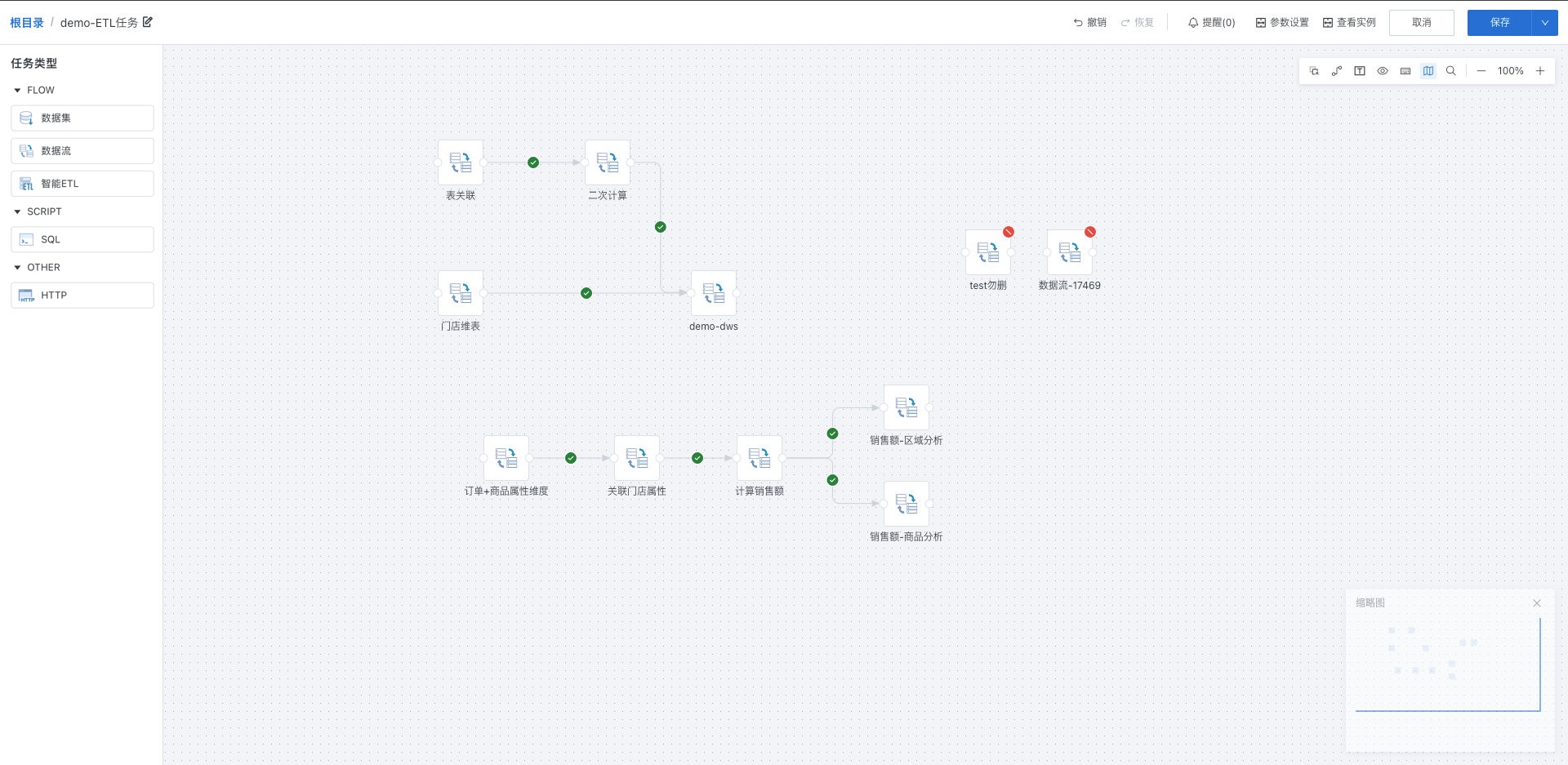
Offline Development Tasks
1. Overview
The offline development module provides low-threshold visual ETL data flow orchestration capabilities, and supports extended task types such as Python scripts and Shell commands to improve development efficiency; supports various operators such as data flows, providing graphical data integration and processing capabilities; at the same time supports efficient task orchestration through loop control, conditional branching, sub-workflows and other methods.
2. Folder Management
Users can manage and query offline development tasks by creating folders.
On the offline development list page, create a new folder or create multi-level folders, assign different permissions to different users, and also perform operations such as renaming folders and moving them to other folders.
Supports distributing folder permissions to different users. Folder permissions are divided into owner and user.
- Folder owner View, delete, rename, create offline development tasks, create sub-folders, move offline development tasks to this folder, move folders to other folders with owner permissions, configure owner/user permissions.
- Folder user View folders, create offline development tasks, move offline development tasks to this folder.
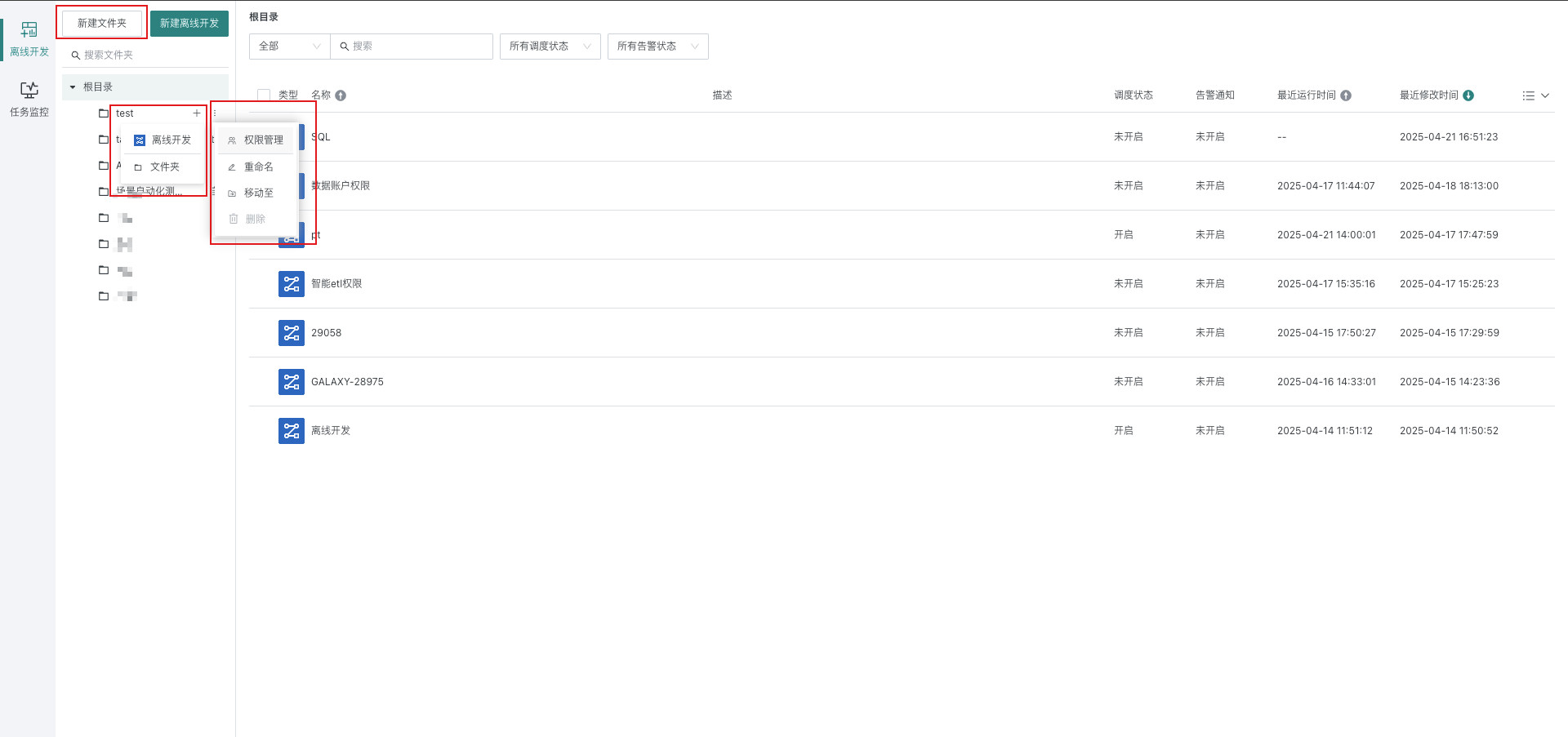
3. Create Offline Development Tasks
Create offline development tasks on the offline development page, and manage them in the task list after completion.
-
Enter the "Offline Development" page and click "New Offline Development".

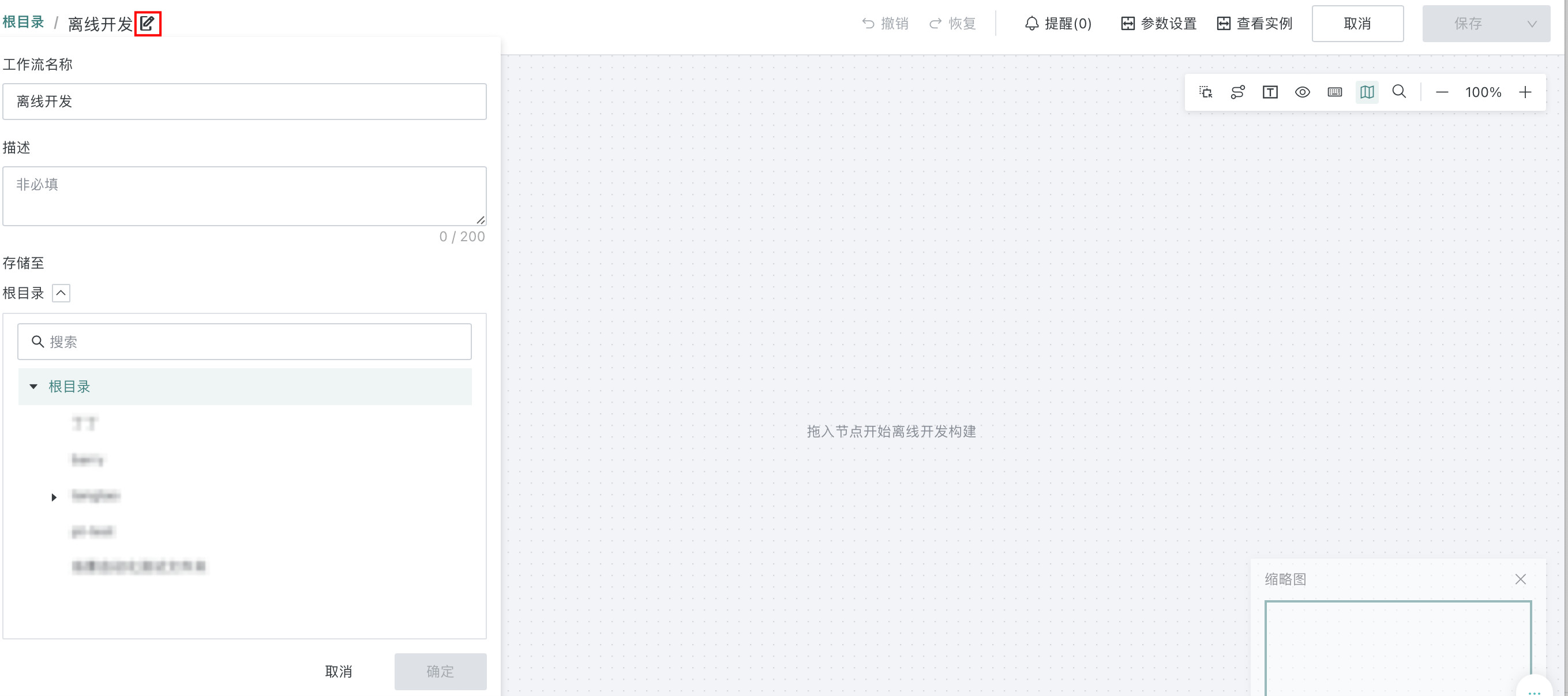
-
Click the edit button, modify the workflow name, configure description information, select the storage path and click "OK".
-
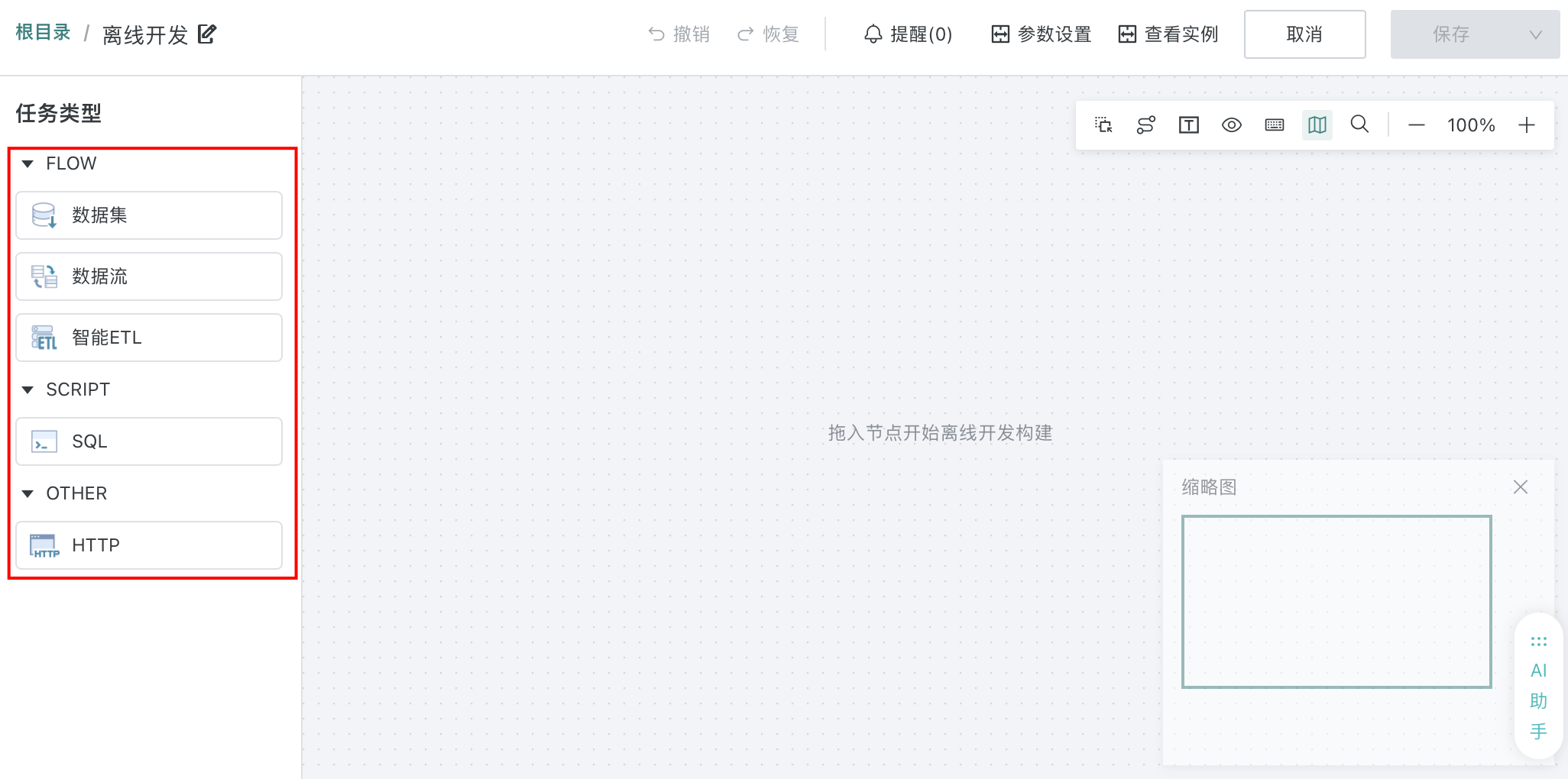
Drag the left-side nodes into the canvas as needed, and add connections between nodes to orchestrate offline development tasks.
- Dataset node related instructions, see Dataset Nodes for details.
- Data Flow node related instructions, see Data Flow Nodes for details.
- Smart ETL node related instructions, see Smart ETL Nodes for details.
- SQL node related instructions, see SQL Nodes for details.
- HTTP node related instructions, see HTTP Nodes for details.
- Task orchestration related instructions, see Task Orchestration Instructions.
-
(Optional) If you need to create workflow parameters, click "Parameter Settings" in the upper right corner to configure. When the workflow is executed, parameters will be dynamically replaced with their corresponding values and take effect in data filtering and other links. Parameter setting related instructions, see Parameter Configuration Instructions for details.
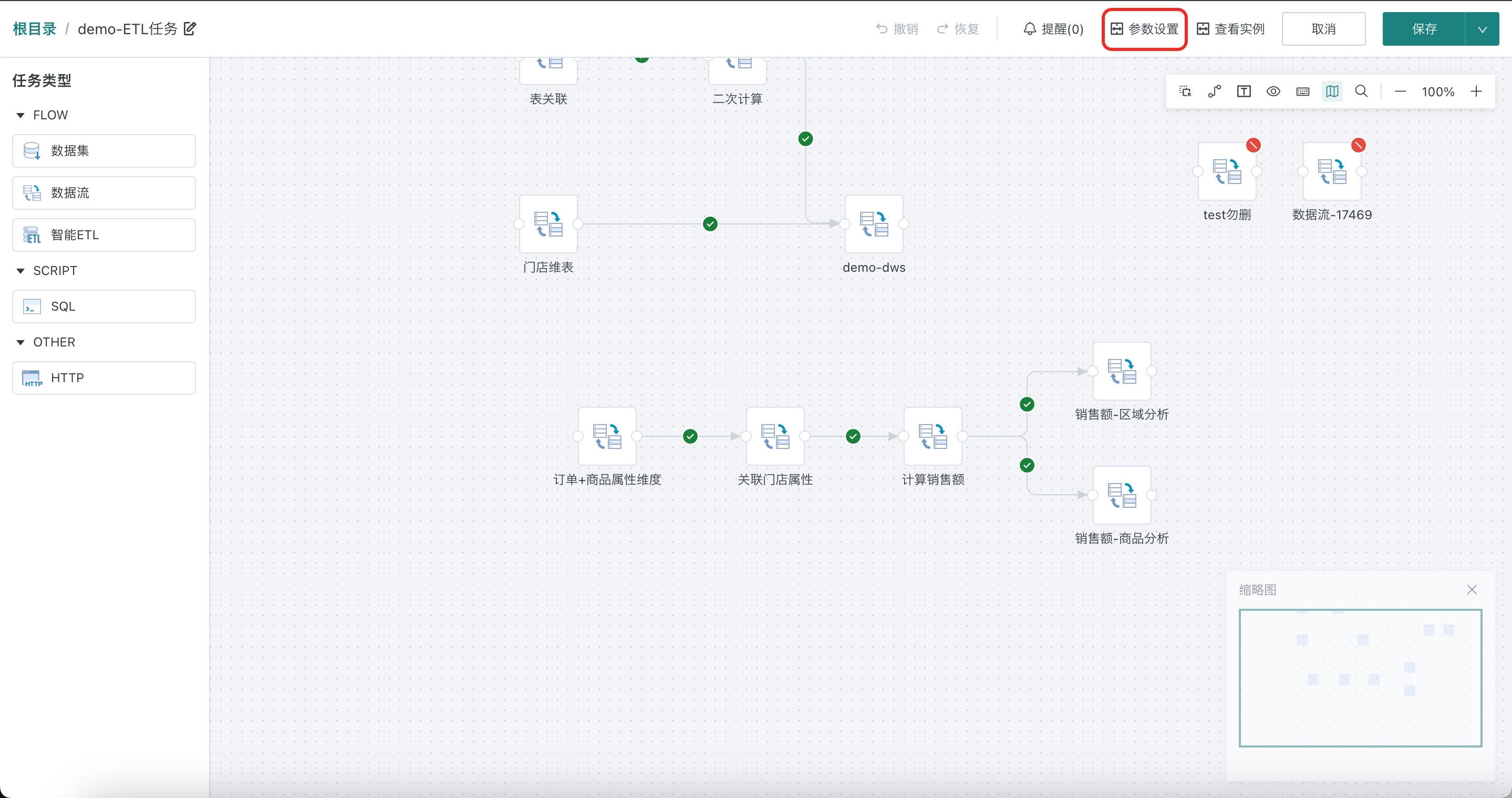
-
After the offline development task configuration is completed, click "Save" in the upper right corner.
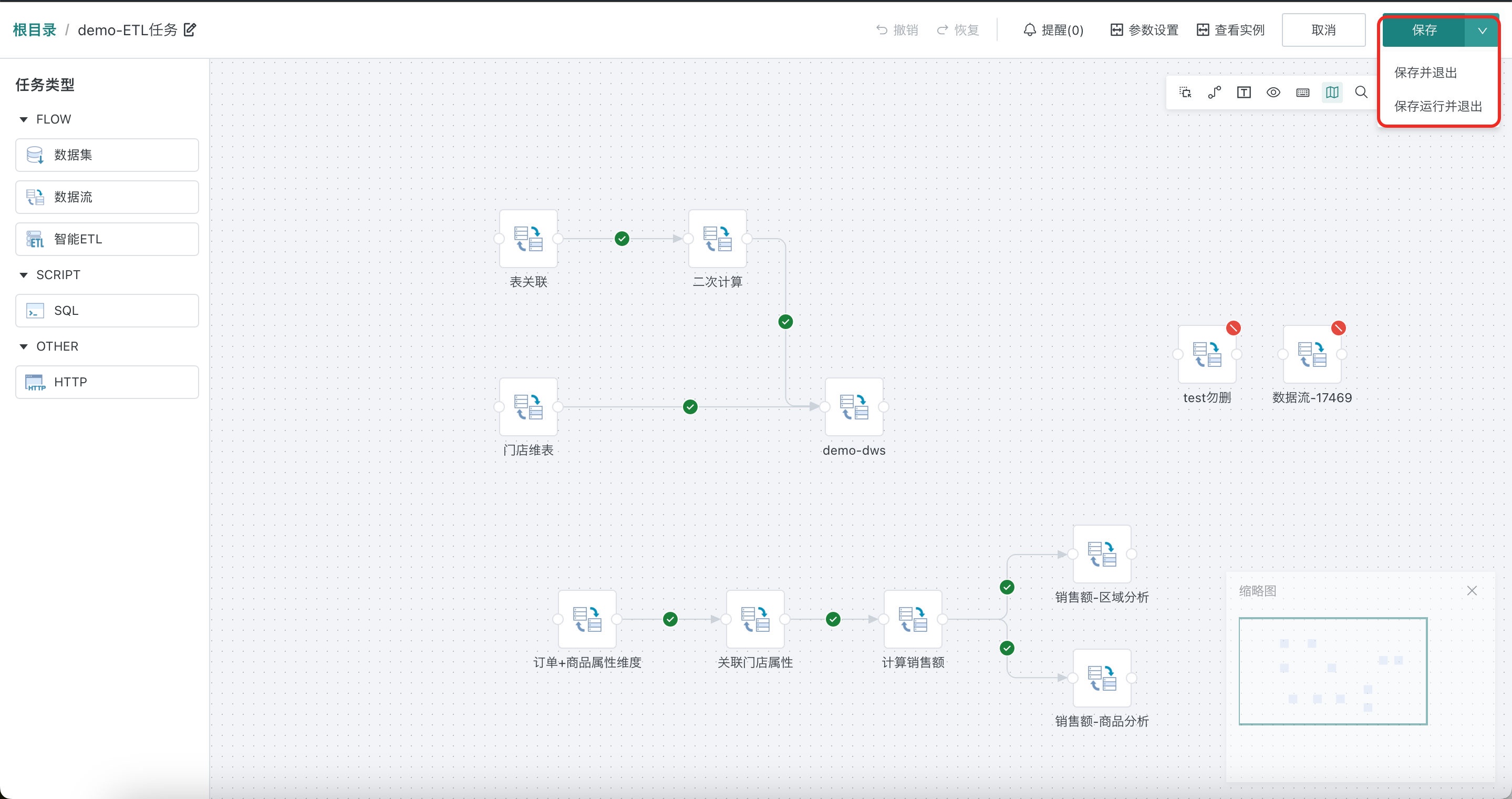
4. Manage Offline Development Tasks
After offline development tasks are created, you can view the created tasks and basic information (including task name, description, creator, creation time, etc.) in the offline development task list, and centrally manage the tasks, performing management operations such as running, editing, and deleting workflows.
-
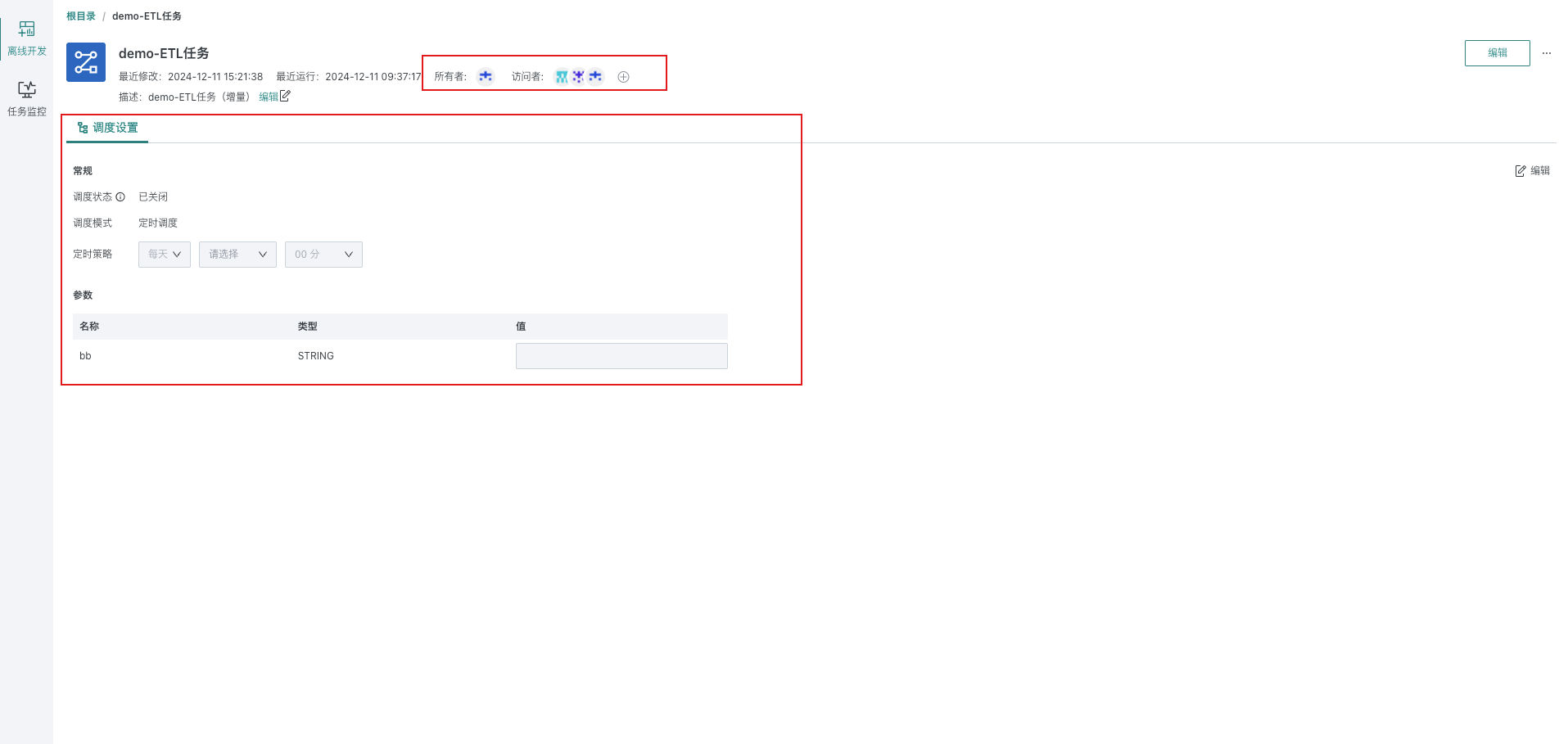
View Tasks
Click on the target task in the list to enter the task details page. This page is mainly used to display the detailed information of the target task and supports workflow property configurations such as permission management and scheduling settings.
- Permission management: View/manage workflow owners and visitors.
- Scheduling settings: Support modifying scheduling status, scheduled scheduling strategies, scheduling parameters and other information.
-
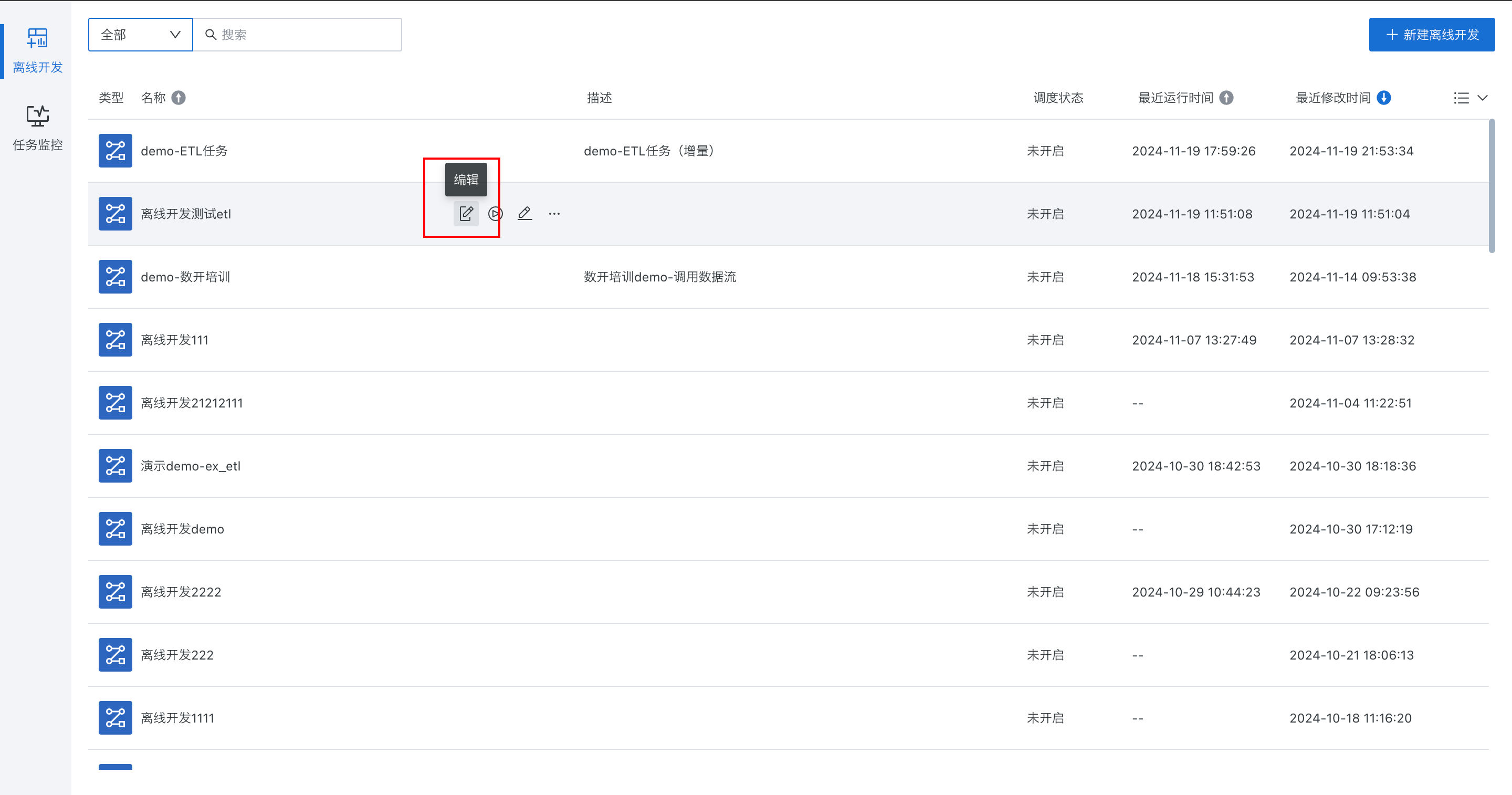
Edit Tasks
Modify existing tasks. After clicking the "Edit" button, jump to the task editing page.
-
Run Tasks
Execute a created task. Each time a task is run, a task instance will be generated correspondingly, used for viewing the status of various nodes in the task of this run and operations management.

-
Rename Tasks
Rename tasks, workflows under the same path cannot have duplicate names. (Currently only supports root directory).

-
Delete Tasks
Delete created workflows. After deletion, the ETLs referenced in the task will be restored to manual running and can be referenced by other tasks.
5. Run Offline Development Tasks
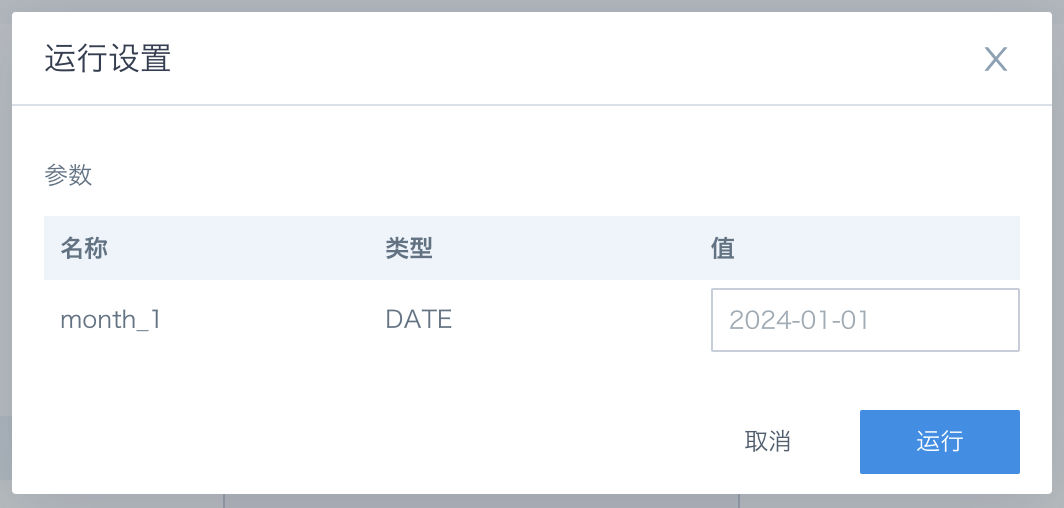
After the workflow task configuration is completed and saved, the workflow can be run through manual/platform scheduling/URL trigger methods. Users can specify the running parameter values under the corresponding running method. If not specified, the parameter default values will be used.
Manual Run Entries:
-
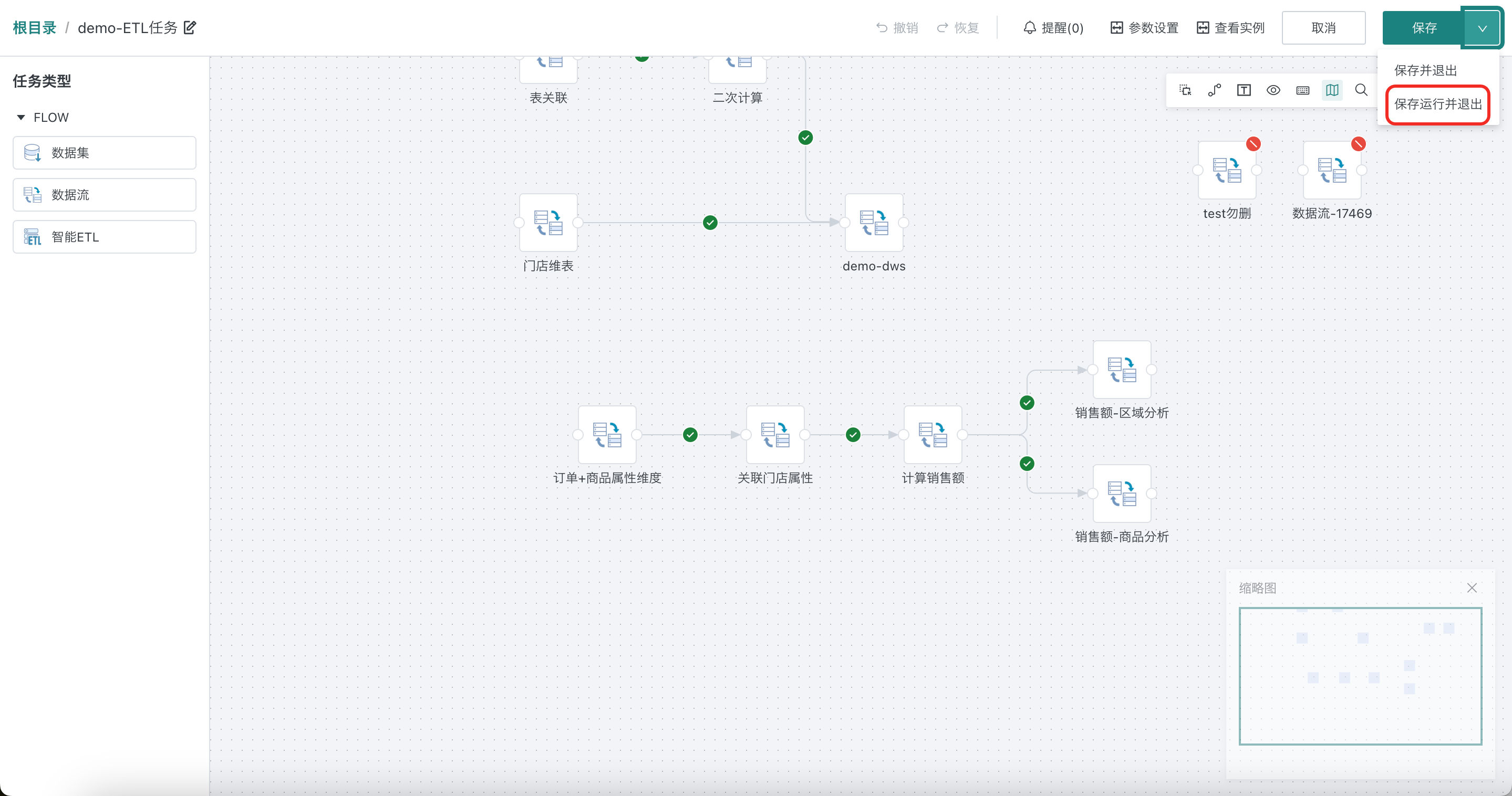
Workflow editing page > Save, run and exit
-
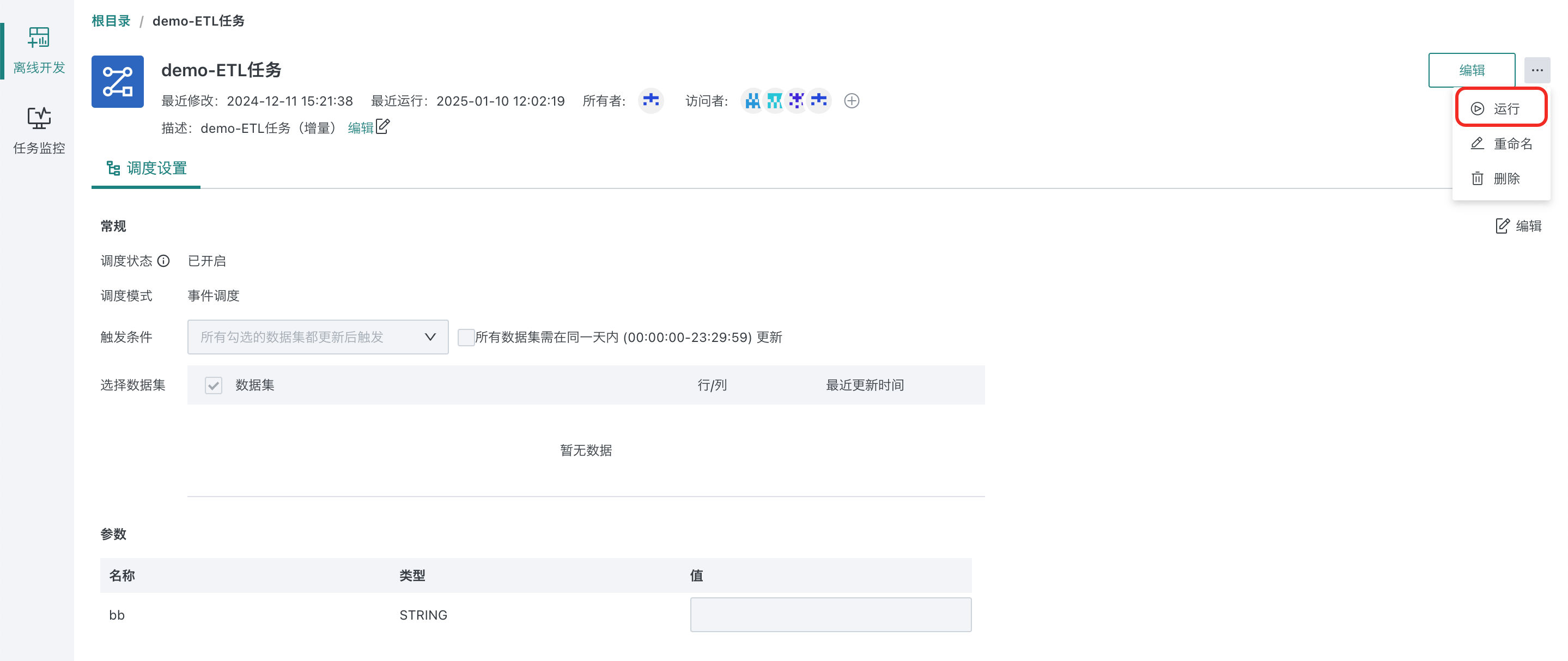
Workflow details page > More operations > Run
-
Workflow list page > Run
6. Parameter Configuration Instructions
Supports creating workflow parameters according to actual business needs, with the scope being the current workflow. When the workflow is executed, parameters will be dynamically replaced with their corresponding values and take effect in data filtering and other links.
Workflow parameter definition:
Click "Parameter List" > Settings to add/modify/delete workflow parameters.
- Name (required): Workflow parameter name, supports input of Chinese/numbers/letters/underscores (not allowed to be empty), parameter names are not allowed to be duplicated.
- Type (required): Workflow parameter storage type, supports selecting text, numeric, and date three types.
- Value (optional): Workflow parameter default value, can be dynamically specified at runtime.
- Description (optional): Used to explain the usage of the current workflow parameter, etc.
In addition, workflow parameter definition also supports directly referencing global parameters.
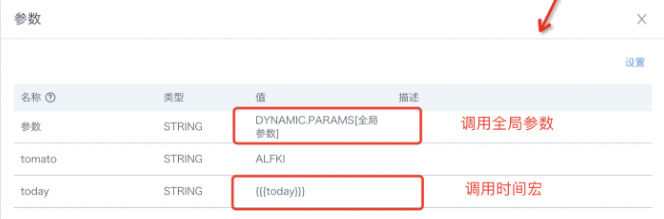
Workflow parameter reference method: [DYNAMIC_PARAMS.parameter_name], when parameter values are not dynamically passed in, the default value defined in the workflow parameters will be taken.
7. Task Orchestration Instructions
Task orchestration refers to the process of orchestrating various tasks involved in business scenarios according to their running order and dependencies based on business requirements.
In offline development task orchestration, connections are used to connect different task nodes to define their execution order and scheduling logic. The direction of the connection arrow indicates the running order of tasks, and the connection style indicates the upstream and downstream scheduling relationship. Currently supports three scheduling relationships: success scheduling, failure scheduling, and sequential scheduling. The overall running logic is as follows:
- Success scheduling: When the upstream runs to completion and the running result is "success", immediately trigger the downstream task to run. If the running result is failure, etc., the downstream tasks will not be executed.
- Failure scheduling: When the upstream runs to completion and the running result is "failure", immediately trigger the downstream task to run. If the running result is success, etc., the downstream tasks will not be executed.
- Sequential scheduling: After the upstream runs to completion, regardless of whether the running result is success/failure, etc., the downstream task will be immediately triggered to run.
- If a downstream task has multiple upstream dependencies, the downstream task can only be triggered to run after all upstream dependency scheduling relationships are satisfied.
- If a task has no upstream dependencies, the task will be triggered to run immediately after the workflow runs.