Creating New Fields
1. Overview
1.1. Function Description
When drawing charts, if the fields provided in the dataset cannot meet user analysis requirements, users can use the create new fields function to generate new fields by performing formula calculations, grouping, and filtering on existing fields, and then conduct data analysis based on these newly created fields.
Creating new fields provides three methods: creating grouping fields, creating filter fields, and creating calculated fields. Users can choose according to actual needs.
1.2. Application Scenarios
For example, in sales data analysis scenarios:
When gross profit data analysis is needed, but the original data only provides sales revenue, quantity, and cost price, gross profit fields can be constructed through creating calculated fields.
When sales revenue needs to be viewed by region dimension, but there is no region information in the data, only store information, grouping fields can be created to place various stores in different regions to complete sales revenue analysis by region dimension;
When specific product categories need to be filtered for sales revenue analysis, such as "Beauty Sales Revenue", "Daily Necessities Sales Revenue", "Food Sales Revenue", etc., filter fields can be created to add filtering conditions "Product Category = Beauty" to sales revenue to generate new "Beauty Sales Revenue" fields to complete sales revenue analysis for specific product categories.
2. Creating Calculated Fields
2.1. Overview
When drawing charts, if existing fields cannot meet user usage scenarios, users can create calculated fields to obtain the required indicators.
There are two ways to create calculated fields: one is to create calculated fields in the dataset, and the other is to create calculated fields in cards. If you want calculated fields to be reusable by all users, it is recommended to create them in the dataset. There is no difference in usage between the two.
Calculated fields support rich scenarios, such as aggregation, four arithmetic operations, window functions, character separation and merging, and complex grouping. Common functions are as follows: Common Spark Functions - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center;
2.2. Function Introduction
The calculated field editor consists of three parts, as shown in the figure below:
-
Field Name: The name of the new field;
-
Field Type: Provides 5 field types: text, numerical, date, time and date, and boolean;
-
The left side is the function list, providing rich functions. In extraction mode, in addition to the listed functions, all spark functions are also supported. For detailed list: Function List - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center;
-
The middle is the field and parameter list: The field list displays all original fields and newly created fields in the current dataset, and the parameter list contains global parameters preset by administrators;
-
The right side is the formula editing area. When you input a formula, corresponding formula prompts will appear below. At the same time, one-click formatting is supported to make function formulas more readable.
-
-
In addition to manually inputting field names, you can also directly click on specific field names in the field or parameter list in the middle area to input fields. Note that when manually inputting, square brackets "[]" need to be added on both sides of the field name so that it will be correctly recognized as a field;
-
When deleting fields or functions, they will be treated as a whole and only need to be deleted once, reducing operation costs;
-
When manually outputting functions, functions will be automatically recommended based on keywords.
-
2.3. Usage Instructions
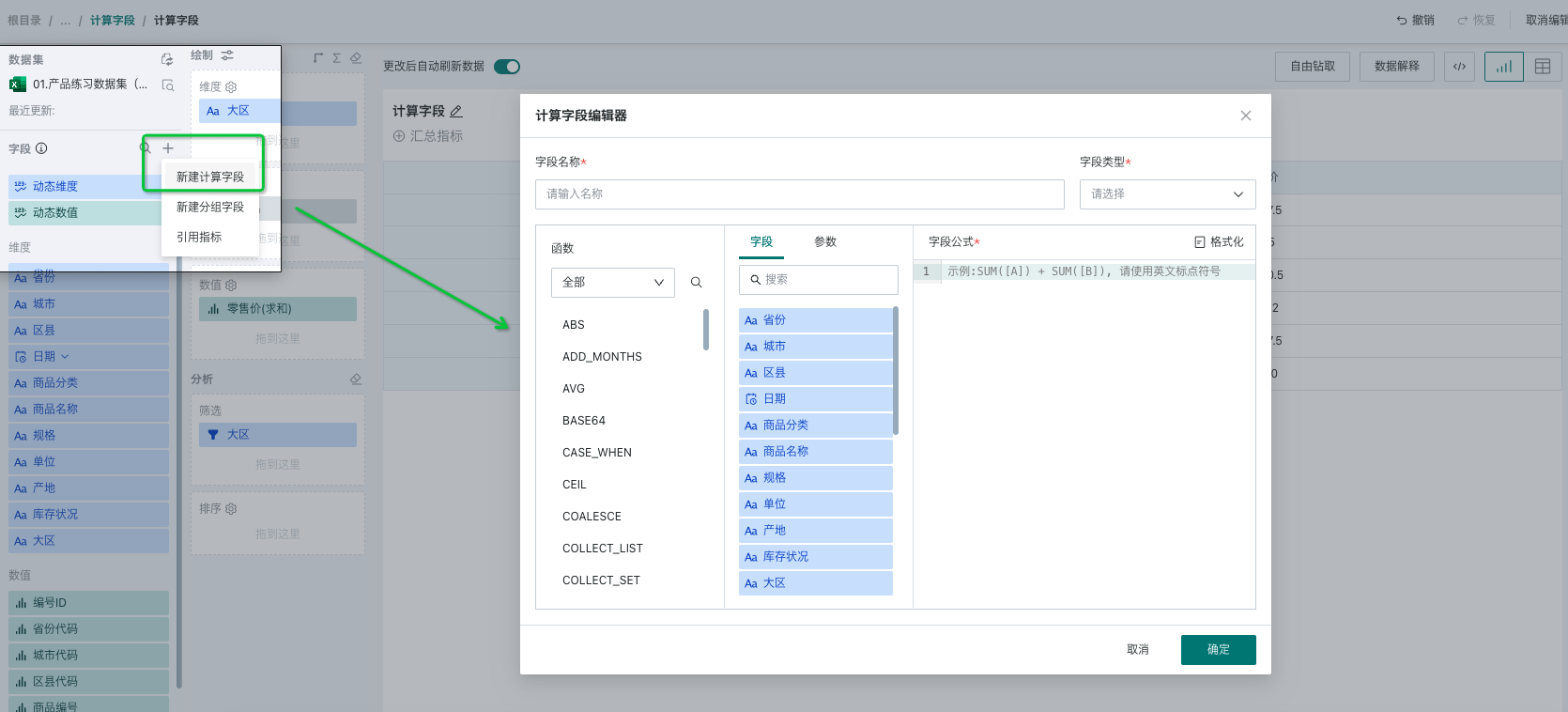
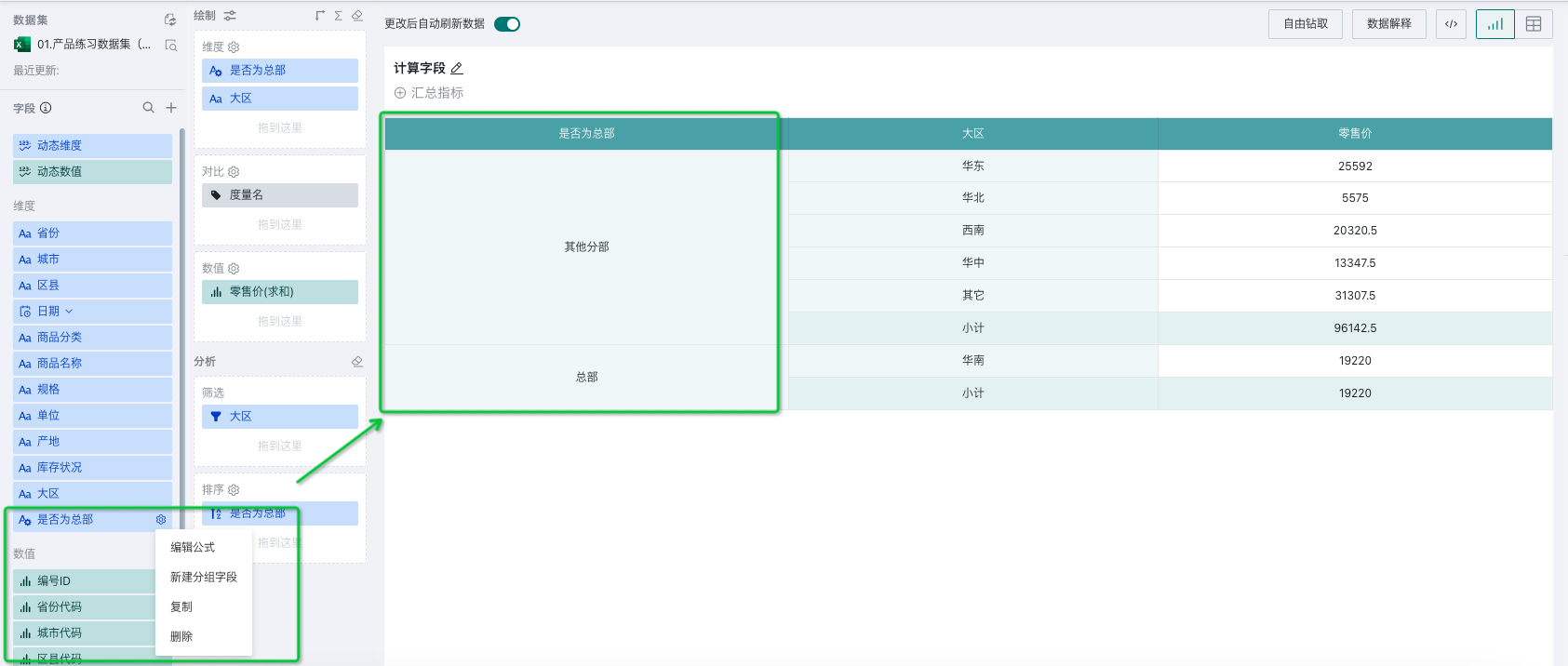
Taking the scenario in the figure below as an example, users want to intuitively display sales data of headquarters and other branches, but the field type of whether it is headquarters is not available in the original dataset (headquarters is in South China region, others are various branches), and the original data only provides the "Region" field. At this time, you can get the "Is Headquarters" field through the case when function based on the region field. The detailed steps are as follows:
- Click the plus sign on the right side of the dataset field area to create a new calculated field, and a calculated field popup will appear.
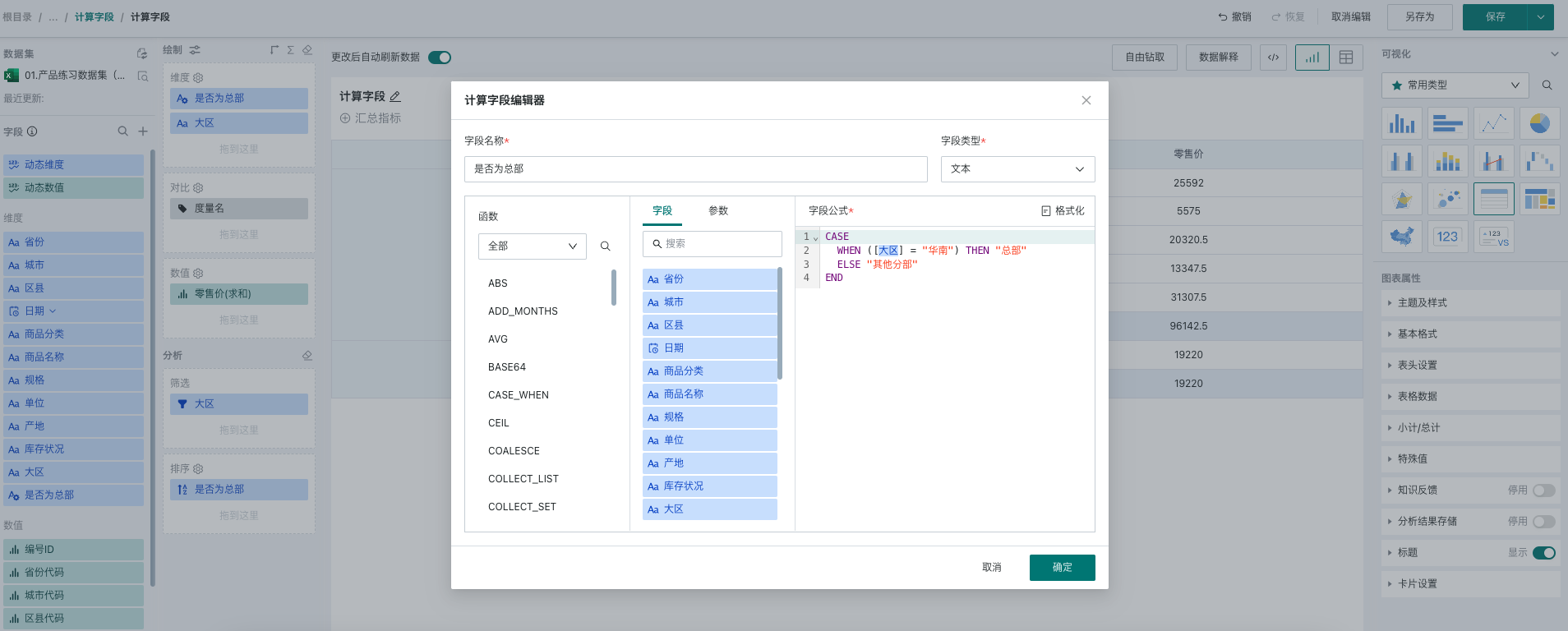
- Edit the calculated field information and formula: Enter "Is Headquarters" in the field name, select text for the field type, and enter the case when function in the field formula. The detailed formula is as follows:
CASE
WHEN ([Region] = "South China") THEN "Headquarters"
ELSE "Other Branches"
END
- After successful creation, we can see the newly added "Is Headquarters" field in the dataset overview interface. At this time, this field will merge other regions except South China region as "Other Branches".
Click the settings button on the right side of the newly created field to modify formulas, group, copy and delete the newly created calculated field.
2.4. Common Usage Scenarios
For more usage scenarios, please refer to the following cases:
-
Field Splitting Case Sharing - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
-
Using Window Functions for Cumulative Calculations - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
-
Distinct Count Function to Implement Window - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
-
Combination Function Usage Cases - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
-
count_if Function Usage Instructions - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
-
Functions to Extract Year and Month - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
-
Sorting Functions and Applications - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center
3. Creating Grouping Fields
3.1. Overview
When you want to group dimension items of dimension fields or measure fields, you can use the create grouping fields function.
For example, dividing field values in the dimension field "Province" into various regions, such as "East China", "South China", etc., using "Region" as the dimension for analysis;
Dividing the measure field "Sales Revenue" into data buckets, 0-100, 100-300, 300-500, to analyze data performance in various ranges.
3.2. Function Introduction
When you need to group dimension or measure fields, that is, merge field values of the same type into a group according to certain conditions, you can use the create grouping fields function.
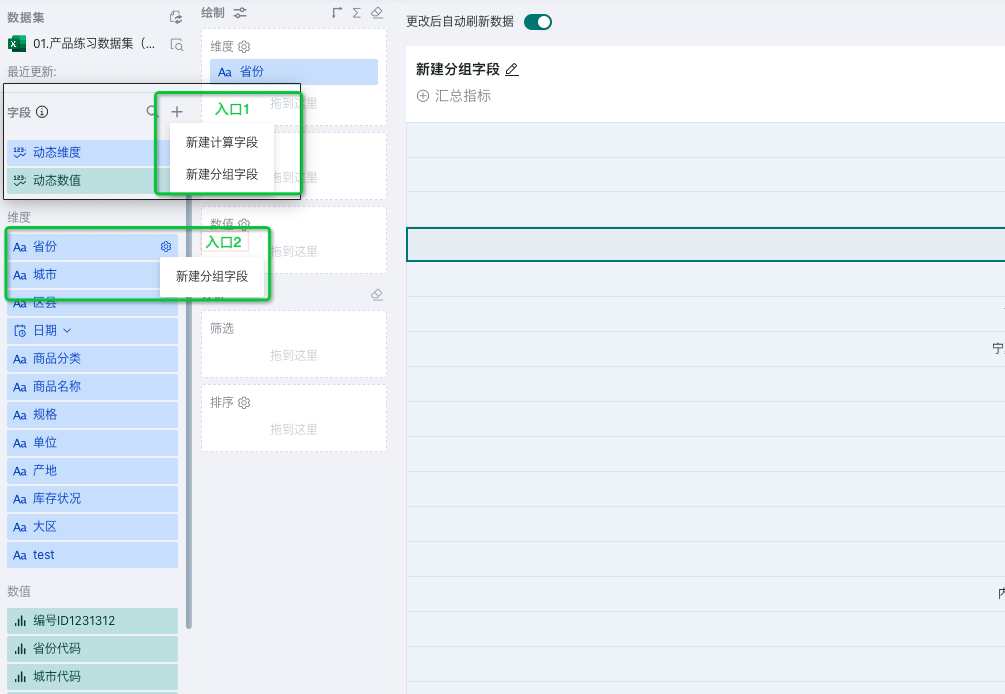
There are two entrances for creating grouping fields, as shown in the figure below: the + on the right side of the top of the field list, or hover over the field name and click the settings button to create grouping fields.
For different types of fields, different grouping methods are provided:
Text Fields: Two grouping methods: items and conditions.
Date (Time) Fields: After grouping date type fields, they will be converted to text type fields, providing three grouping methods: items and fixed step size, custom step size.
Numerical: After grouping numerical type fields, they will be converted to dimension fields, providing three grouping methods: items and fixed step size, custom step size.
3.3. Usage Instructions
Text Type
For text type dimension fields, two grouping methods are provided: items and conditions. Ungrouped fields support merging items and individual items.
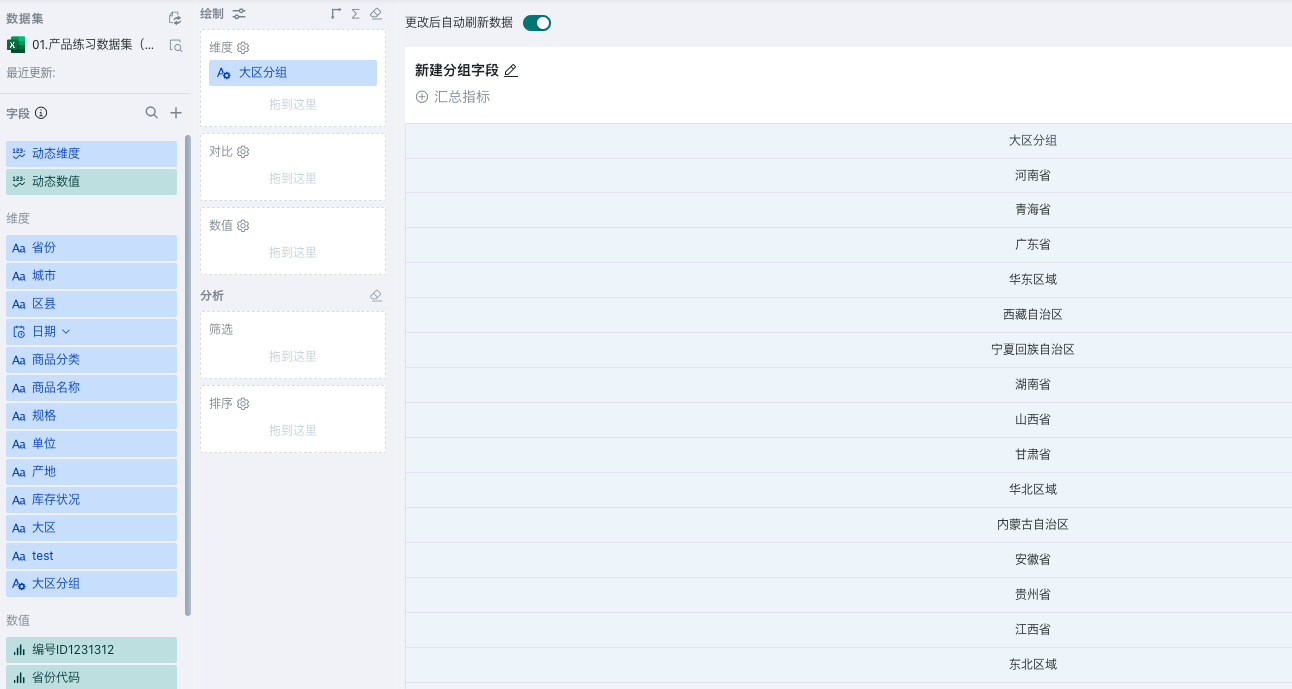
- Items: Manually select and group one by one according to dimension items, as shown in the figure below:
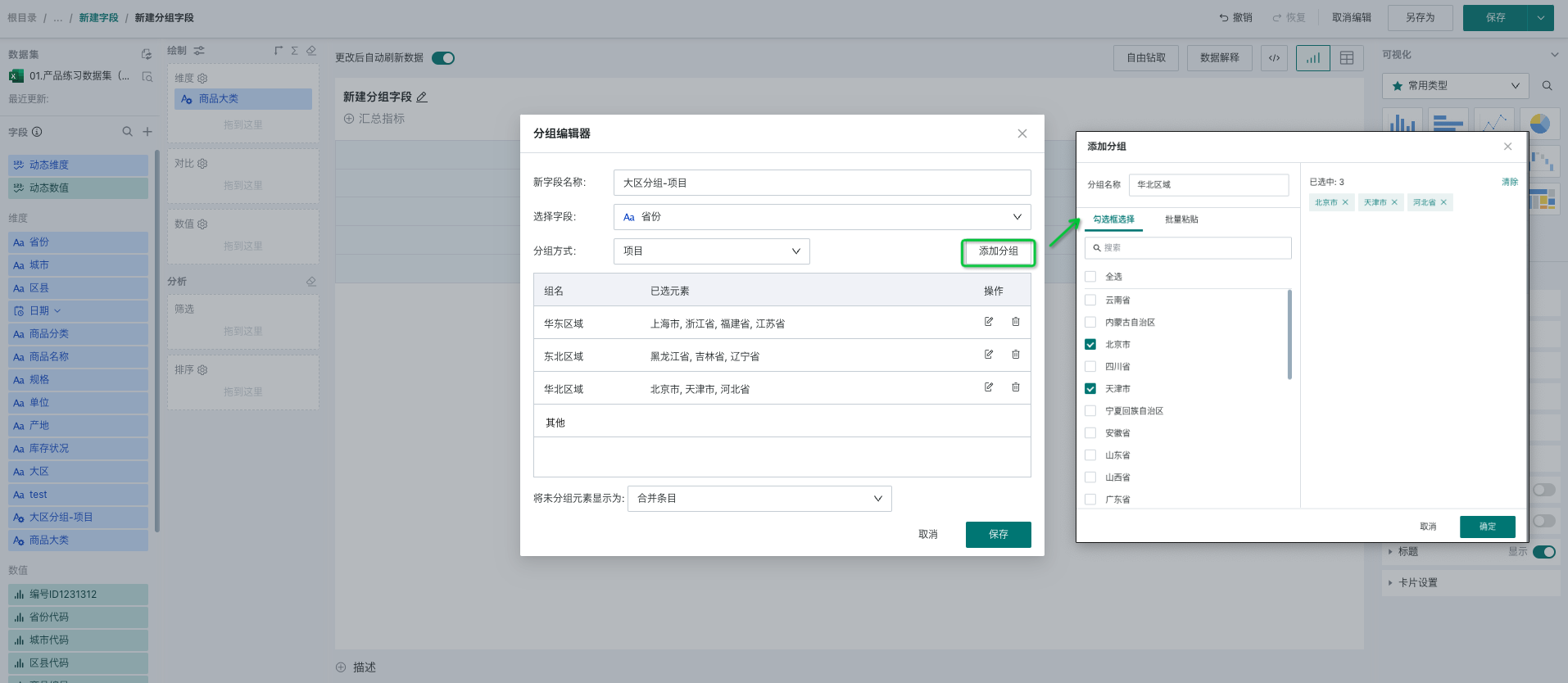
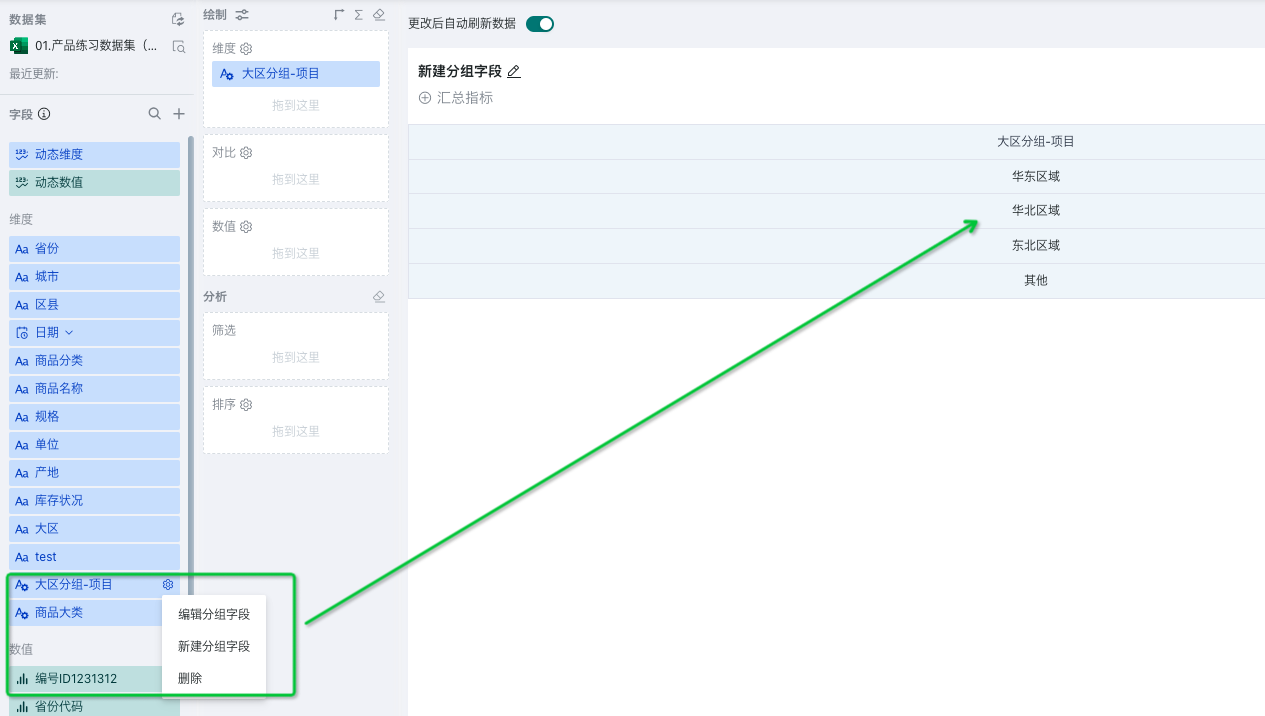
After successful creation, we can see the newly added "Region Grouping" field in the dimension field bar. Hover over the field, and a settings icon will appear on the right side of the field, allowing you to edit, regroup, and delete the newly created grouping field.
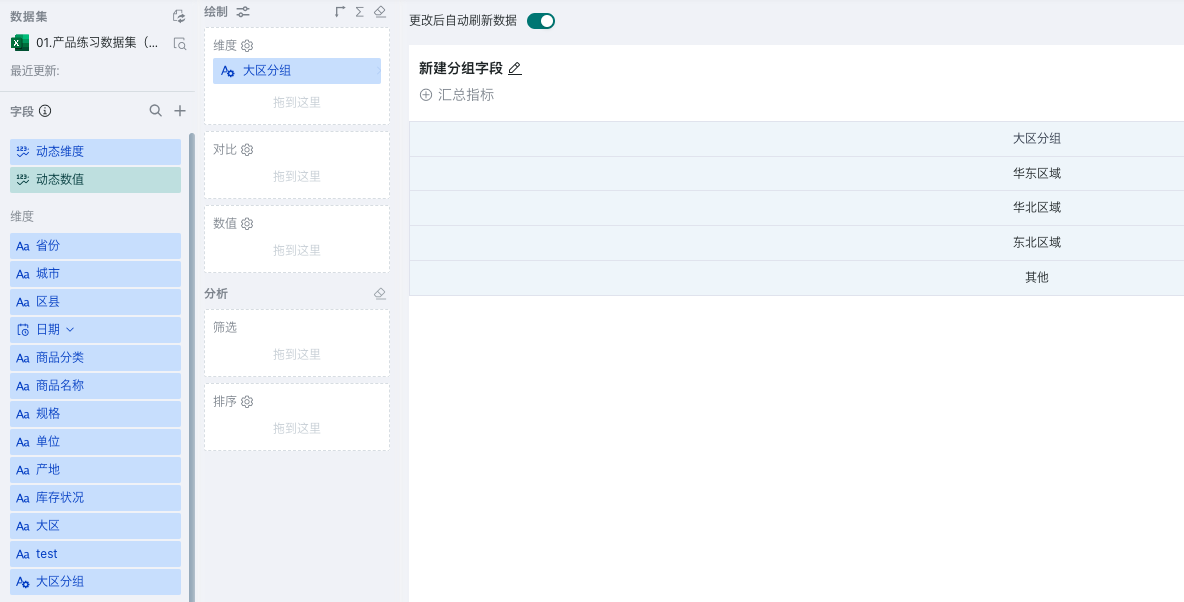
Ungrouped fields support two methods: individual items and merging items. Merging items will merge all unclassified dimension items into "Others", while individual items will treat all unclassified dimension items as one group each, displayed at the same level as other groups.
| Individual Items | Merging Items |
 |  |
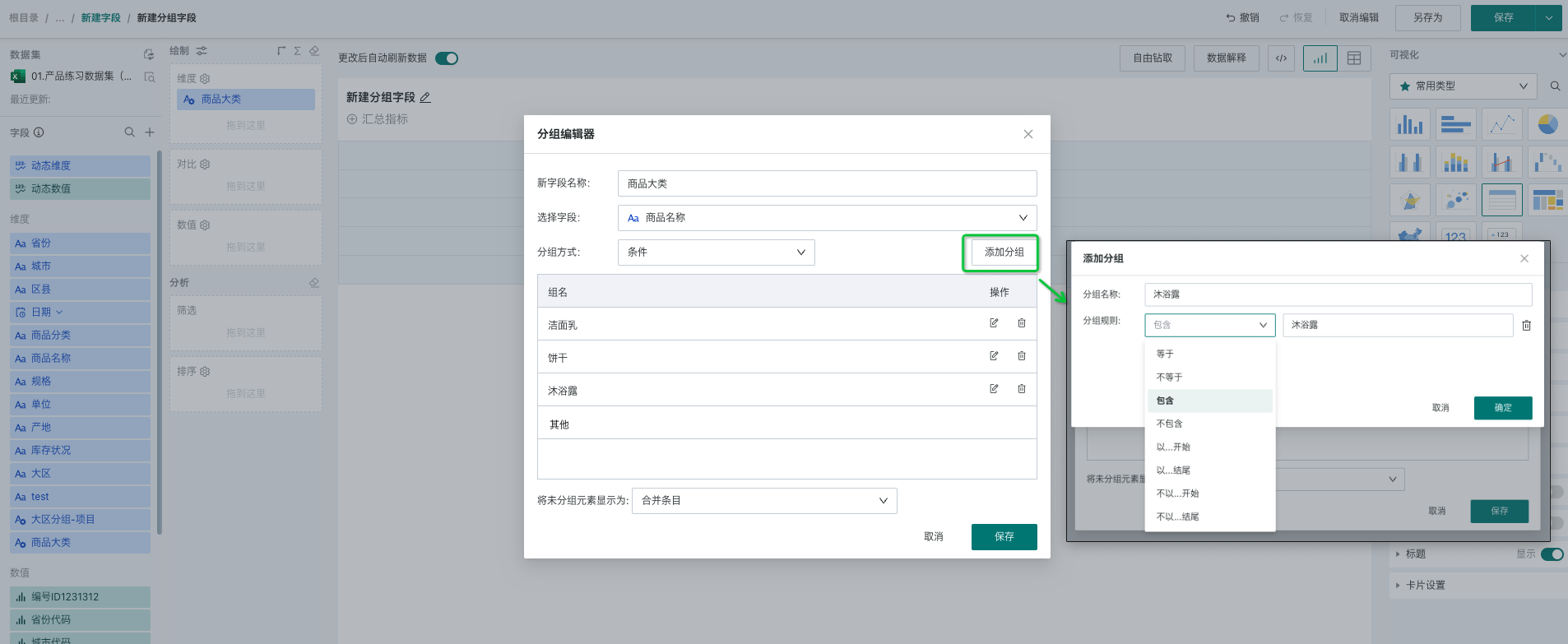
- Conditions: According to specified conditions, data that meets this condition is treated as a group. Supported judgment operators include "equal, not equal, contain, not contain, start with, end with, not start with, not end with" 8 types, as shown in the figure below:
Date Type
After grouping date (time) type fields, they will be converted to text type fields, providing three grouping methods: items and fixed step size, custom step size. Ungrouped fields support merging items and individual items.
-
Items: Manually select and group one by one according to dimension items, which is consistent with the logic of grouping dimension fields by items.
-
Fixed Step Size: When you want to group dates according to certain rules, such as grouping several days/weeks/months/quarters/years, you can use this configuration to quickly achieve it.
-
-
Support configuring aggregation methods, that is, the granularity of date aggregation: day, week, month, quarter, year;
-
Start time setting, required;
-
Grouping step size: positive integer, such as grouping step size of 2, when aggregation method is month, it means every two months as a group, and the resulting grouping interval is left-closed and right-closed.
-
For example, when analyzing sales situations every half month since 2022, data needs to be grouped every 15 days. At this time, you can configure the aggregation method as day, start time as January 1, 2022, and grouping step size as 15, to get the dimension field for every half month.
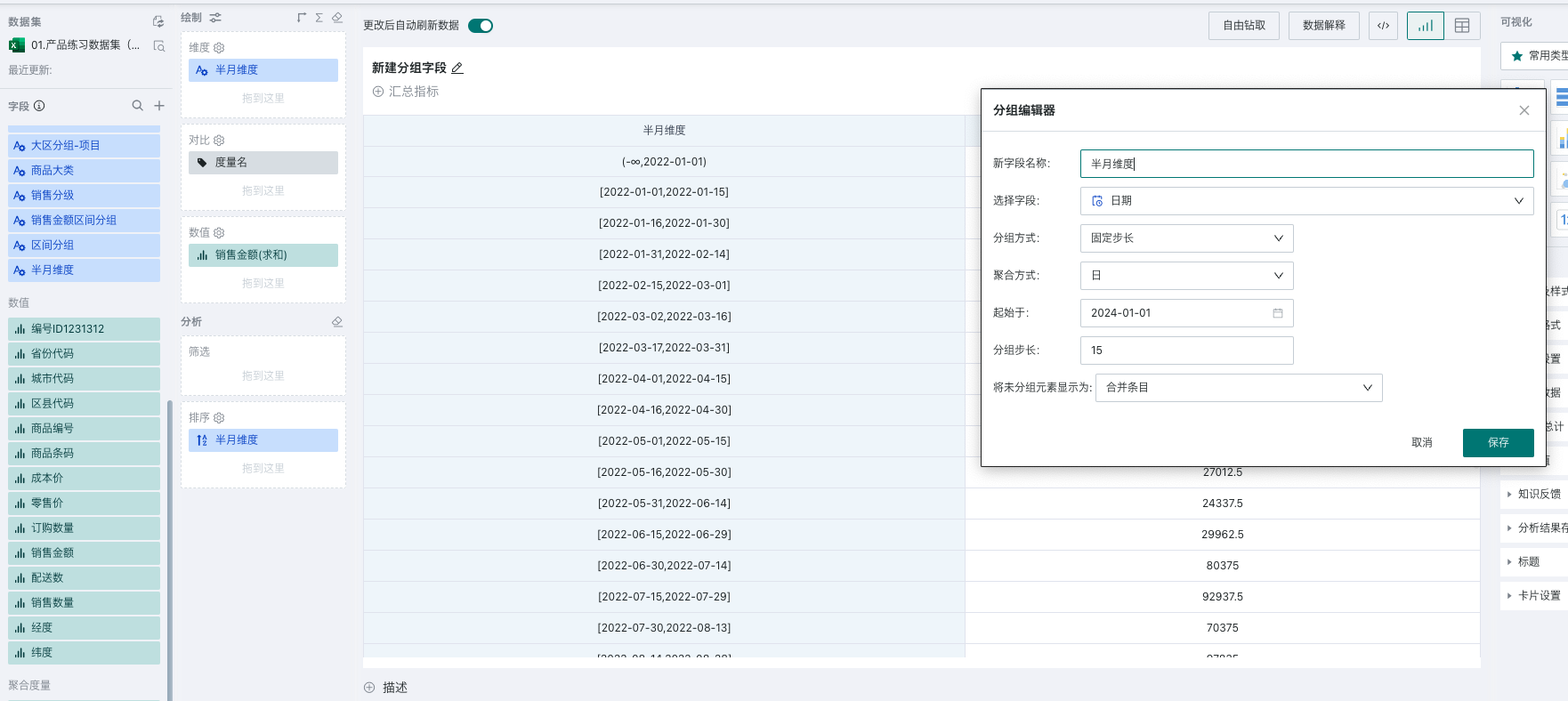
- Custom Step Size: When you want to specify several time periods as a group, you can use custom step size, which only provides day granularity selection. As shown in the figure below, you will get the following groups, with each interval grouped according to the actually set interval, and dimension items as group names.
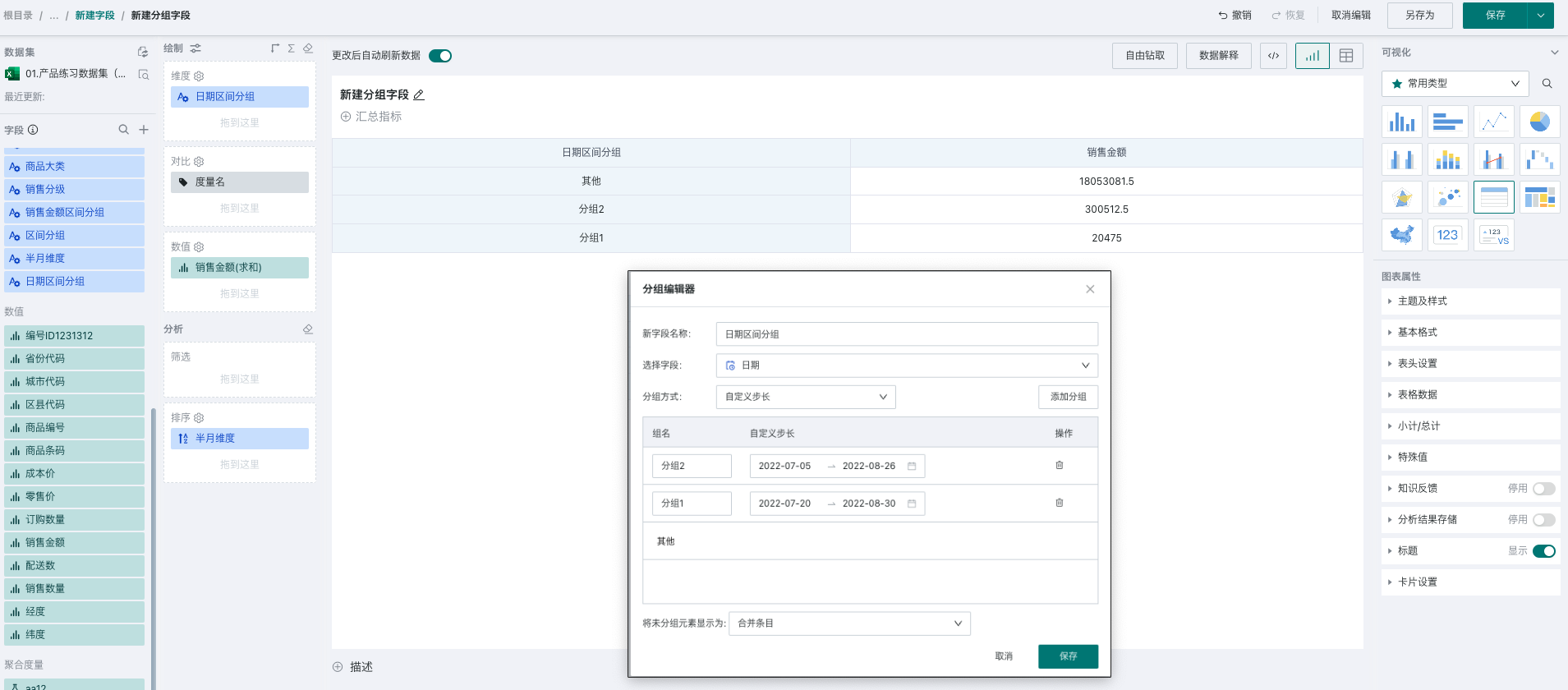
Numerical Type
After grouping numerical type fields, they will be converted to dimension fields, providing three grouping methods: items and fixed step size, custom step size. Ungrouped fields support merging items and individual items.
-
Items: Manually select and group one by one according to dimension items, which is consistent with the logic of grouping dimension fields by items.
-
Fixed Step Size: When you want to do fixed step size grouping within a specified interval range, you can quickly achieve it through this configuration, as shown in the figure below, grouping sales revenue in the range of 0-5000 with 1000 as the fixed step size. At this time, you will get the following groups, with each interval defaulting to left-closed and right-open, and dimension items as interval ranges.
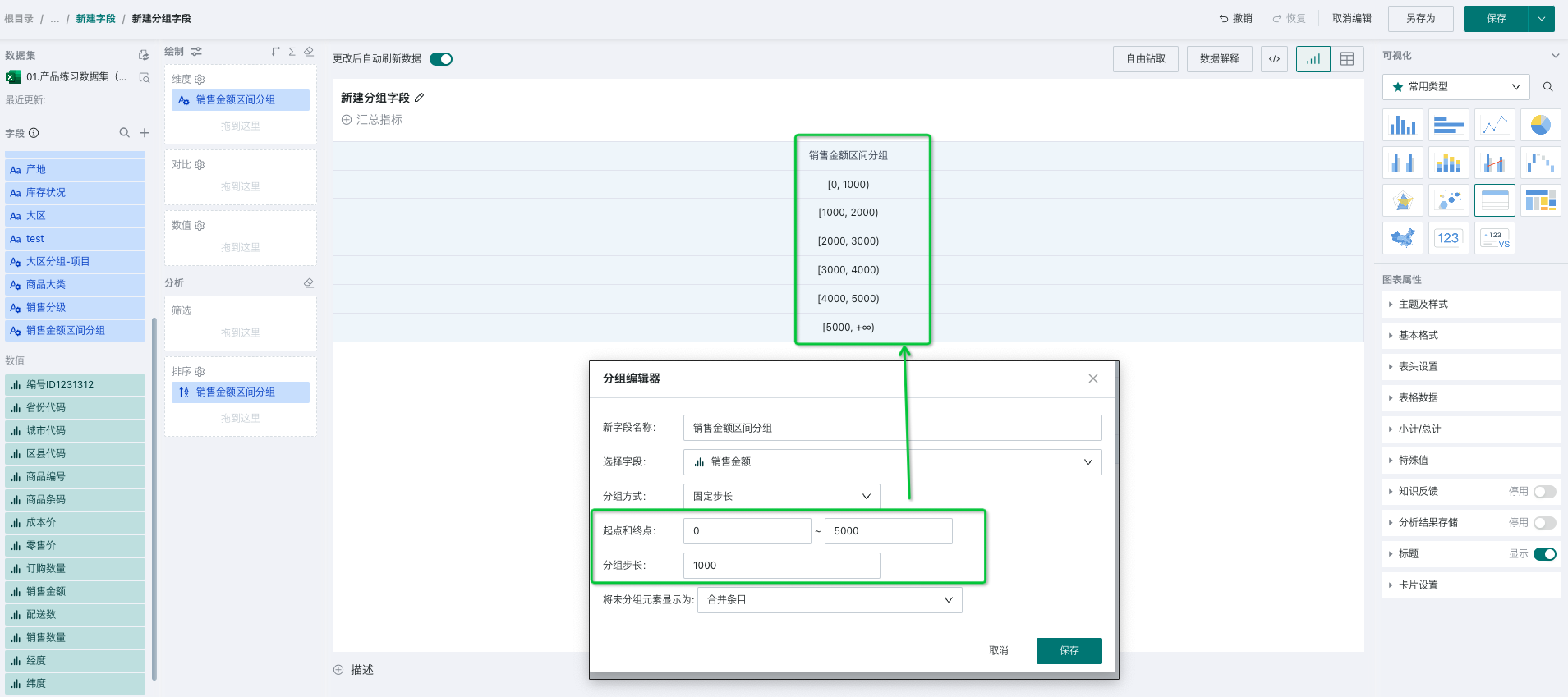
- Custom Step Size: When you want to customize the range of each group of data, you can use custom step size. In addition to customizing interval ranges, you can also customize the open/closed state on both sides of the interval, as shown in the figure below. At this time, you will get the following groups, with each interval grouped according to the actually set interval, and dimension items as group names.
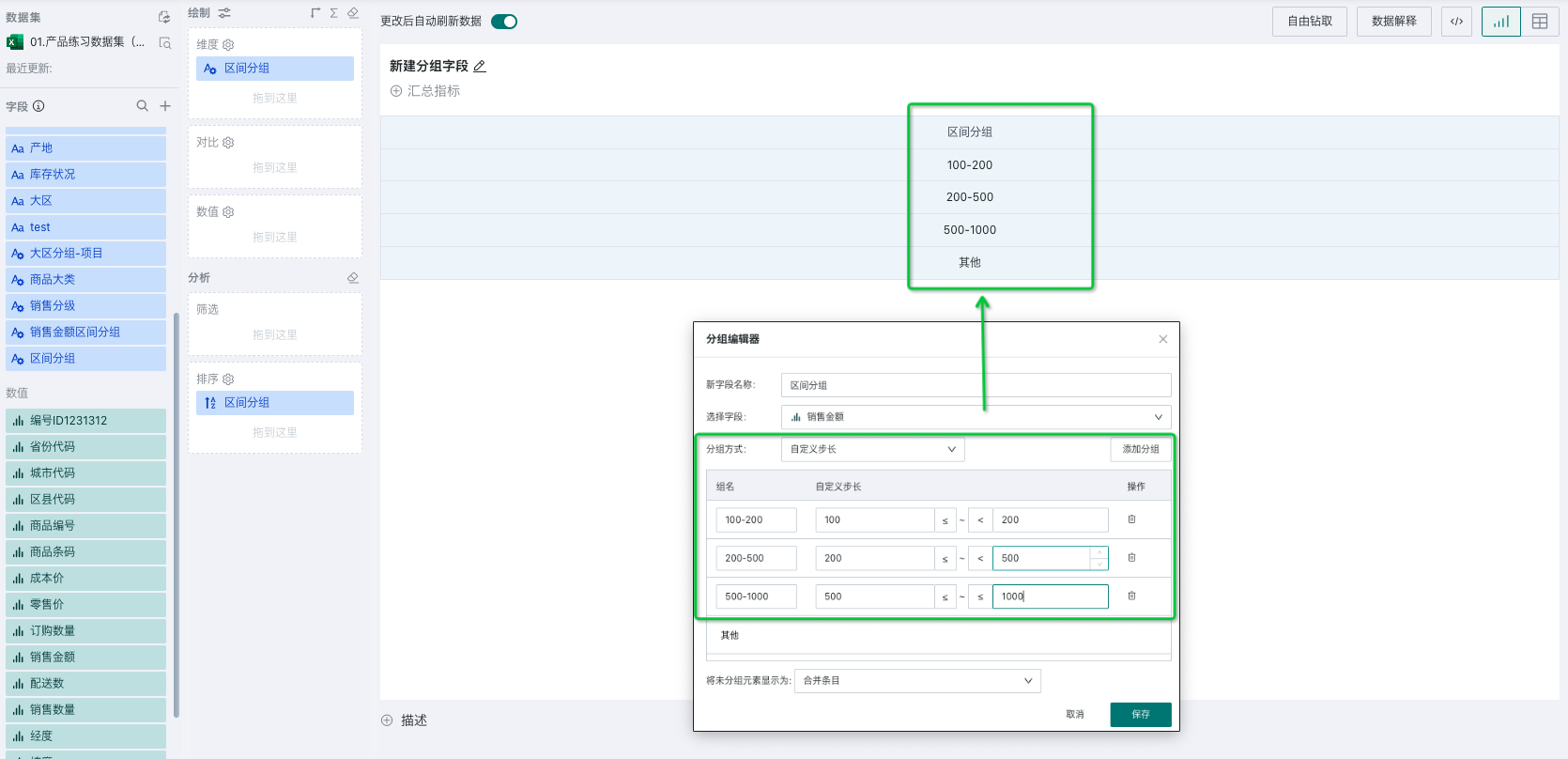
4. Creating Filter Fields
4.1. Overview
When you need to view data under specific conditions, you can use create filter fields to achieve this, setting filtering conditions for that field to complete indicator analysis under specific conditions.
4.2. Function Introduction
Filter fields filter existing measure fields according to certain conditions to form a new field. It supports adding AND and OR combination conditions for filtering, with a maximum of 5 levels of conditions.
Usage restrictions: Only supports creating filter fields based on measure fields. Dimensions, calculated fields, and aggregation measures are not supported.
Function entrance: Field list - measure fields - hover over the field name and click the settings button on the right to create filter fields.
4.3. Usage Instructions
Scenario 1 Using Text Type Fields for Filtering
When filtering a certain measure based on text type fields, all dimension items in the text field will be displayed, and users can select the required dimension items for setting according to actual business scenarios. It supports AND and OR combination conditions with multi-level nesting.
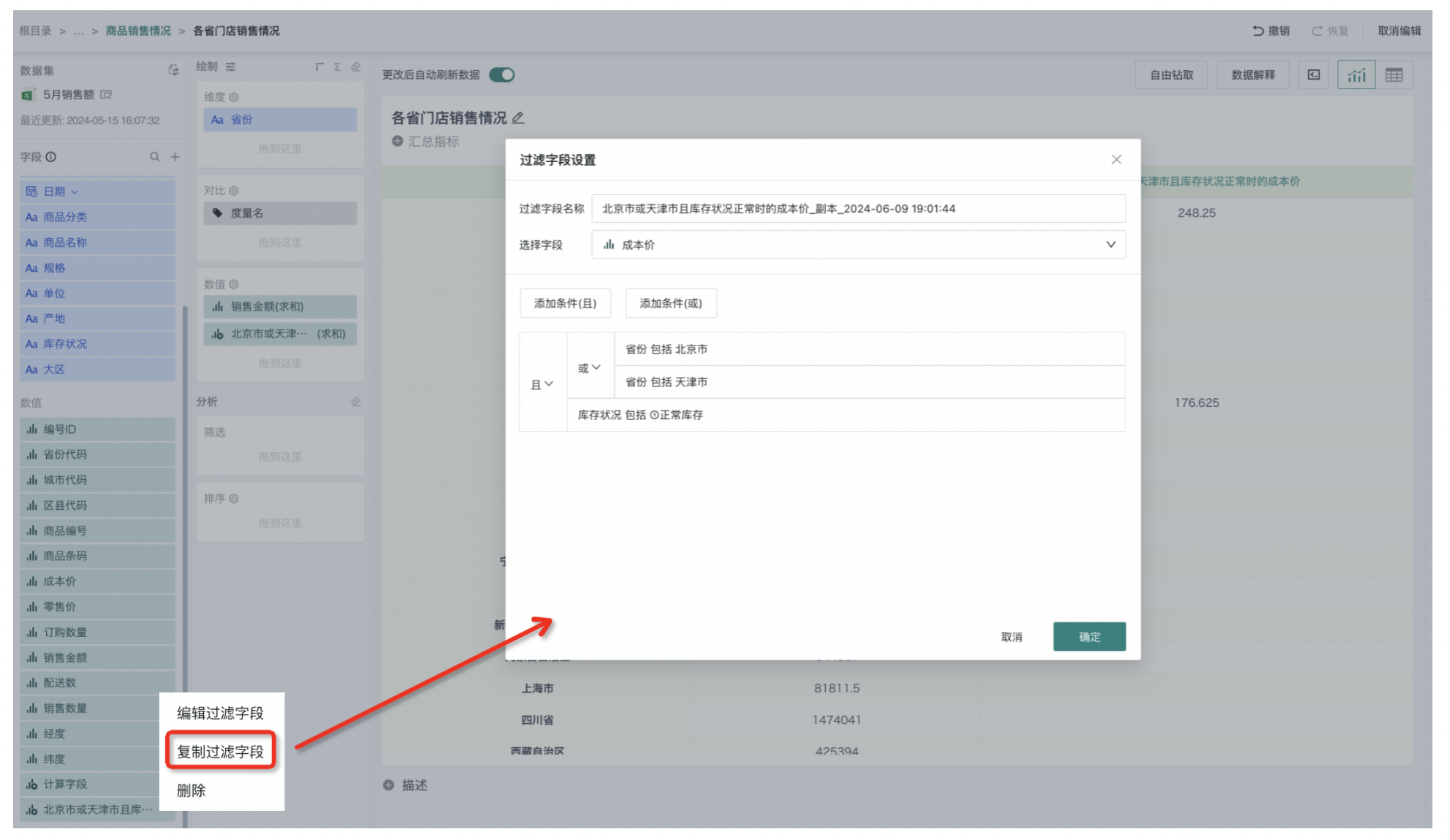
For example, filtering out the total cost price of different unit products when the province is Beijing or Tianjin and the inventory status is normal.
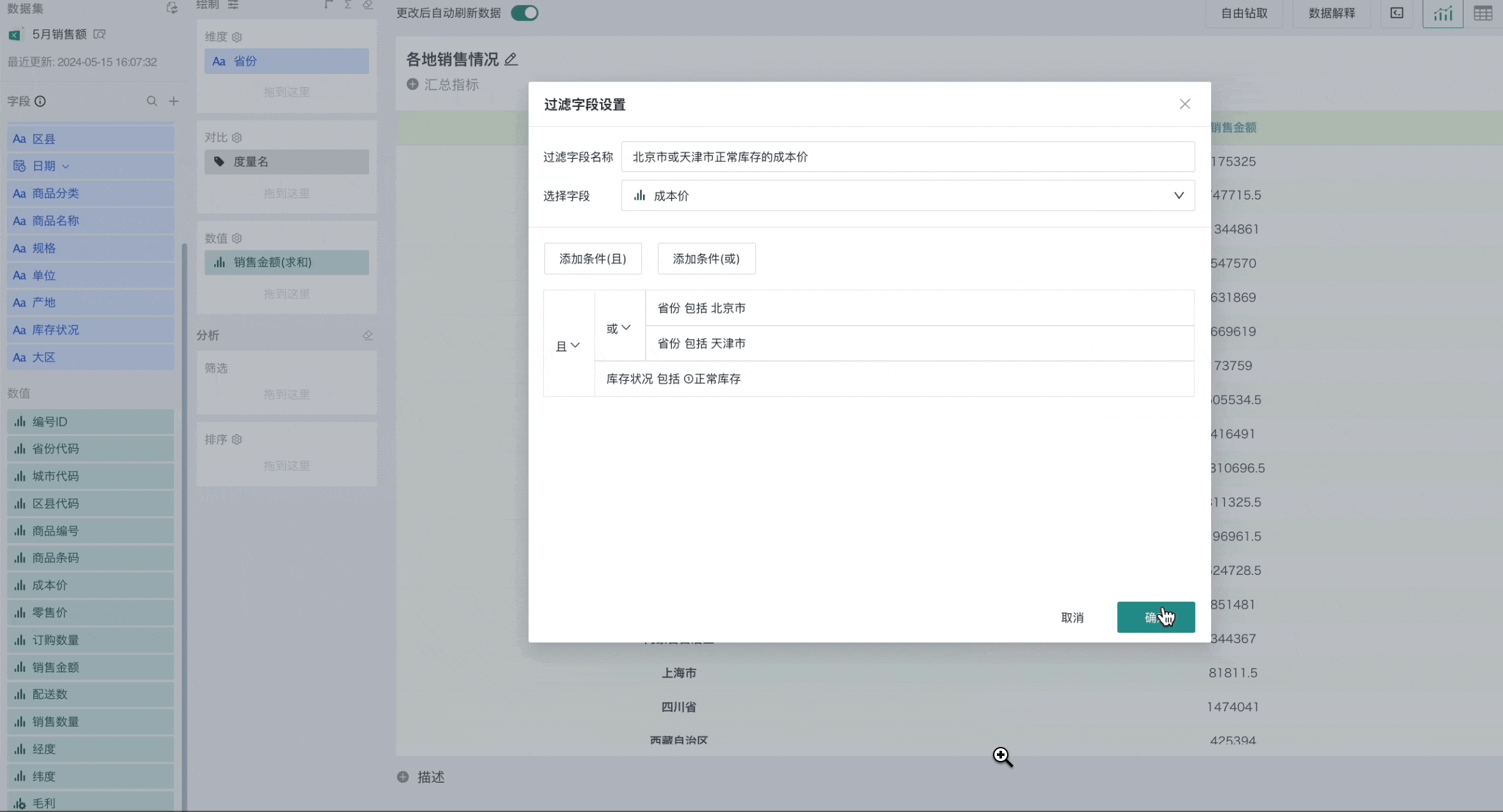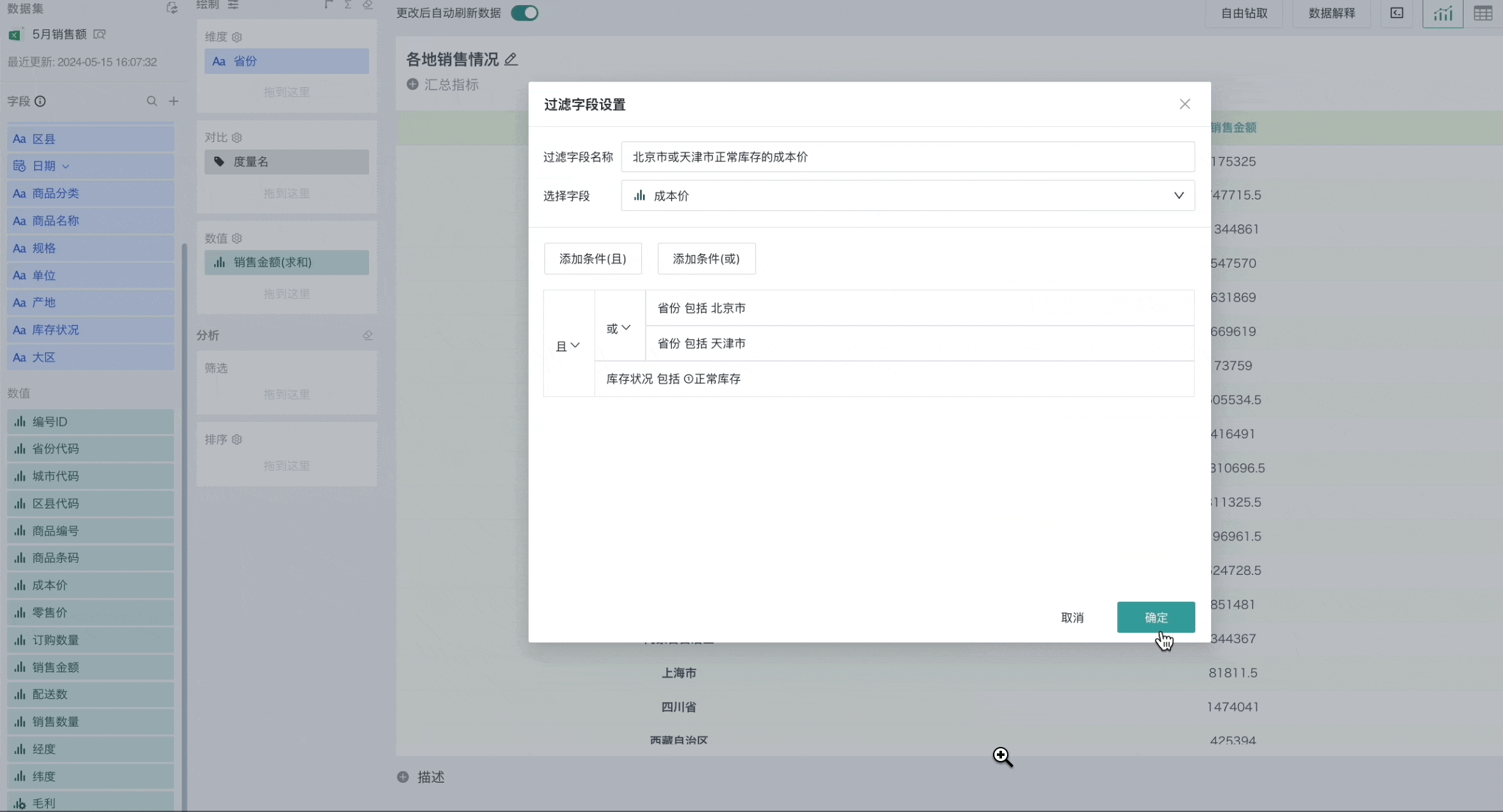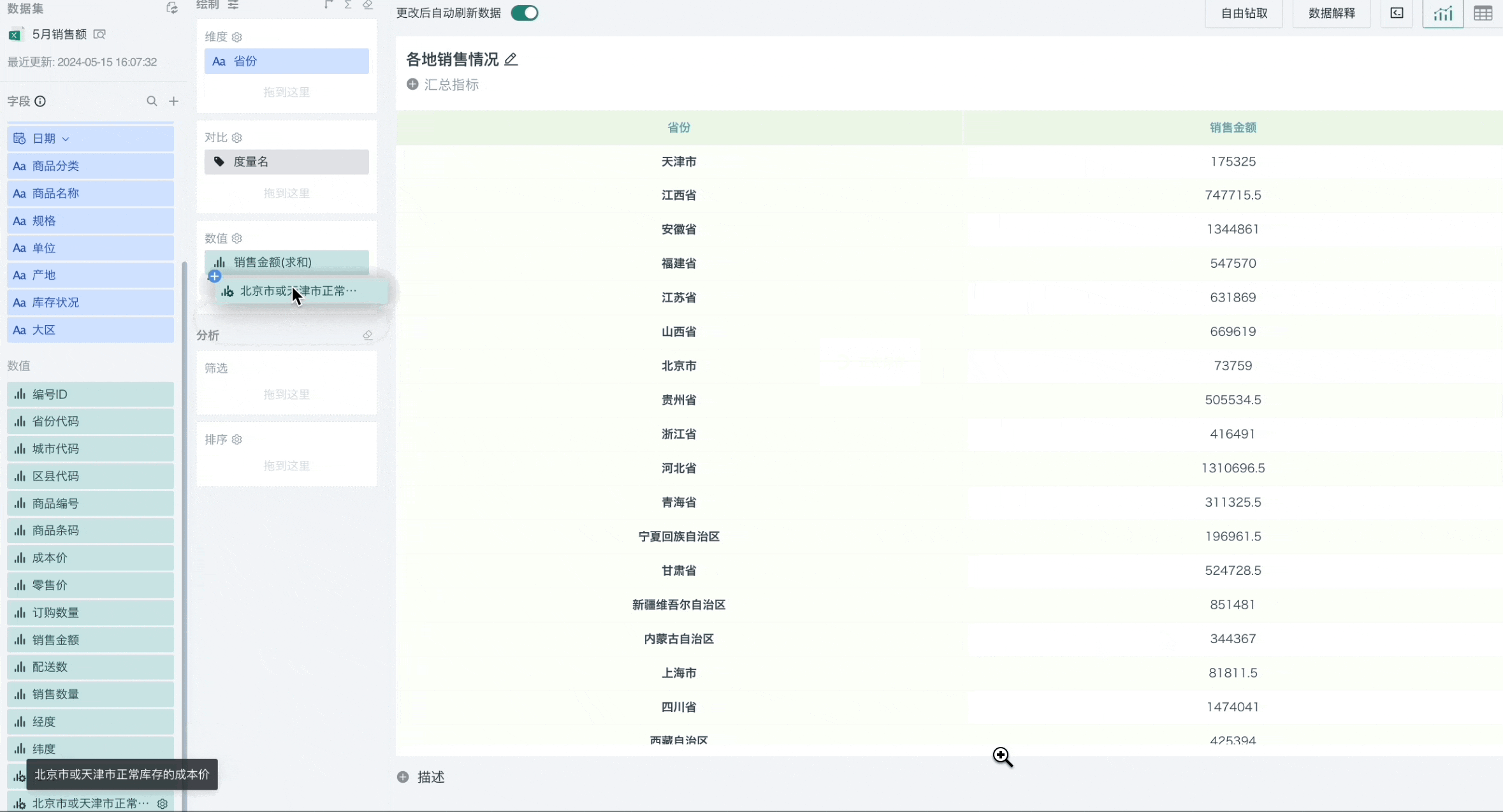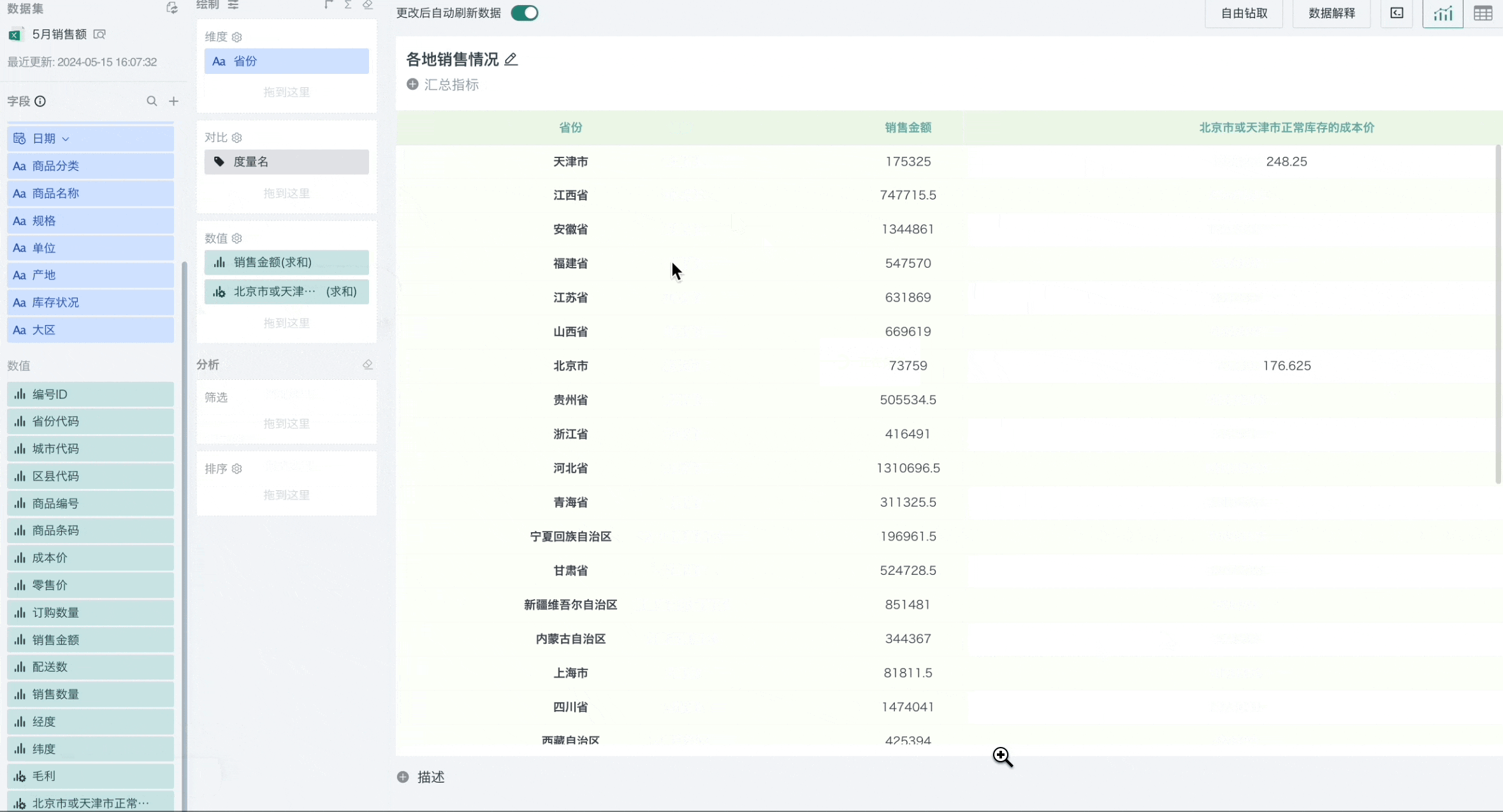
Scenario 2 Using Date Type Fields for Filtering
When filtering a certain measure based on date or time type fields, you can choose fixed time or dynamic time. Dynamic time provides quick options such as past 7 days. If the provided quick dynamic time does not meet requirements, you can also use custom time macros for configuration.
For example, filtering out sales revenue for the past 7 days.
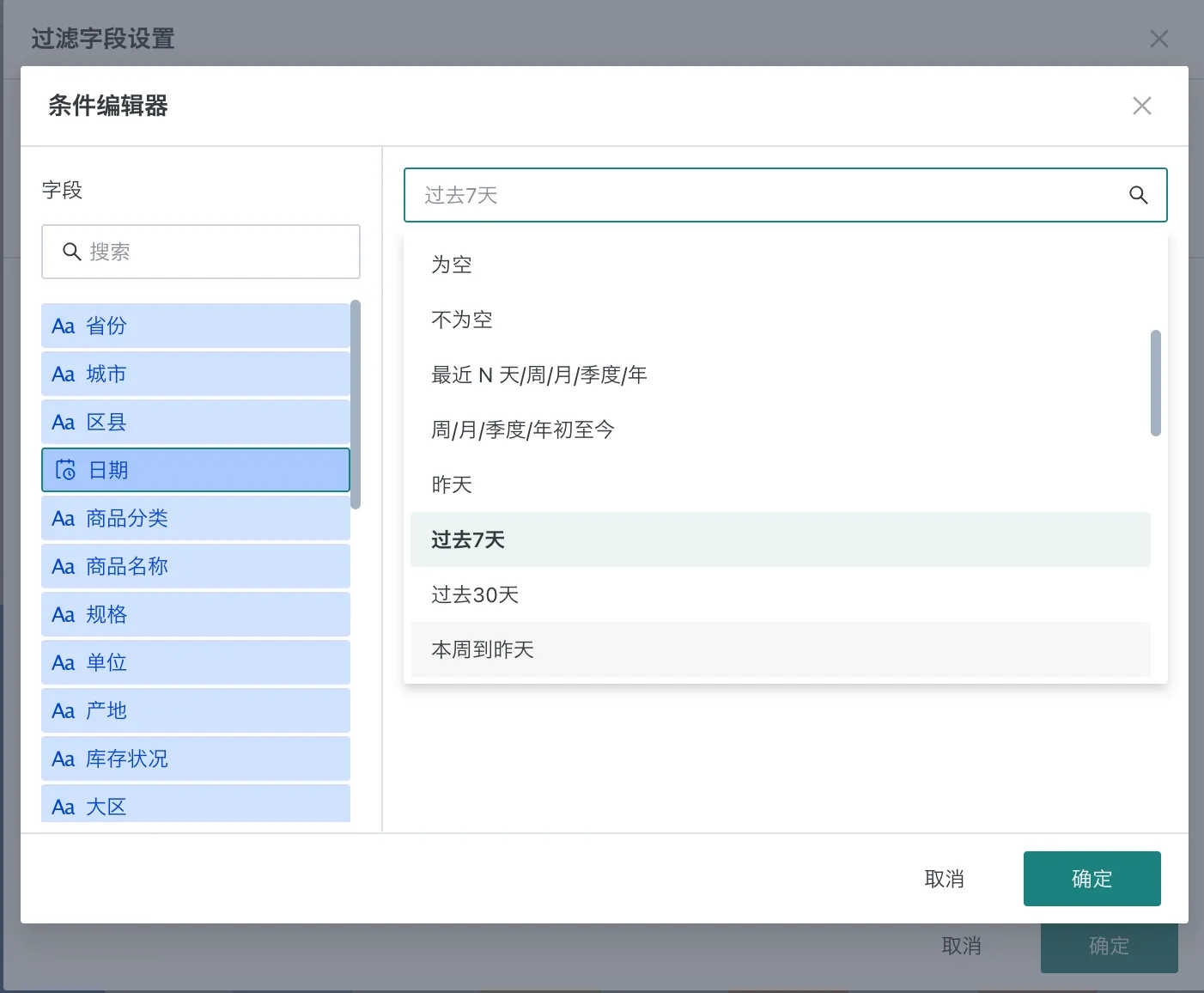
Recent N Days/Weeks/Months/Quarters/Years Configuration Example
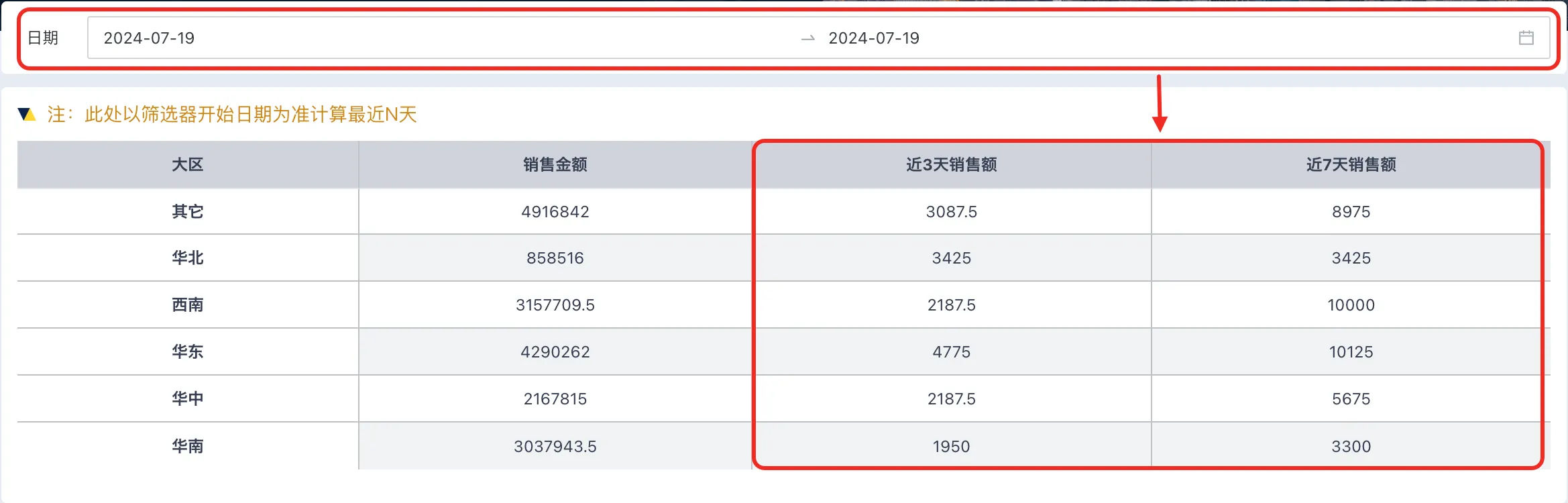
For example, the following card shows sales revenue by region, and we want to add filter fields to dynamically calculate sales revenue data for the past 3 days and past 7 days based on the date filter.
-
Select the configuration button of "Sales Revenue" in the left measures and select "Create Filter Field".
-
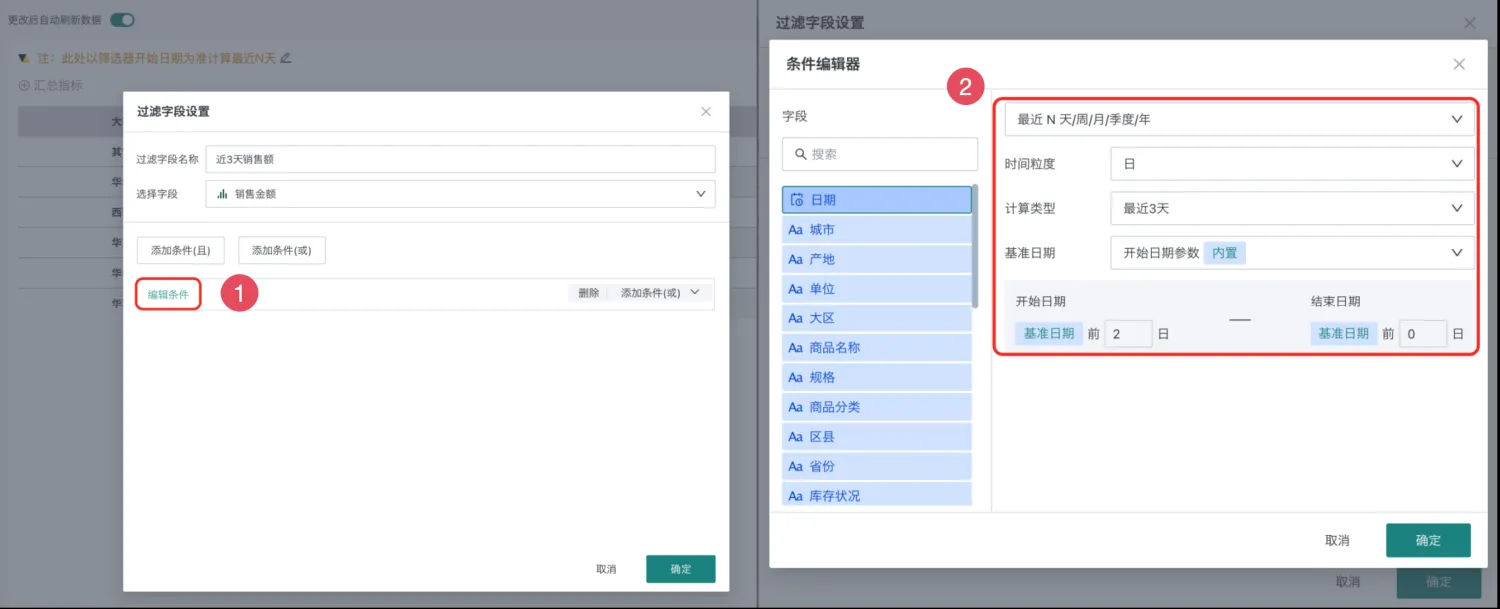
In the filter field settings, click Edit Conditions, and in the condition editor popup, select the "Date" field on the left and configure as shown in the figure on the right.
As shown in the figure, if the base date is selected as "Start Date Parameter", when linking with the date filter, the start time selected by the date filter will be used as the base. (For example, if the filter interval start date is July 15th, then the past 3 days will be July 13-15)
Note:
- Only date interval filters with day granularity are supported.
- Only date fields support being filtered, time fields do not support.
-
Repeat the above steps to add the "Past 7 Days Sales Revenue" field.
-
Drag the newly created fields into the measure area and save the table.
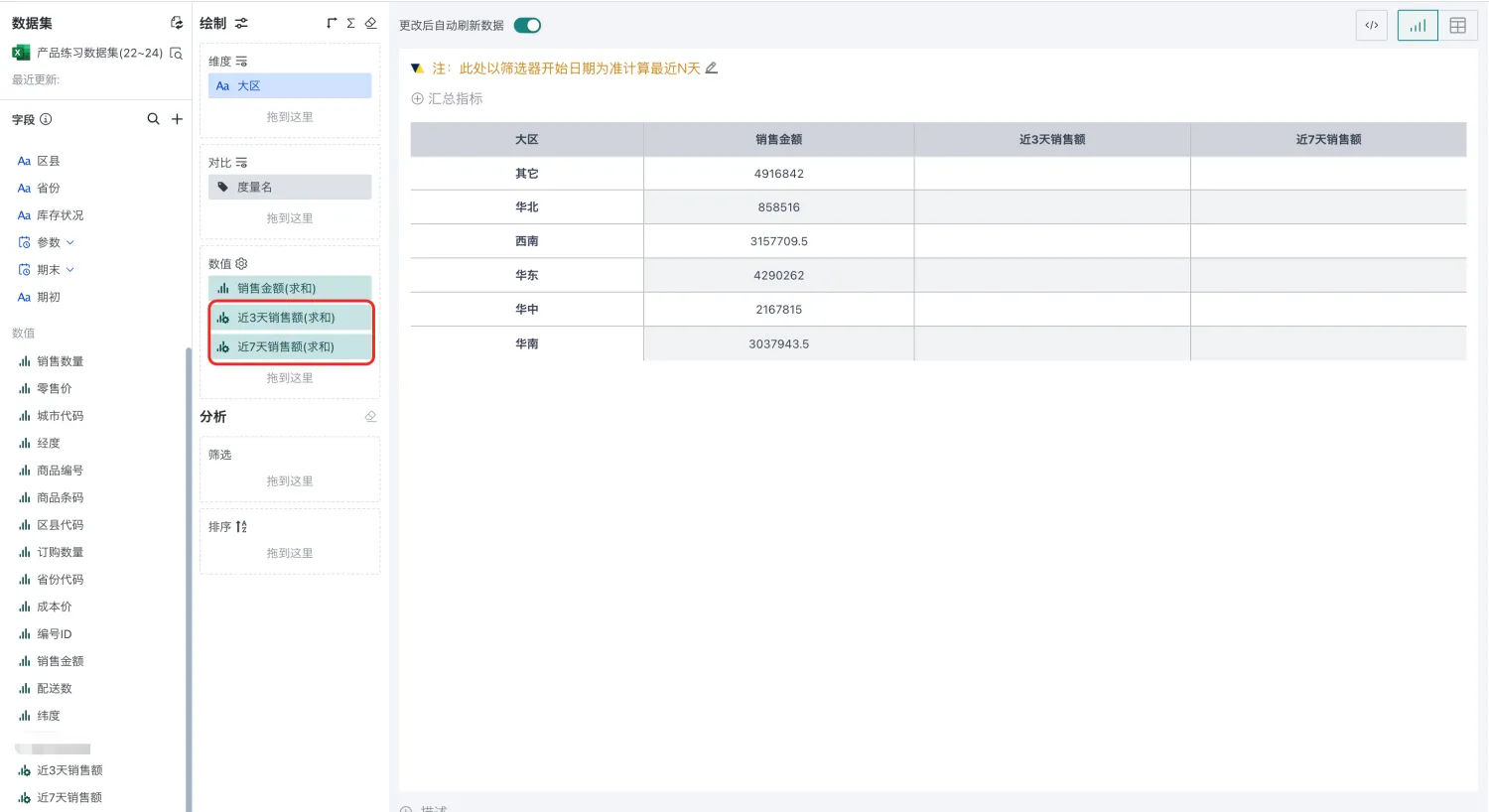
-
Create a new date filter, link to the target card in the linkage section, and configure the linkage parameters on the right as shown in the figure.
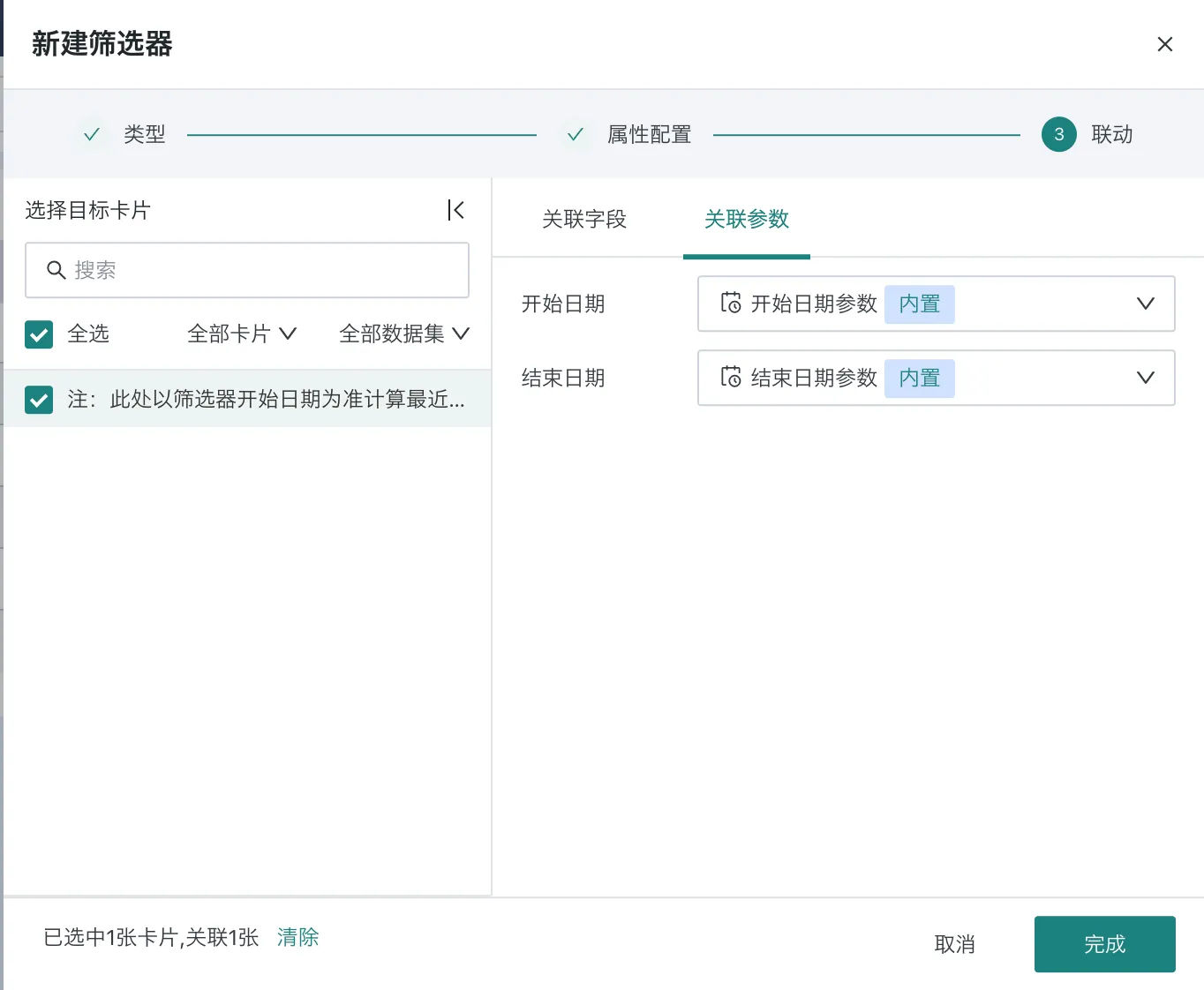
-
After completion, the card will dynamically calculate sales revenue data for the past 3 days and past 7 days based on the filter date.
Week/Month/Quarter/Year-to-Date Configuration Example
For example, the following card shows sales revenue by region, and we want to add filter fields to dynamically calculate monthly cumulative sales revenue and yearly cumulative sales revenue data based on the date filter.
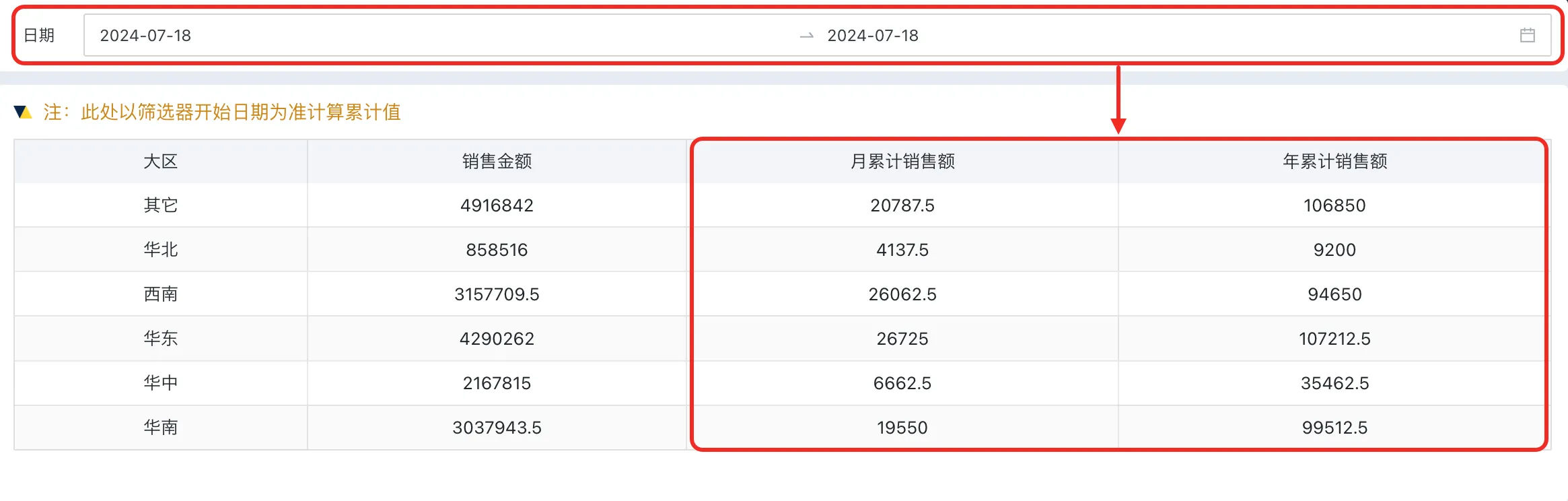
-
Select the configuration button of "Sales Revenue" in the left measures and select "Create Filter Field".
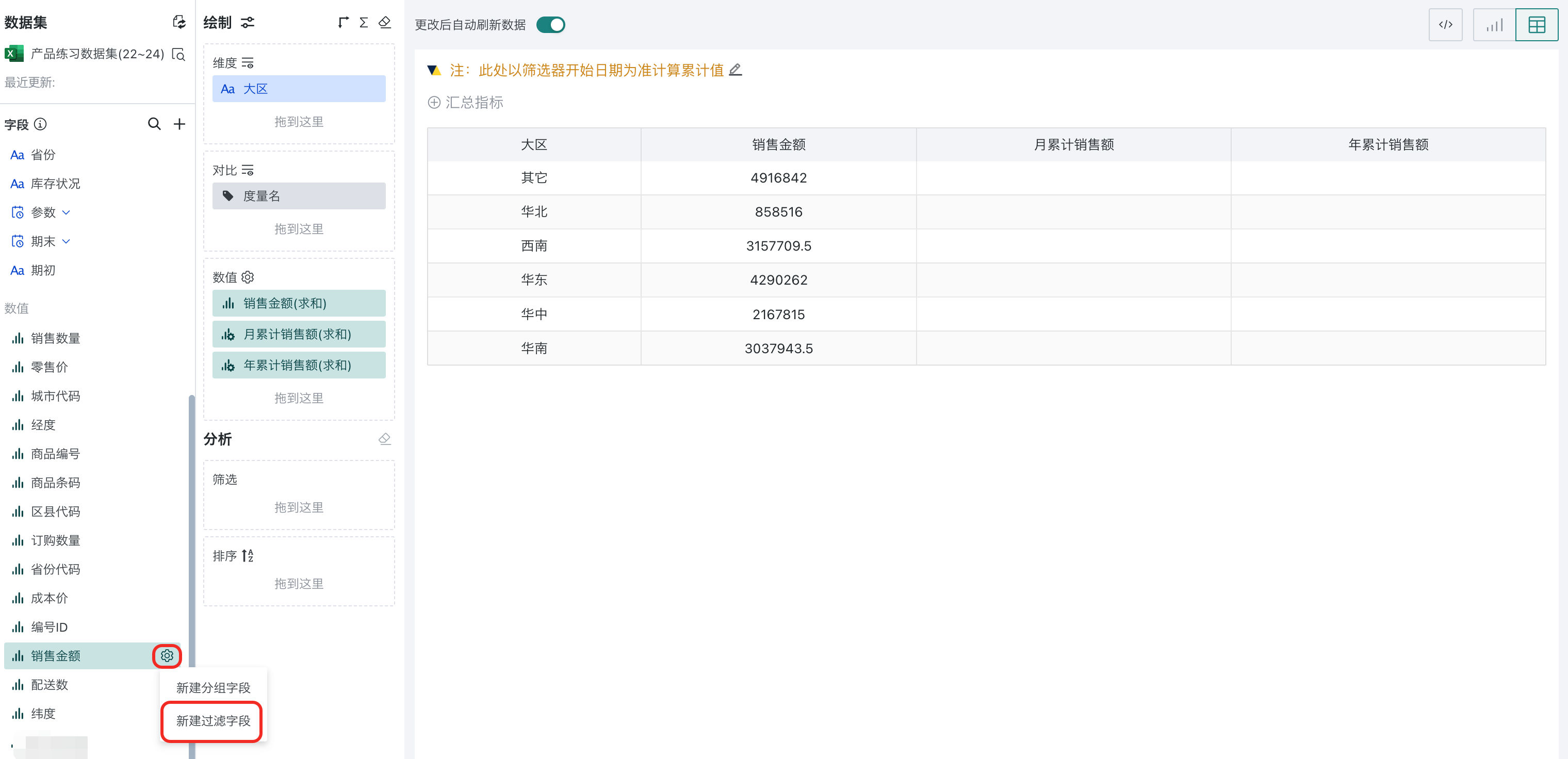
-
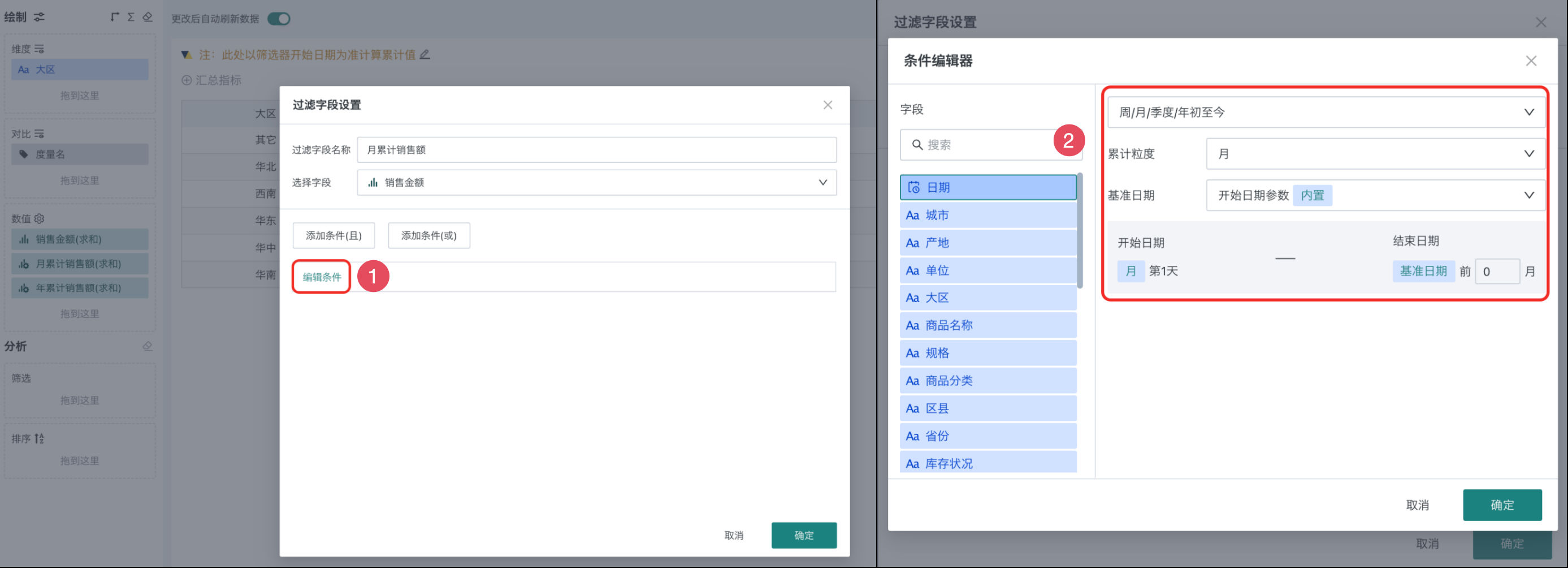
In the filter field settings, click Edit Conditions, and in the condition editor popup, select the "Date" field on the left and configure as shown in the figure on the right.
As shown in the figure, if the base date is selected as "Start Date Parameter", when linking with the date filter, the start time selected by the date filter will be used as the base. (For example, if the filter interval start date is July 15th, then monthly cumulative sales revenue will be the cumulative amount from July 1st to July 15th)
Note:
- Only date interval filters with day granularity are supported.
- Only date fields support being filtered, time fields do not support.
-
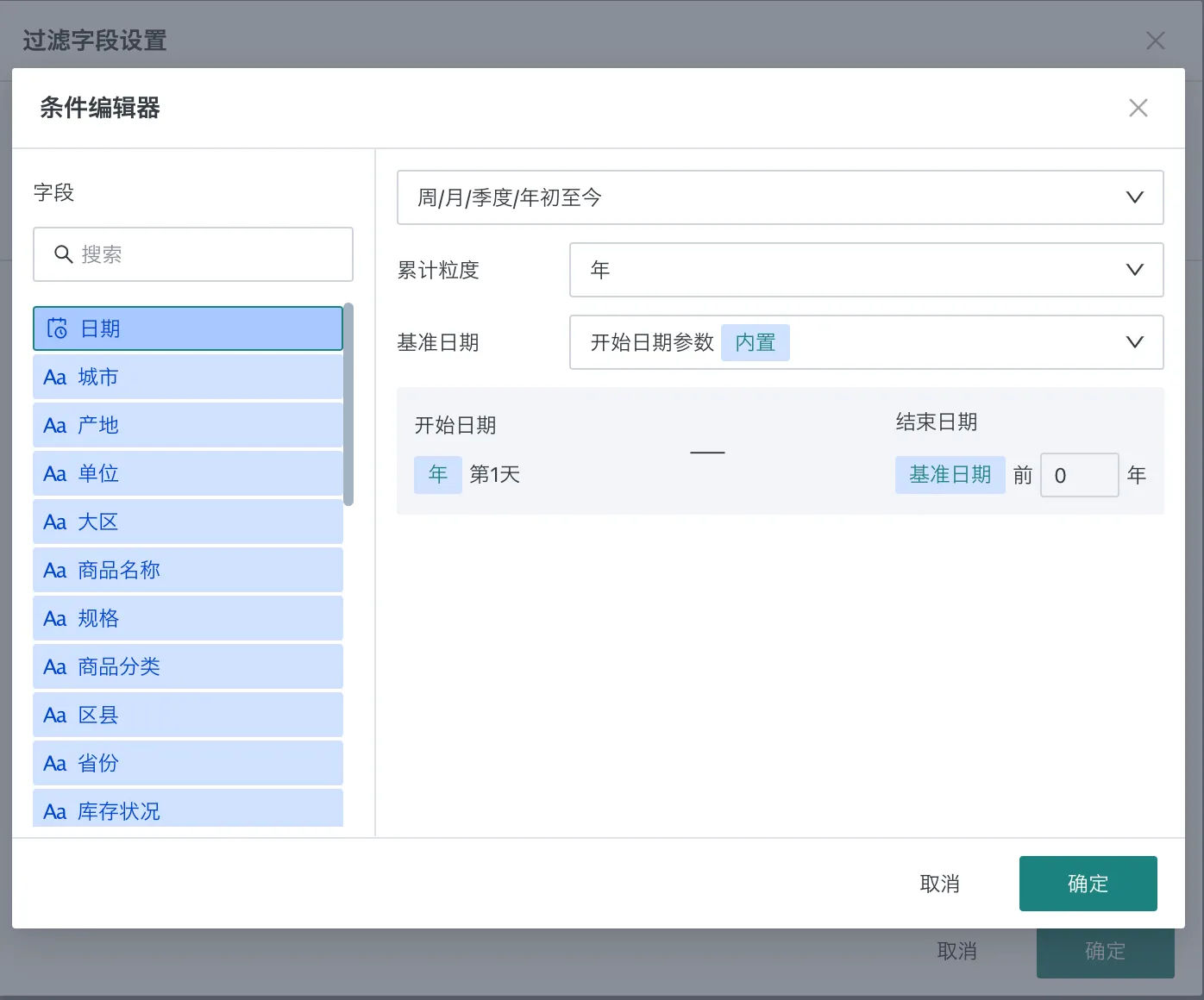
Repeat the above steps to add the "Yearly Cumulative Sales Revenue" field (for example, if the filter interval start date is July 15th, 2024, then yearly cumulative sales revenue will be the cumulative amount from January 1st to July 15th, 2024).
-
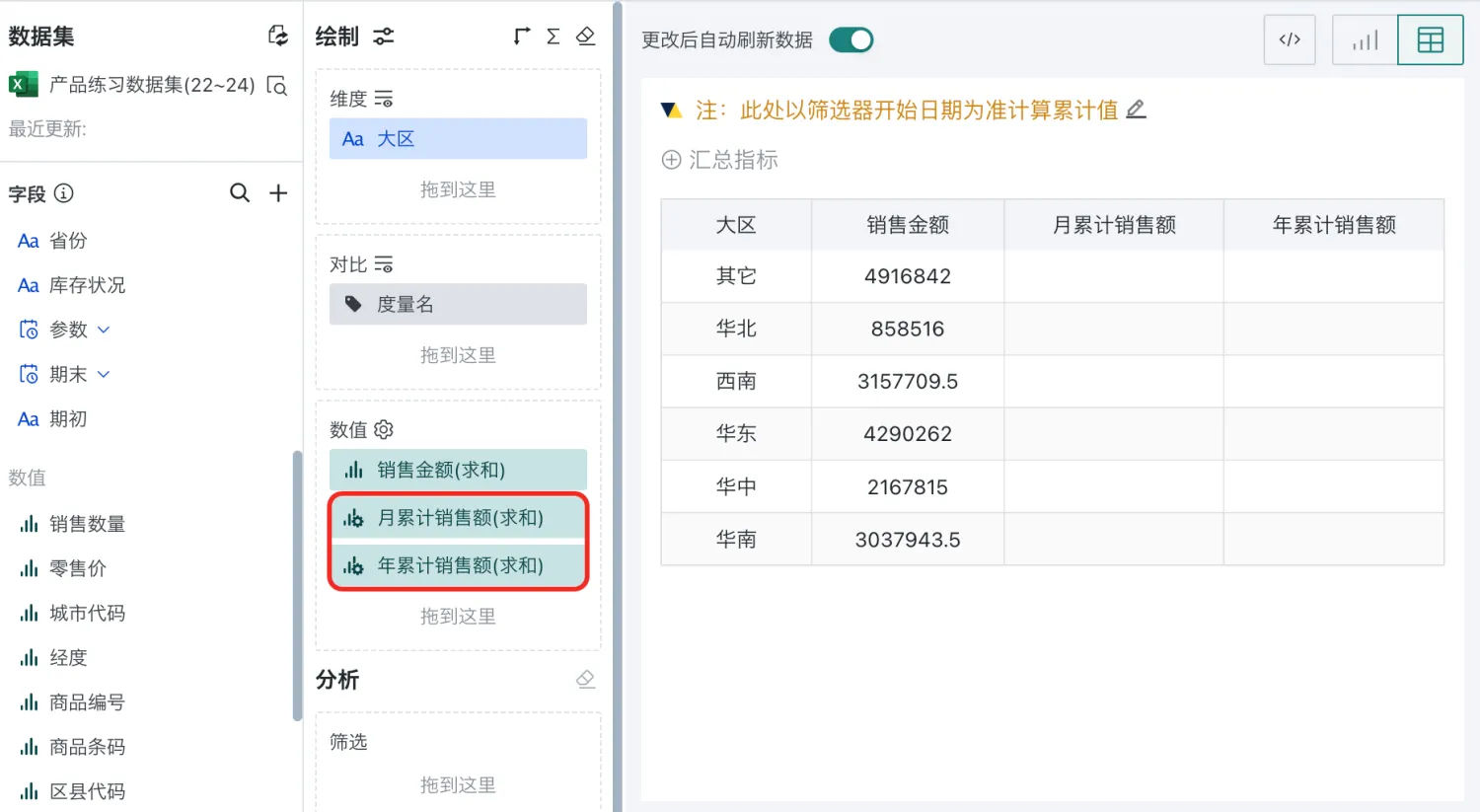
Drag the newly created fields into the measure area and save the table.
-
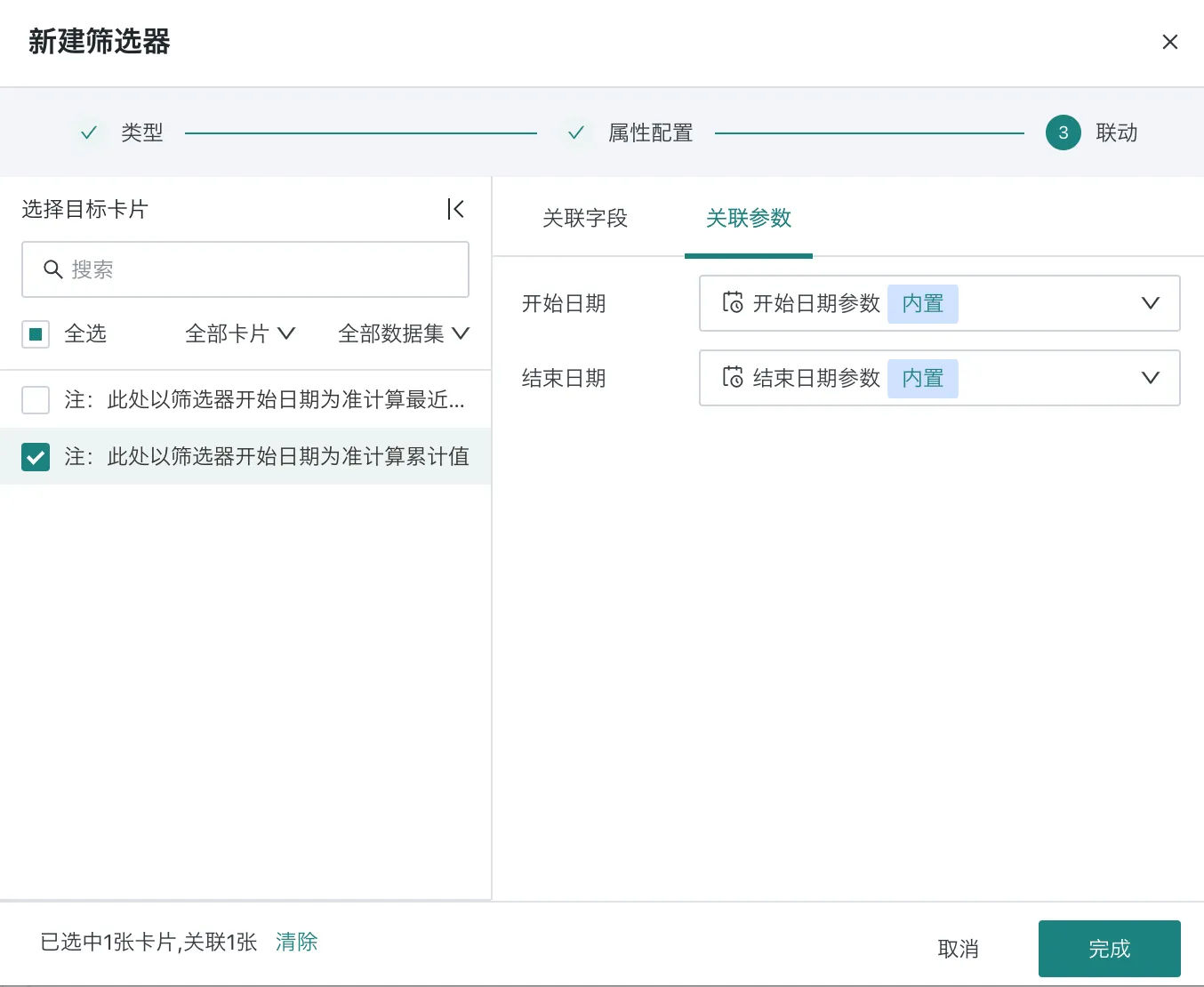
Create a new date filter, link to the target card in the linkage section, and configure the linkage parameters on the right as shown in the figure.
-
After completion, the card will dynamically calculate monthly cumulative and yearly cumulative sales revenue data based on the filter date.
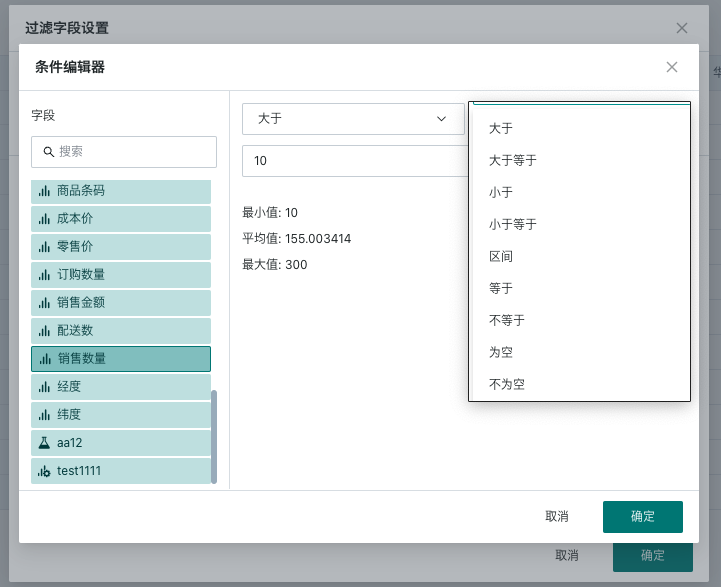
Scenario 3 Using Numerical Type Fields for Filtering
When filtering a certain measure based on numerical type fields, various judgment operators are provided, such as greater than, less than, interval, etc. For example, if you want to view sales revenue with sales quantity > 10, you can use the configuration shown in the figure below.
Other Operations
Drag the created filter field into the drawing area - measures to display the filtered values. Click the settings icon on the right side of the newly created field to edit, copy and delete the newly created filter field. When users click "Copy Filter Field", they will enter its editing interface. In this interface, users can generate new filter fields by modifying measure fields and conditions.