Tree Filter
1. Overview
1.1. Feature Introduction
Tree filters are typically used to display hierarchical filter content. Depending on the actual application scenario, they support filtering individual leaf nodes during filtering, or directly filtering child nodes. When the hierarchy is complex and there are many options, the tree structure also facilitates searching.
1.2. Application Scenarios
Common application scenarios:
-
Geographic information: "Country-Province-City-District-County";
-
Group enterprises with multi-level management departments: "Group-Subsidiary-Department";
-
E-commerce industry with multi-level categories/tags;
-
Banking industry hierarchy: "Head Office-Branch-Sub-branch".
2. Operation Steps
2.1. Create Tree Filter
On the page, there are two entry points to create a tree filter: creating a new filter in the filter bar, and creating a new card - selecting the card type as filter.
- Filter bar - New filter.
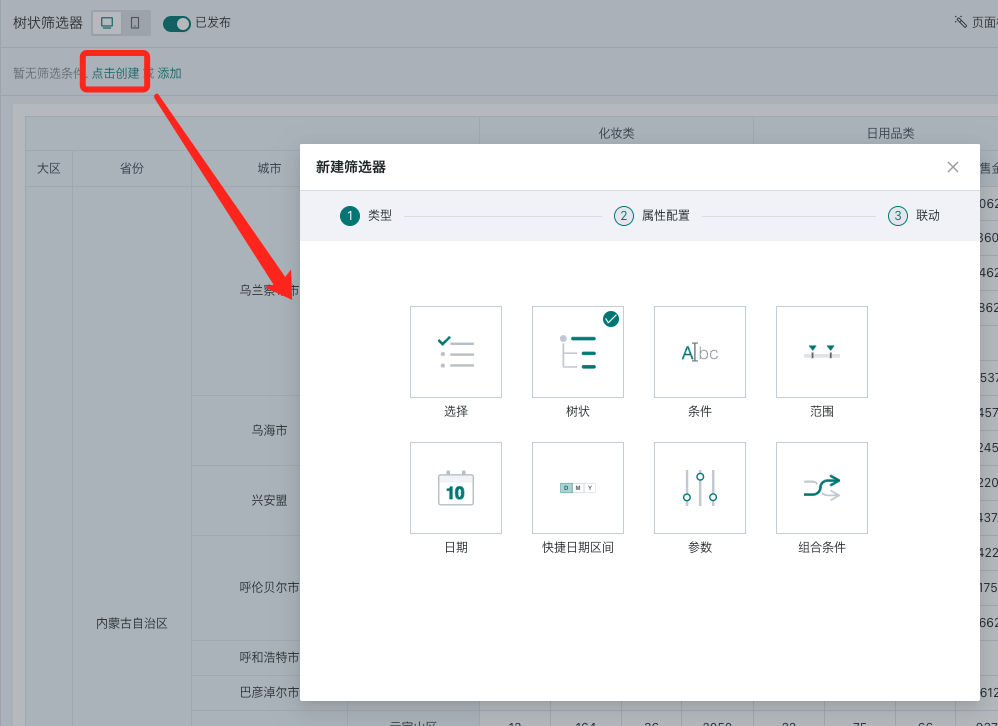
- Page - New card - Select filter.
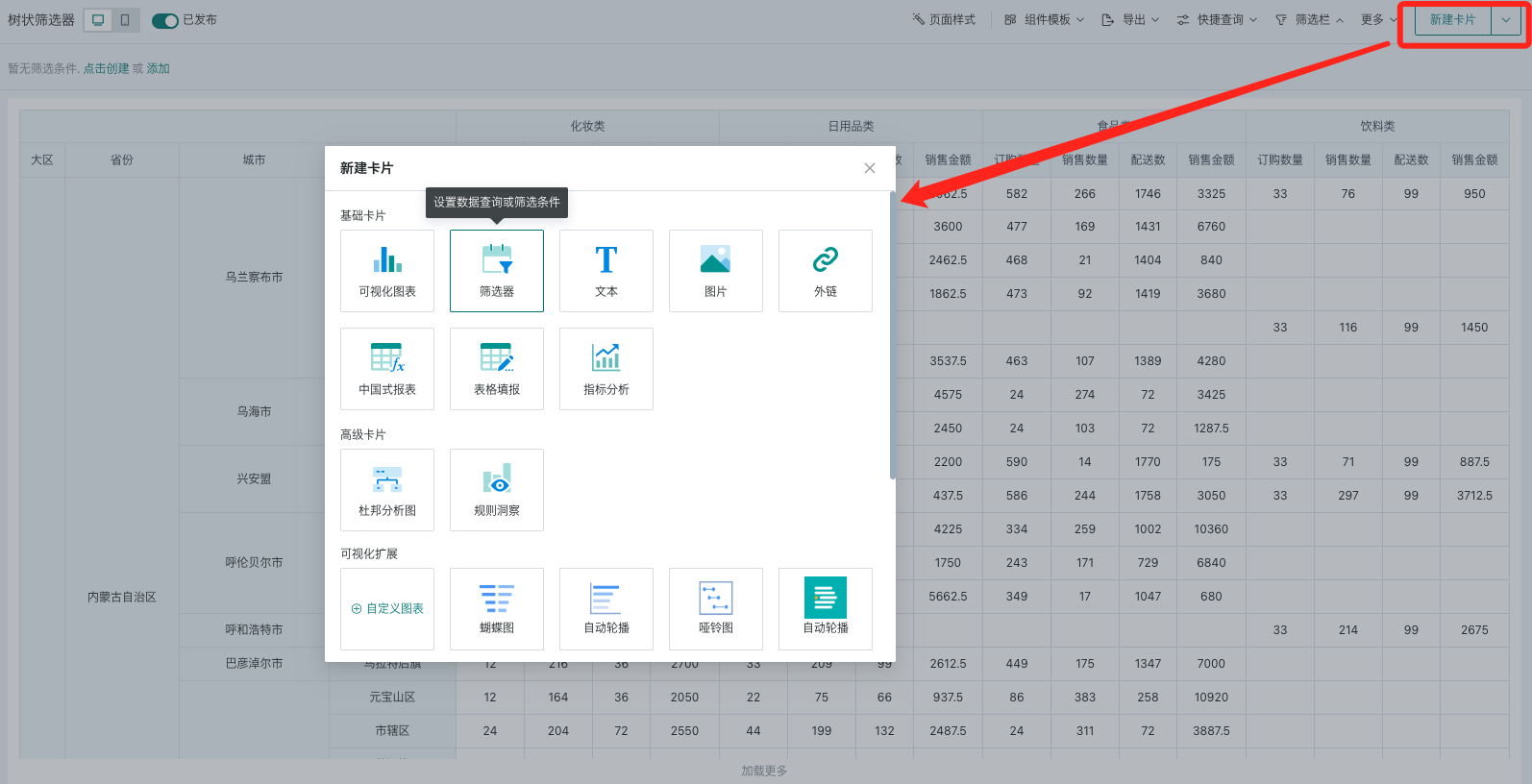
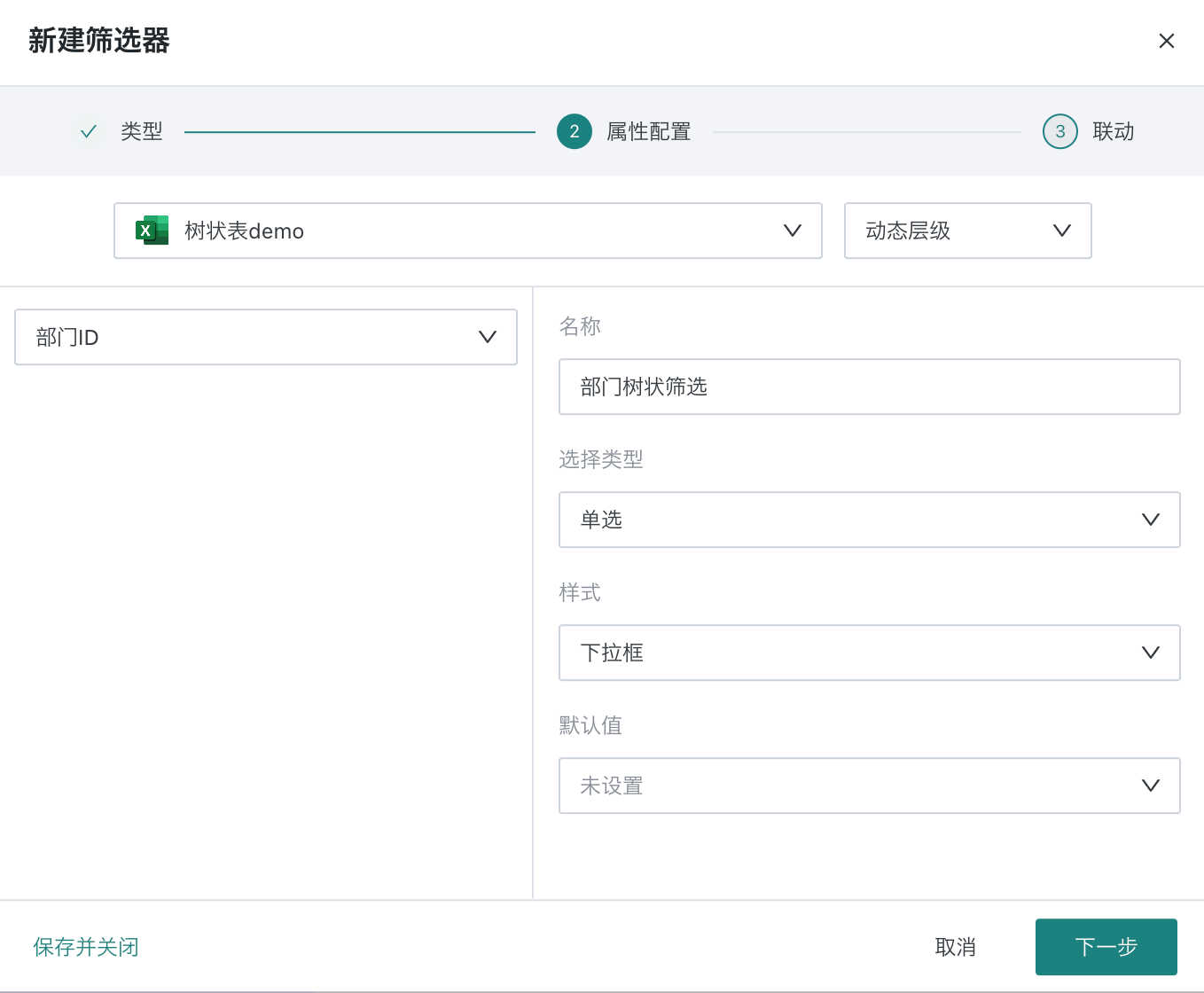
Select the filter type as "Tree" to enter the tree filter attribute editing popup.
2.2. Filter Attribute Configuration
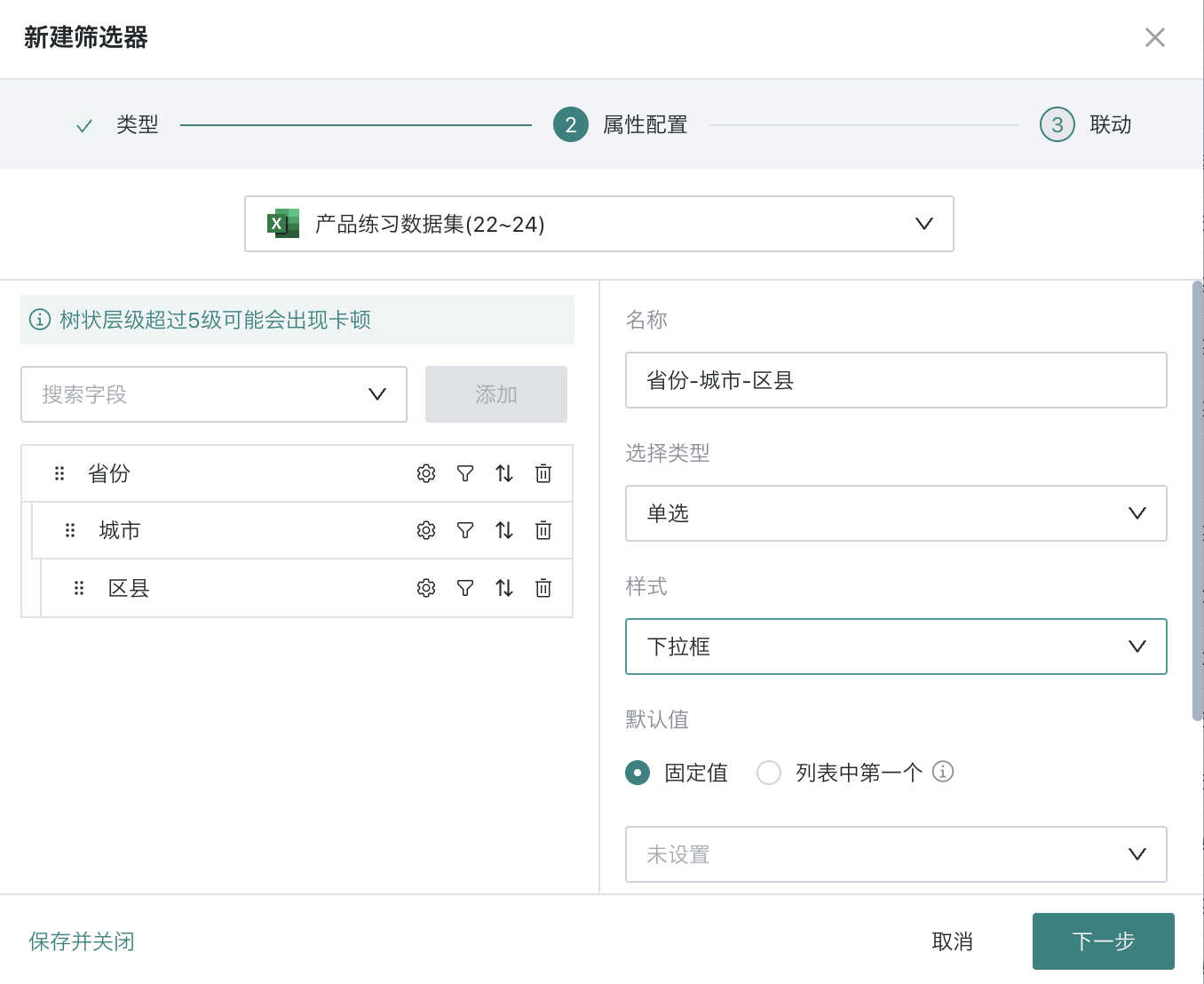
When setting up a tree filter, first select the source dataset, then select the multi-level fields that need to be filtered by consumers.
-
Support setting the selection type as single or multiple selection, then select a suitable style;
-
You can choose the filtering method and also set the default value of the filter.
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Select Dataset | You can quickly select the current page's dataset or search for a new dataset. |
| Select Fields | Need to sequentially select the fields corresponding to leaf nodes, up to 5 can be selected; Like selection filters, it supports the "Display Field" function: after setting the display field, consumers will see the filter and linkage conditions as display fields, but the actual linkage conditions remain as linkage fields. After selecting fields, you can "sort" the display order in the filter. |
| Name | Defaults to the combined name of the selected fields, can be modified. |
| Selection Type | Single selection (default): Users can only select one option when using;Multiple selection: Users can select multiple options when using. |
| Style | Dropdown: Options are collapsed in a dropdown box;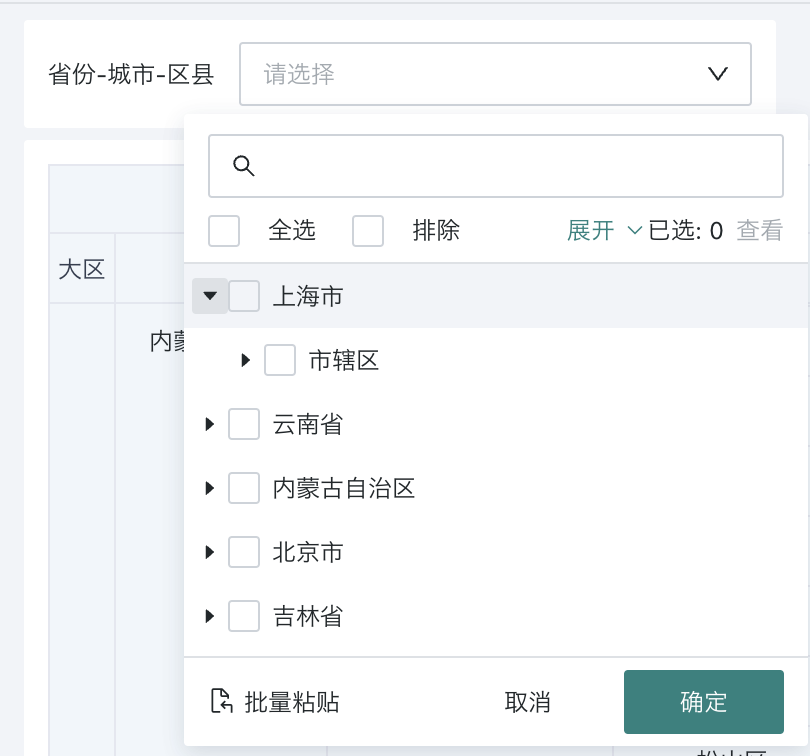 Flat layout: Options are displayed flat on the page. 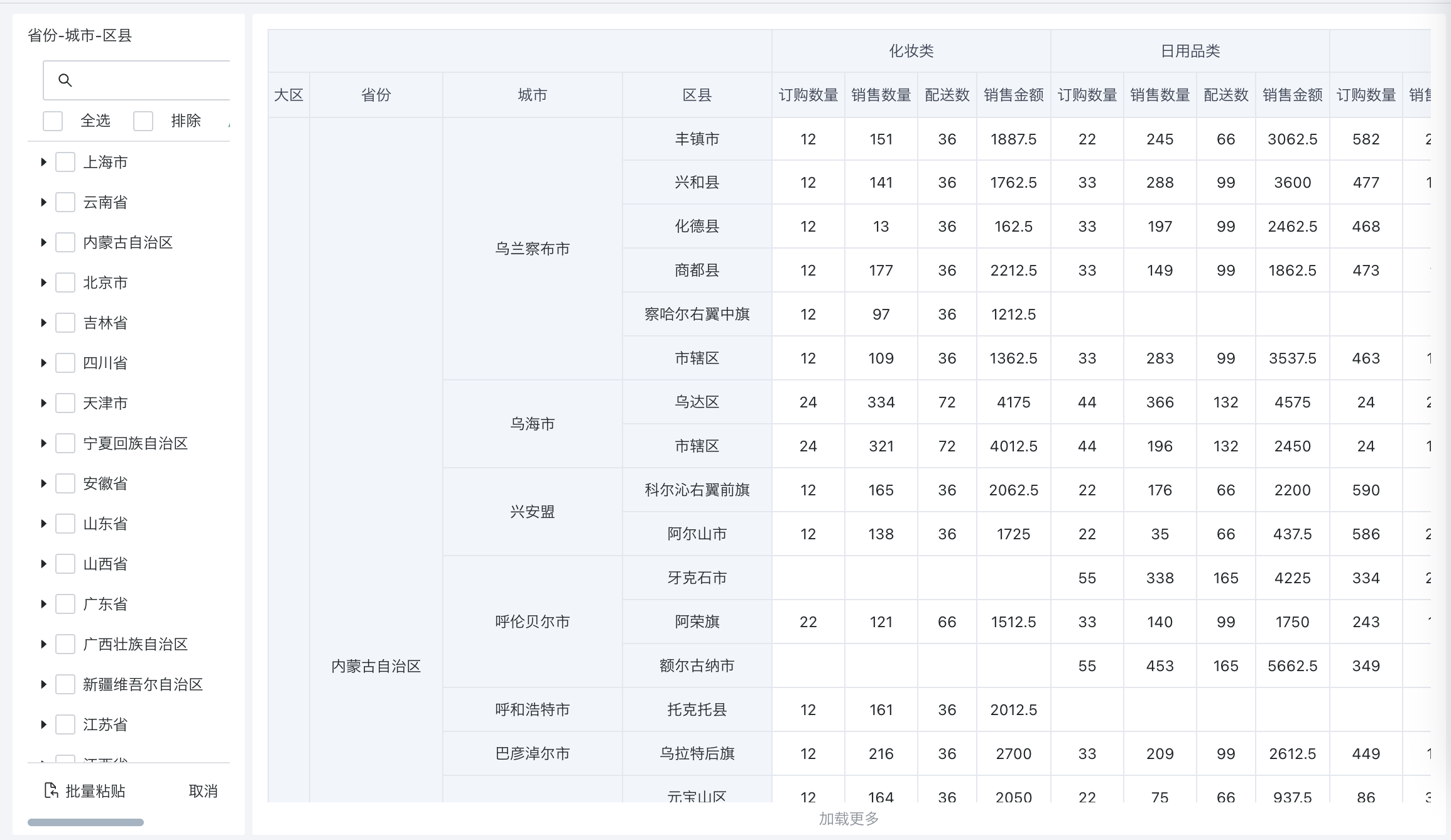 Note: When tree filters are in the filter bar, only "dropdown" style is supported; When tree filters are in the layout, both "dropdown" and "flat layout" styles are supported, which can be set according to user habits. |
| Default Value | When a default value is set, users will see data filtered by the default value after entering the page; supports fixed value and first in the list (first pick). Fixed value: According to single/multiple selection configuration, select one or more fixed values as the default value; First in the list (first pick): When the default value of the tree filter is "first item in the list", the data seen each time you enter the page is filtered and displayed according to the latest field value. |
| Filtering Method | Without path (default): Only displays all end-level content of selected items in the input box, only need to configure the linkage relationship of end-level fields;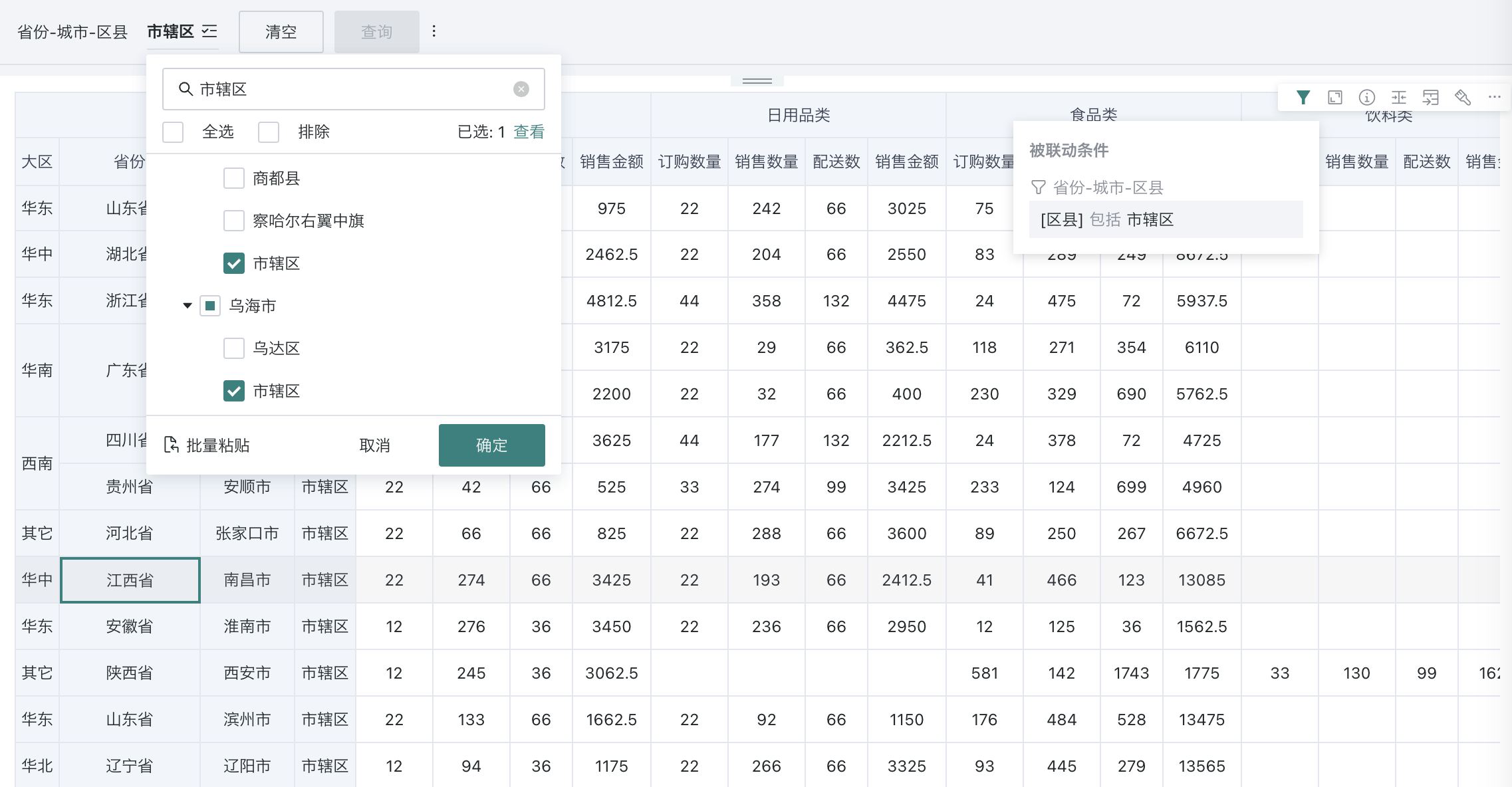 With path: When changed to with path, selecting an option will include all leaf node information of that option, requiring configuration of linkage relationships for each level field. 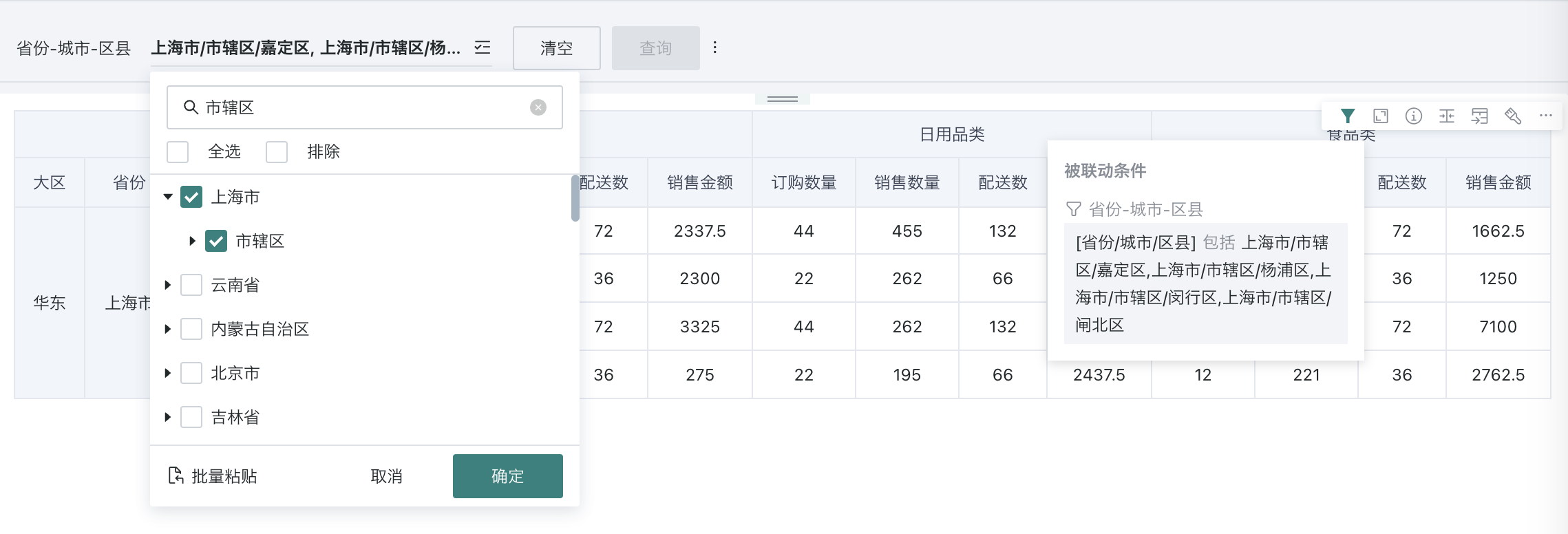 Note: Each time you switch, you need to reconfigure the linkage relationship and jump information. Note: When Selection Type is single selection, you can configure "Select any level". |
| Advanced Configuration |
When checked, once a level of the tree filter has null/empty values and all levels to the end are null/empty values, the null value options from that level to the end level will be abbreviated and displayed as the value of the previous level; if each level is null, only one level of null will be retained; and when the filter passes parameters, only the last non-null value will be passed as the filter condition.
|
Note: When the selected dataset has fields associated with tree fields, you can choose fixed level or dynamic level.
- Fixed level: Multi-level filtering with fixed levels, all configuration items are the same as described in the table above.
- Dynamic level: Only supports single selection of fields associated with tree fields, dynamically displays data in tree structure according to tree fields for filtering.
For complete description of tree fields and tree filter association with tree tables, see [Tree Table Related Configuration](../../../0-Basic Card Creation/0-Visualization Charts/1-Table Types.md#2.3.%20Tree Table).
Default fixed level as shown:
If the data source contains tree fields, dynamic level as shown:
If you need to edit the filter's attributes again, you need to find the "Edit" function in the filter card's toolbar to re-enter the filter attribute configuration popup.
2.3. Set Linkage Target Card
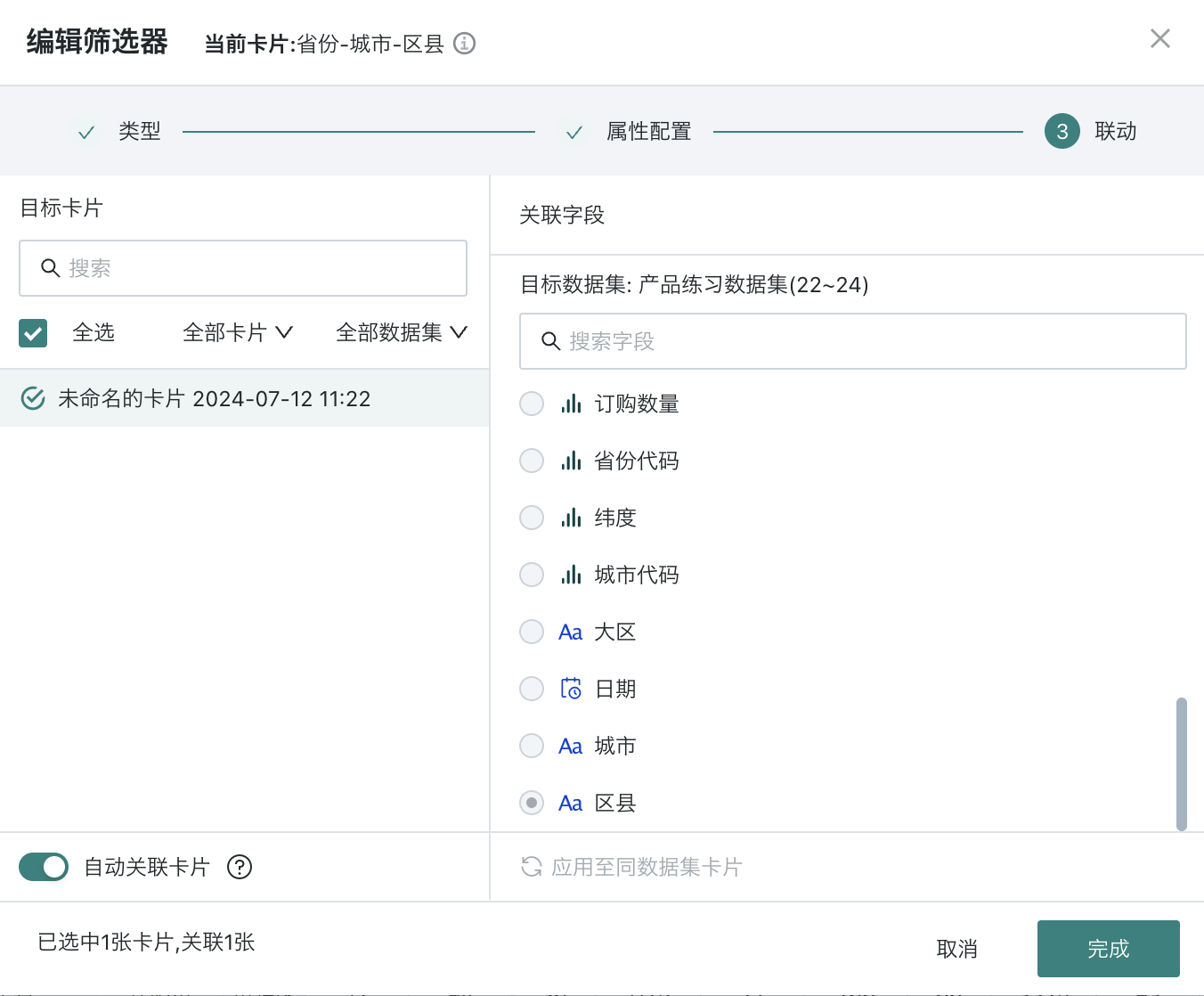
When linking, you need to select the target card and the corresponding filter field/parameter. After setting, changes in the filter will link and change the data presented by the associated card.
Filtering method is "Without path": When linking, only need to link the end-level node field (parameter);
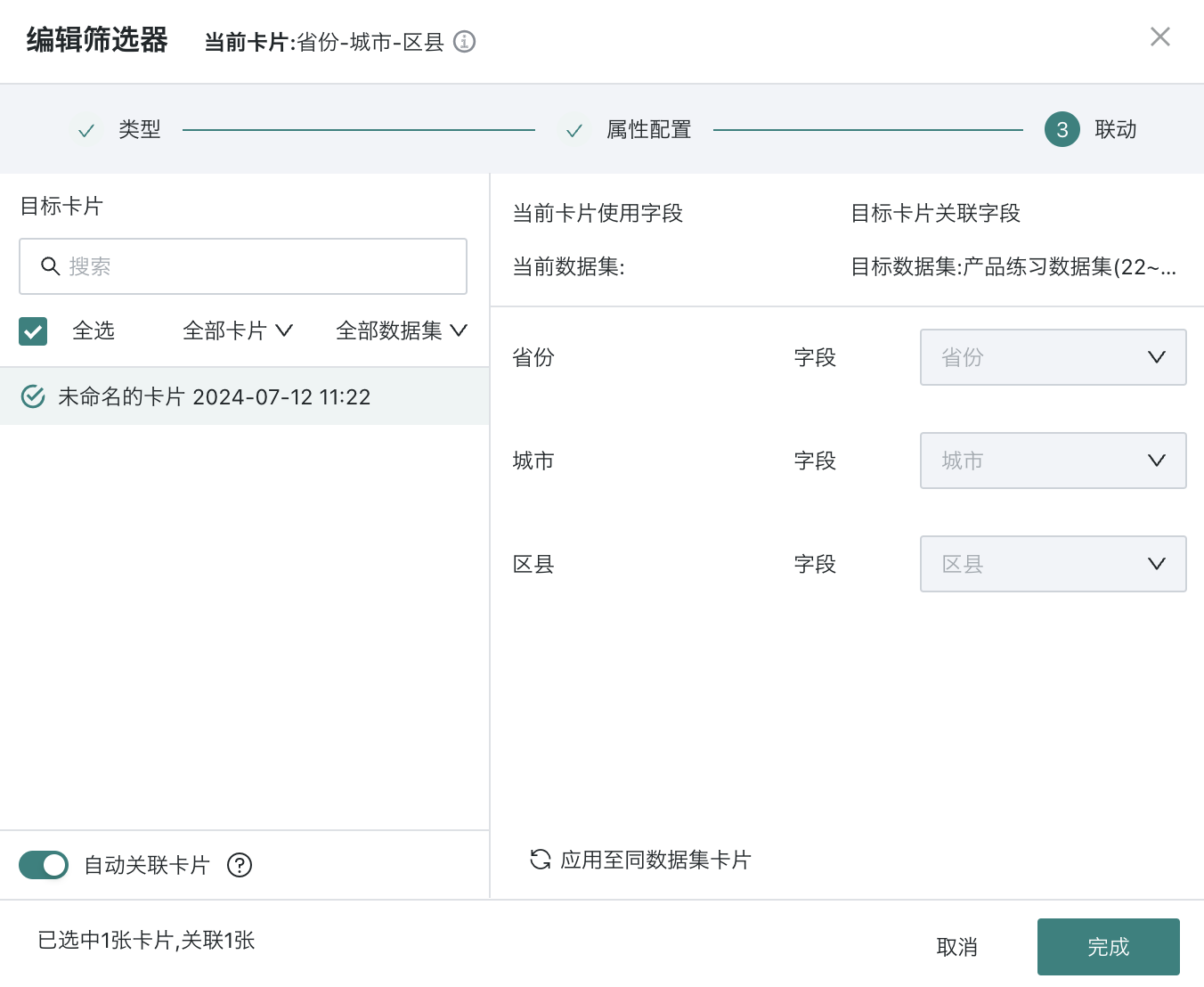
Filtering method is "With path": When linking, need to link each level node field (parameter).
-
Auto-link card: After the filter enables auto-link, it will automatically link visualization cards with the same field name; auto-linked cards can be manually unlinked;
-
Apply to cards with the same dataset: Click to apply to cards with the same dataset, and it will automatically link other cards under the same dataset with the corresponding field. Cards applied to the same dataset can be manually unlinked.
If you need to edit the filter's linkage relationship again, you need to find the "Linkage" function in the filter card's toolbar to re-enter the filter linkage configuration popup.
2.4. Using the Filter
Usage
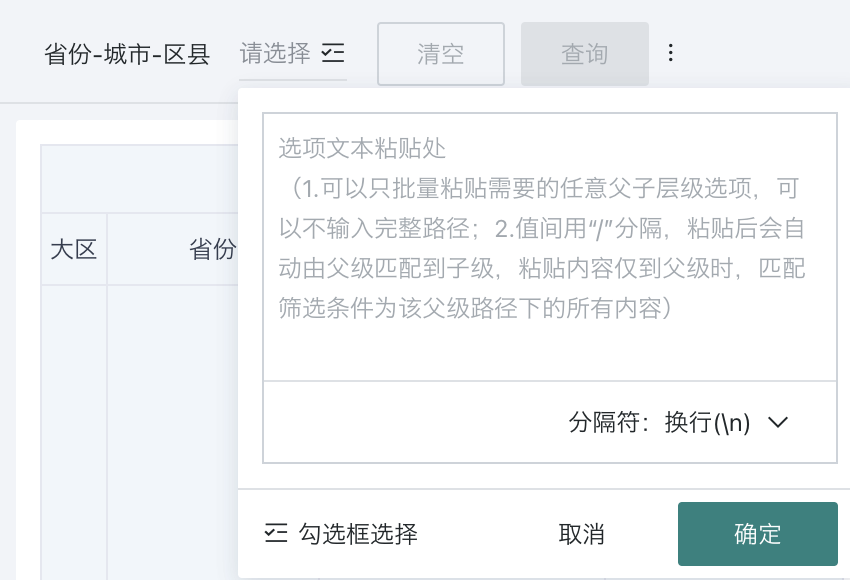
When users use it, the maximum number of options is 1000; you can fuzzy search options, batch paste, and view selected
-
Fuzzy search: Case insensitive, but some direct-connected database syntax does not support case insensitivity;
-
Batch paste: After copying the options with one click, you can automatically match the option list according to the name, reducing the number of clicks.
Note:
When the filtering method is "With path", the pasted content must be complete multi-level information. If only one field's content is pasted, it will default to start recognition from the leaf node.
Example:
For a tree filter with path for province-city-district/county,
At this time, if you need to input information for a certain district/county: you should input xx Province/xx City/xx County, so that the correct data can be matched;
If you input: xx County, it will use xx County to match the province field data, which cannot match the correct data.
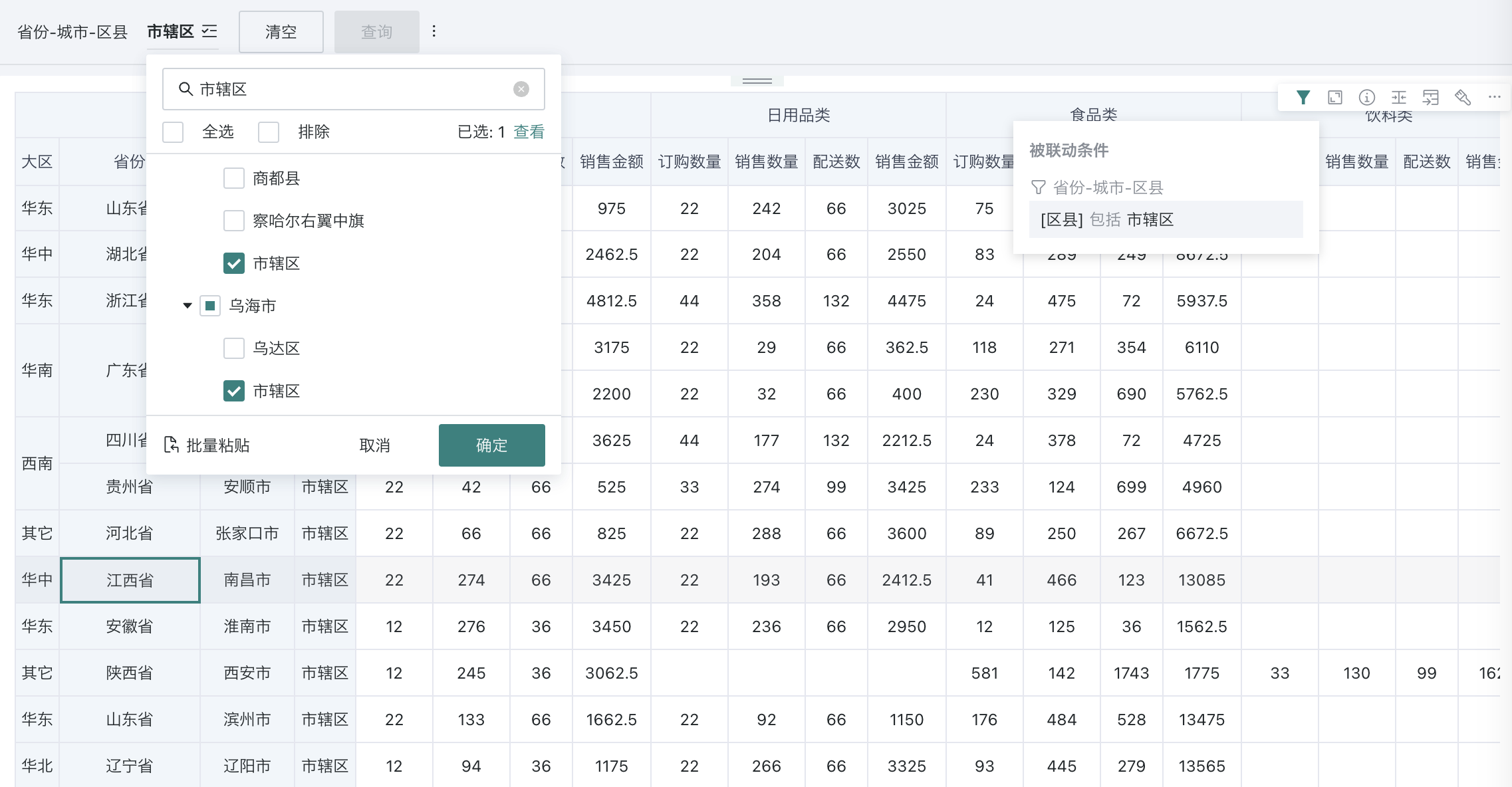
View Filter Effect
After filtering, the filter will take effect on each linked card, and the card will present the data after filtering; when users browse the card, they can hover the mouse over the "small funnel" icon in the card toolbar to view the current filter conditions.
- Filtering method is "With path":
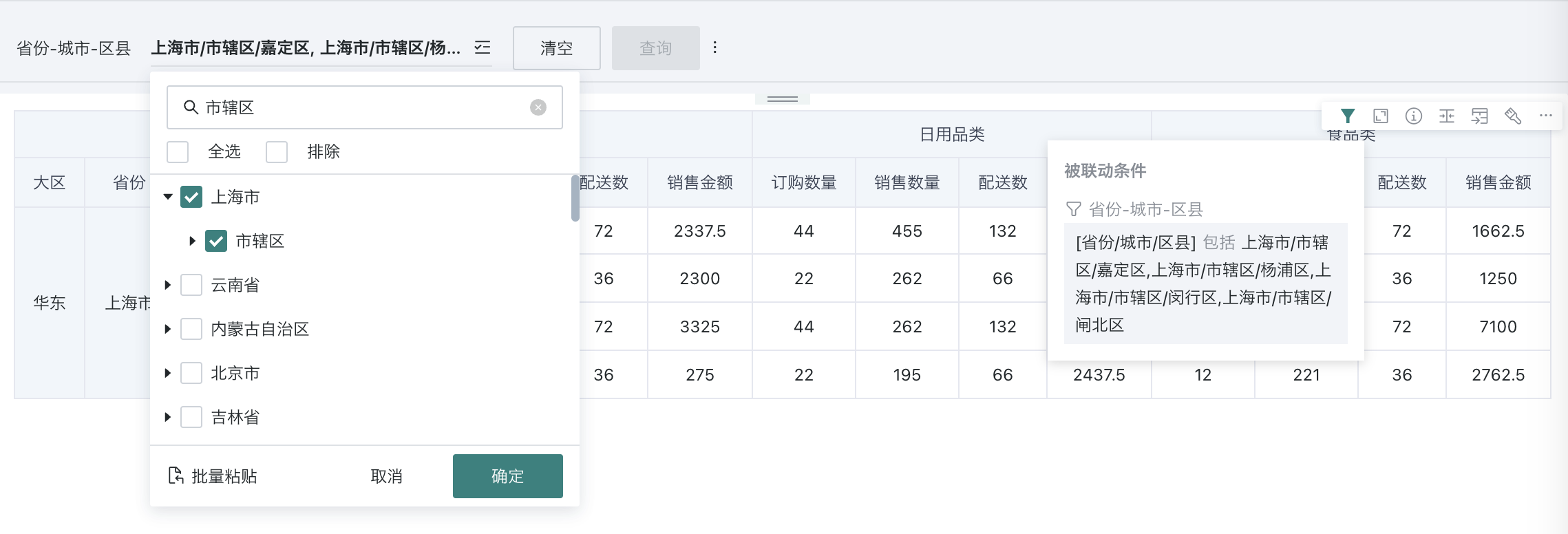
- Filtering method is "Without path":