Range Filter
1. Overview
1.1. Feature Introduction
Set up a range filter, select a numeric field, and you can filter a specific numeric field of the associated card.
1.2. Application Scenarios
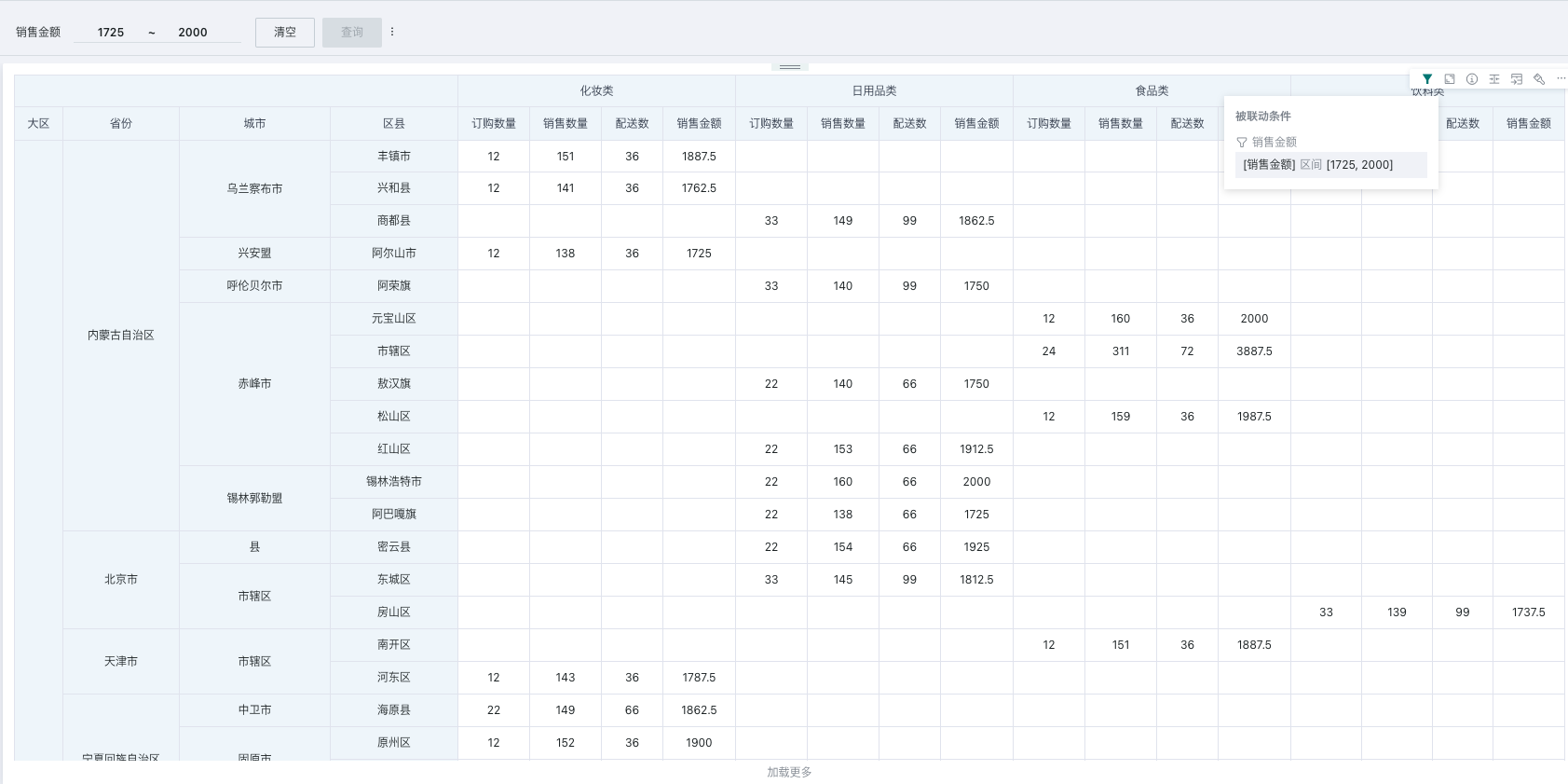
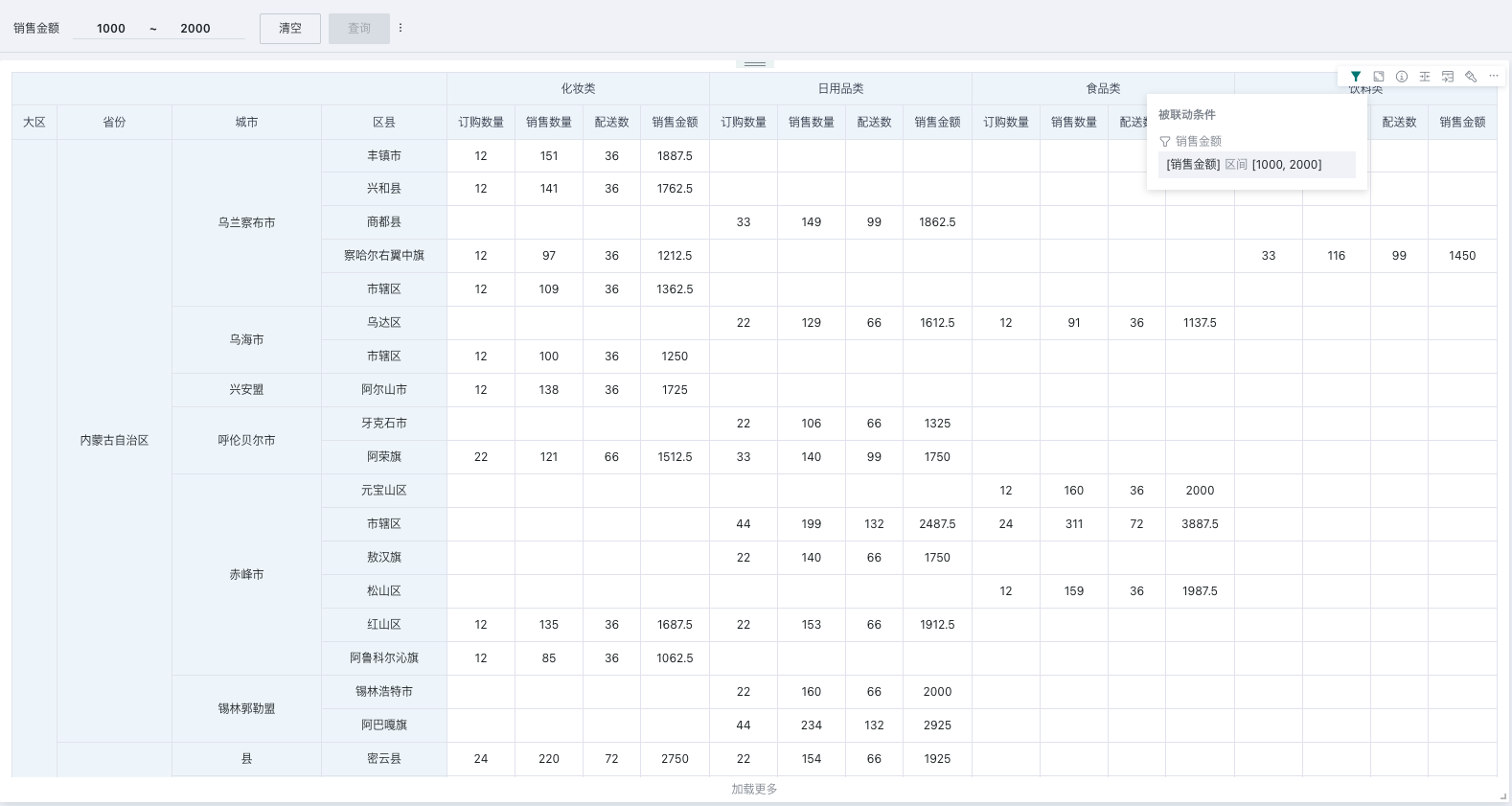
Filter numeric fields on cards in the dashboard to screen out data content that meets certain indicator standards.
For example: Filter data where "Sales Amount" is between 1000 and 2000.
2. Operation Steps
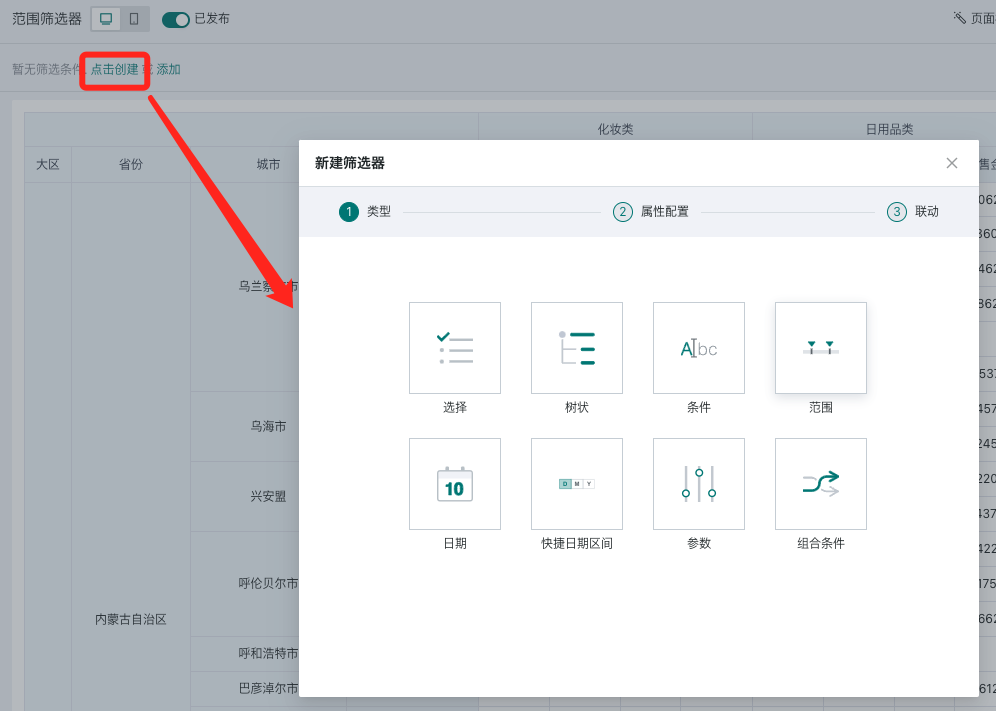
2.1. Create Range Filter
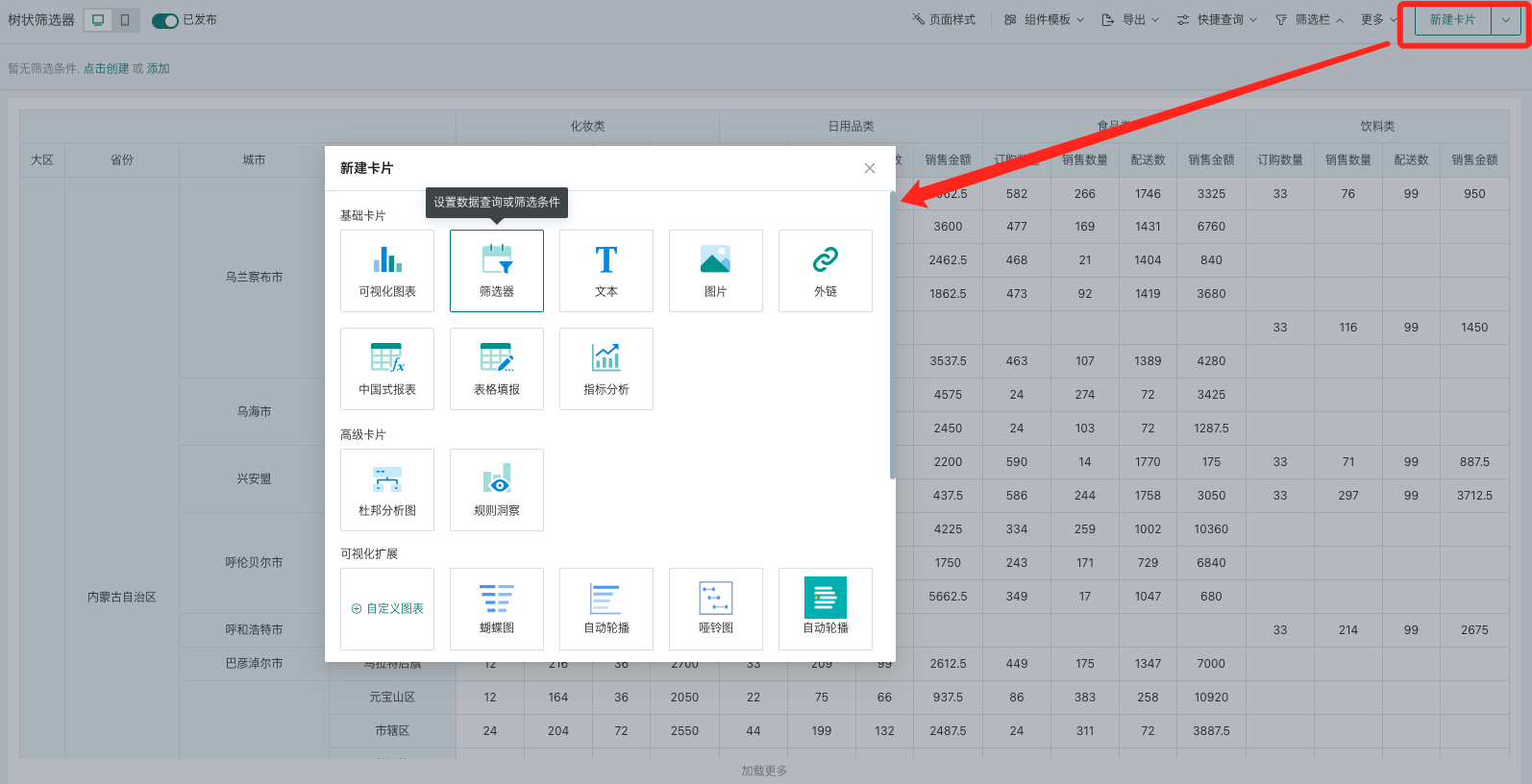
On the page, there are two entry points to create a range filter: creating a new filter in the filter bar, and creating a new card - selecting the card type as filter
- Filter bar - New filter
- Page - New card - Select new filter
Select the type as "Range" to enter the range filter editing popup.
2.2. Filter Attribute Configuration
When setting up a range filter, first select the source dataset, then select the field that needs to be filtered by consumers.
-
For numeric range filtering, you can separately set whether the filtering level filters detail data or result data;
-
Support setting the filter's operator and default value.
| Operation | Description | Notes |
| Select Dataset | You can quickly select the current page's dataset or search for a new dataset | |
| Select Field | It is recommended to select a numeric field | If you select a dimension field and it's detail filtering, since you can only input numeric values, the filtering is likely to be invalid |
| Name | Defaults to the selected field name, can be modified | |
| Filter Level | Detail filtering (default): Filter the detail data of the dataset corresponding to the associated card, then perform subsequent calculations and aggregation on this basis. Aggregation filtering: Need to set the aggregation method, after setting, it will filter the aggregated data of the associated card according to the set aggregation method, which will affect "Subtotal and Total", "Ranking-Row/Column Ranking/Dimension Group Ranking", "Percentage" results. Result filtering: Need to set the aggregation method, after setting, it will filter the final result data of the associated card according to the set aggregation method, without affecting any calculations. | After enabling the Analysis Engine 2.0 switch, you can use aggregation filtering and result filtering functions |
| Operator | Greater than, Greater than or equal to, Less than, Less than or equal to, Range (default), Equal to, Not equal to, Is null, Is not null | |
| Default Value | Optional, you can enter a numeric range according to the selected operator.Greater than, Greater than or equal to, Less than, Less than or equal to, Equal to, Not equal to: Enter a threshold value.Range: Enter a numeric range, including start and end values. |
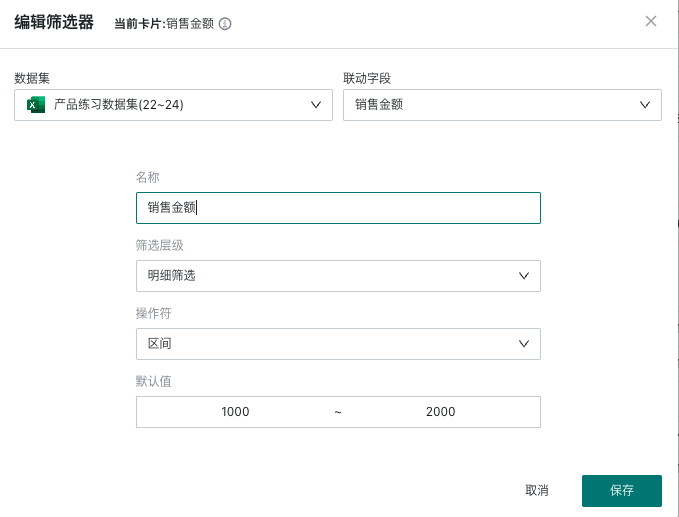
If you need to edit the filter's attributes again, you need to find the "Edit" function in the filter card's toolbar to re-enter the filter attribute configuration popup.
2.3. Set Linkage Target Card
When linking, you need to select the target card and the corresponding filter field. After setting, changes in the filter will link and change the data presented by the associated card.
-
Auto-link card: After the filter enables auto-link, it will automatically link visualization cards with the same field name; auto-linked cards can be manually unlinked;
-
Apply to cards with the same dataset: Click to apply to cards with the same dataset, and it will automatically link other cards under the same dataset with the corresponding field. Cards applied to the same dataset can be manually unlinked.
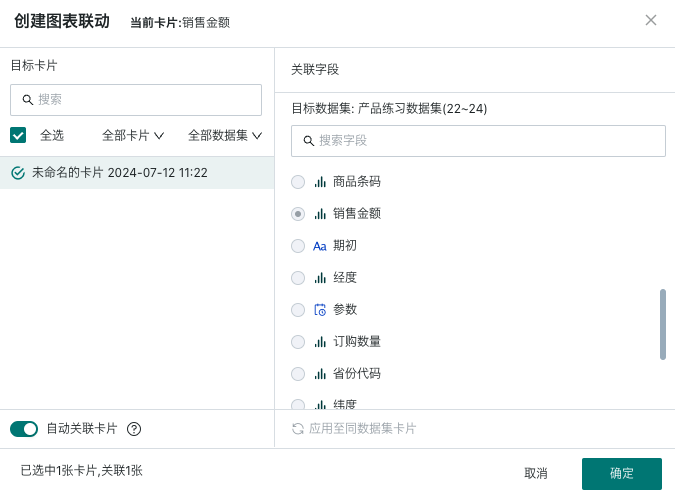
Note:
1. When initiating linkage, the field, filter level, aggregation method, and value set in the filter will be passed into the card to take effect;
2. When linking cards, Chinese-style reports, form cards, and detail tables are not supported;
3. If linkage is configured with these cards first, then the filter is switched to aggregation filtering/result filtering, the linkage relationship will still be disabled.
If you need to edit the filter's linkage relationship again, you need to find the "Linkage" function in the filter card's toolbar to re-enter the filter linkage configuration popup.
2.4. Using the Filter
Usage
When users use it, the effective order of different filter levels: Detail filtering > Aggregation filtering > Result filtering;
When edit page filtering conflicts with external filters, at this time, judge the filter field + filter level + aggregation method. When all are consistent, external filters take priority, otherwise they take effect in order;
In the following exceptional cases, filter conditions cannot take effect:
-
The filter's filter level is "Aggregation filtering, Result filtering", which conflicts with the field type of the associated card, and the card's edit page field cannot take effect with the aggregation method set by the filter (for example: filter's aggregation method = sum, but the card field is dimension-province). Reason: Field type conflict, cannot calculate;
-
The filter's filter level is "Aggregation filtering, Result filtering", and the filter field used is an aggregated measure (no need to set aggregation method, formula has it built-in). At this time, the calculation formula becomes a regular calculation field, and linkage to the same field in the card cannot take effect. Reason: When using regular fields for aggregation filtering and result filtering, the aggregation method cannot be empty;
-
When the type of a calculation field changes, it becomes a field that cannot use the original aggregation method (for example: filter's aggregation method = sum, field formula changes from sum to dimension), filtering cannot take effect. Reason: Field type does not match the aggregation method.
View Filter Effect
After filtering, the filter will take effect on each linked card, and the card will present the data after filtering;
When users browse the card, they can hover the mouse over the "small funnel" icon in the card toolbar to view the current filter conditions.