Smart ETL Nodes
1. Overview
After entering the offline development task editing page, you can drag the "Smart ETL" node from the left side into the canvas and configure it.
This chapter details the configuration items of Smart ETL nodes.
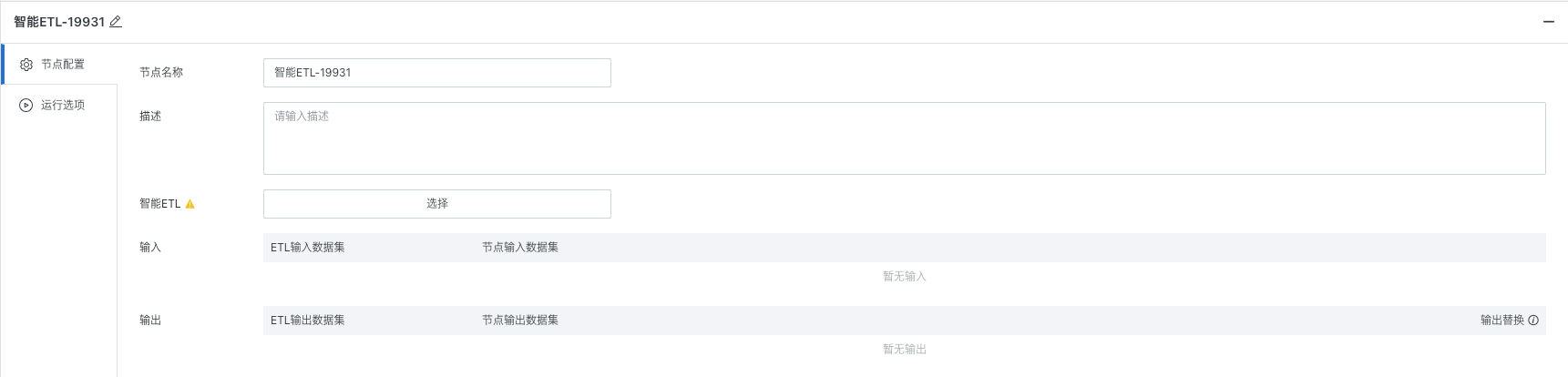
2. Node Configuration
Fill in basic information (optional) for the current task node, enter node name and description in the input boxes. This information can help you better understand and manage nodes, making the entire offline development task process clearer and easier to maintain.
-
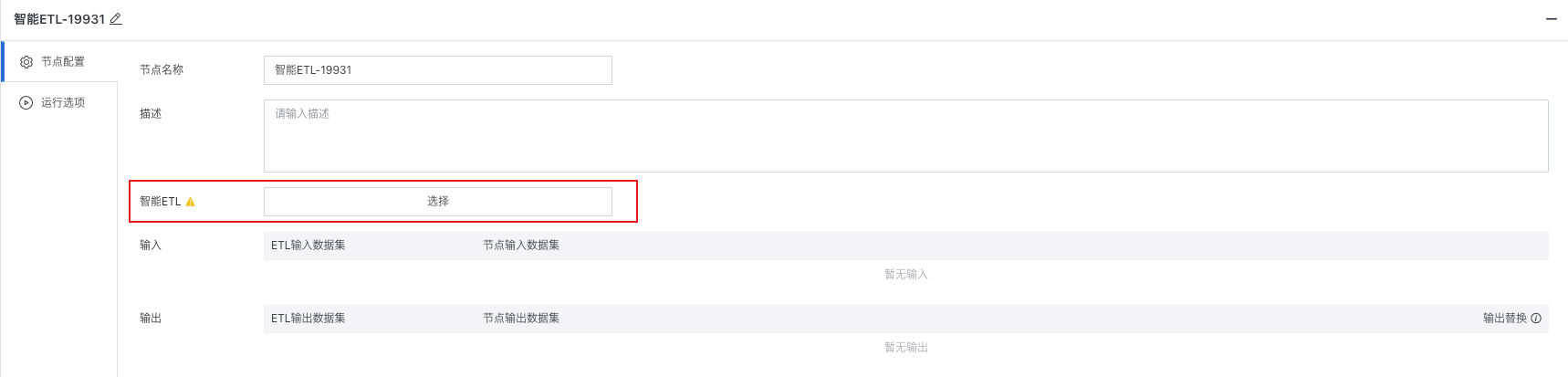
Select the Smart ETL that needs to be scheduled
-
Supports viewing/replacing ETL in the node:
- View ETL: After clicking the task name in "Smart ETL", jump to the ETL task page.
- Replace ETL: Click the "Replace" button to the right of "Smart ETL" to re-specify the ETL as the task node of the workflow.
Tips:
- It is necessary to ensure that the ETL owner is consistent with the current workflow owner, and the ETL is not referenced by other workflows before selection/replacement can be performed.
- If the workflow owner is a regular user, the ETLs displayed in the ETL selection popup are the ETLs that the user has owner permissions for.
- If the workflow owner is an administrator (or an administrator edits a workflow owned by a regular user), the current ETL selection popup will still display all ETLs. At this time, you need to select ETLs that the workflow owner has owner permissions for.
- After referencing the ETL in the workflow, the original update strategy of the ETL will automatically become invalid and be changed to "Follow workflow update".
-
Input/Output Configuration
After selecting the ETL, the platform will automatically parse and display the ETL's input dataset and output dataset list, and can perform data filtering/replacement operations on the original ETL's input/output based on business scenario needs.
-
Input Configuration
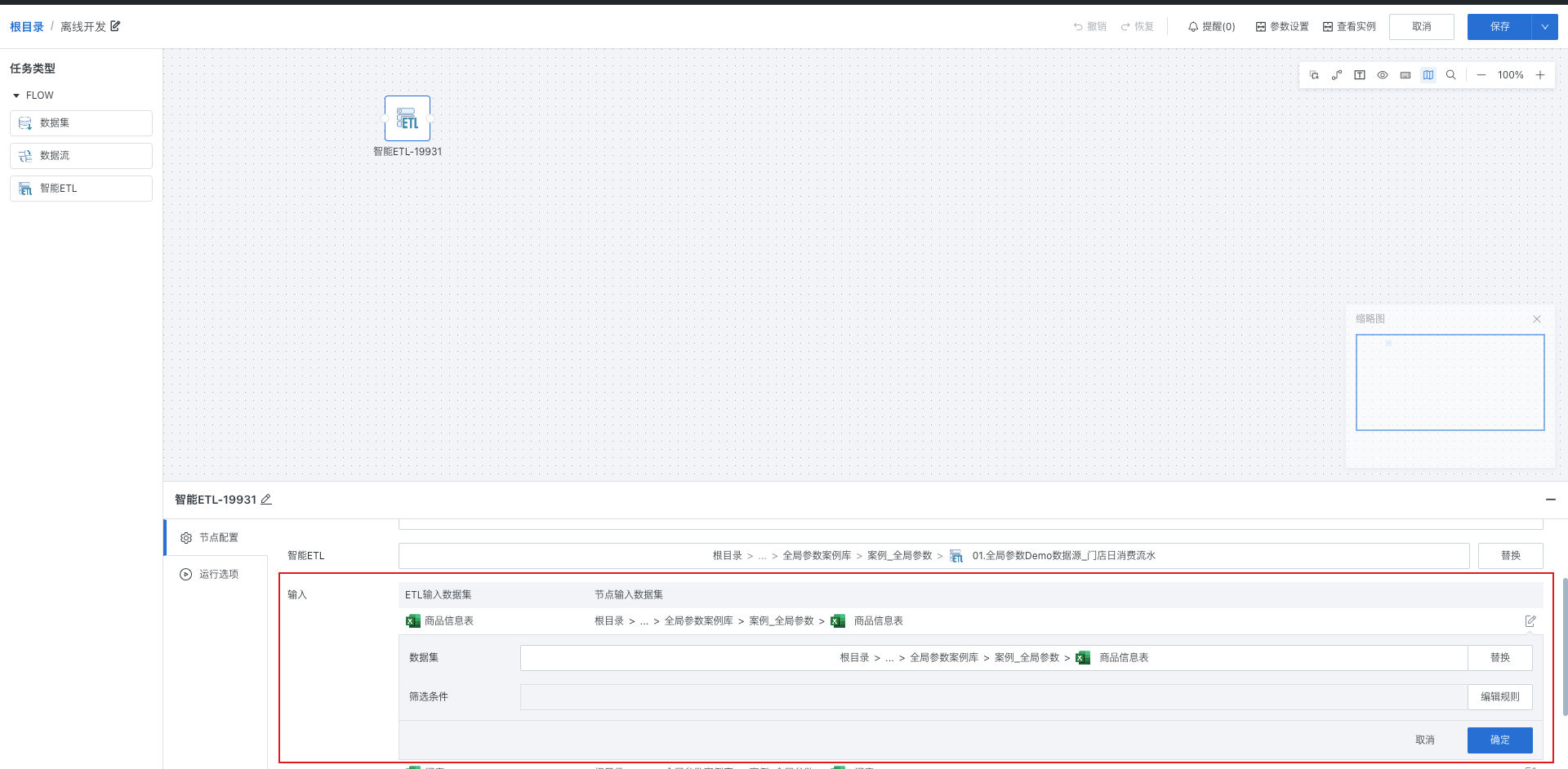
Node input dataset: The actual input data passed when running the current ETL through the workflow. By default, the node input dataset is the original input dataset of the ETL.
If you need to replace the node input dataset or perform data filtering as needed: Click the "Input > Modify" button:
-
Replace: Replace the node input dataset. The replaceable scope is all Guan-index type datasets that the current workflow owner has owner/user permissions for (same as the selectable scope of ETL input datasets).
-
Edit rules: Filter the current dataset through filter conditions, supports referencing global parameters, workflow parameters (see workflow parameter related content in this article for details), and time macros.
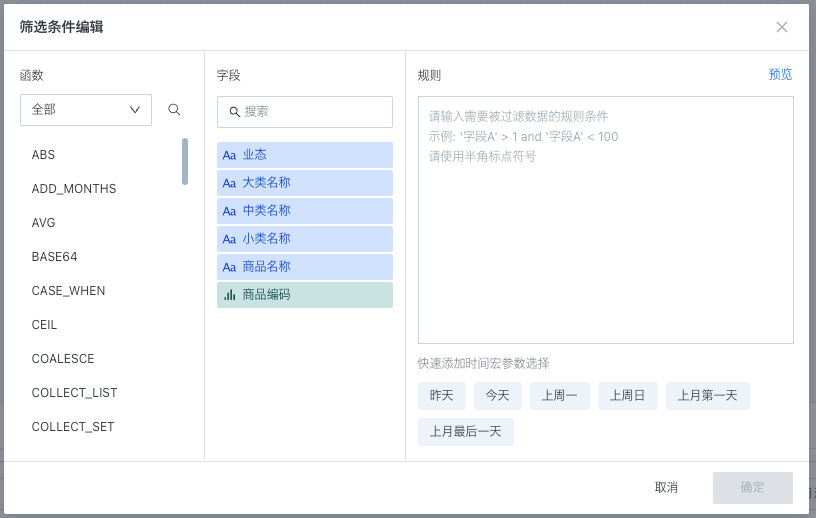
-
Output Configuration
Node output dataset: The offline development dataset that actually stores the running result data when running the current ETL through the workflow.
By default (i.e., when input replacement is not enabled), the node output dataset is the original output dataset of the ETL. When running the ETL, data will be directly written to the ETL's default output dataset.
If you need to perform incremental updates on the output dataset, or perform full updates while ensuring the data structure remains unchanged, you need to check "Output Replacement" and configure the output dataset to be replaced:
After enabling "Output Replacement", the data generated by ETL running will be output to the replaced dataset in incremental/full mode according to the "Output Replacement" configuration (the original ETL output dataset will no longer perform data writing).

-
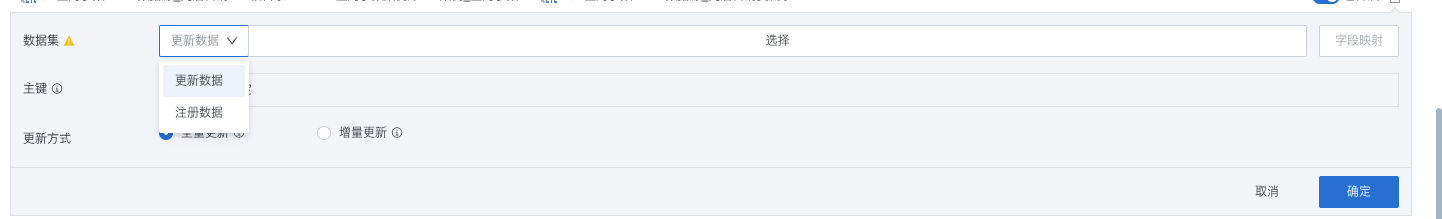
Select target output dataset:
-
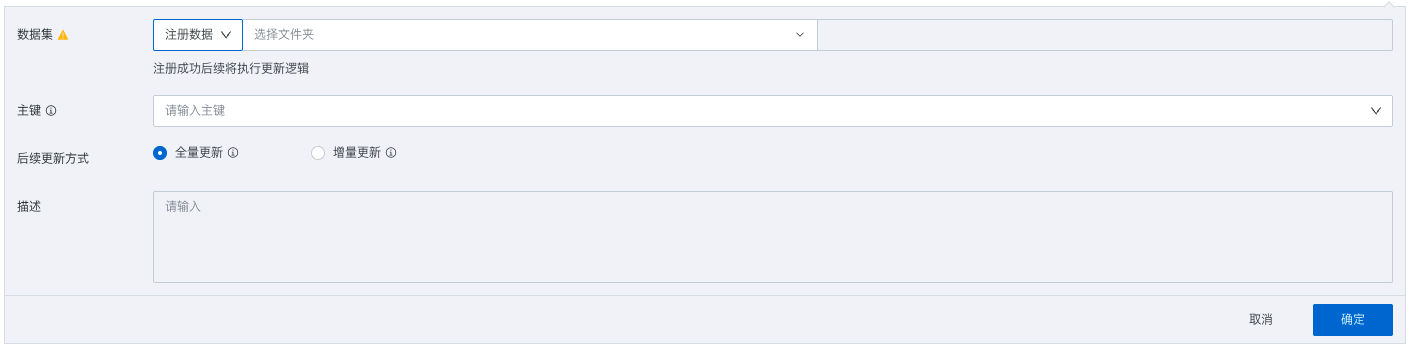
Register data: When the target output dataset does not exist, select the register data mode, fill in dataset name, storage path, primary key (optional) and other information. After creating a new advanced scheduling dataset, the update data logic will be executed subsequently.
-
-
Update data: When the target output dataset exists, select the update data mode, directly reference the target dataset to be replaced, and update the dataset.
-
Supports "Field Mapping" to perform same-name mapping between ETL output fields and target dataset fields, and modify field mappings.
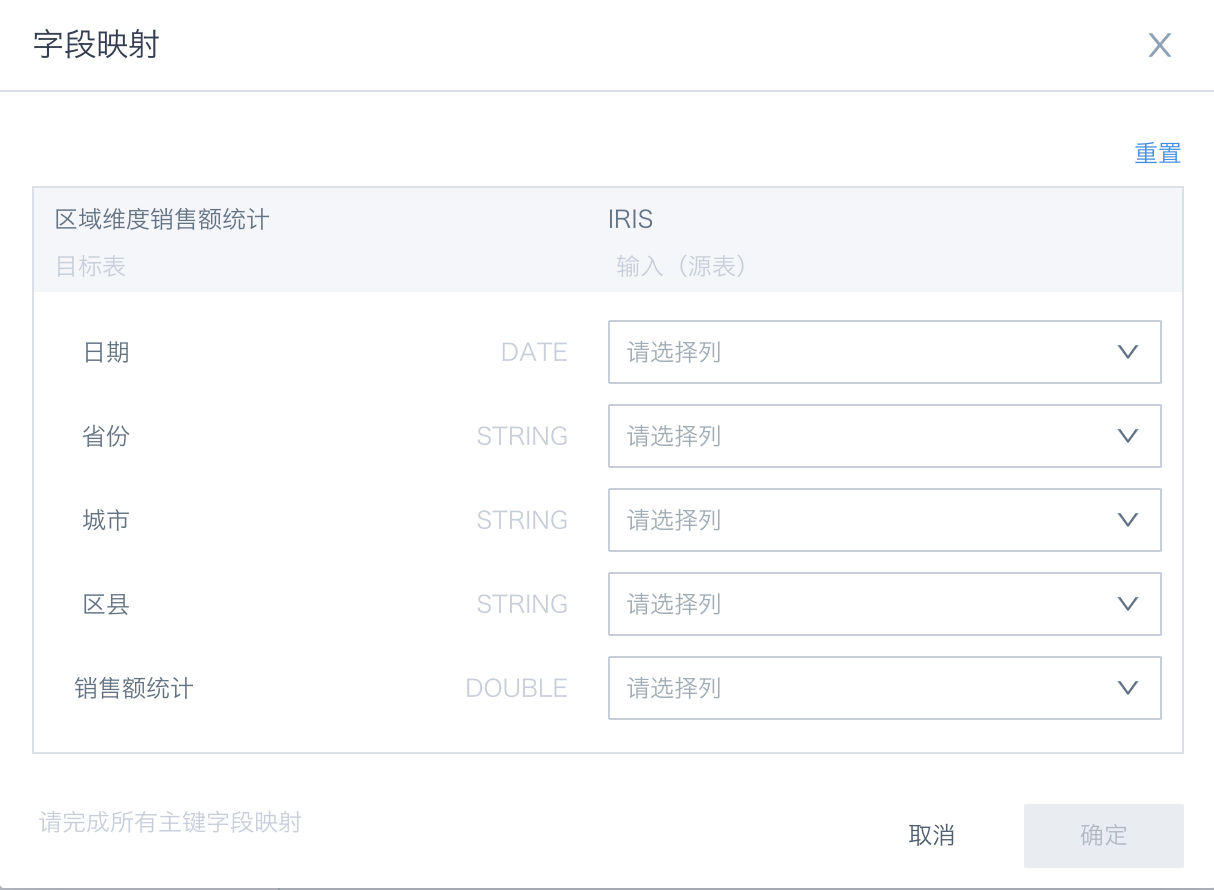
-
Output selectable dataset scope: Offline development datasets that the workflow owner has owner permissions for.
-
-
Subsequent update method: The update method for the dataset after selecting or creating the node output dataset.
- Full update: Clear historical data from the target dataset before writing
- Incremental update: Retain existing data in the target dataset before writing
-
If the dataset has a primary key set, deduplication will be performed based on the primary key during writing
-
Supports configuring "Predecessor cleaning rules". Before data writing, data will be cleaned according to the predecessor cleaning rules, then incremental update will be executed.
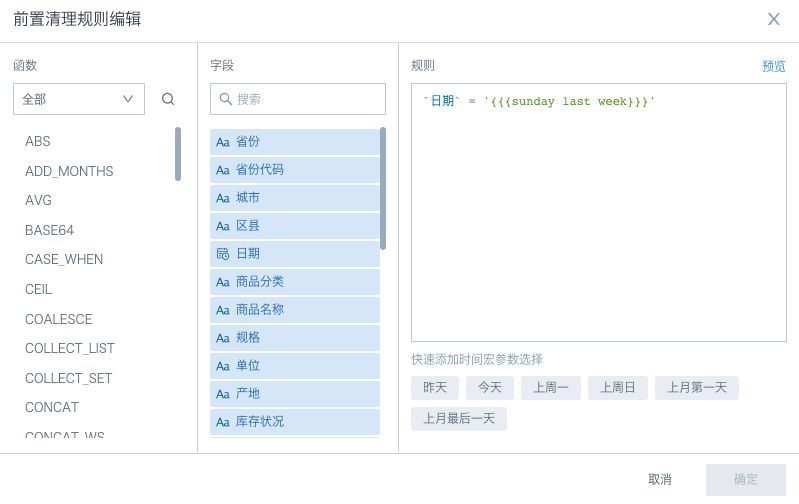
-
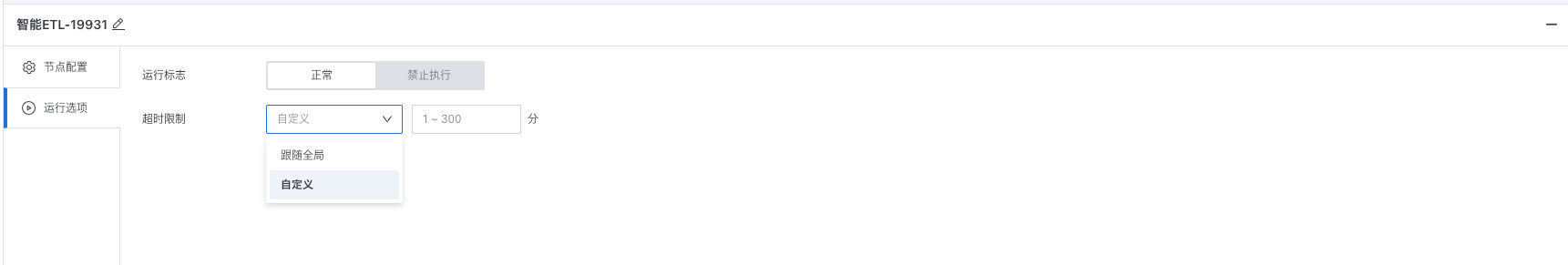
3. Running Options
According to the complexity of the task and the actual situation of the running environment, choosing appropriate "Running flag" and "Task operator ETL node running timeout limit" can improve task execution efficiency and reliability.
-
Running flag: Set the corresponding node's execution strategy during runtime according to scheduling needs:
- Prohibit execution: After the workflow runs to this node, it will directly skip execution, commonly used for temporary data problem troubleshooting, partial task running control and other scenarios.
- Normal: Run the node according to the existing scheduling strategy, the default running flag for nodes.
-
Timeout setting: Supports custom timeout time/follow global timeout time. If the ETL does not complete running within the set time, it will be automatically killed to avoid occupying the task queue or computing resources for a long time and blocking the normal running of other tasks.