HTTP Nodes
1. Overview
This node is used to execute HTTP-type tasks, such as common POST, GET and other request types, and determines whether the node is successful based on the corresponding status code.
2. Node Configuration
Fill in basic information (optional) for the current task node, enter node name and description in the input boxes. This information can help you better understand and manage nodes, making the entire offline development task process clearer and easier to maintain.
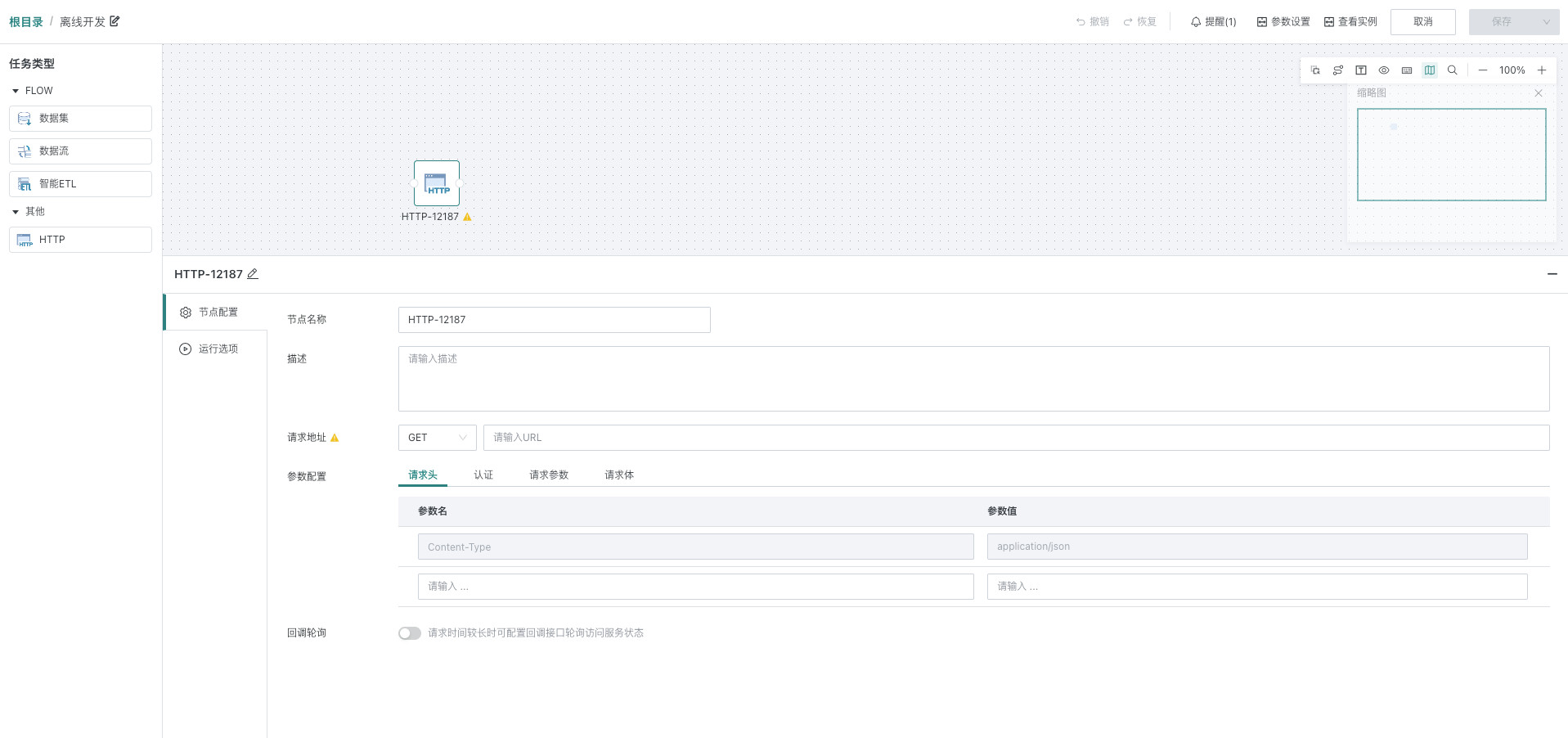
- Request address: Supports GET/POST, defaults to GET, specifies the URL address for HTTP requests
- Request parameter configuration:
| Configuration Item | Description |
| Request Headers | Consists of key/value pairs, telling the server the type of resource needed. |
| Authentication | Currently only supports 2 authentication methods: API Key and Token: API Key: API key is the name given to a secret token of some form, submitted with Web service (or similar) requests to identify the source of the request. Token: Token refers to having the permission to request interfaces on behalf of user roles within a specified valid time. |
| Request Parameters | Fields and conditions that need to be obtained, and supports global parameters (see Global Parameters for details), time macros, and workflow parameters (see Workflow Parameters for details).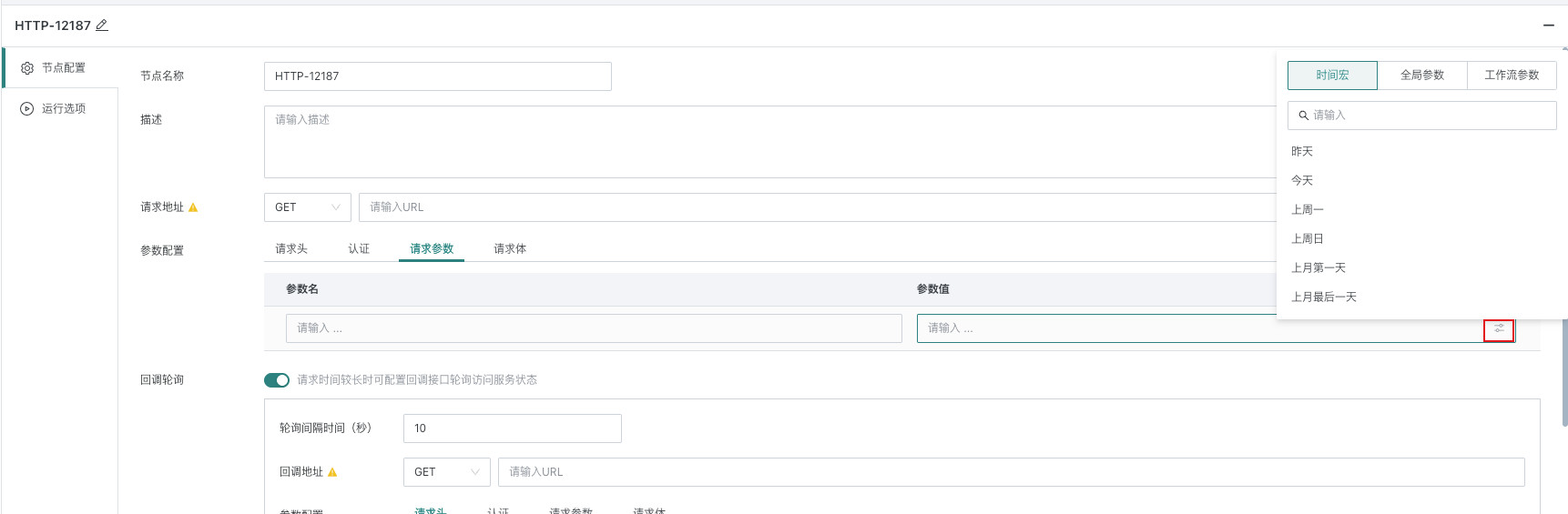 |
| Request Body | JSON format only: Encapsulates request parameters for POST request messages, supports global parameters, time macros, and workflow parameters.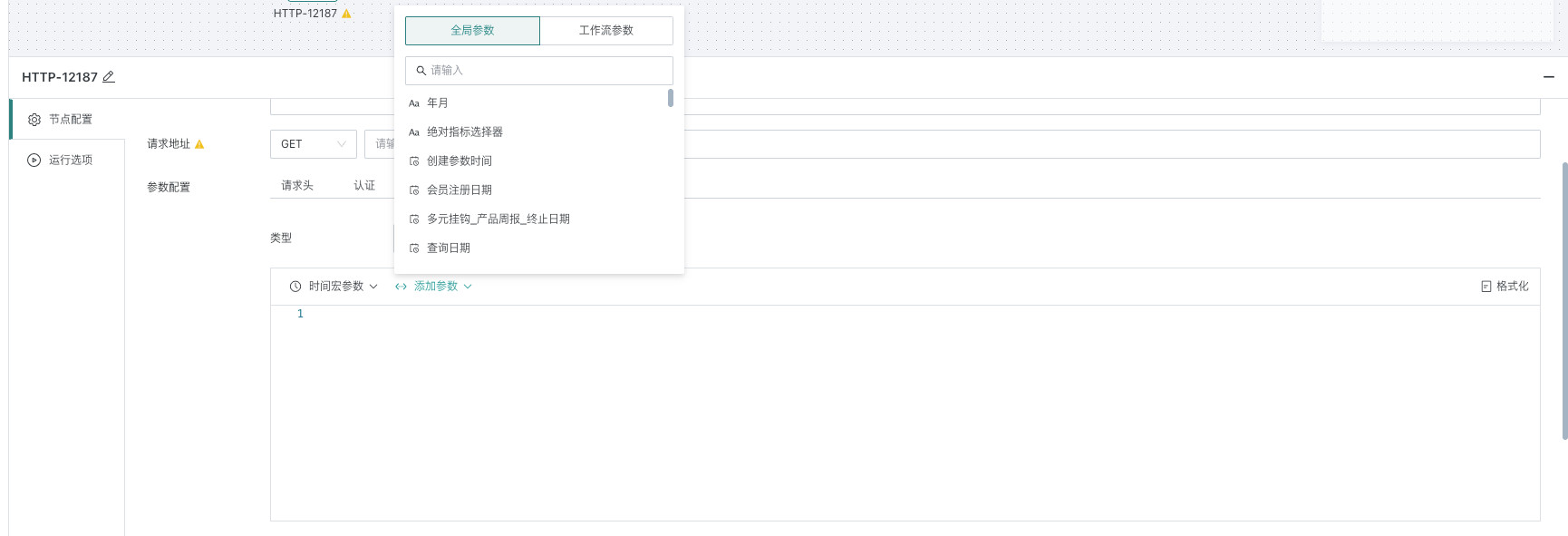 |
- Validation conditions: After meeting the set conditions, this node will run successfully. If the response status code does not start with 2, such as 200, 201, etc., it will report an error and end.
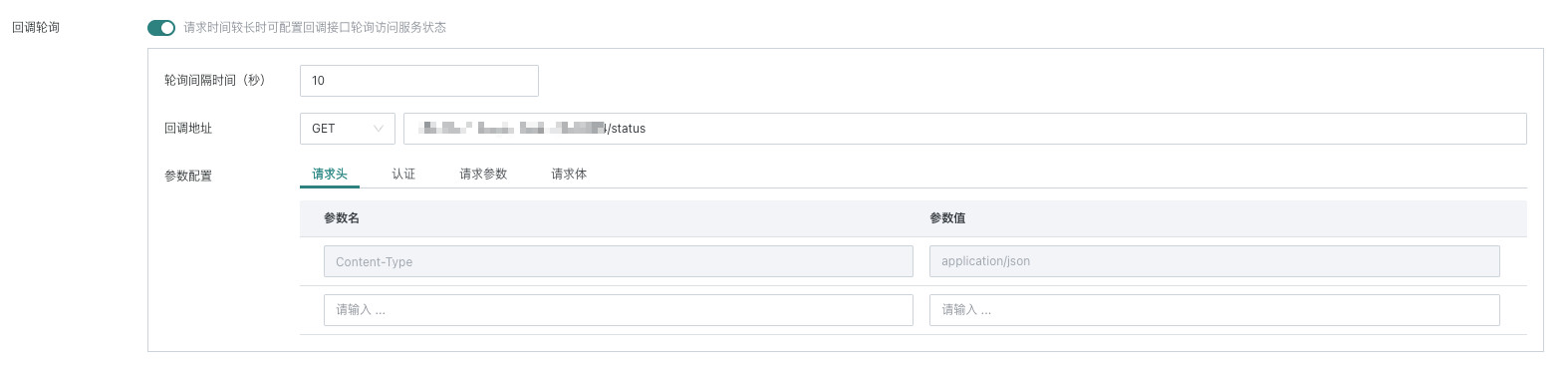
- Callback polling configuration: When the interface request time is long, you can configure the callback interface to poll and access the request status.
| Configuration Item | Description |
| Polling Interval (seconds) | Poll once every X seconds |
| Callback Address | Supports GET/POST, defaults to GET, specifies the URL address for callback |
| Request Headers | Consists of key/value pairs, telling the server the type of resource needed. |
| Authentication | Currently only supports 2 authentication methods: API Key and Token: API Key: API key is the name given to a secret token of some form, submitted with Web service (or similar) requests to identify the source of the request. Token: Token refers to having the permission to request interfaces on behalf of user roles within a specified valid time |
| Request Parameters | Fields and conditions that need to be obtained, and supports global parameters (see Global Parameters for details), time macros, and workflow parameters (see Workflow Parameters for details). |
| Request Body | JSON format only: Encapsulates request parameters for POST request messages, supports global parameters, time macros, and workflow parameters. |
Callback considerations:
- The parameters returned by the main node request must be
{
"taskId": "xxxxxx",
...
}
-
BI will automatically extract taskId and append it to the callback address
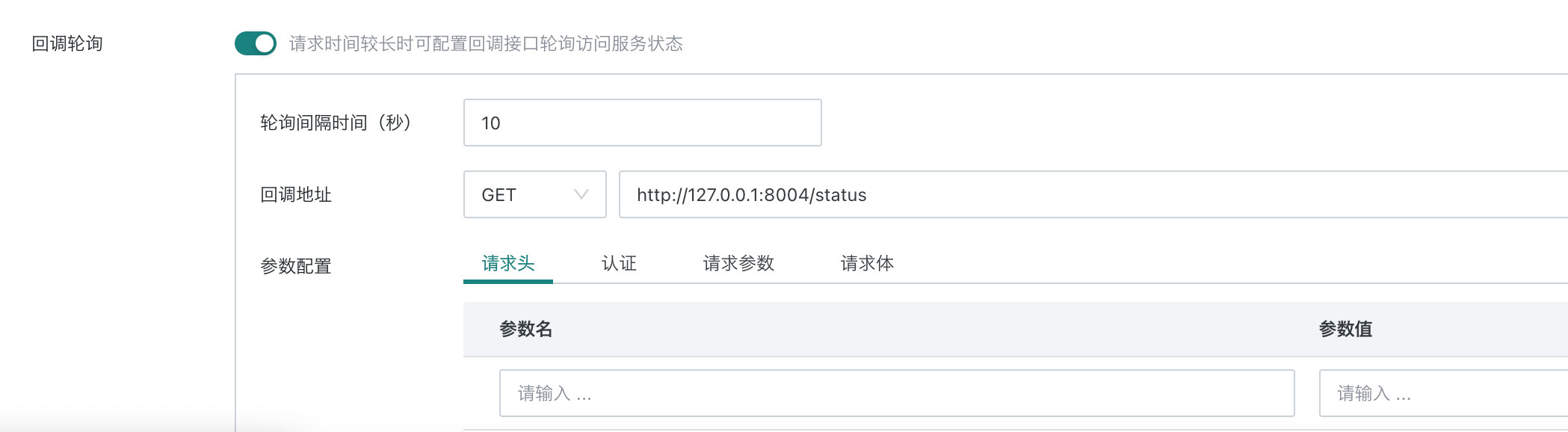
For example, for this URL, after automatic concatenation it becomes: http://127.0.0.1:8004/status/xxxxxx
-
Callback return result validation:
- The return result format is: { "status": "xxxxxx" .......}
- If the response status code does not start with 2, such as 200, 201, etc., it will directly report an error and end
- If the status value is PROCESSING, continue polling, otherwise end. Status SUCCESS means success, otherwise failure
- Pay attention to service infinite loop issues
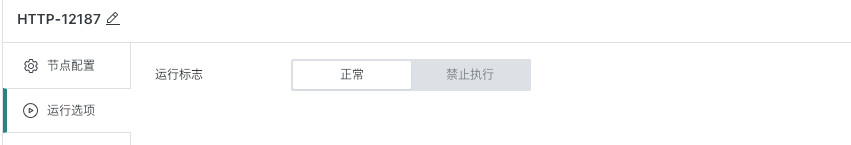
3. Running Options
-
Running flag
- Prohibit execution: After the workflow runs to this node, it will directly skip execution, commonly used for temporary data problem troubleshooting, partial task running control and other scenarios.
- Normal: Run the node according to the existing scheduling strategy, the default running flag for nodes.
-
Failure retry: Synchronized with the failure retry strategy configured by the dataset itself.
4. Practice of Calling Python Services Through HTTP
Python API service dependencies
flask
request
jsonify
cachetools
Python service script
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from cachetools import TTLCache
import time
import uuid
import io
import contextlib
import sys
app = Flask(__name__)
# Thread pool (maximum 10 concurrent tasks)
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10)
# 2 days converted to seconds
two_days_in_seconds = 2 * 24 * 60 * 60
# Create a cache object with TTL of 2 days for each entry
task_cache = TTLCache(maxsize=100, ttl=two_days_in_seconds)
def run_python_code(code, taskId):
""" Execute Python code and store results """
try:
result = execute_code(code)
task_cache[taskId] = {"taskId": taskId, "status": "FINISHED", "log": result}
except Exception as e:
task_cache[taskId] = {"taskId": taskId, "status": "FAILED", "error": str(e)}
@app.route("/run_code", methods=["POST"])
def run_code():
""" Submit code task, execute asynchronously """
data = request.get_json()
code = data.get("code", "").strip()
if not code:
return jsonify({"error": "No code provided"}), 400
# Generate unique taskId
taskId = str(uuid.uuid4())
# Record task start
task_cache[taskId] = {"taskId": taskId, "status": "PROCESSING"}
# Submit task to thread pool
executor.submit(run_python_code, code, taskId)
return jsonify({"taskId": taskId, "status": "PROCESSING"})
@app.route("/status/<taskId>", methods=["GET"])
def check_status(taskId):
""" Query task status """
if taskId not in task_cache:
return jsonify({"taskId": taskId, "status": "FAILED", "error": "Task not found"}), 404
task_info = task_cache[taskId]
if task_info["status"] == "FAILED":
return jsonify({"taskId": taskId, "status": "FAILED", "error": task_info["error"]}), 500
return jsonify(task_info)
# Function to execute code
def execute_code(code):
# Use StringIO to capture print output
output_buffer = io.StringIO()
try:
# Redirect standard output to output_buffer
with contextlib.redirect_stdout(output_buffer):
exec(code)
# Get captured output
output = output_buffer.getvalue()
return output.strip() # Return captured output
except Exception as e:
# If code execution fails, return error message
return f"Code execution failed: {str(e)}"
finally:
# Close StringIO buffer
output_buffer.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8004, debug=True) # Listen on all addresses, port 8004
Configure HTTP node
Configure parameters in the request body
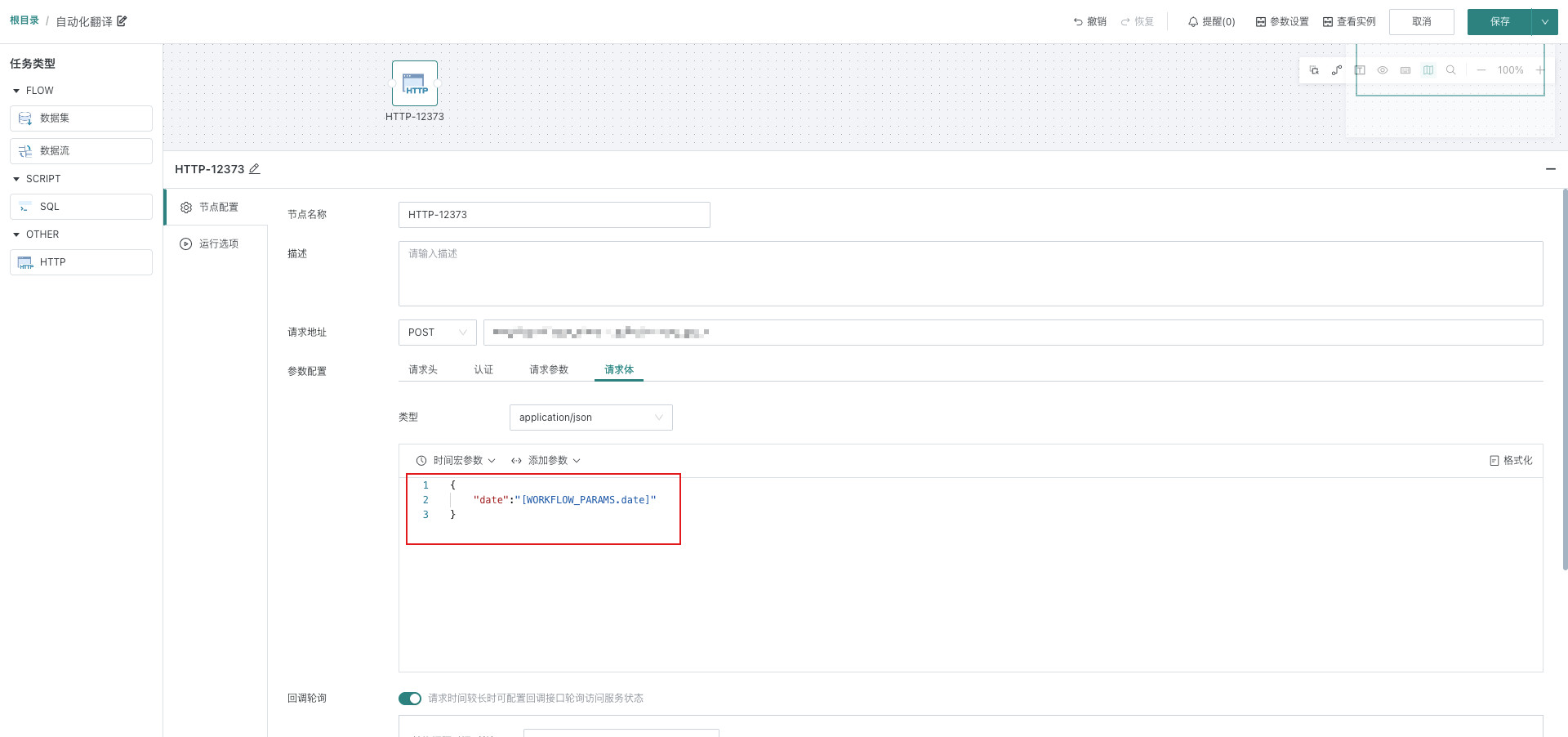
Configure callback interface