Cumulative Calculation
1. Overview
1.1 Application Scenarios
By accumulating a series of data daily, monthly, or by other criteria, you can obtain the overall situation or trend, which can represent the growth or accumulation of a certain quantity, or reflect the change of an indicator over a period of time.
For example, in business scenarios, you can track the progress of annual sales targets in real time based on monthly cumulative sales.
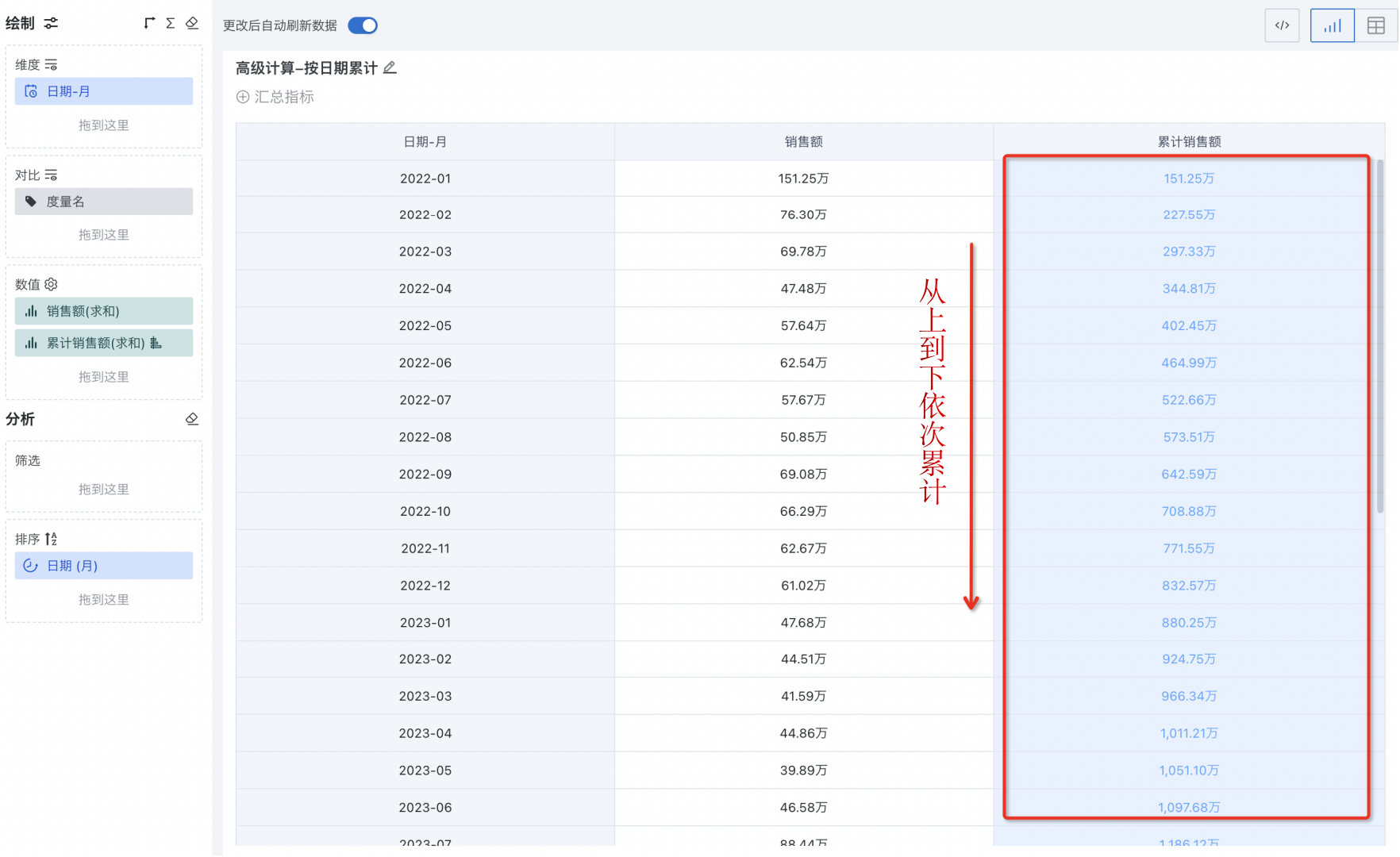
1.2 Feature Introduction
In the navigation bar, select "Data Analysis > Target Card" and enter the card editing page. In the left "Drawing" area, drag the target value field, click the field, and select "Advanced Calculation > Cumulative Calculation" from the dropdown.
-
Supports cumulative calculation by date-type fields. In this case, there must be a date field in the dimension, and cumulative calculation is supported by week, month, quarter, current year, and all years according to different date granularities.
-
Supports cumulative calculation by text-type fields. In this case, global row-by-row accumulation and group accumulation by a certain dimension are supported.
2. Operation Steps
2.1 Cumulative Calculation by Date Field
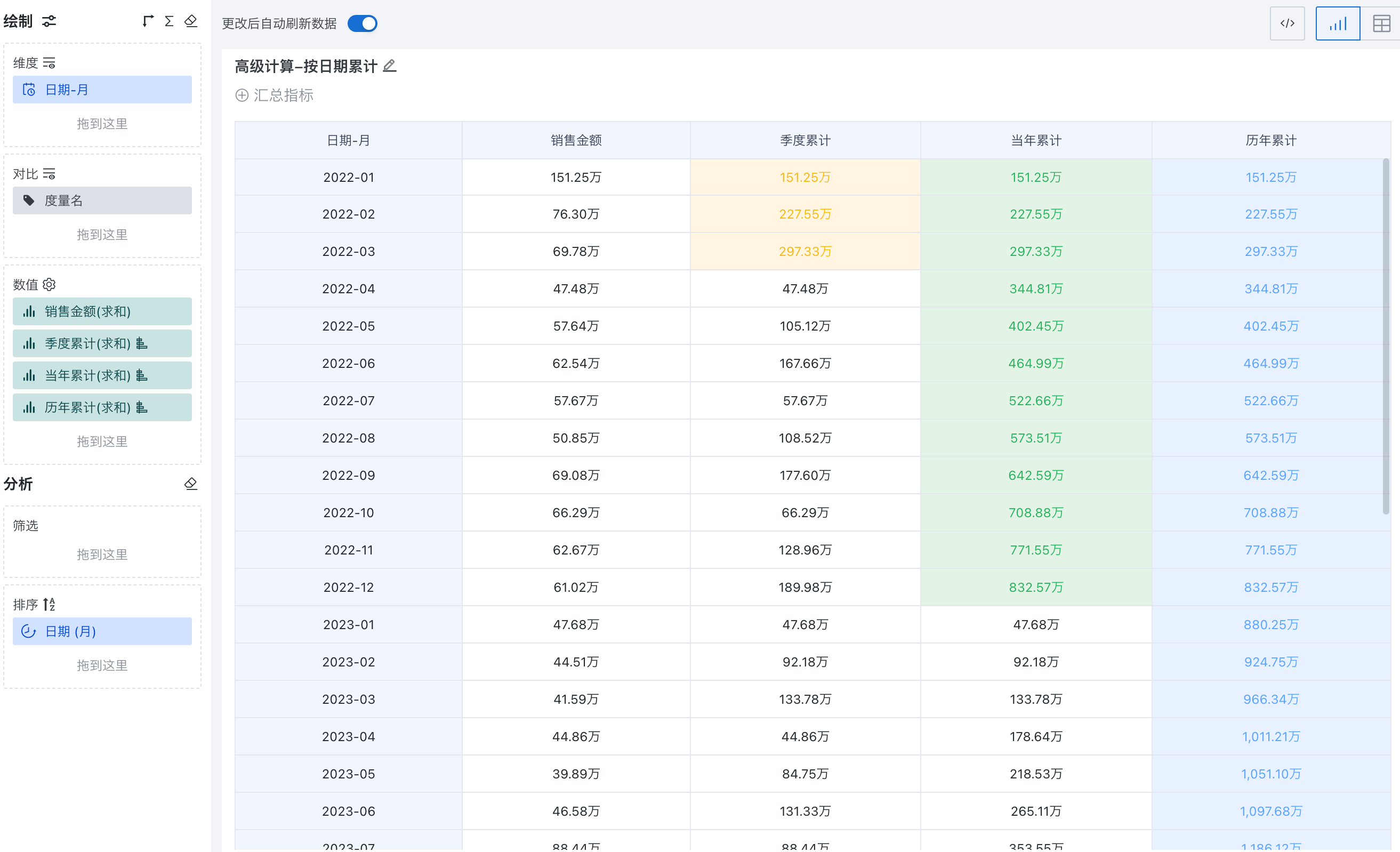
Taking cumulative calculation by monthly date granularity as an example, you can set "Quarterly Cumulative", "Current Year Cumulative", and "All Years Cumulative".
-
Quarterly Cumulative: Accumulates from the first day of the quarter to the current date, and recalculates for each quarter.
-
Current Year Cumulative: Accumulates from the first day of the year to the current date, and recalculates for each year.
-
All Years Cumulative: Accumulates from the first day of the first year with data to the current date, and accumulates all data in chronological order.
Below is an example of creating a sales amount cumulative table to calculate quarterly, current year, and all years cumulative sales (right side of the figure). Sample dataset: Product Practice Dataset (22~24).xlsx.
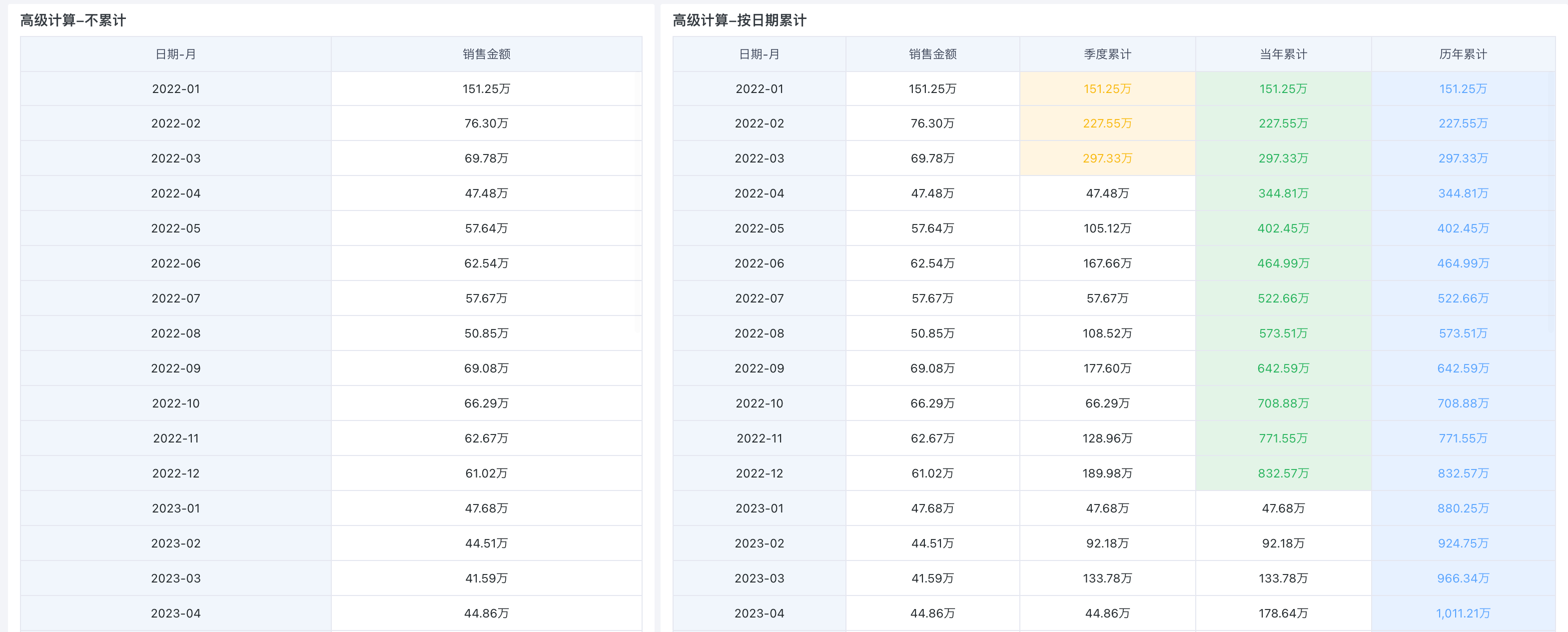
-
In the drawing area, drag "Date (Month)" into the dimension bar and "Sales Amount" into the value bar. For display purposes, drag "Sales Amount" into the value bar three times and set aliases as "Quarterly Cumulative", "Current Year Cumulative", and "All Years Cumulative" respectively.
-
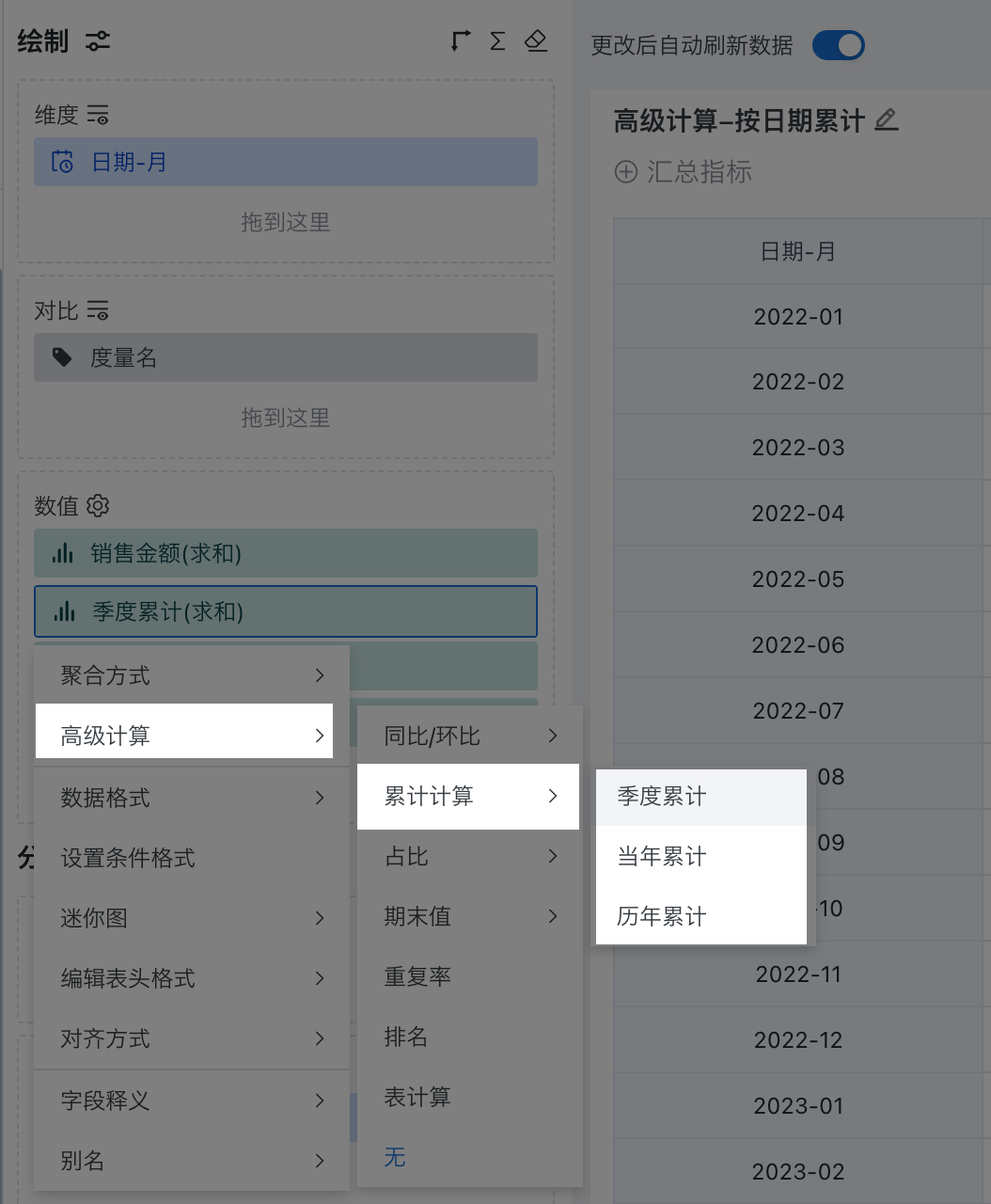
Configure cumulative calculation: Click the "Quarterly Cumulative" field, select "Advanced Calculation > Cumulative Calculation" from the dropdown, and select "Quarterly Cumulative" as the cumulative range in this example. Similarly, configure "Current Year Cumulative" and "All Years Cumulative".
- View the effect of cumulative calculation by date.
2.2 Cumulative Calculation by Text-Type Field
2.2.1 Global Cumulative
Global cumulative refers to cumulative calculation row by row for global data.
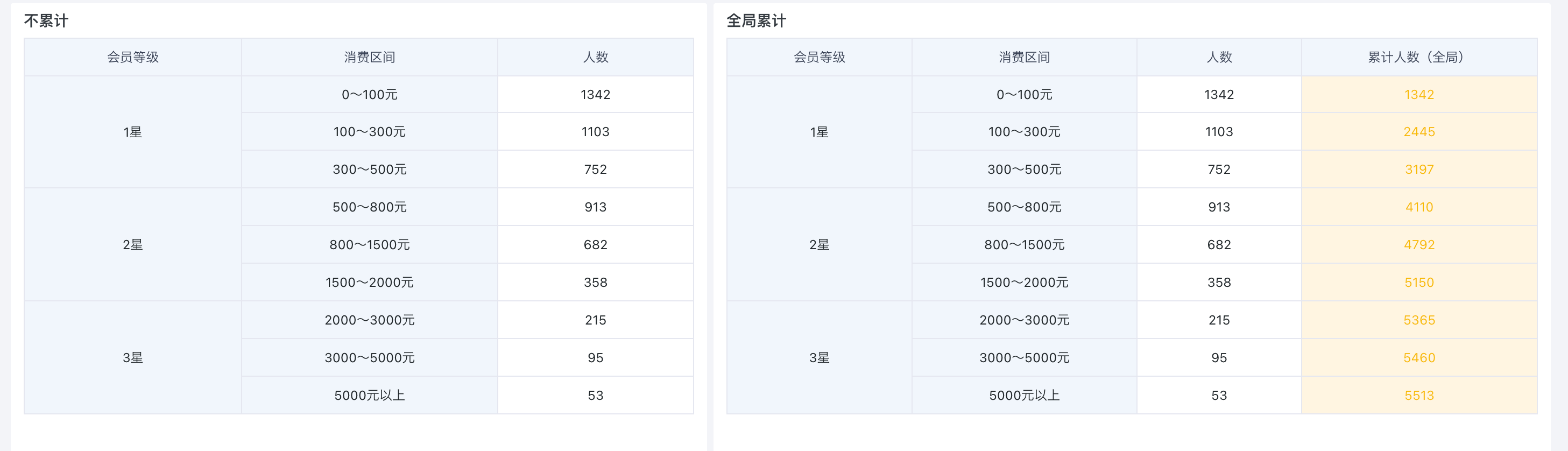
Below is an example of creating a "Cumulative Number of Consumers Table" to calculate the cumulative number of people for different membership levels and consumption intervals. Sample dataset: Cumulative Calculation - Consumption Level.xlsx.
-
In the drawing area, drag "Membership Level" and "Consumption Interval" into the dimension bar, and "Number of People" into the value bar. For display purposes, drag "Number of People" into the value bar again and set the alias as "Cumulative Number (Global)".
-
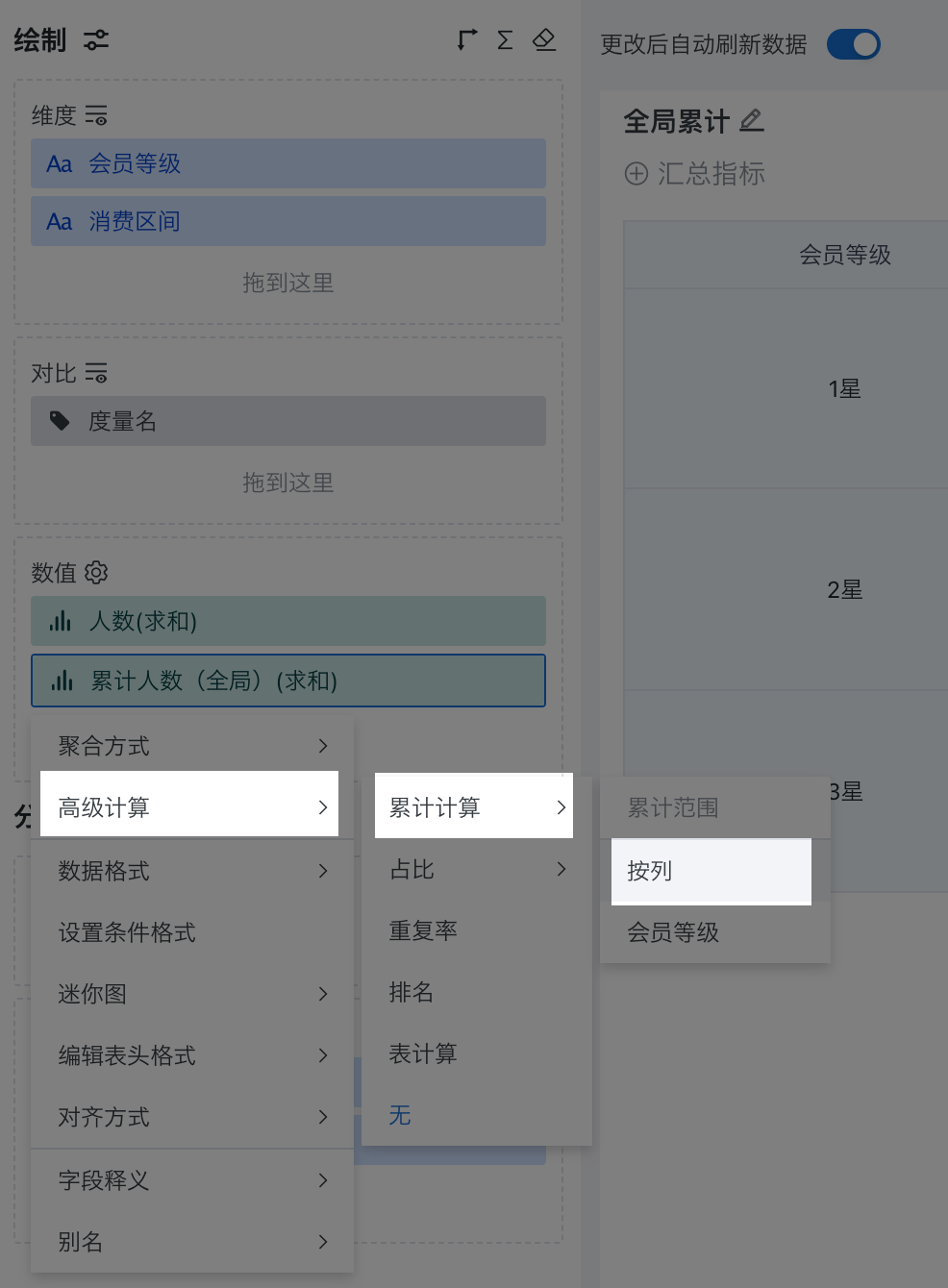
Click the "Cumulative Number (Global)" field, select "Advanced Calculation > Cumulative Calculation" from the dropdown, and select "By Column" as the cumulative range in this example.
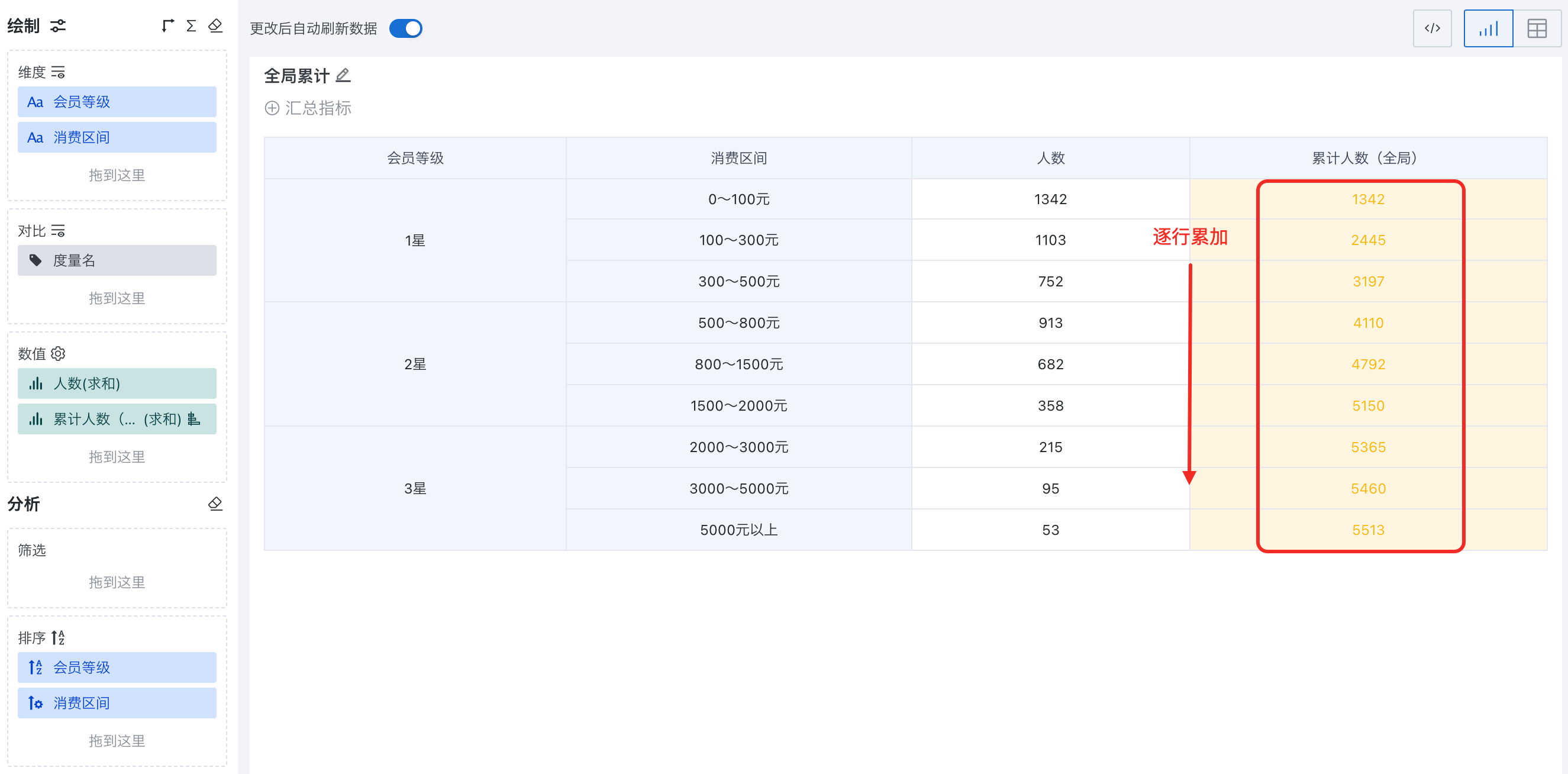
- View the effect of global cumulative calculation by column.
As shown, the "Cumulative Number (Global)" column is accumulated row by row.
2.2.2 Group Cumulative (By a Certain Field)
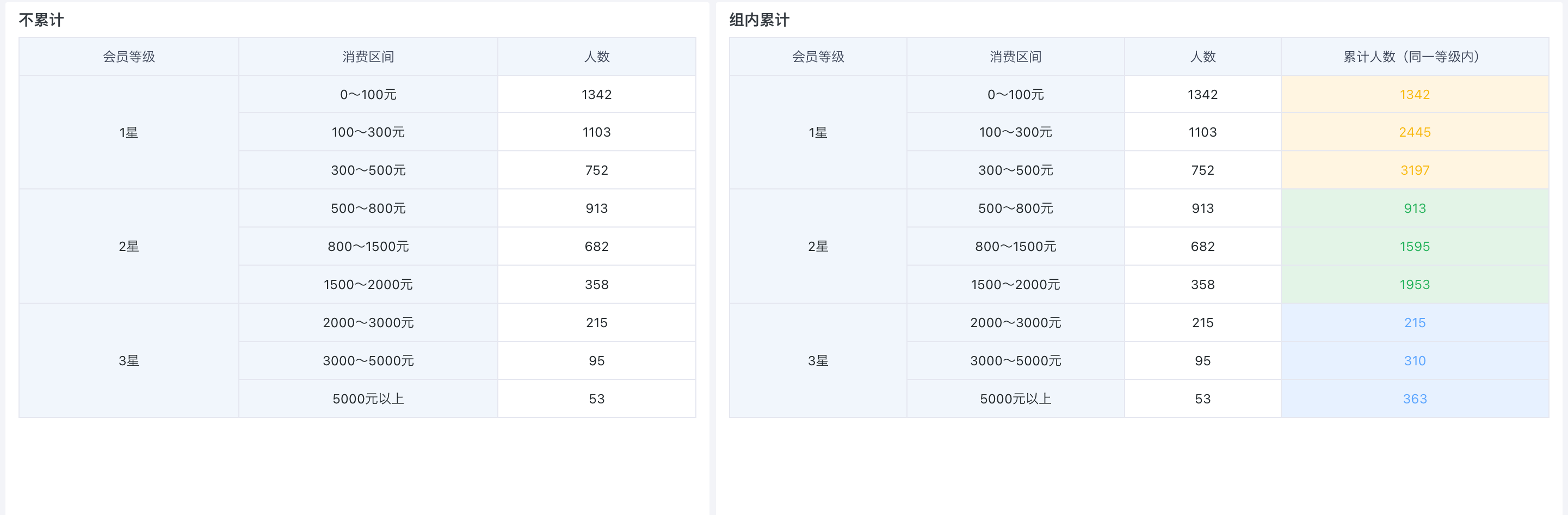
Group cumulative refers to cumulative calculation within a group by a certain dimension field.
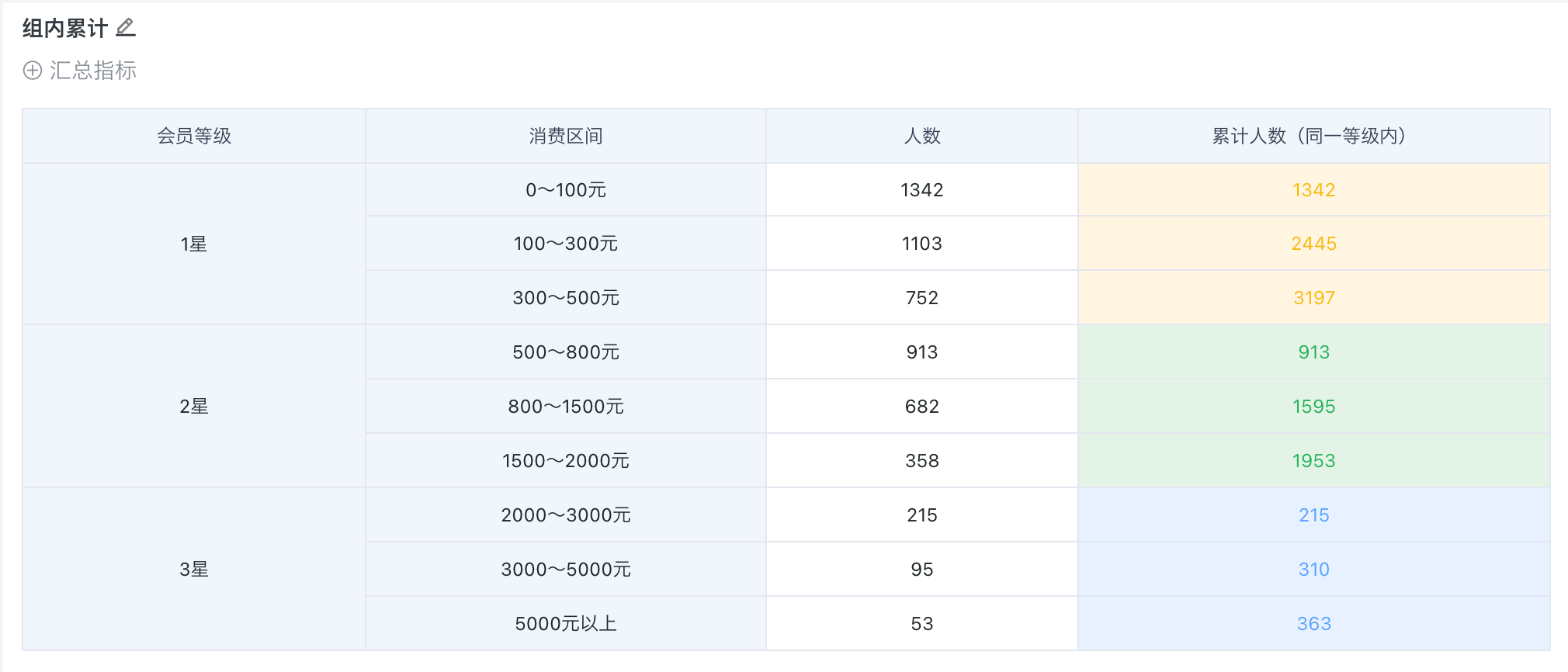
Below is an example of creating a "Cumulative Number of Consumers by Membership Level Table" to calculate the cumulative number of people for each consumption interval within different membership levels. Sample dataset: Cumulative Calculation - Consumption Level.xlsx.
-
In the drawing area, drag "Membership Level" and "Consumption Interval" into the dimension bar, and "Number of People" into the value bar. For display purposes, drag "Number of People" into the value bar again and set the alias as "Cumulative Number (Within Same Level)".
-
Click the "Cumulative Number (Within Same Level)" field, select "Advanced Calculation > Cumulative Calculation" from the dropdown, and select "Membership Level" as the cumulative range in this example.
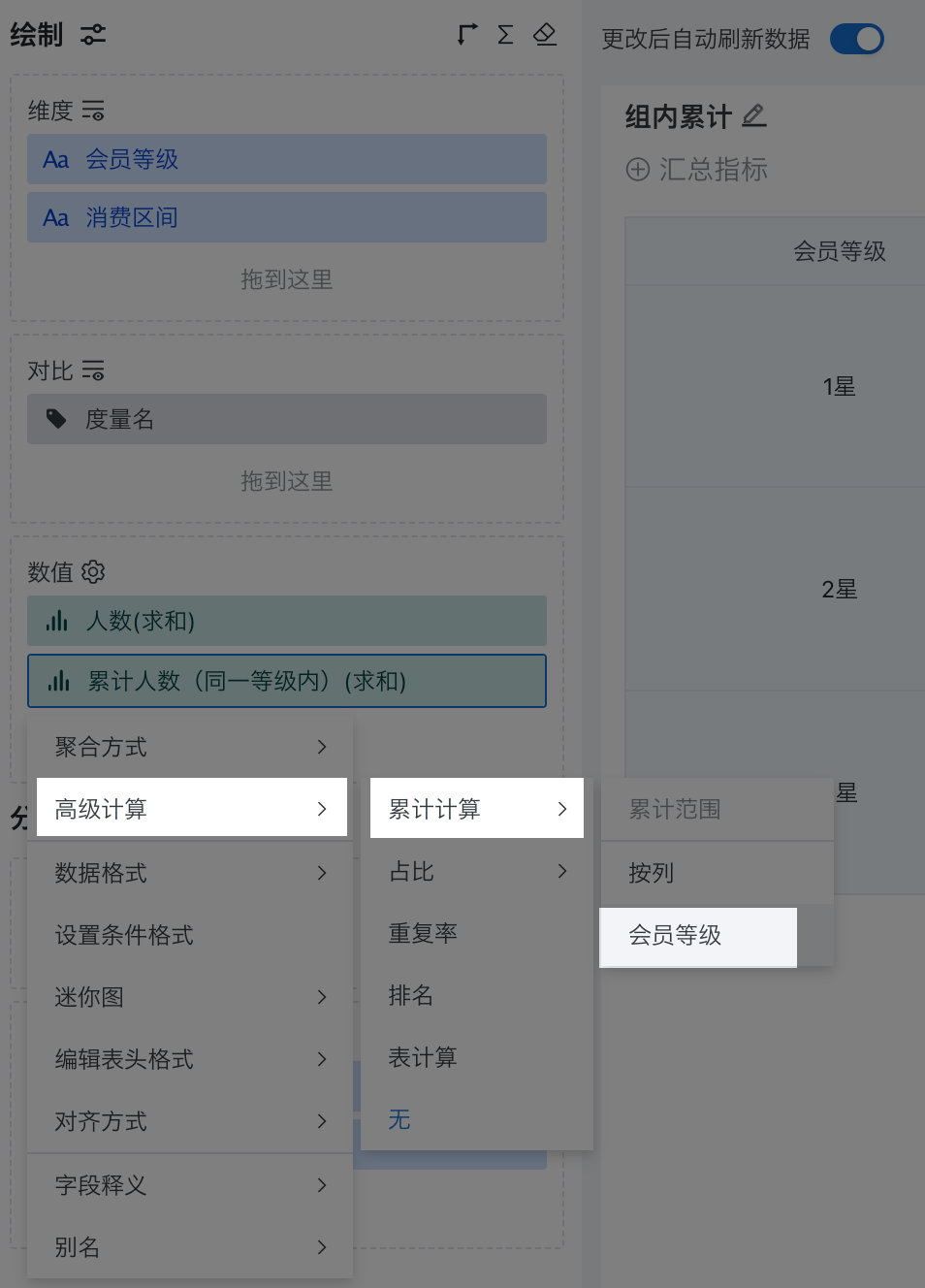
- View the effect of cumulative calculation by "Membership Level".
3. Usage Restrictions
-
The finest granularity for date-type fields only supports up to day; cumulative calculation for hour, minute, and second is not supported. When there is a date field with hour, minute, and second granularity in the dimension, it is treated as a day granularity field.
-
Cumulative calculation is not supported for detail tables.
-
Only charts with dimensions support cumulative value calculation; charts without dimensions (such as indicator cards) are not supported.