Visualization Plugin Development Guide
1. Overview
Making good use of visualization plugins can give data higher value and extend Guandata BI's and personal visualization analysis capabilities. This article will introduce visualization plugin development. If users already have certain frontend foundation capabilities or have some understanding of BI products, they will find it easier to get started.
2. Usage Guide
2.1. Development Preparation
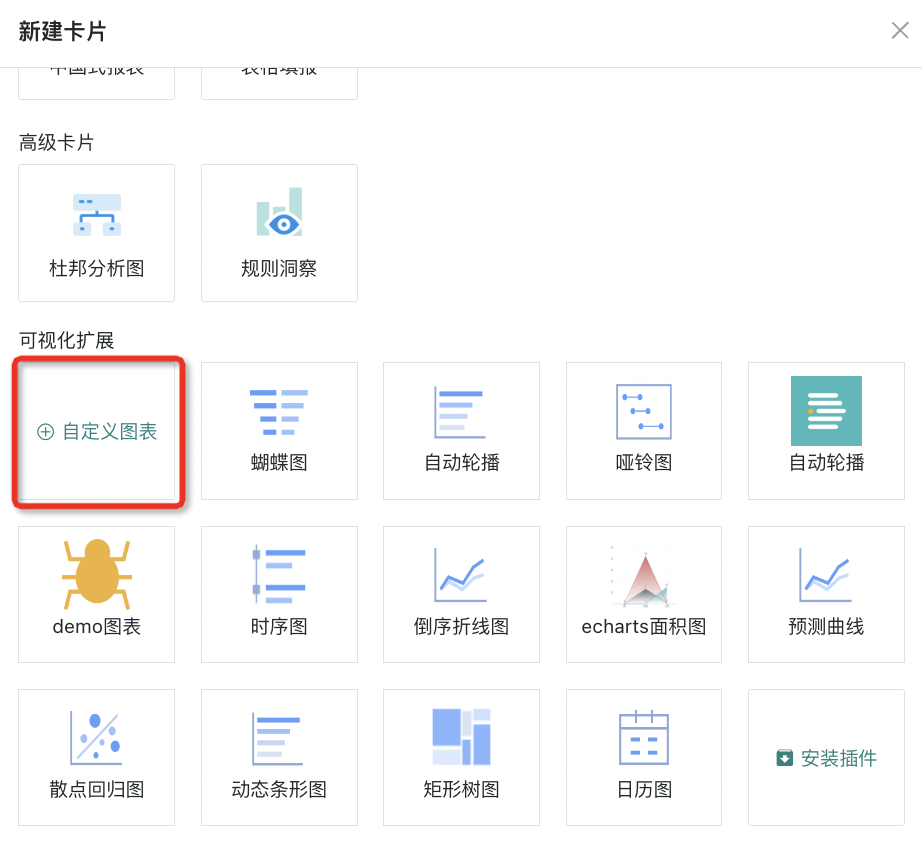
1. Enter the dashboard page, click the "Create New Card" button in the upper right corner of the page, and the following popup will appear. Select "Custom Chart".
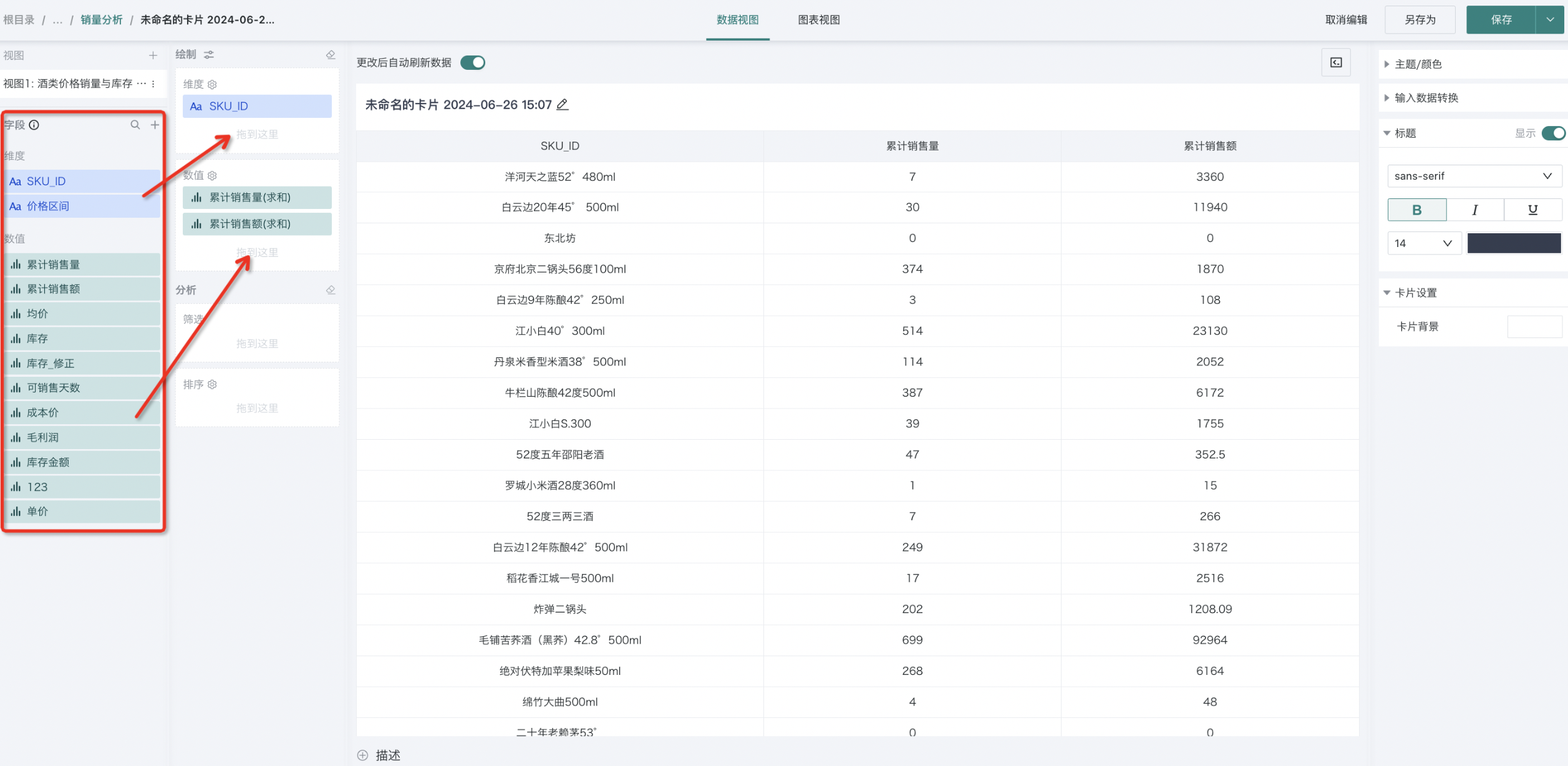
2. Select a dataset for the card and click OK to enter the card editing page. Drag the corresponding fields from the left field area to the corresponding positions in the drawing area to obtain chart drawing data.
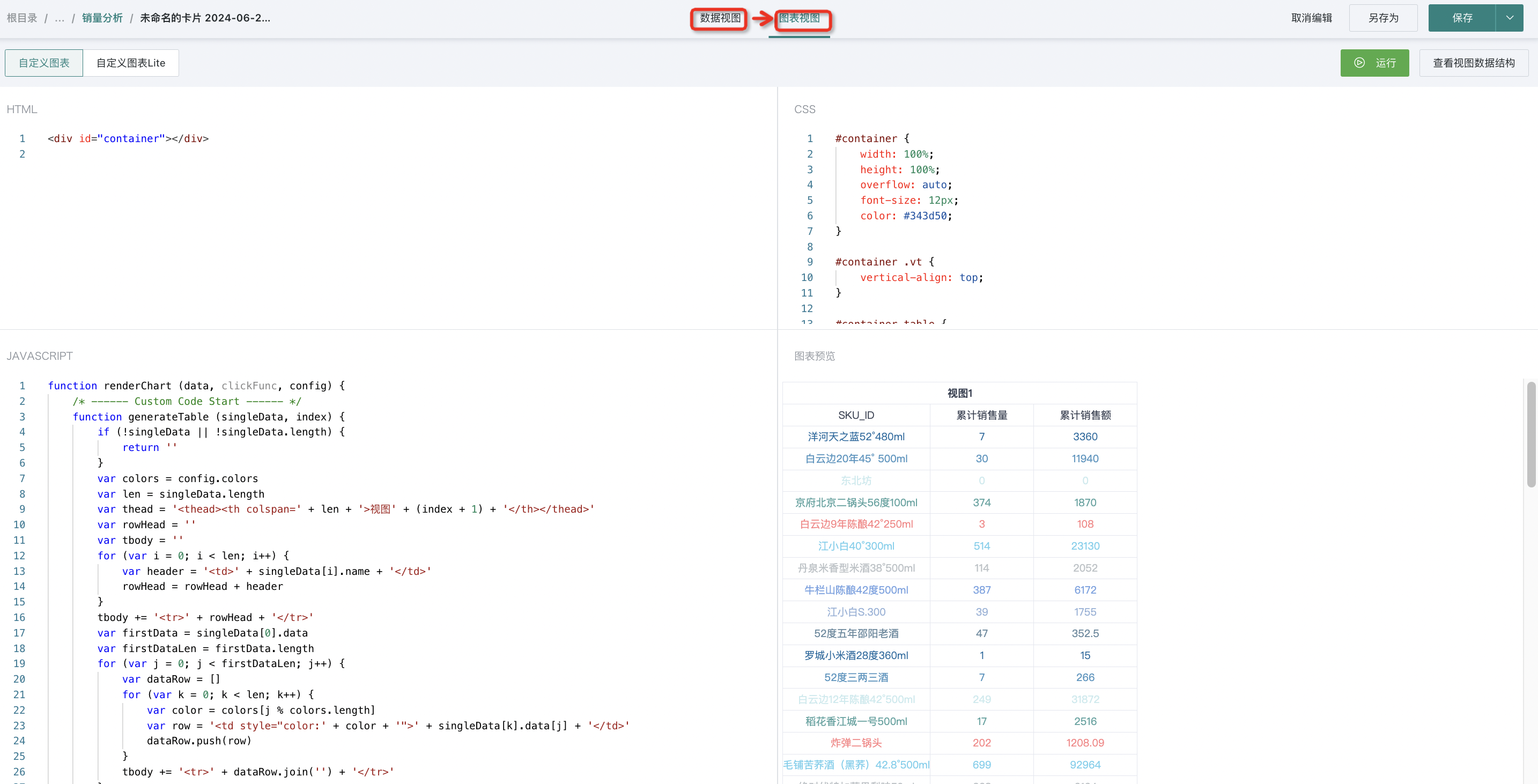
3. Switch views by clicking at the top of the page, switching from Data View to Chart View.
The above steps basically complete all preparation work, and now we officially enter development.
2.2. Development Area Introduction
(1)Editing Area (from top to bottom, left to right, refer to the figure below)
a. Run Button: Used to view the effect after code writing is completed;
b. View Data Structure: Data obtained from the data view, unified format, will be explained later;
c. HTML Writing Area: Generally, just write a container for the chart. The CDN link library needed for chart drawing is also written here;

d. CSS Writing Area: Style area, does not support preprocessor languages like SCSS/LESS, only supports native CSS;
e. Javascript Writing Area: See point (2) below for details;
f. Chart Preview Area: Where the chart is finally drawn, as shown in the figure below. We have made a default table display for each newly created custom card, where you can see the combined use of our data and other configurations (such as the use of theme colors).
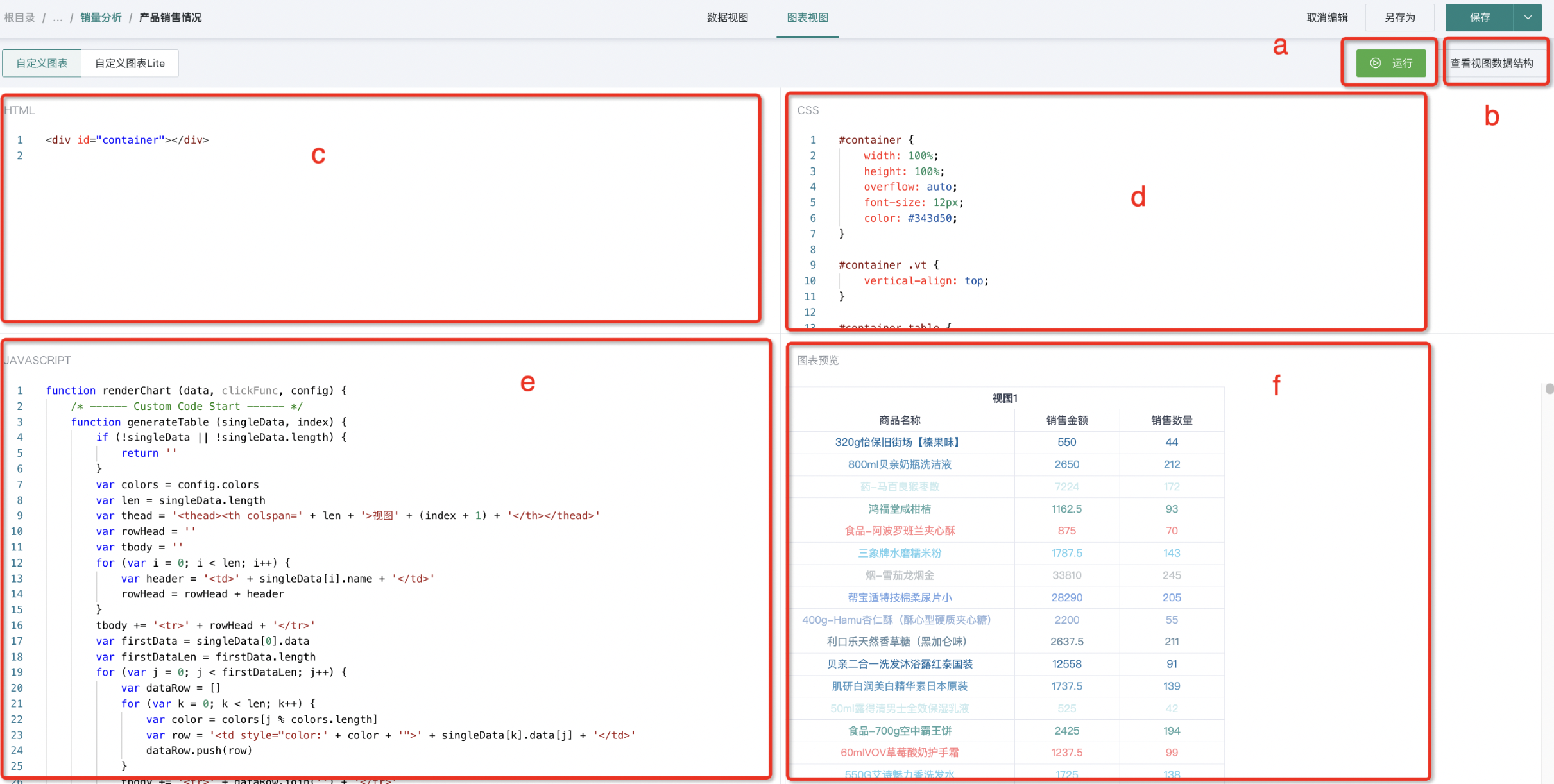
Note: The four areas c, d, e, f in the canvas support dragging and maximizing.
(2)Key Area: Javascript Area
// Guandata's built-in rendering function, generally no need to modify
function renderChart (data, clickFunc, config) {
/* ------ Custom Code Start ------ */
// This is where you write your code
/* ------ Custom Code End ------ */
}
// Guandata's plugin code, used to control the final chart rendering
new GDPlugin().init(renderChart)
If you want to display a prompt in the chart area when the input parameters do not meet the conditions, you can customize the prompt as follows:
function renderChart (data, clickFunc, config) {
if(data[0].length === 0) {
const dom = document.getElementById('container')
dom.innerHTML = "Data is empty"
return
}
}
3.2 Render Function Parameters
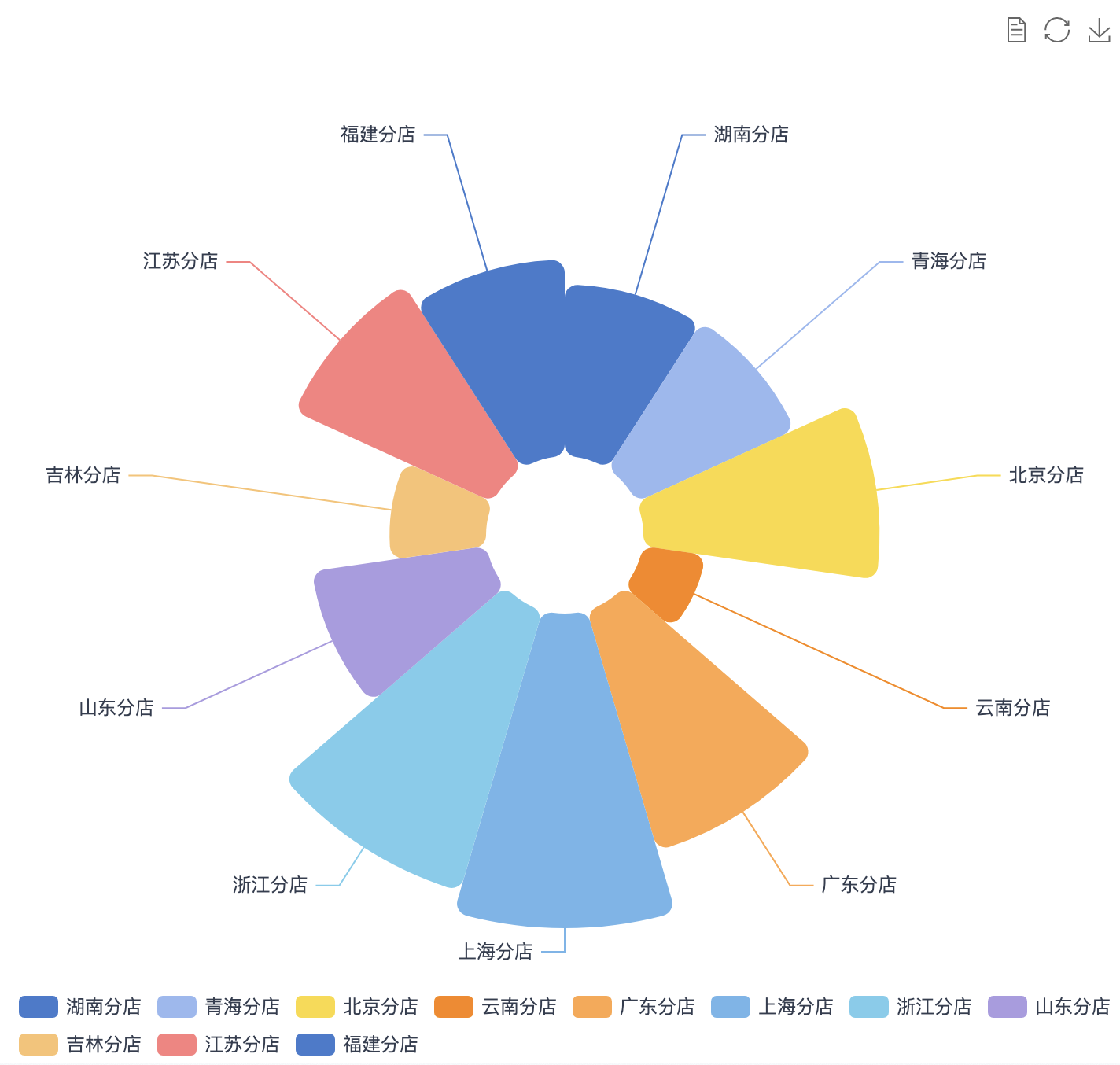
(1)data: Data obtained by dragging fields in the data view area, format as follows:
[
// View 1 data
[
{
"name": "Store Name",
"numberFormat": null,
"data": [
"Guangdong Branch",
"Fujian Branch",
"Zhejiang Branch",
"Jiangsu Branch",
"Qinghai Branch",
"Hunan Branch",
"Shandong Branch"
]
}
],
// View 2 data
[
{
"name": "Region",
"numberFormat": null,
"data": [
"GD",
"FJ",
"ZJ",
"JS",
"QH",
"HN",
"SD"
]
}
]
]
The entire data format is an array, with each view's data as an array element. Each element in this data corresponds to the data of fields dragged into the Data View, and corresponds one-to-one with the table in the Data View.
(2)clickFunc: Charts often need to jump or have linkage functions between charts. From the parameter name, it can be seen that this is a click function. When jumping or linking, we often look at more detailed data from a certain dimension, so we have also standardized the input parameter format of clickFunc:
function clickFunc(data) {}
// data format is as follows:
{
clickedItems: [ {
idx: [ 1, 2 ], // Column index path. eg. Third column of second view dataset [ 1, 2 ]
colName: 'xxx', // Column name
value: [ 'xxx', 'yyy' ], // Value format
} ]
}
(3)config: Settings for custom cards passed from outside, specifically including the following values:
const { theme, colors, customOptions, language } = config
a. theme: // Theme, corresponding values are LIGHT and DARK, adapting to our platform's theme to make chart styles better adapt to the platform.
b. colors: // Theme colors, configurable on the right side of Data View, corresponding to an array, format as follows.
[
"#4379CE",
"#99B8F1",
"#FADB37",
"#FC8602",
"#FFA748",
"#72B5EB",
"#78CDED",
"#AC9AE2",
"#FAC36F",
"#FD7F7F",
]
c. customOptions: // Custom configuration settings. Since it's a plugin, it should come with chart configurations, so we support custom chart configurations to facilitate better chart settings after plugin installation.
// customOptions is an object, fields can be defined according to the chart, then used
{
showLabel: false,
fontSize: 12,
}
d. language: Current system language, supported in version 5.6.0.
4. Development Practice
After the overall introduction above, we can start practicing. Let's take drawing a simple eCharts chart as an example:
(1)HTML
(2)CSS
#container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
(3)Javascript
const myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('container'))
const customOptions = {
showToolbox: true
}
function renderChart (data, clickFunc, config) {
/* ------ Custom Code Start ------ */
// Read configuration
const { theme, colors } = config
const isDarkTheme = theme === 'DARK'
// Use default configuration for configuration, will be integrated later
const { showToolbox } = customOptions
// Use data from view dataset 1
const seriesData = data[0]
const [ names, values ] = [ seriesData[0].data, seriesData[1].data ]
const option = {
legend: {
top: 'bottom',
textStyle: {
color: isDarkTheme ? '#D1D8E3' : '#343D50',
}
},
toolbox: {
show: showToolbox,
feature: {
mark: { show: true },
dataView: { show: true, readOnly: false },
restore: { show: true },
saveAsImage: { show: true }
}
},
series: [
{
name: 'Nightingale Chart',
type: 'pie',
radius: [ 50, 250 ],
center: [ '50%', '50%' ],
roseType: 'area',
itemStyle: {
borderRadius: 8
},
data: names.map((name, index) => ({
name,
value: values[index],
})),
}
],
color: colors,
label: {
color: isDarkTheme ? '#D1D8E3' : '#343D50',
},
};
myChart.setOption(option)
myChart.on('click', function (params) {
const { name, seriesIndex } = params
clickFunc({
clickedItems: [
{
idx: [ 0, seriesIndex ],
colName: seriesData[0].name,
value: [ name ],
}
]
});
myChart.resize()
/* ------ Custom Code End ------ */
}
new GDPlugin().init(renderChart)
(4)Display
For more help on using visualization plugins, please visit Guandata BI Video Tutorial Website.