Filter Data Rows
1. Function Description
By defining filter conditions, precise filtering of datasets can be achieved to meet different business needs. Supports adding multiple filter rules, filtering out Null values, and setting filter trigger conditions, etc.
In actual business scenarios, when source data contains a large amount of dirty data, or when analysis only needs partial data, the Filter Data Rows operator can be used to achieve this.
| Usage Scenario | Business Example |
|---|---|
| Filter Invalid Data | E-commerce platform order data cleaning: When processing e-commerce order data, there may be abnormal orders caused by system errors or malicious attacks. Through filtering data rows, invalid order records can be excluded to ensure subsequent analysis is based on valid order data |
| Extract Data Subset | Regional sales data extraction: For nationwide sales data, you may only care about performance in a specific region. Through filtering data rows, you can extract sales data for that region for detailed analysis and reporting Quarterly financial report data extraction: In financial data processing, extract data for a specific quarter to generate quarterly financial reports. Through filtering data rows, you can select data for a certain quarter |
2. Operation Steps
-
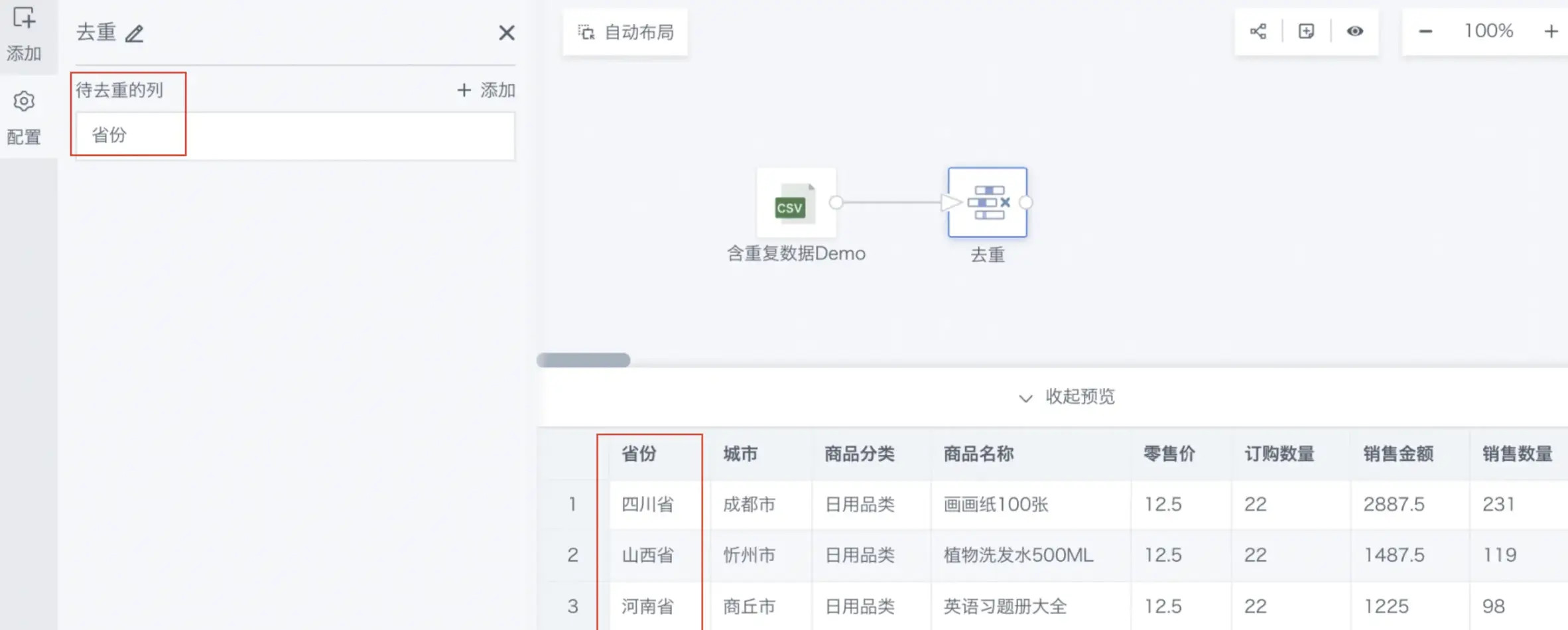
Drag the Filter Data Rows operator from the data flow operator area into the right canvas editing area;
-
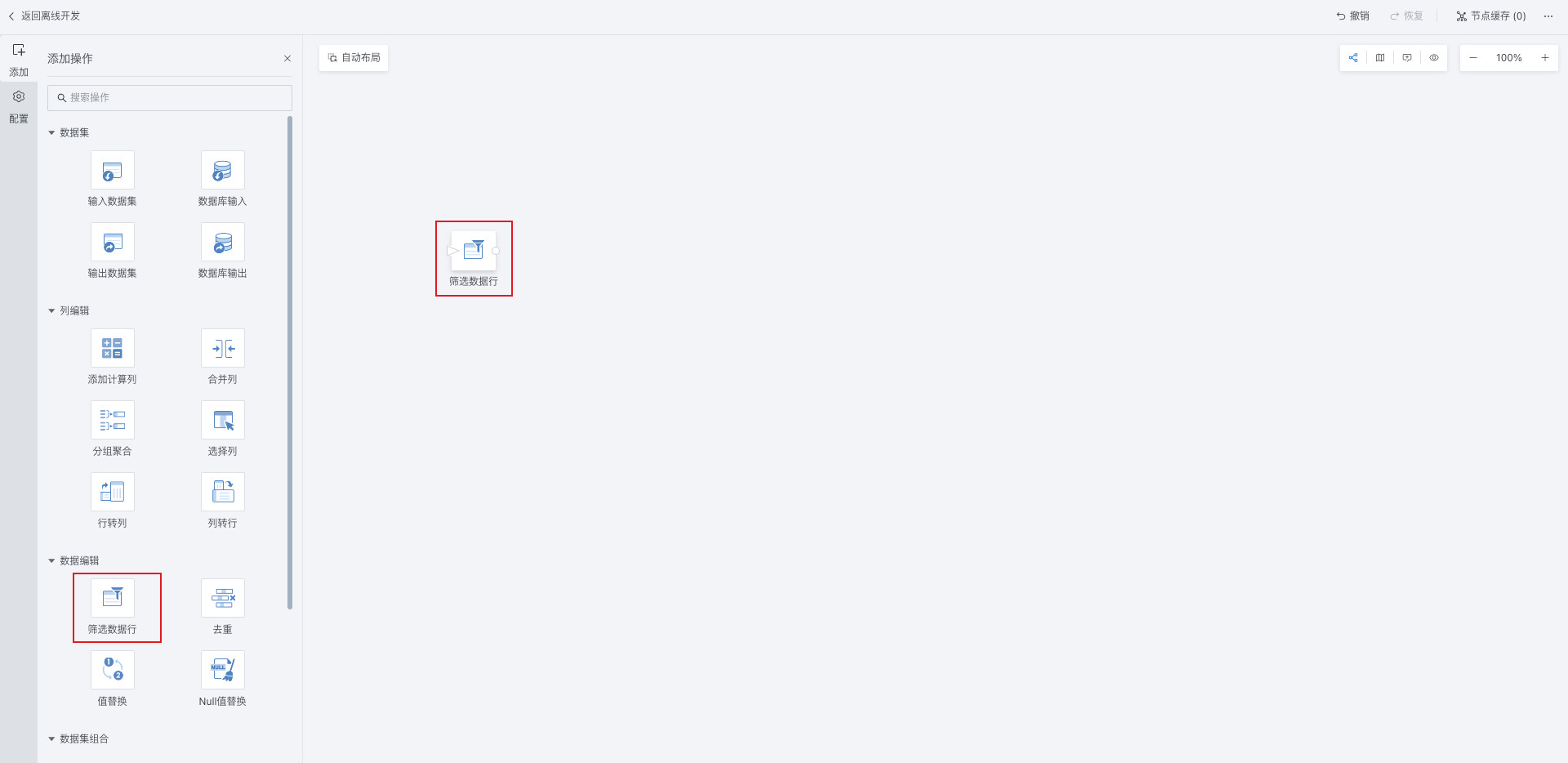
Click the Filter Data Rows operator and add Filter Rules (supports multiple rules);
-
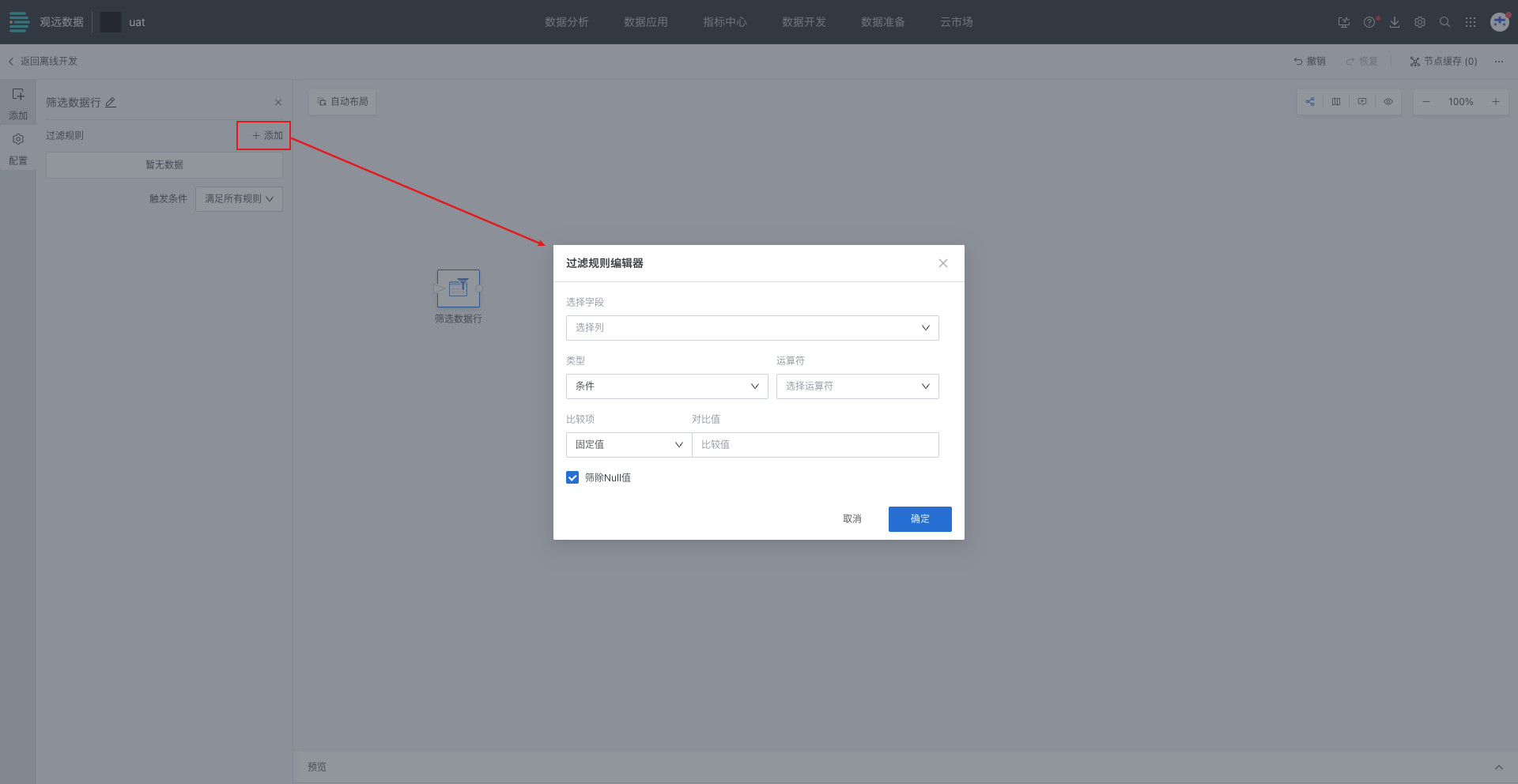
When configuring filter rules, select fields, filter types and related configurations, filter out Null values, and click OK;
Supports selecting time macro parameters, global parameters, and workflow parameters as comparison items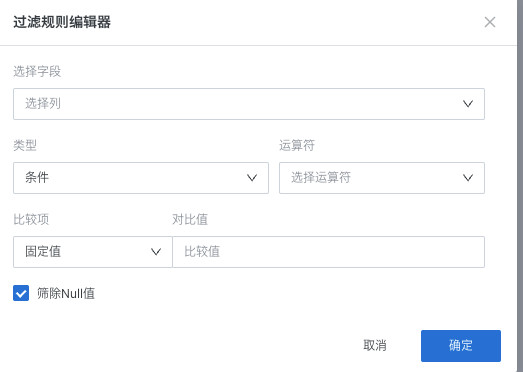
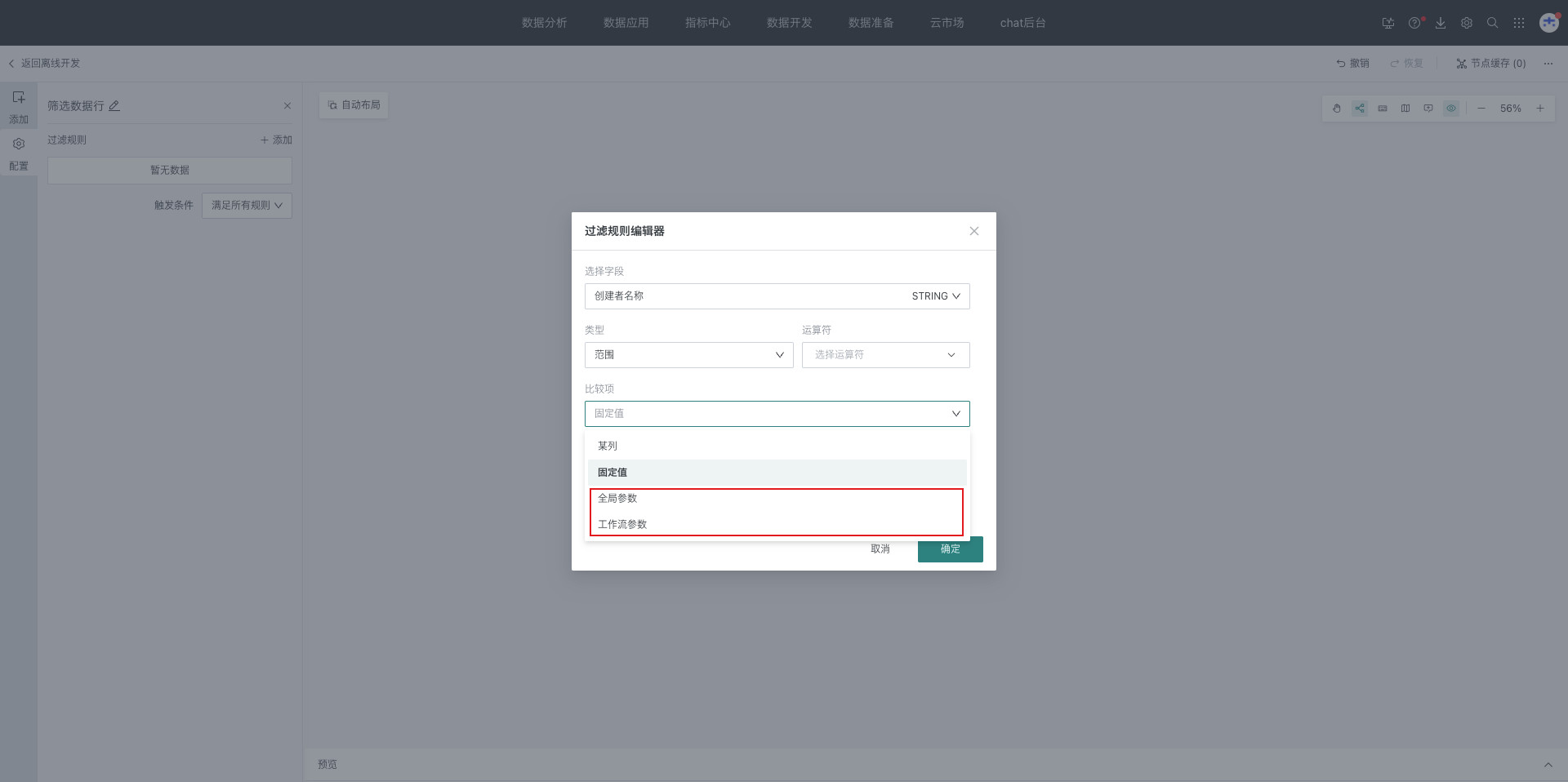
Different filter types support different parameter situations
| Filter Category | Filter Type | Operators | Supports Time Macros and Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text | Select | - | Not supported |
| Range | Less than, Less than or equal, Greater than, Greater than or equal, Equal, Not equal, Interval | Supported, comparison item dropdown list adds workflow parameters and global parameters, linked comparison value selects text type workflow parameters and global parameters | |
| Equal to Null value, Not equal to Null value | Not supported | ||
| Condition | Equal, Not equal, Contains, Not contains, Starts with, Ends with, Not starts with, Not ends with | Supported, comparison item dropdown list adds workflow parameters and global parameters, linked comparison value selects text type workflow parameters and global parameters | |
| Numeric | Select | - | Not supported |
| Range | Less than, Less than or equal, Greater than, Greater than or equal, Equal, Not equal, Interval | Supported, comparison item dropdown list adds workflow parameters and global parameters, linked comparison value selects text type workflow parameters and global parameters | |
| Date | Select | - | Not supported |
| Range | Less than, Less than or equal, Greater than, Greater than or equal, Equal, Not equal, Interval | Supported, comparison item dropdown list adds time macros, workflow parameters and global parameters, linked comparison value selects date type workflow parameters and global parameters | |
| Equal to Null value, Not equal to Null value, Others (yesterday, last week, etc.) | Not supported |
-
Configure the trigger rules for filter conditions;
-
Click OK and preview the data results.
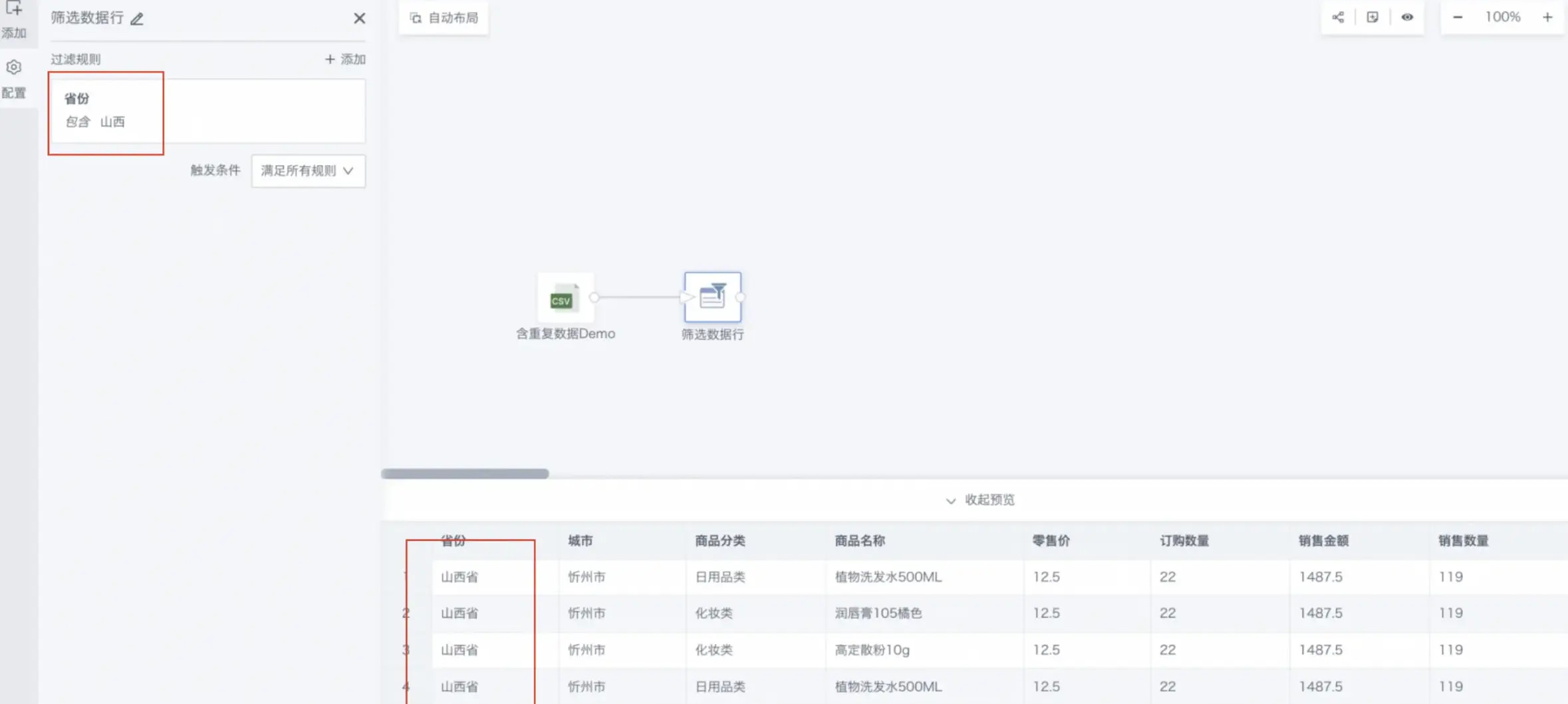
Supports filtering of four data types: text filtering, numeric filtering, date filtering, and boolean filtering. Different filter categories support different filter types.
| Filter Category | Supported Filter Types |
|---|---|
| Text Filter | Select, Range, Condition |
| Numeric Filter | Select, Range |
| Date Filter | Select, Range |
| Boolean Filter | Condition |
| Filter Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Select | Uses condition defaulting to "equal" to filter data, input comparison value (certain numeric value, key text, specific date), find data rows that meet the conditions |
| Range | Uses conditions such as "greater than", "interval", "equal to Null value" to filter data. Input comparison value (certain numeric value), find data rows that meet the conditions |
| Condition | Uses conditions such as "equal", "contains", "starts with" to filter data, input comparison value (key text), find data rows that meet the conditions |
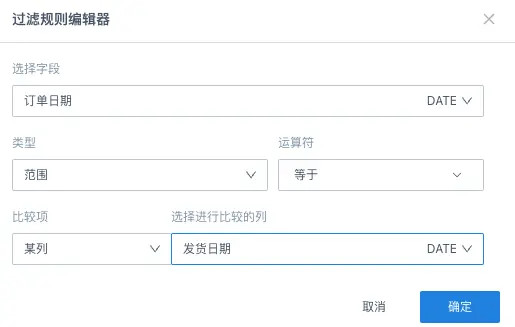
Additionally, in range filters and condition filters, filter rules can not only be set as logical condition filtering for fixed values, but can also set logical condition filtering between columns and columns.
For example, to filter out "order data where users successfully shipped on the same day they placed the order", you can select "Order Date" equals "Shipment Date" (comparison column).
Note: When adding multiple filter conditions, supports setting trigger conditions as Meet All Rules or Meet Any Rule.
3. Specific Case
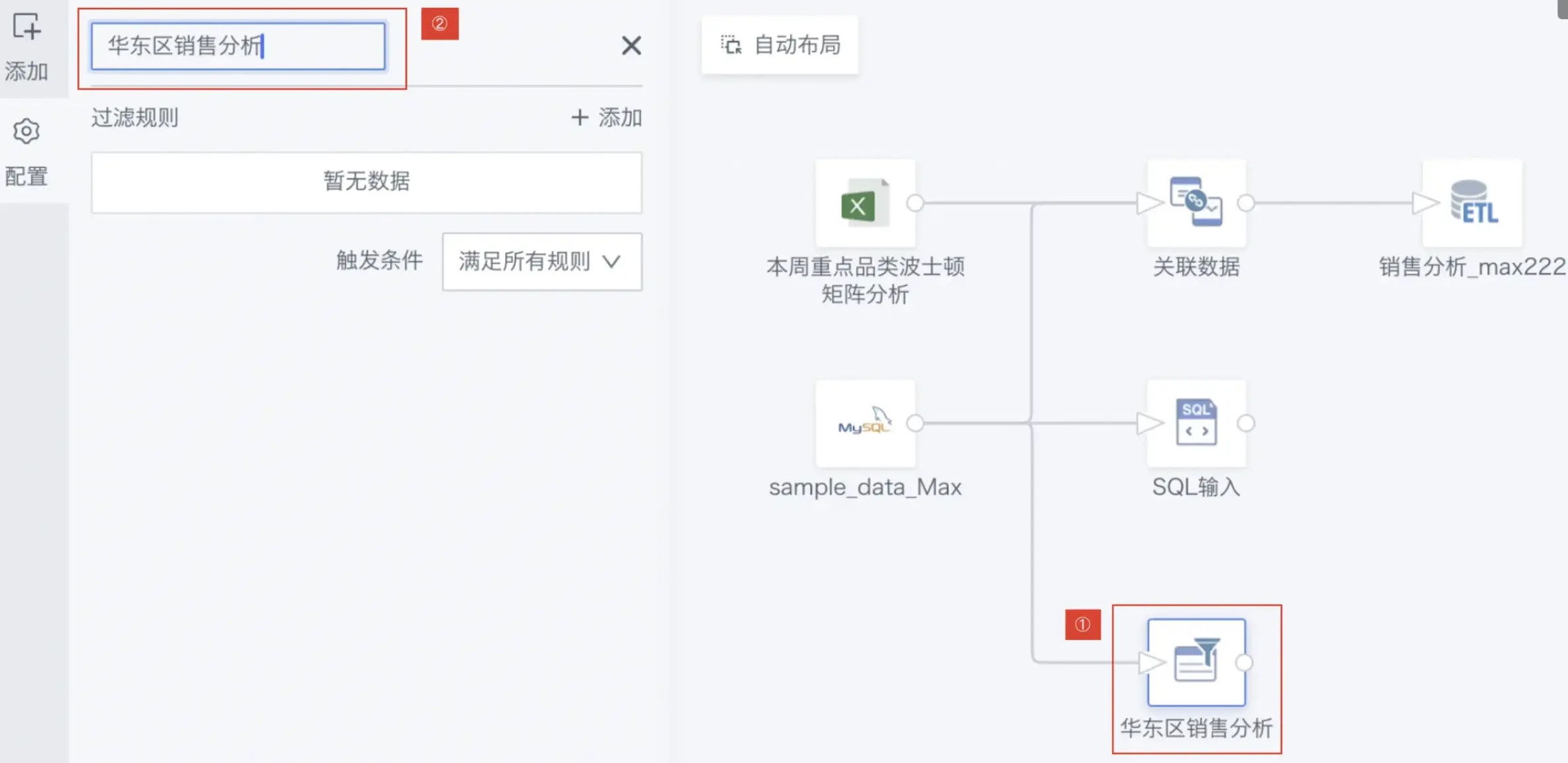
The following introduces configuring an East China Regional Sales Analysis as an example.
-
Add Filter Rules.
The upstream node is nationwide sales data.
- Drag the Filter Data Rows operator from the ETL operator area into the right canvas editing area and connect it after the upstream node;
- Click the Filter Data Rows operator. The left area becomes the current operator configuration area. Rename it according to business needs, such as "East China Regional Sales Analysis";
- Click Add to open the filter.
- Rule editor popup.

-
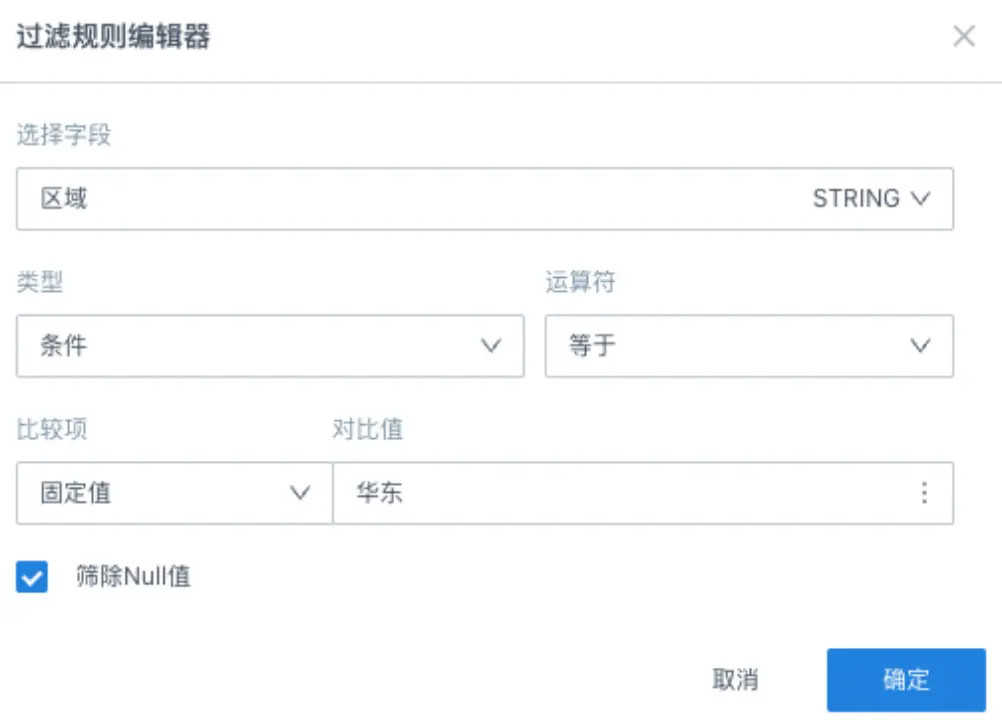
Configure Filter Rule Editor:
- Select Field: Region
- Type: Condition
- Operator: Contains
- Comparison Item: Fixed Value
- Input Comparison Value: East China
- Filter Out Null Values: Checked
-
Preview Data Results:
Click OK and preview the data results.