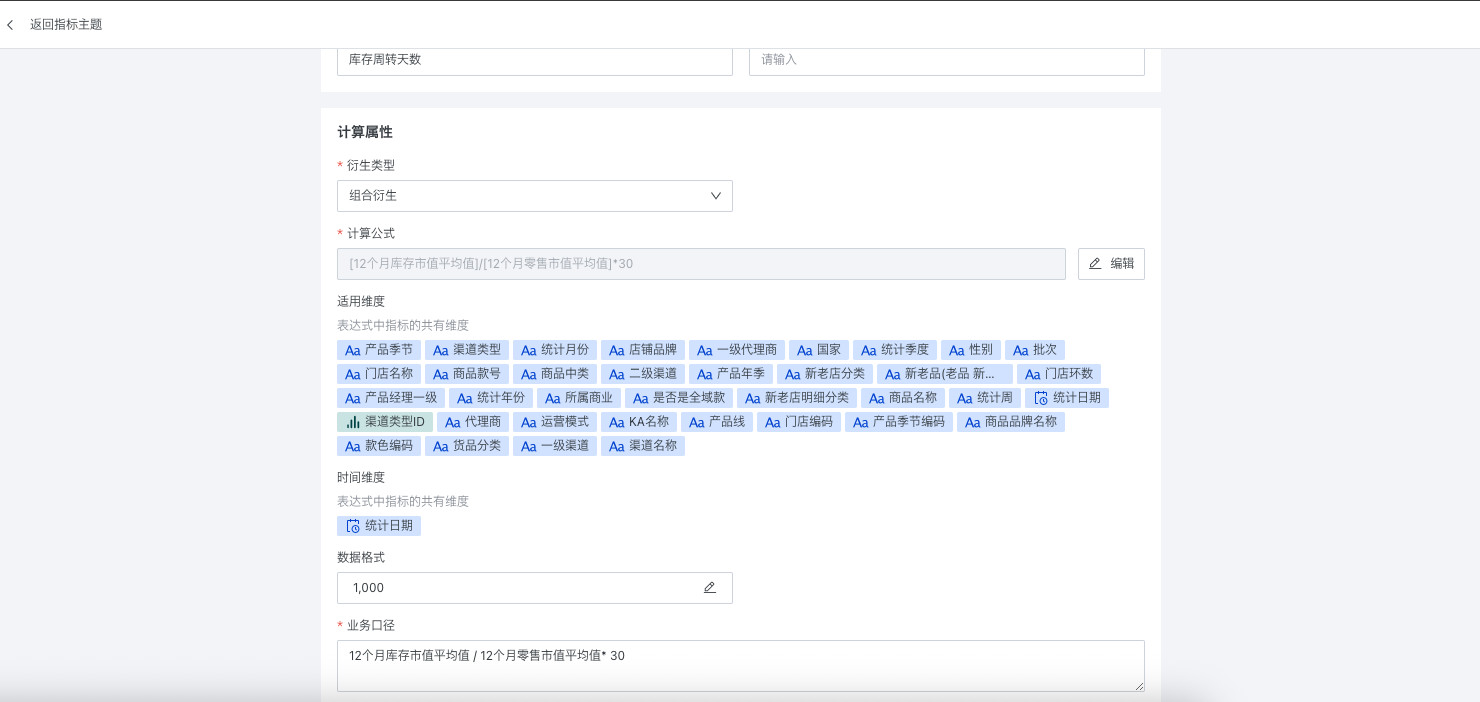
7 Combined Derivation Metrics
Combined derivation supports configuring calculation formulas on derived metrics to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations on multiple derived metrics. For example:
Inventory turnover days = (12-month average inventory market value / 12-month average retail market value) * 30.
The calculation formula only supports referencing other derived metrics, and the derivation type must be recent N days/cumulative calculation/end-of-period value. Only addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division logic can be configured, and functions are not supported.