Overview
1. Overview
1.1. Function Overview
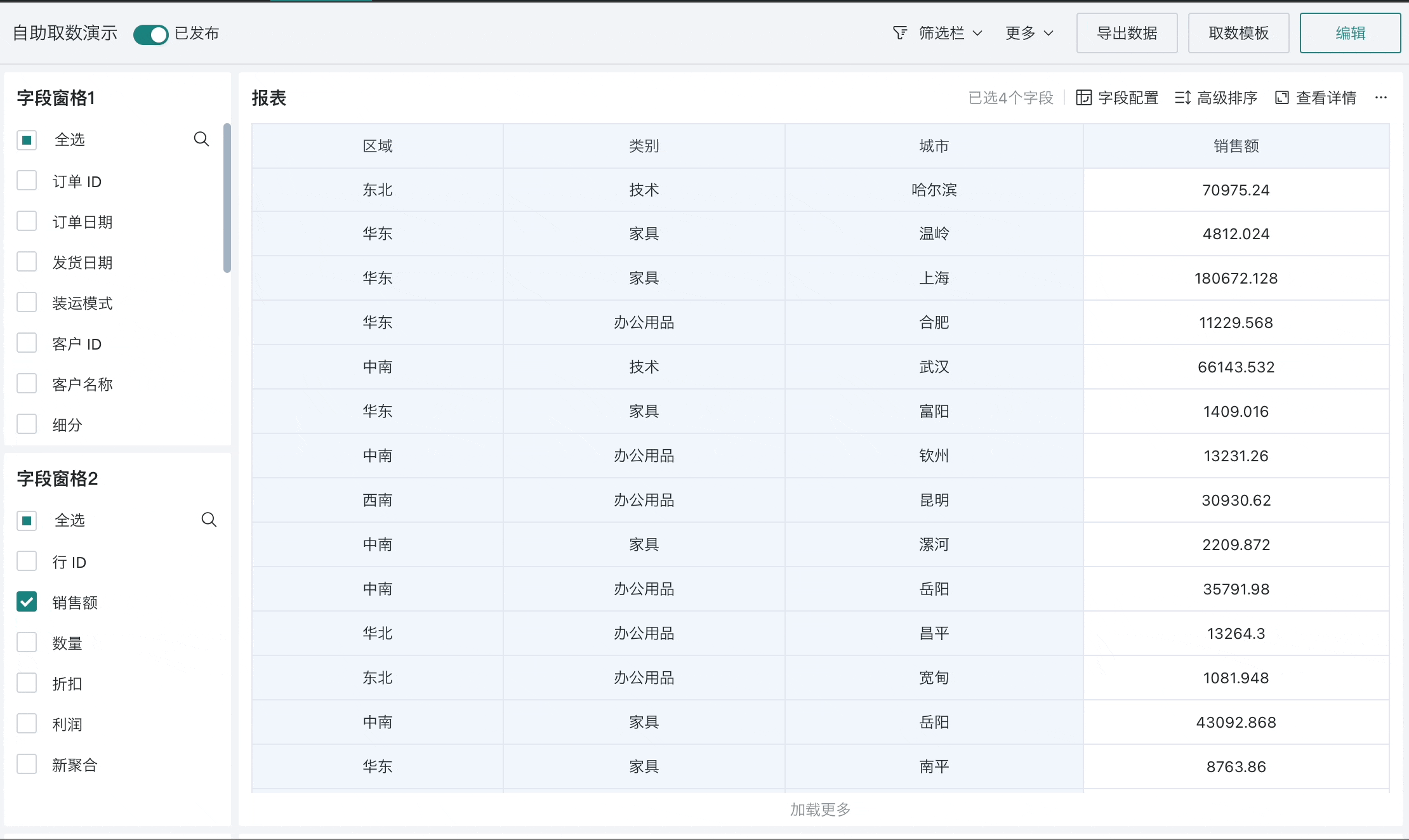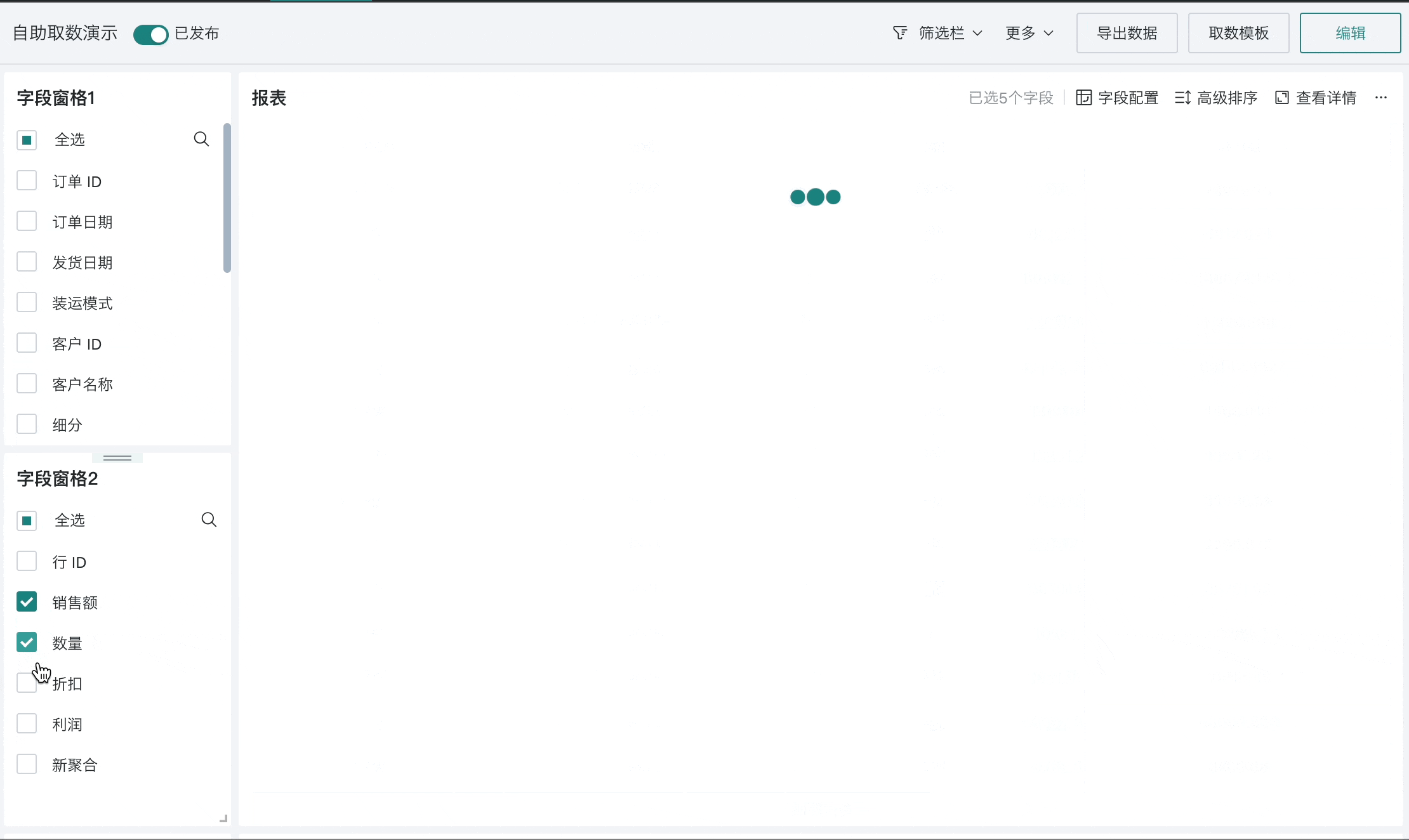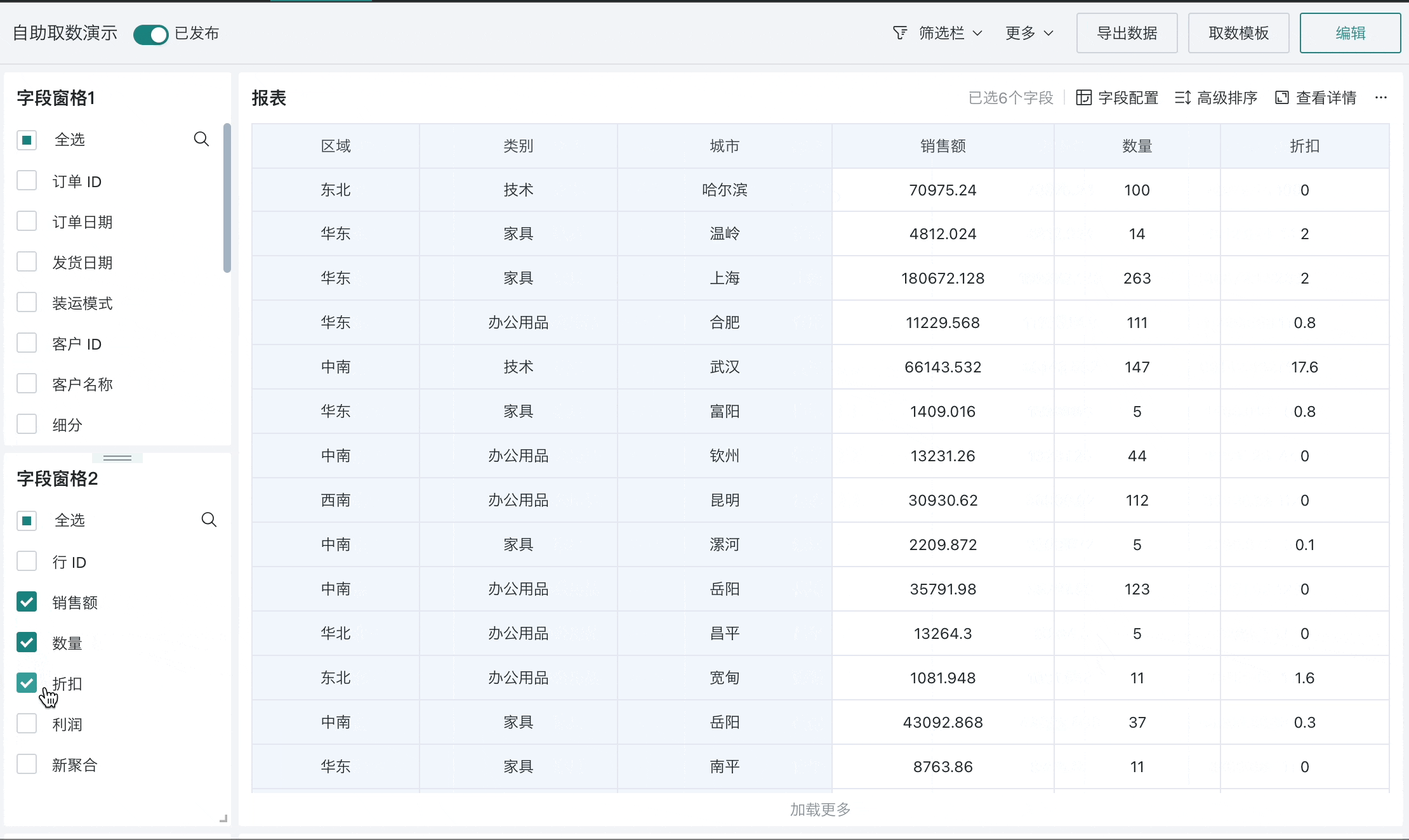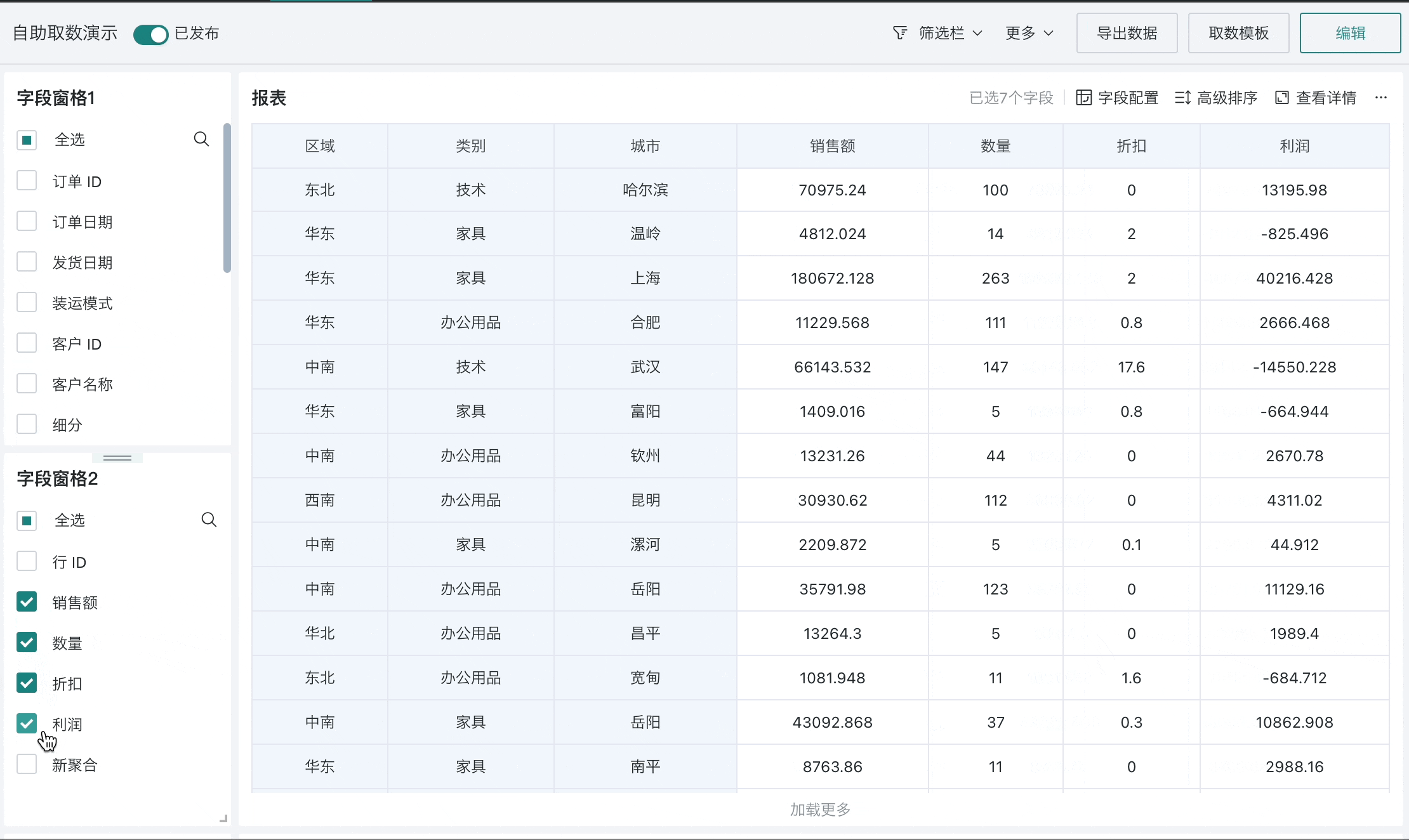
Self-service data query refers to flexible report building and ad-hoc query functionality that enables end users to build custom data reports through an interface-based approach based on templates, completing self-service data extraction and ad-hoc queries.
1.2. Scenarios and Value
Self-service data query can effectively help users with zero data development experience to easily obtain data. Facing frequently changing data requirements, there's no need to wait for the development department to schedule, and drag-and-drop operations can quickly and simply obtain data.
- For technical personnel: Reduce tedious work
Technical personnel can use self-service data query (custom reports) to create some basic analytical wide tables for business colleagues to use; business colleagues can select fields based on templates to build their own custom reports, meeting their daily data extraction and analysis needs.
From now on, technical personnel don't need to frequently create many reports for business colleagues to meet their different dimensional combination analysis needs, saving time, reducing workload, and focusing on the data architecture itself.
- For end business users: Lower the threshold for business self-service analysis
End business users' data extraction and analysis needs will be full of uncertainty due to different purposes or rapid business iterations. Also, because the vast majority of end users focus more on business decisions, they may lack knowledge and skills related to technology, and may encounter obstacles during the process of querying or analyzing due to lack of database knowledge.
Using the custom report module, technical personnel who better understand database knowledge can design a "semantic layer" to encapsulate the calculation of data indicators in the custom report templates. End business users only need to use pre-arranged custom reports and select the required indicators to complete current data query work without having to worry about the implementation of indicator calculations.
- Low cost, short cycle, high output
Low production cost: No need to understand complex business analysis logic, no need to master the UI capabilities for creating refined dashboards;
Short cycle: After building basic templates, no need to spend too much time, and can perform a large amount of data analysis work based on datasets;
High output: Doing it once can meet the combined analysis of many complex dimensions and indicators in future business development.
2. Beginner's Guide
To help users systematically master the self-service data query functionality, we have organized the following processes for the two major business scenarios of creating and using self-service data query.
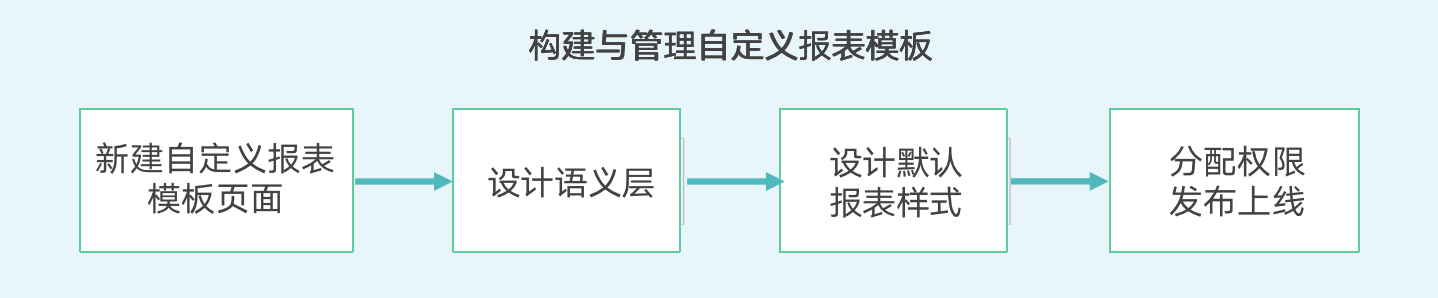
2.1. Building and Managing Self-service Data Query Templates
-
Target audience: Enterprise IT personnel, data analysts, etc.
-
Usage process:
For details, please refer to [《Creating Self-service Data Query》](1-Creating Self-service Data Query.md) and [《Managing Self-service Data Query》](2-Managing Self-service Data Query.md).
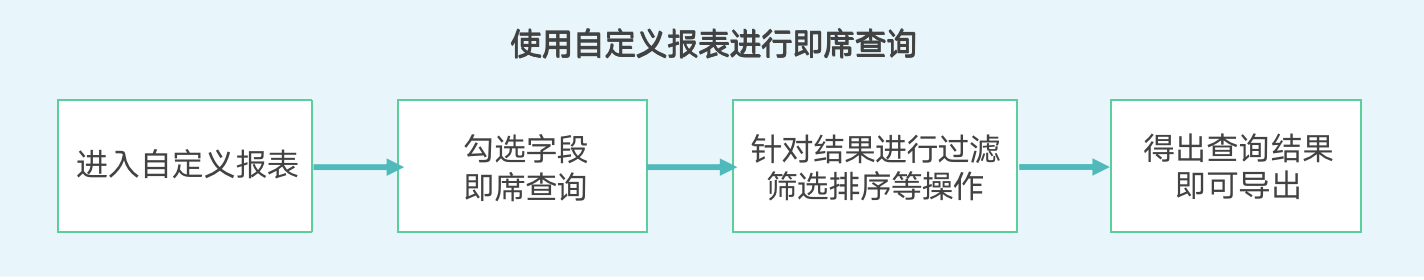
2.2. Using Self-service Data Query for Ad-hoc Queries
-
Target audience: End business personnel
-
Usage process:
For details, please refer to [《Using Self-service Data Query》](3-Using Self-service Data Query.md).