Ranking
1. Overview
1.1. Application Scenarios
Ranking calculation refers to sorting a set of indicators through specific algorithms or formulas and giving the ranking of each indicator in the sort, making it convenient for users to compare data sizes.
For example, when evaluating sales performance in different regions, ranking can be used to intuitively display the sales amount of each region.
1.2. Feature Introduction
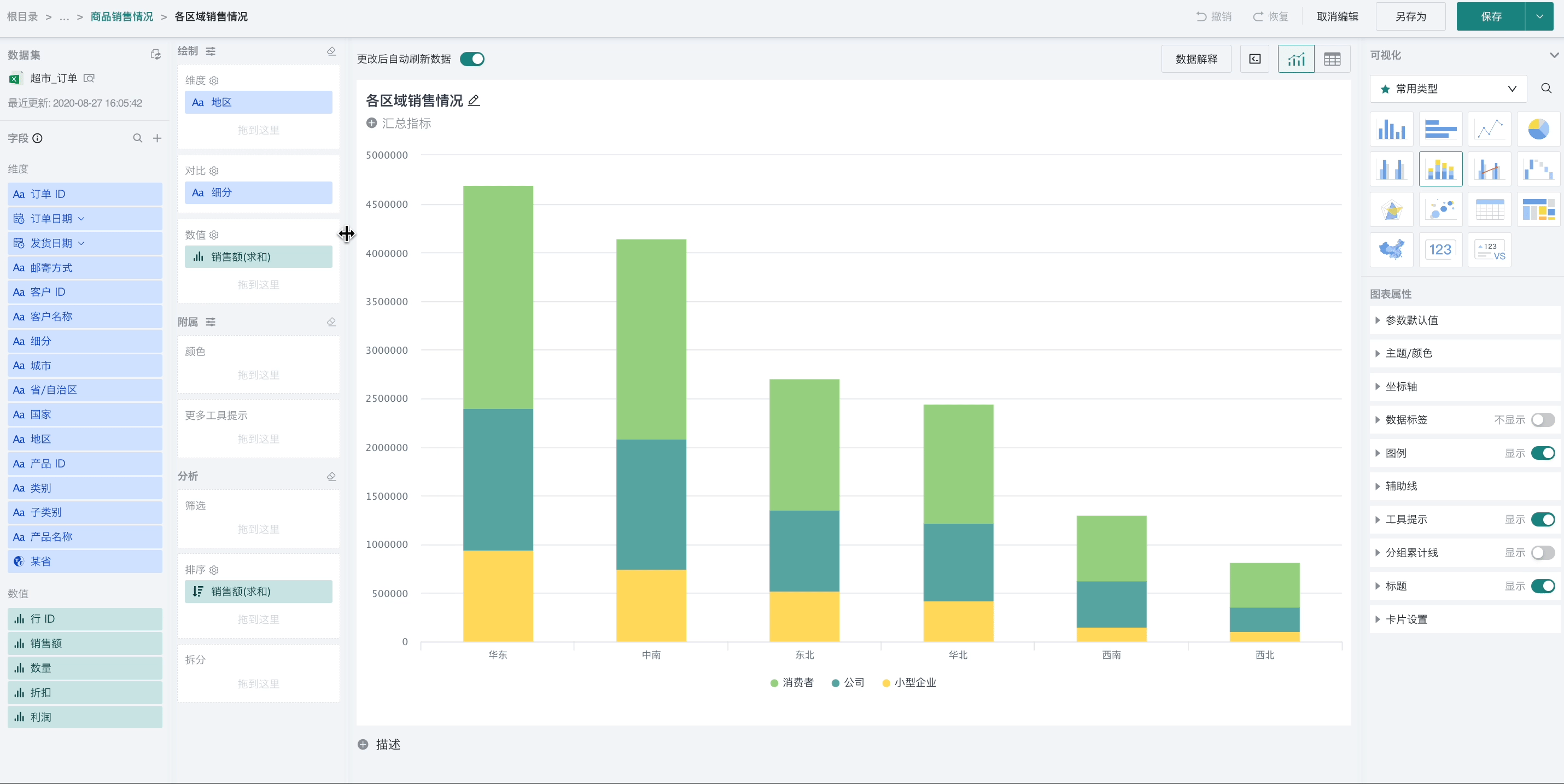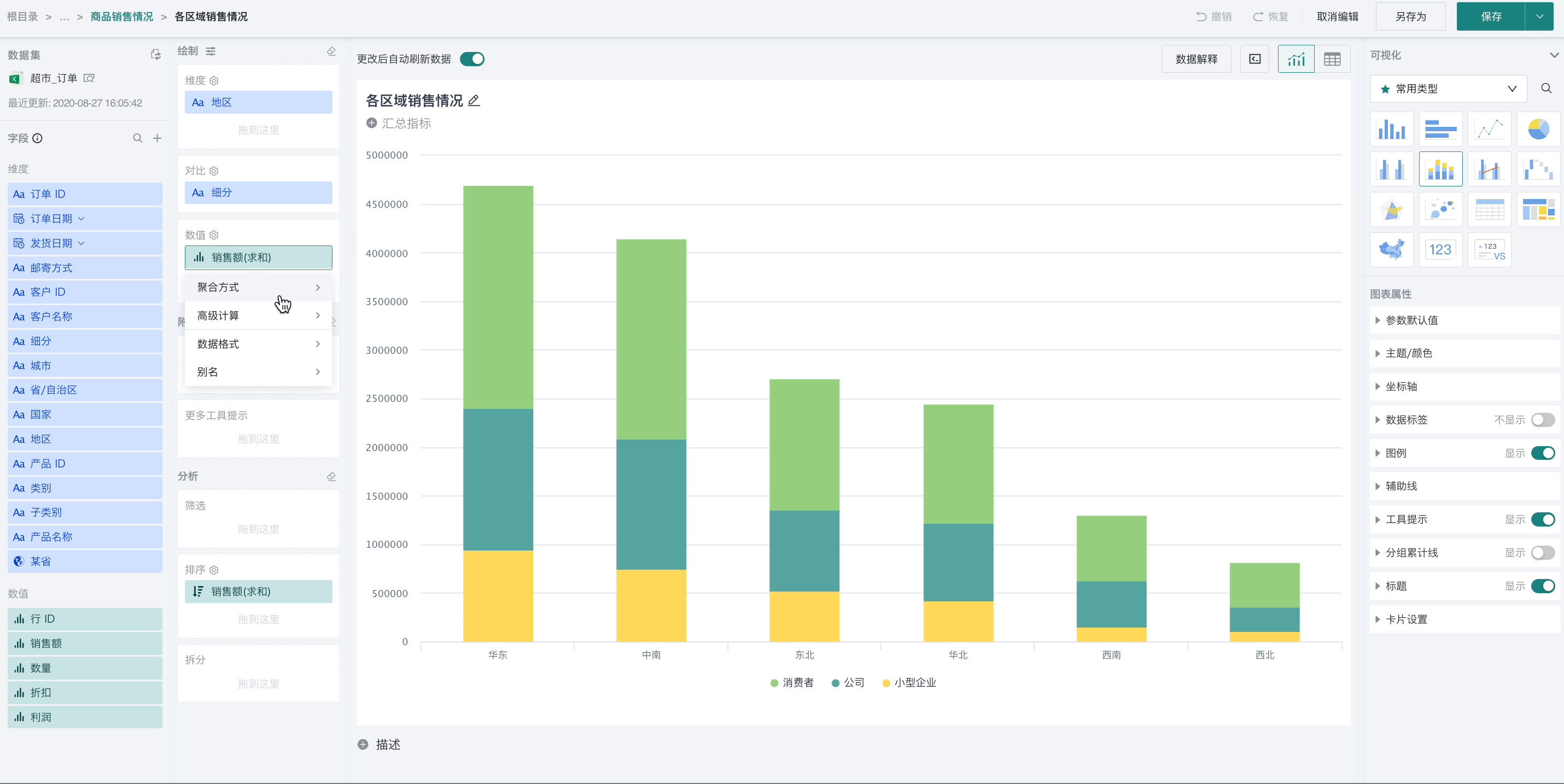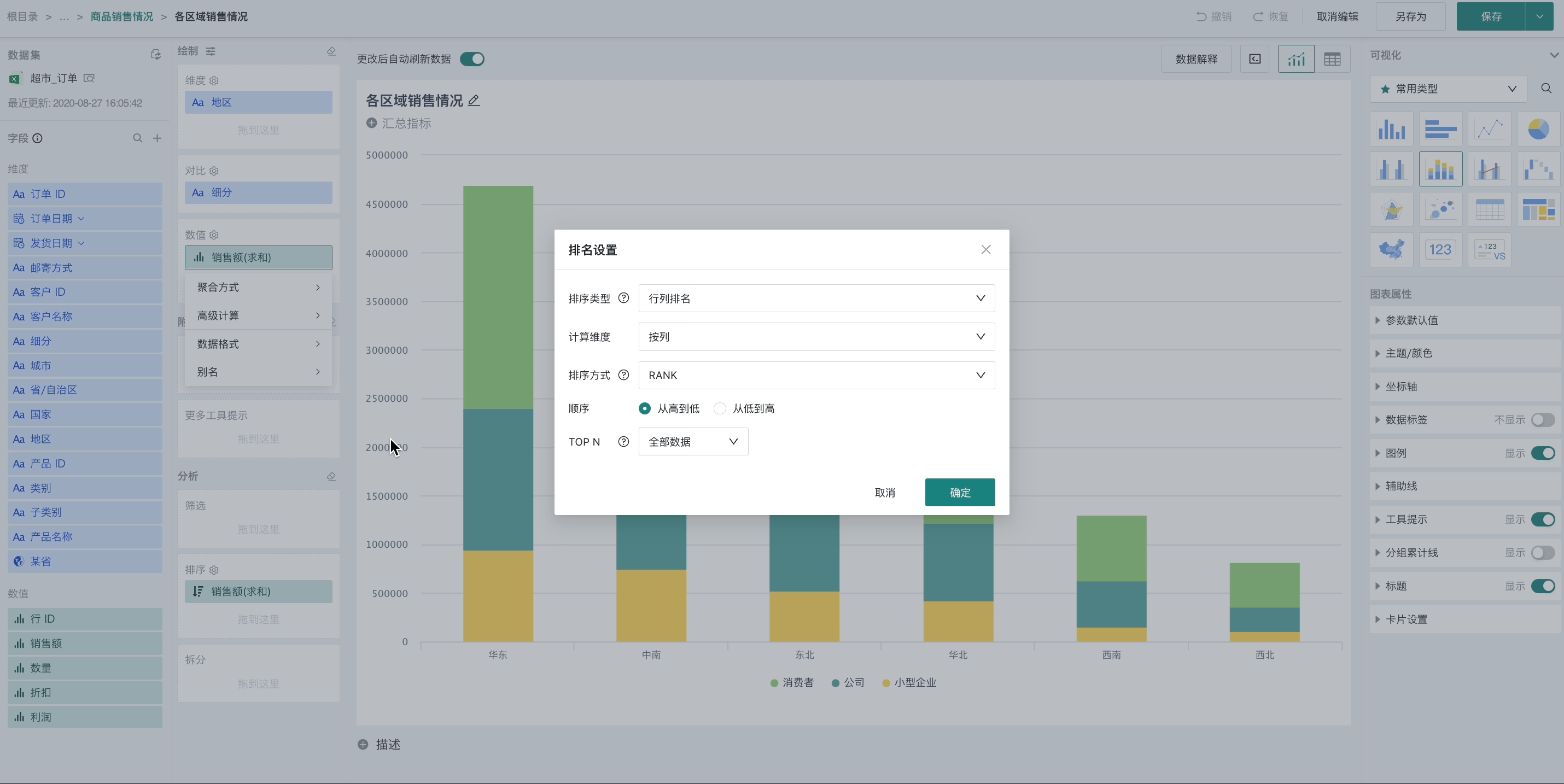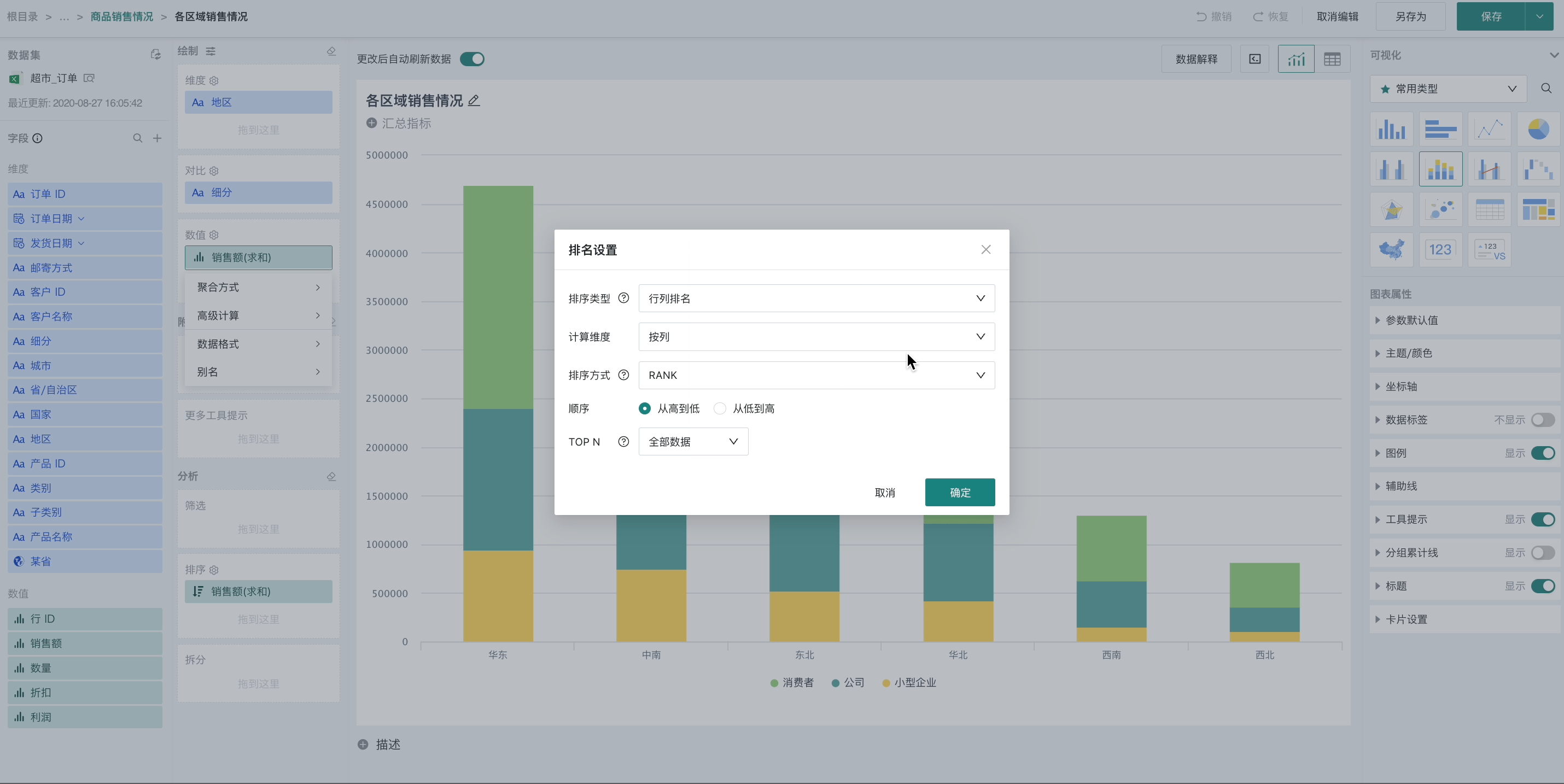
In the value bar, click the field to be ranked, and select "Advanced Calculation - Ranking" from the dropdown menu to pop up the ranking setting box. At this time, the current group will be ranked according to the value size. Users can choose ascending (from small to large) or descending (from large to small) ranking.
2. Quick Start
Supports configuration of ranking type, calculation dimension, sorting method, sorting order, and TOPN. Details are as follows.
-
Ranking type: Supports row/column ranking (global ranking), dimension item ranking (global ranking), and dimension group ranking (group ranking), three types
-
Calculation dimension: According to different ranking types, different calculation dimensions can be selected (such as by row, by column, or specific dimension fields).
-
Sorting order: Supports two types, from high to low (descending) and from low to high (ascending).
-
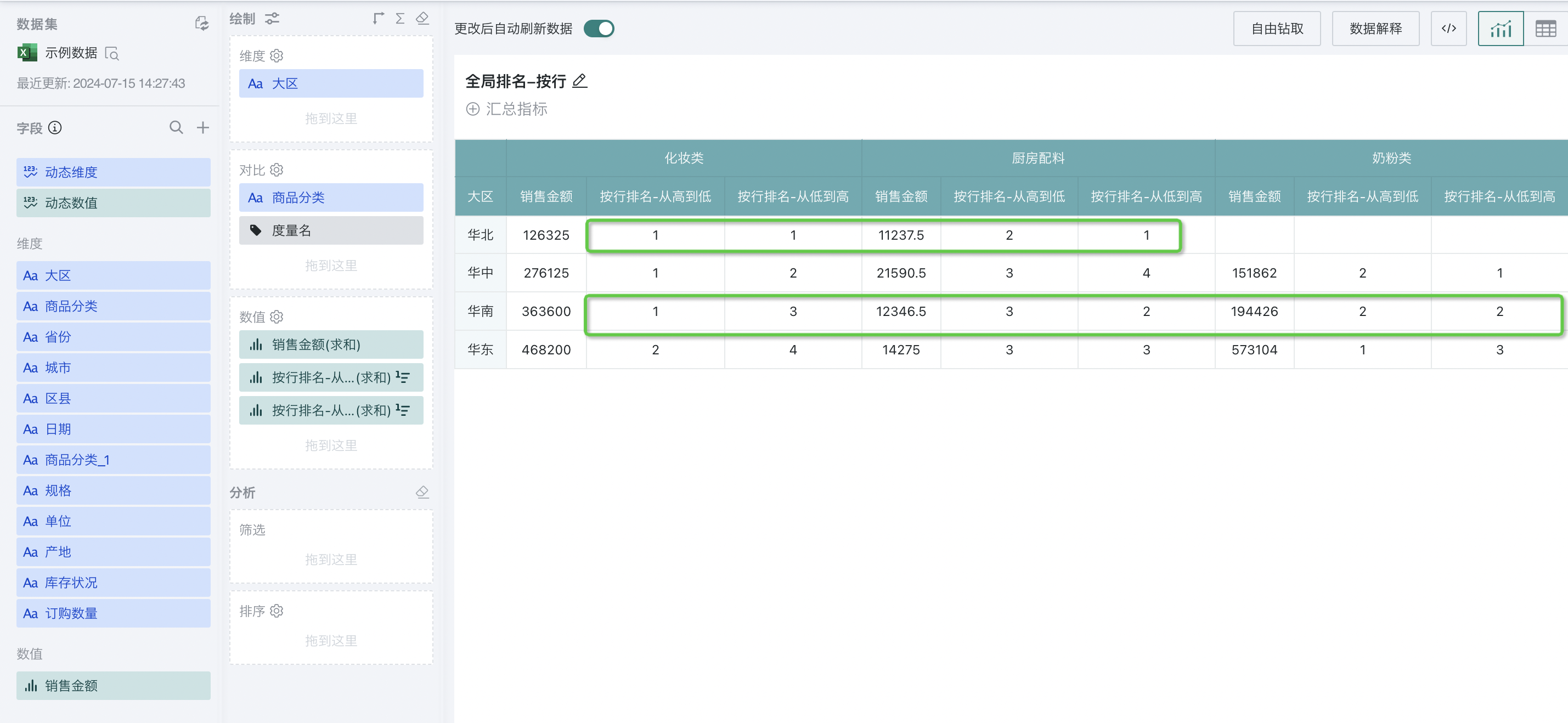
Sorting method: Supports three types: RANK, DENSE_RANK, ROW_NUMBER. When there are no duplicate rankings, the results of these three methods are the same and any can be selected; when there are duplicate rankings, the three methods differ, and you can choose the method that meets the actual scenario. The detailed logic is as follows:
| Sorting Method | Description | Example Screenshot |
|---|---|---|
| RANK (Ranking with gaps) | Assigns the same rank to equal values, and equal values take up space. The highest value is ranked 1, the next two equal values are ranked 2, and the next value is ranked 4. E.g., (1, 2, 2, 4) | 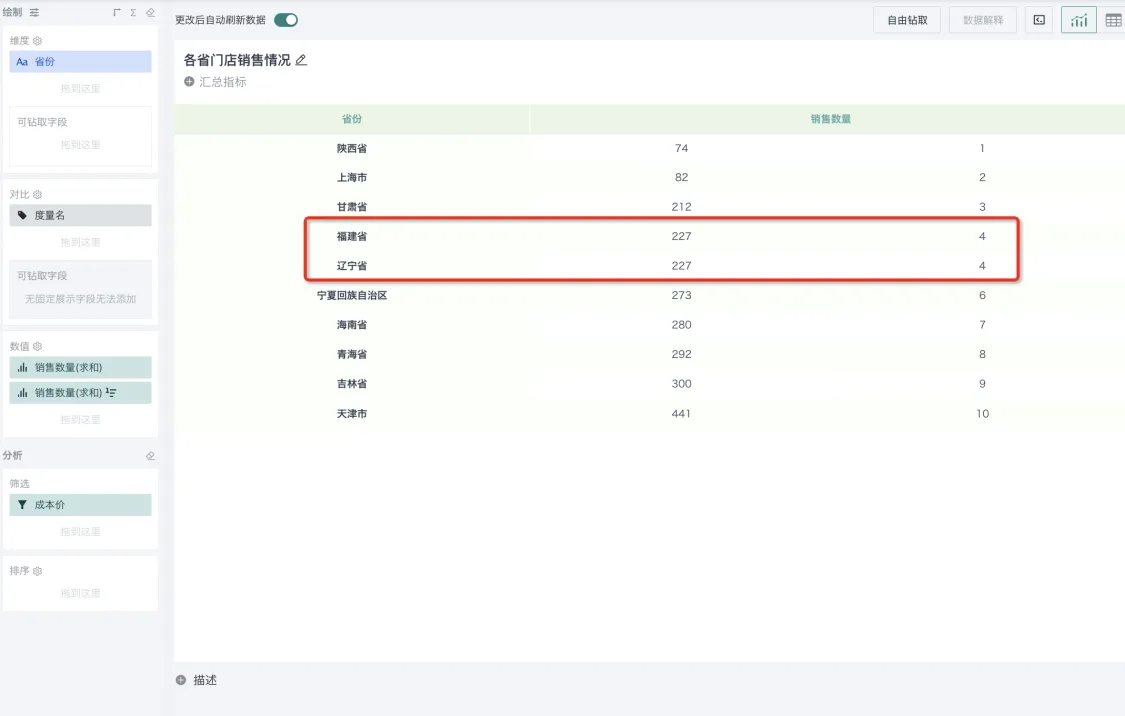 |
| DENSE_RANK (Ranking without gaps) | Duplicate values have the same rank, and the next number in the ranking sequence, and equal values do not take up space. E.g., (1, 2, 2, 3) | 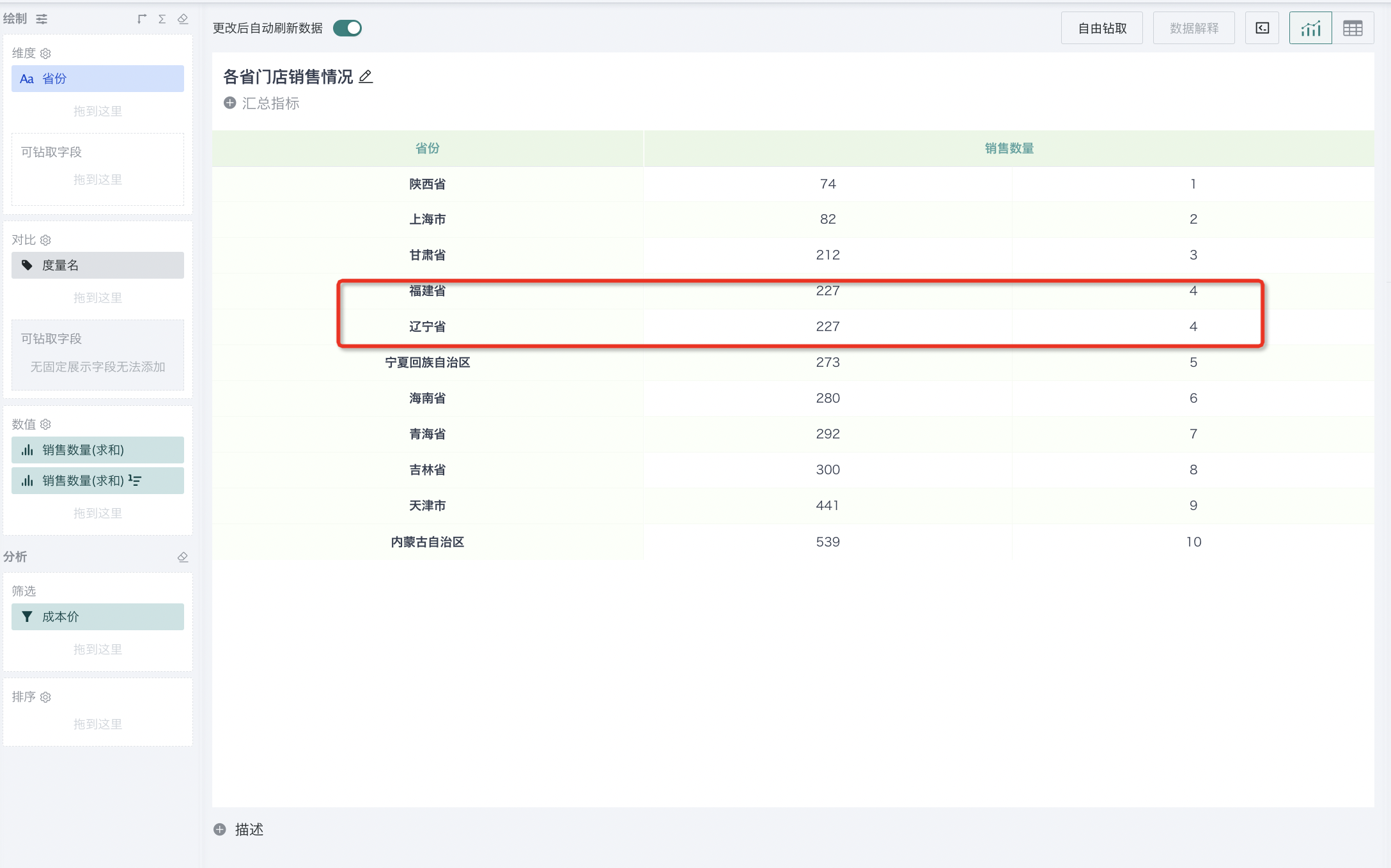 |
| ROW_NUMBER (Unique ranking) | Assigns different rankings to duplicate values according to the ranking direction. E.g., (1, 2, 3, 4) | 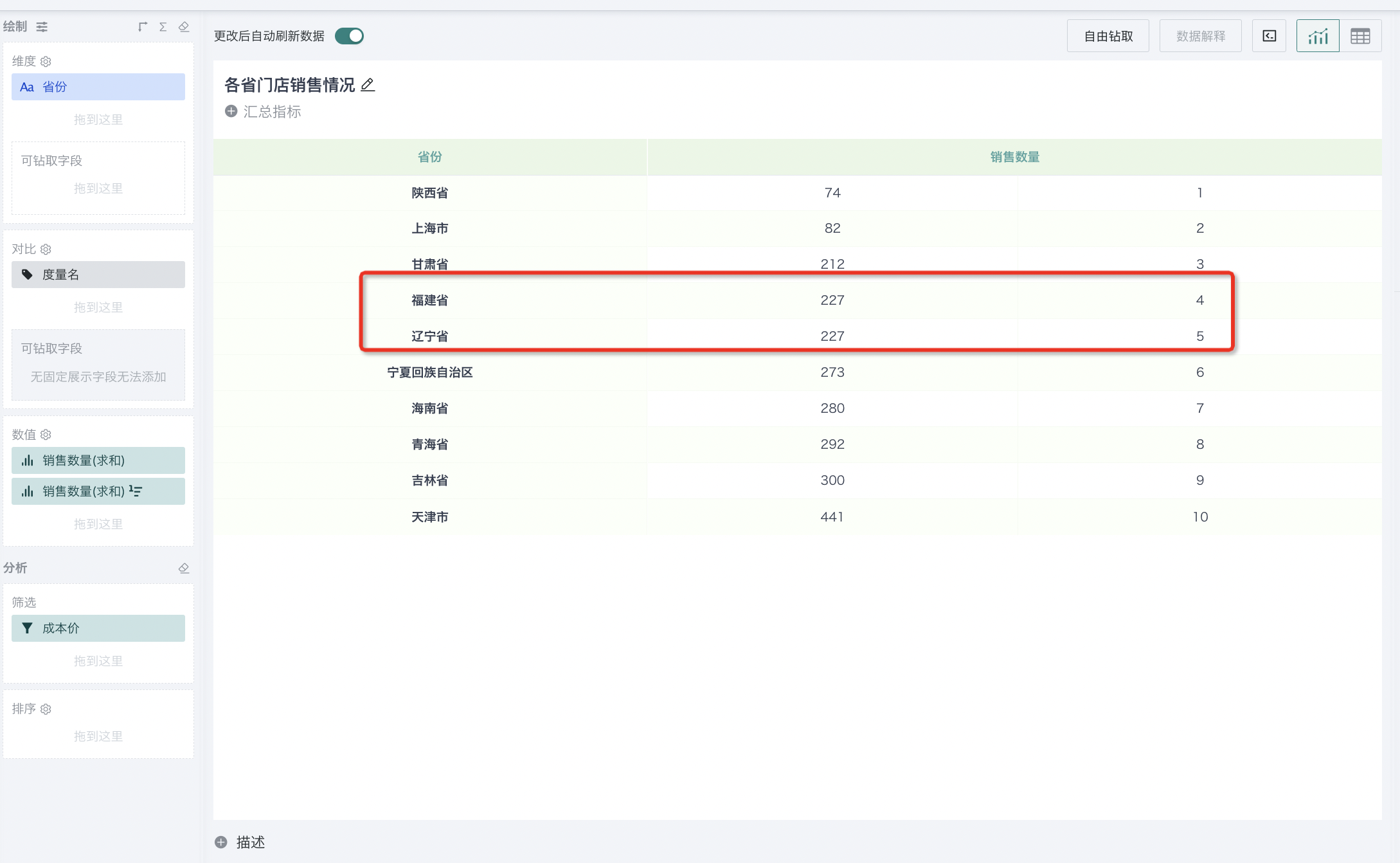 |
The specific effect is as follows:
2.1. Global Ranking
Global ranking is achieved by setting the ranking type to "row/column ranking" and "dimension item ranking" functions, supporting ranking calculation by row, by column, and by specified dimension.
By column means ranking all values corresponding to dimension items, by row means ranking all values corresponding to comparison items, and by specified dimension means ranking all values of the current dimension value globally.
2.1.1. By Column
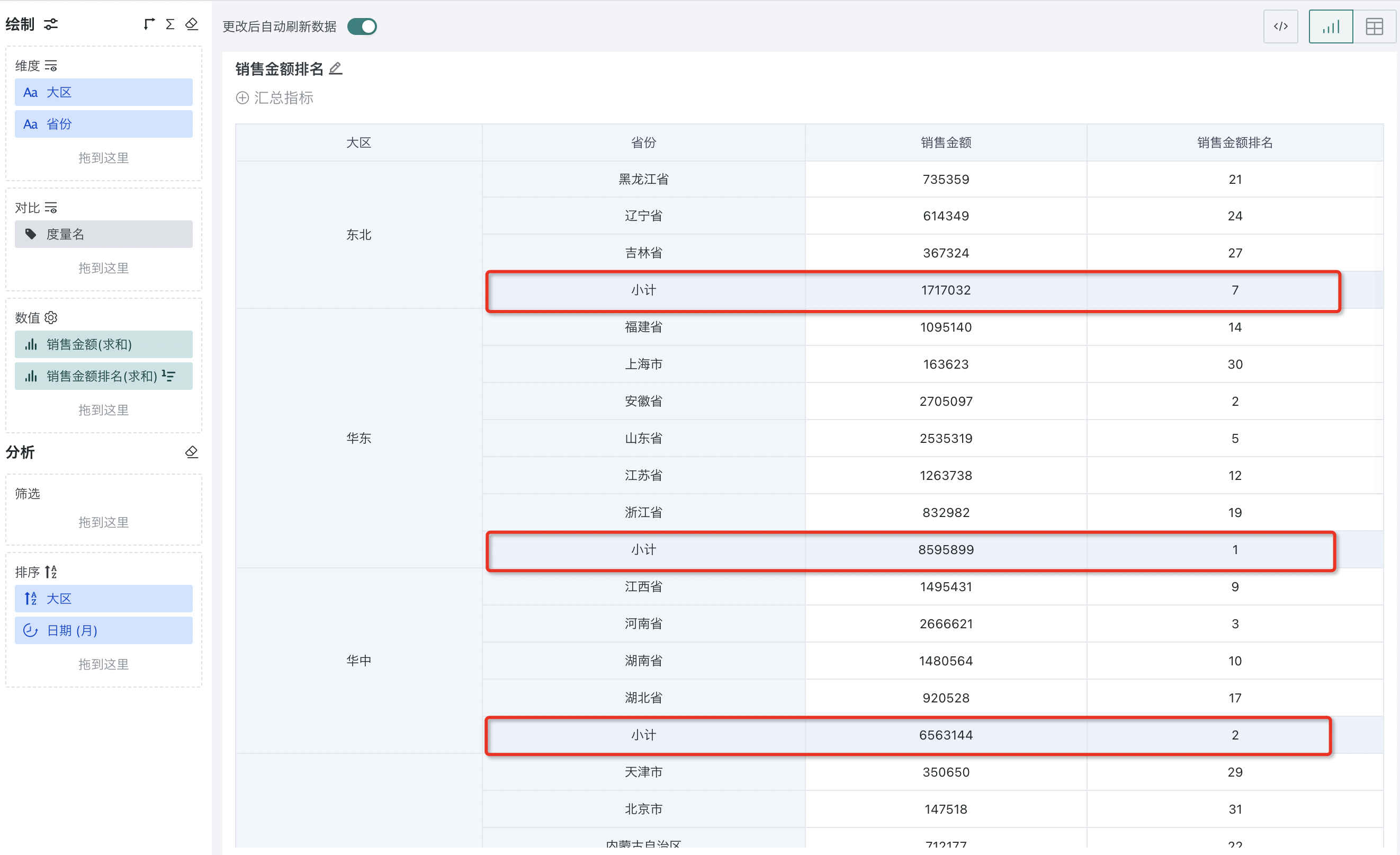
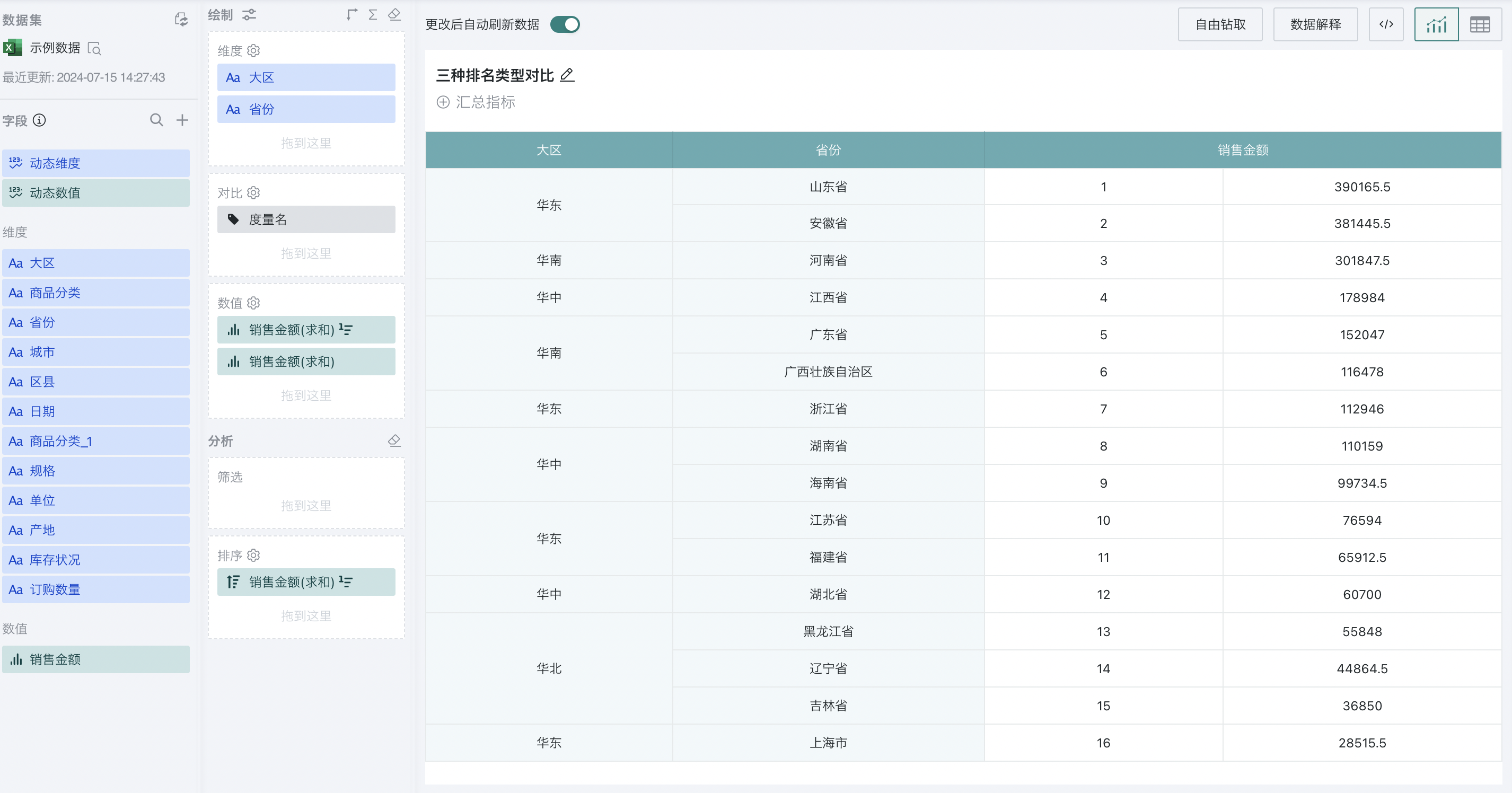
For example, to analyze the ranking of sales amount of each province nationwide:
Step 1. Create a normal table, drag "Region" and "Province" into the dimension bar, and "Sales Amount" into the value bar, as shown below:
Step 2. Click "Sales Amount" and select "Advanced Calculation - Ranking". The ranking configuration popup appears, as shown below:
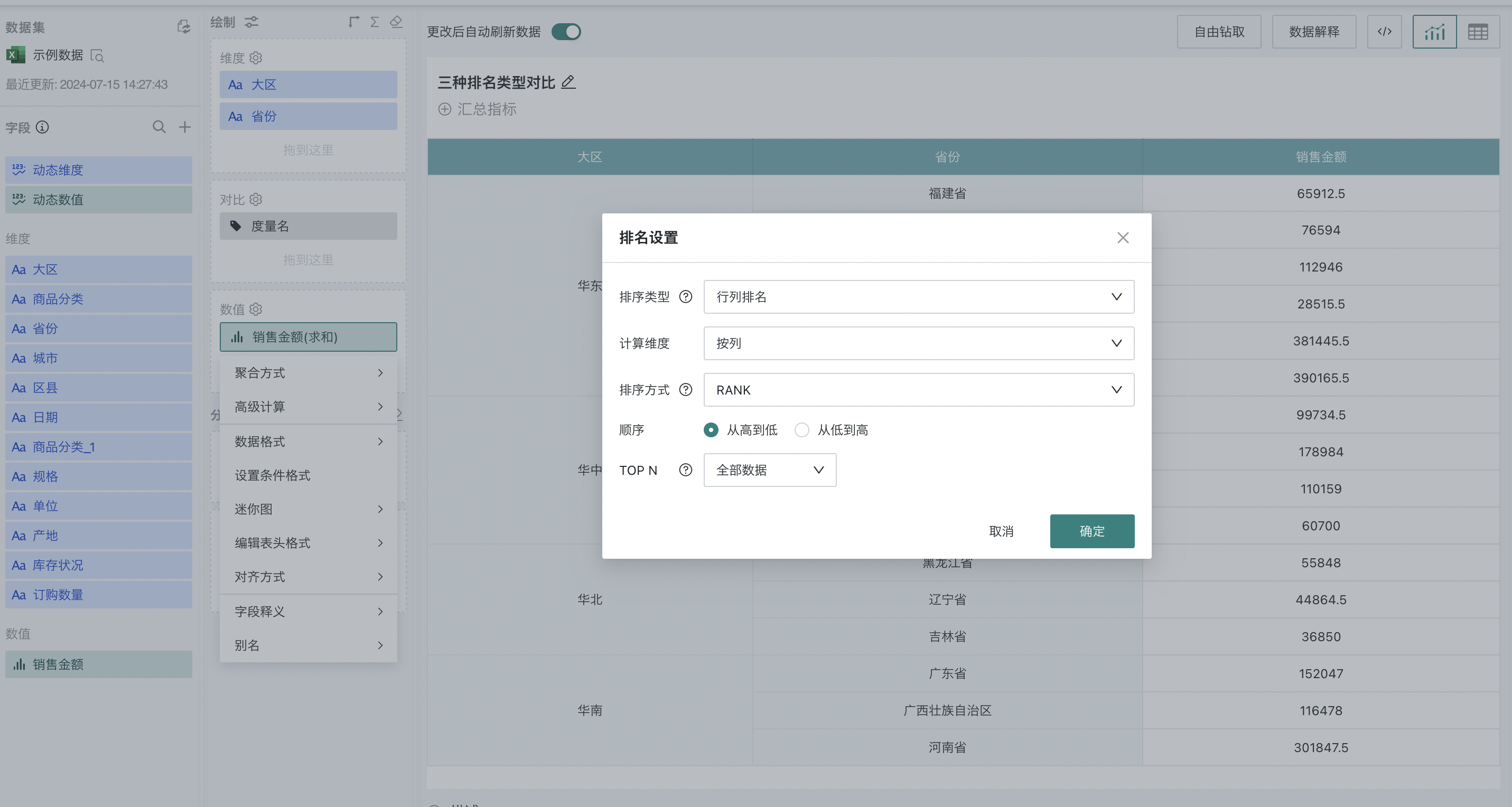
Step 3. Select "row/column ranking" as the ranking type, "by column" as the calculation dimension, and "from high to low" as the order. At this point, you can rank the provinces nationwide by sales amount.
2.1.2. By Row
For example, to analyze the ranking of sales amount of different product categories in each region:
Step 1. Create a normal table, drag "Region" into the dimension bar, "Product Category" into the comparison bar, and "Sales Amount" into the value bar, as shown below:
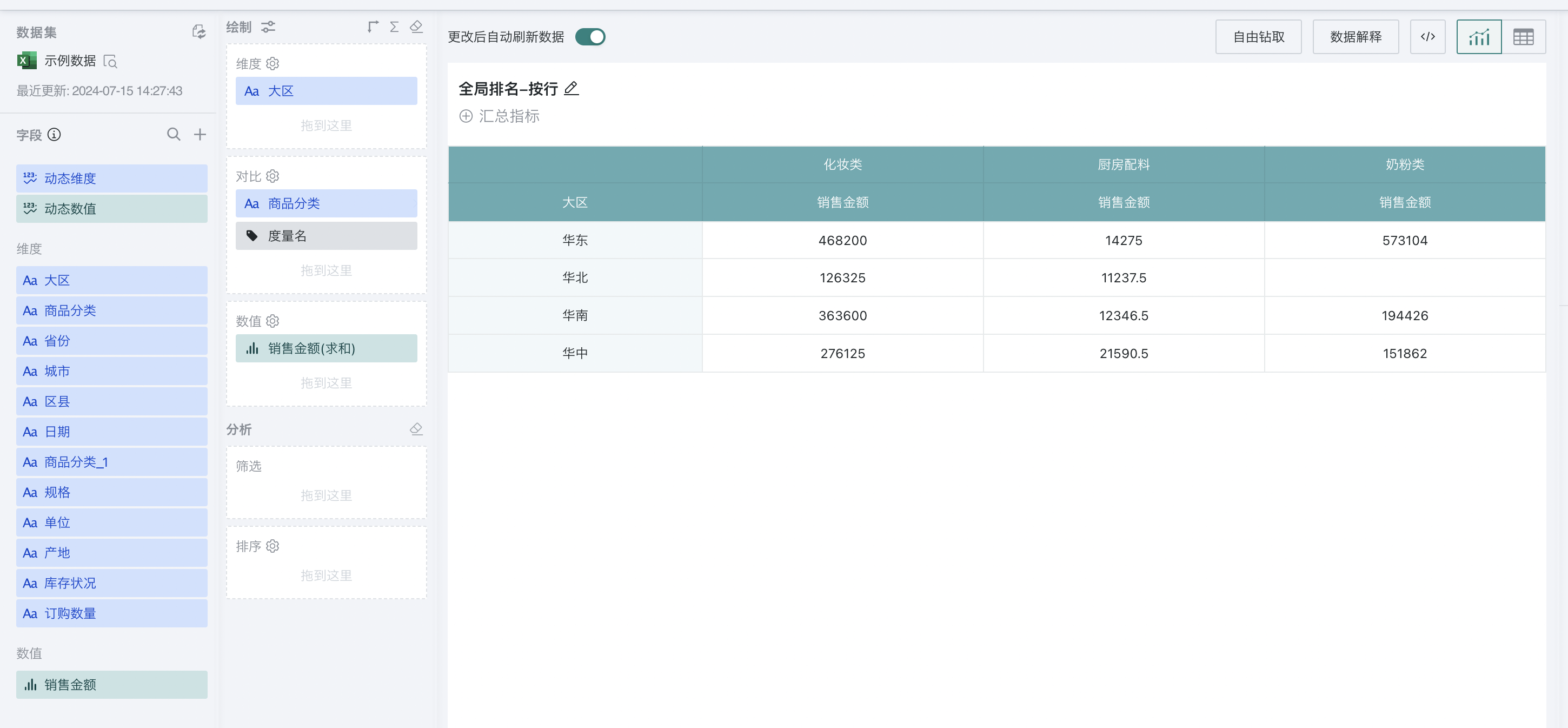
Step 2. Click "Sales Amount" and select "Advanced Calculation - Ranking". The ranking configuration popup appears, as shown below:
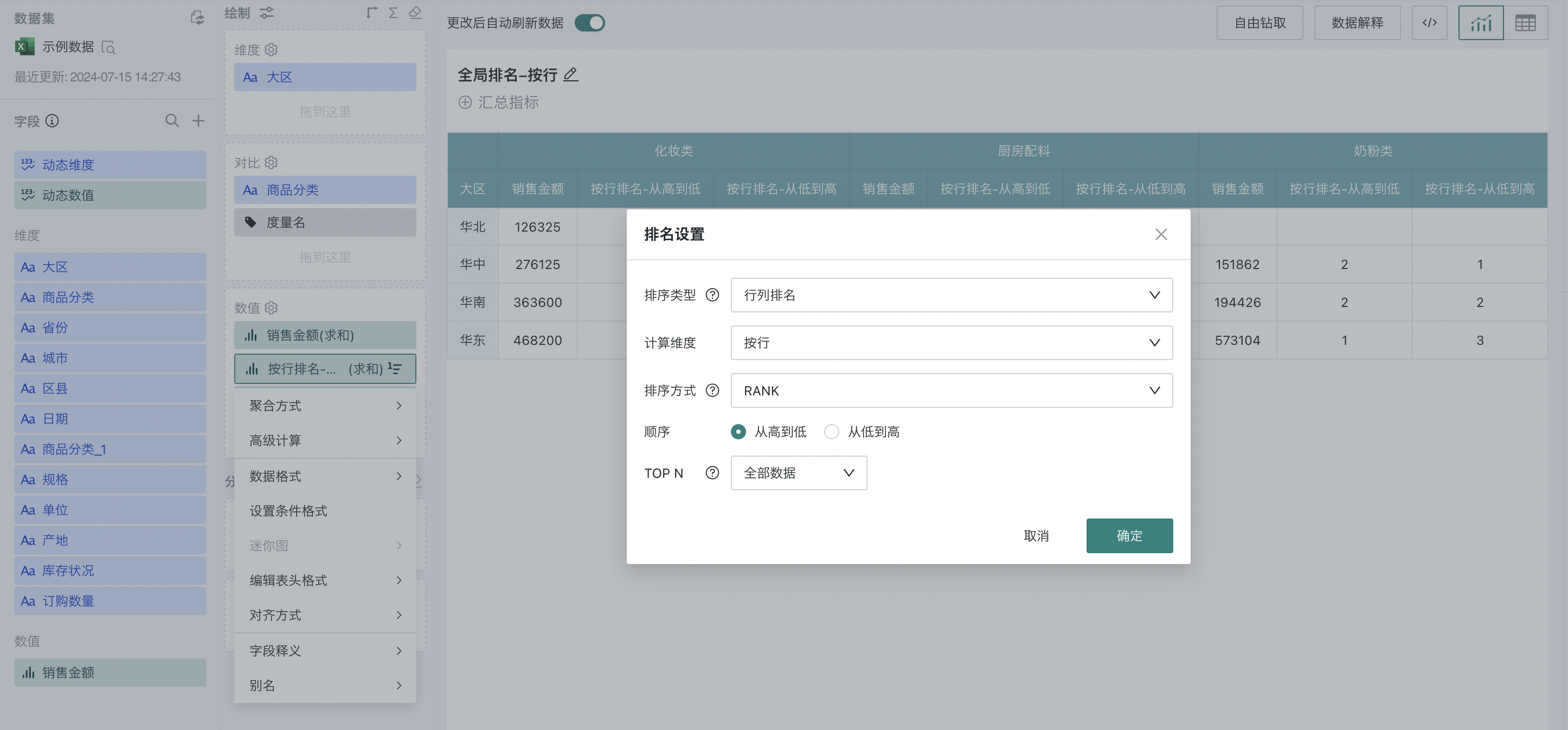
Step 3. Select "row/column ranking" as the ranking type, "by row" as the calculation dimension, and "from high to low" as the order.
At this point, the sales amount of different product categories in each region will be ranked, as shown below:
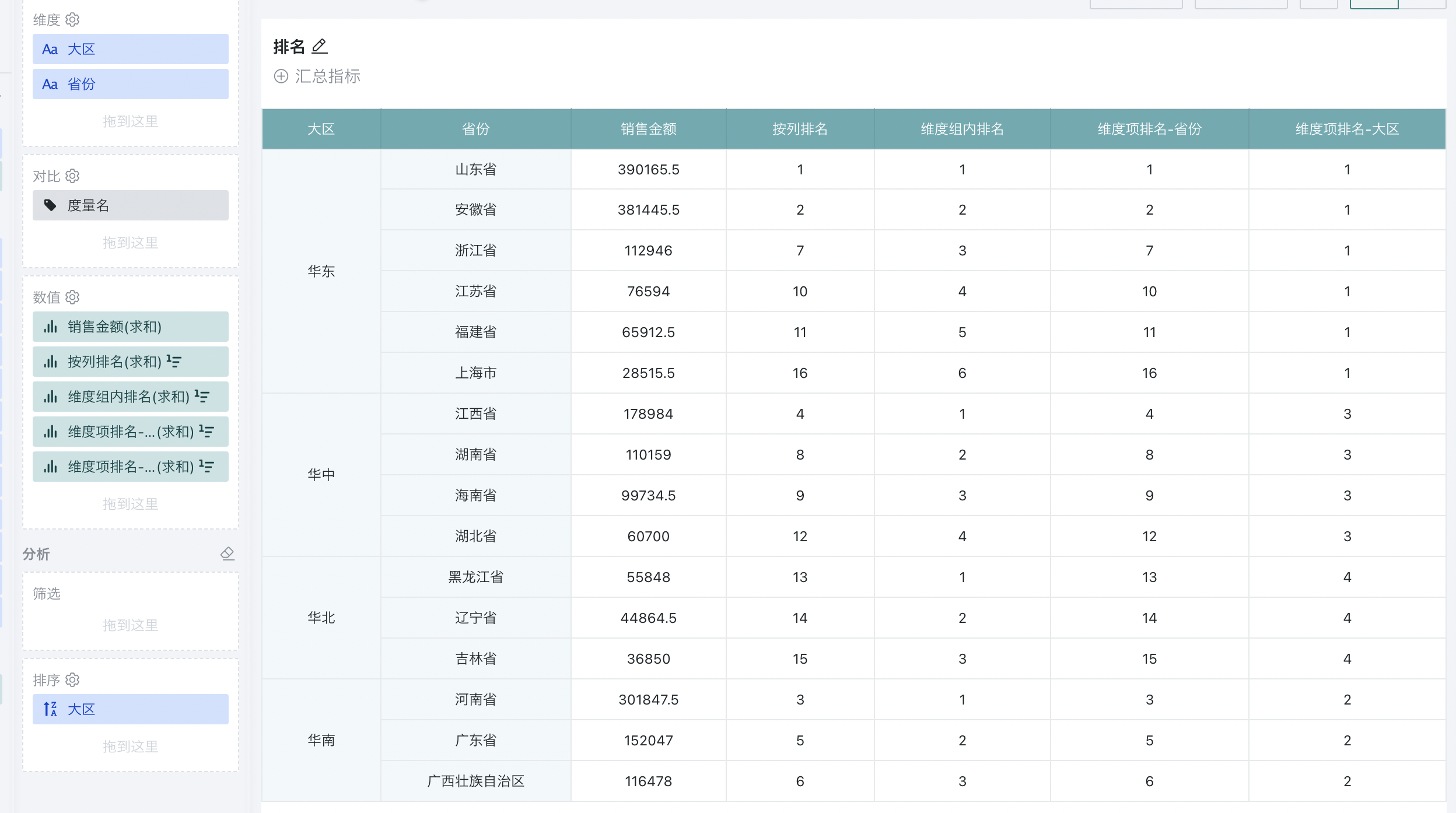
2.1.3. Ranking by Specified Dimension
Ranking by specified dimension is achieved by setting the ranking type to "dimension item ranking".
For example, to analyze the ranking of sales amount of different provinces in each region and the ranking of sales amount of each region:
Step 1. Create a normal table, drag "Region" and "Province" into the dimension bar, and "Sales Amount" into the value bar, as shown below:
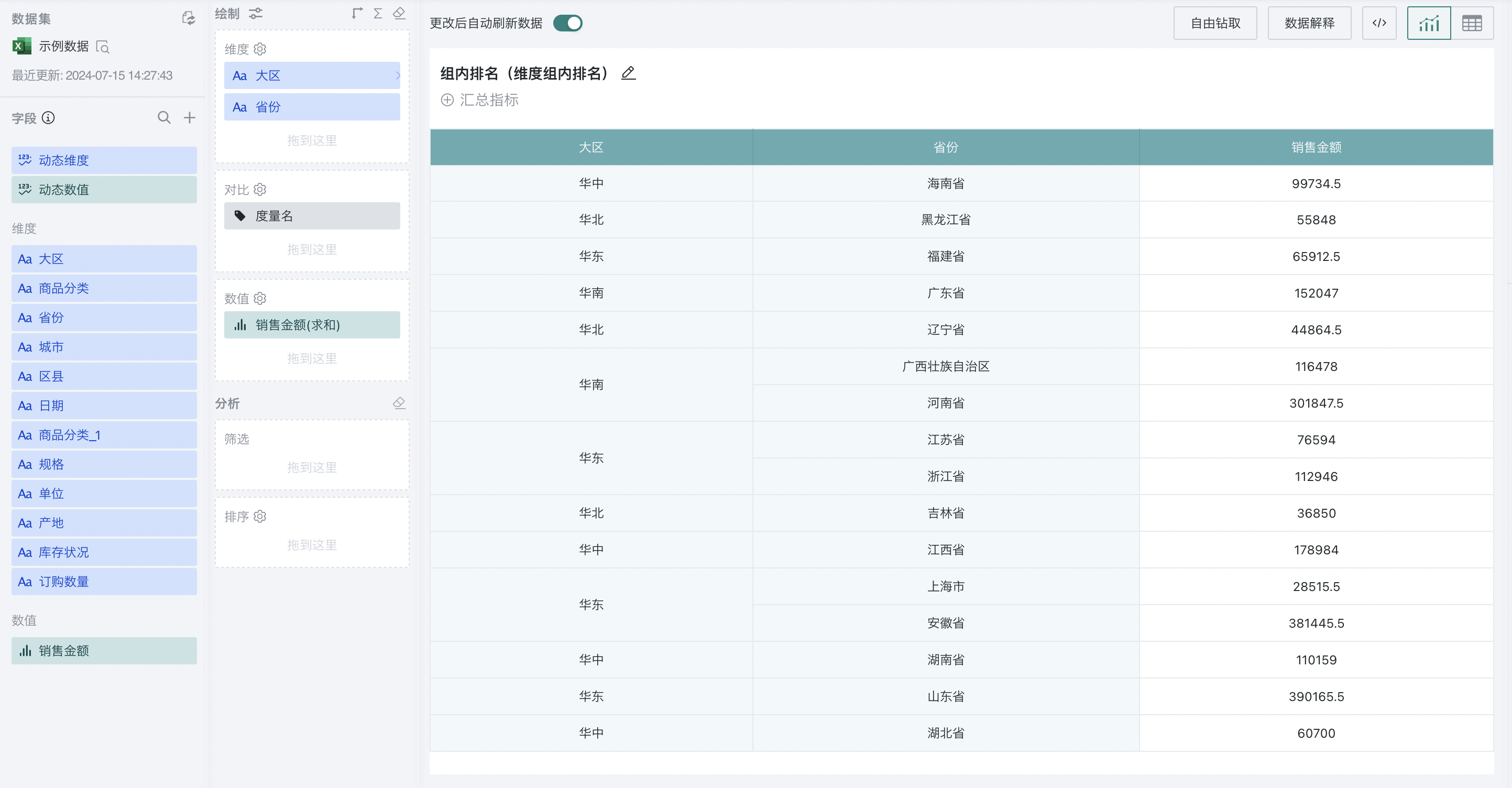
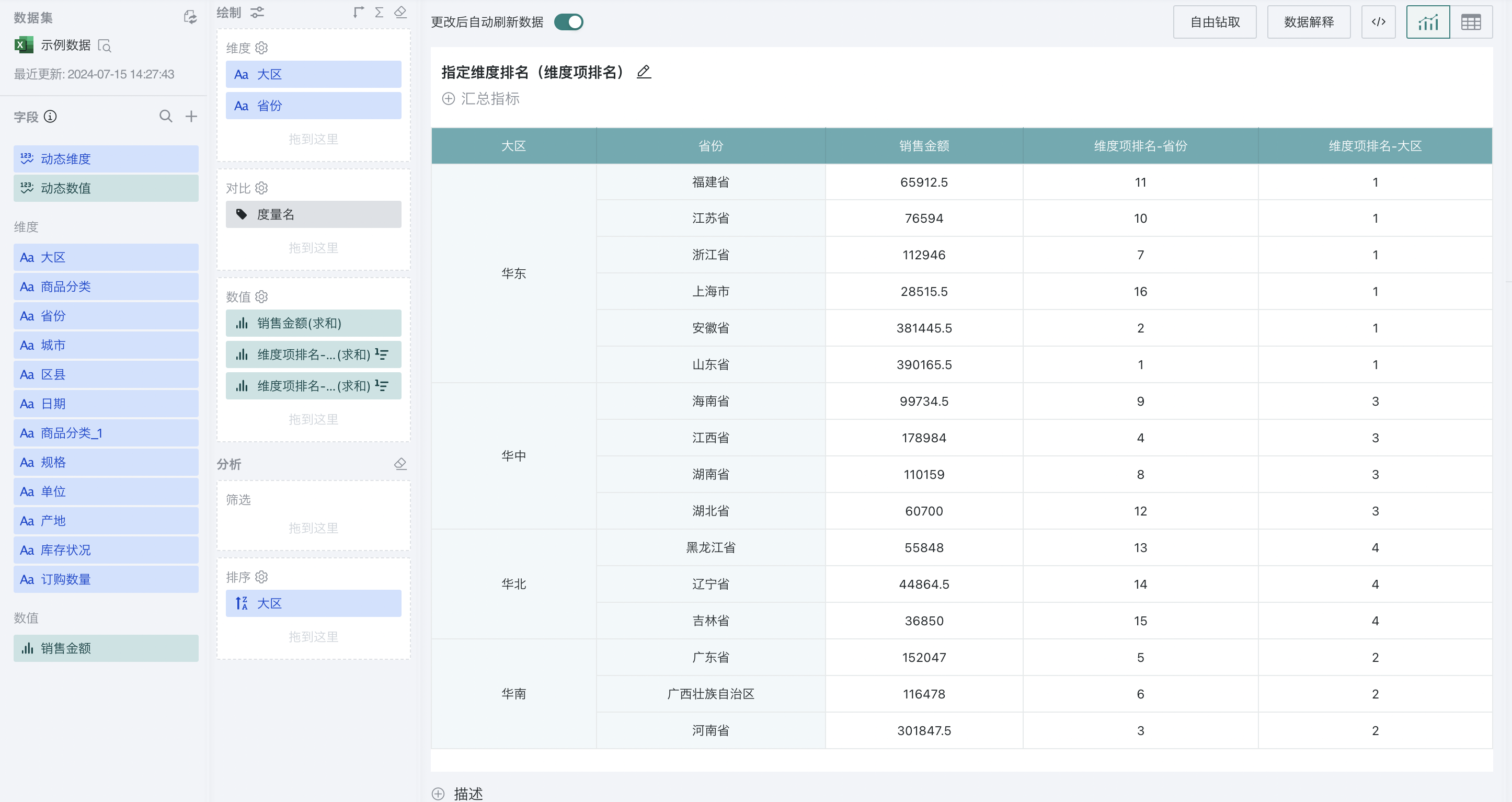
Step 2. Click "Sales Amount" and select "Advanced Calculation - Ranking". The ranking configuration popup appears. Select "dimension item ranking" as the ranking type, and select "Province" and "Region" as the calculation dimensions, and "from high to low" as the order.
At this point, when "Region" is selected, the ranking will be performed at the region level; when "Province" is selected, the global ranking will be performed at the province level, which is the same as the effect of global ranking by column.
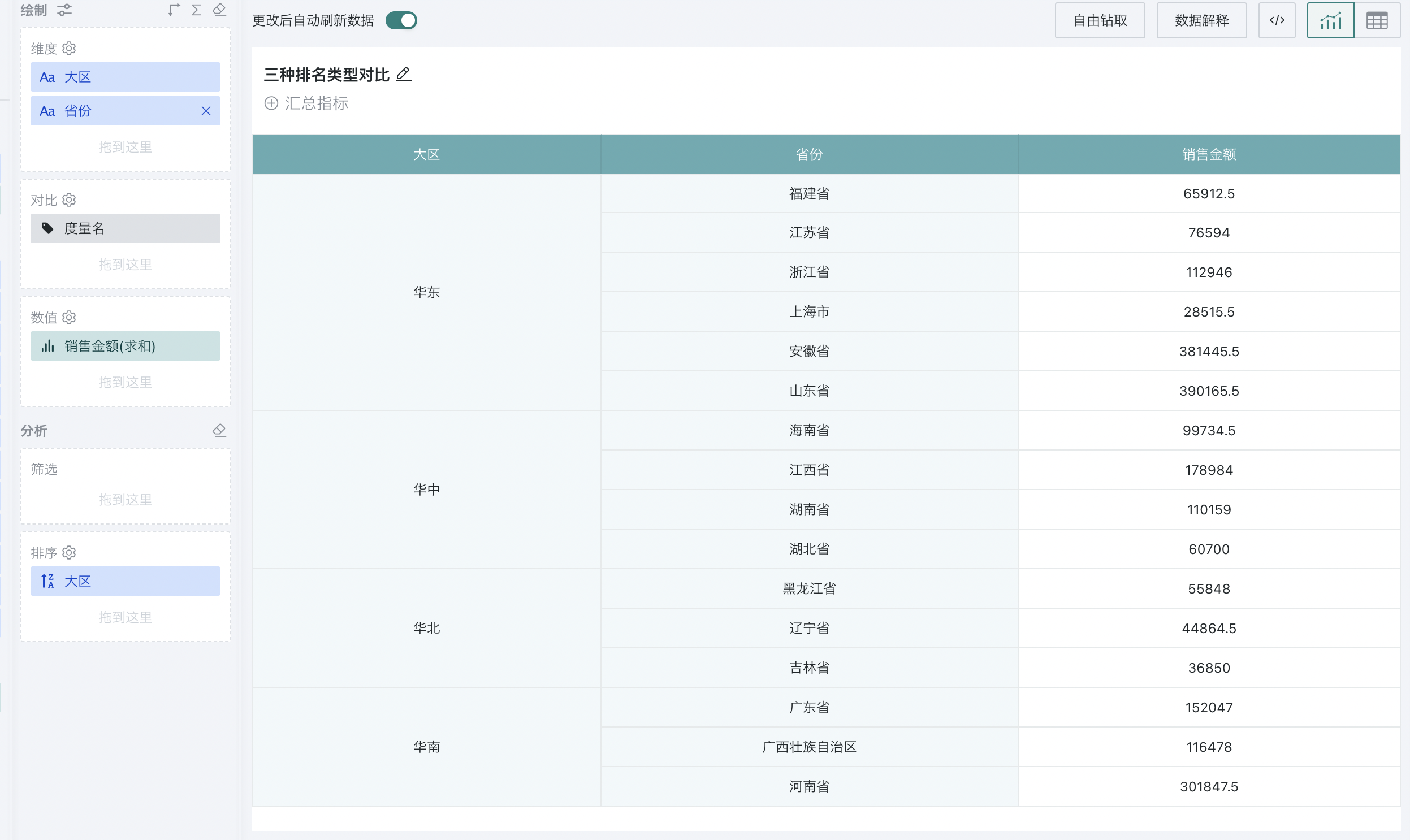
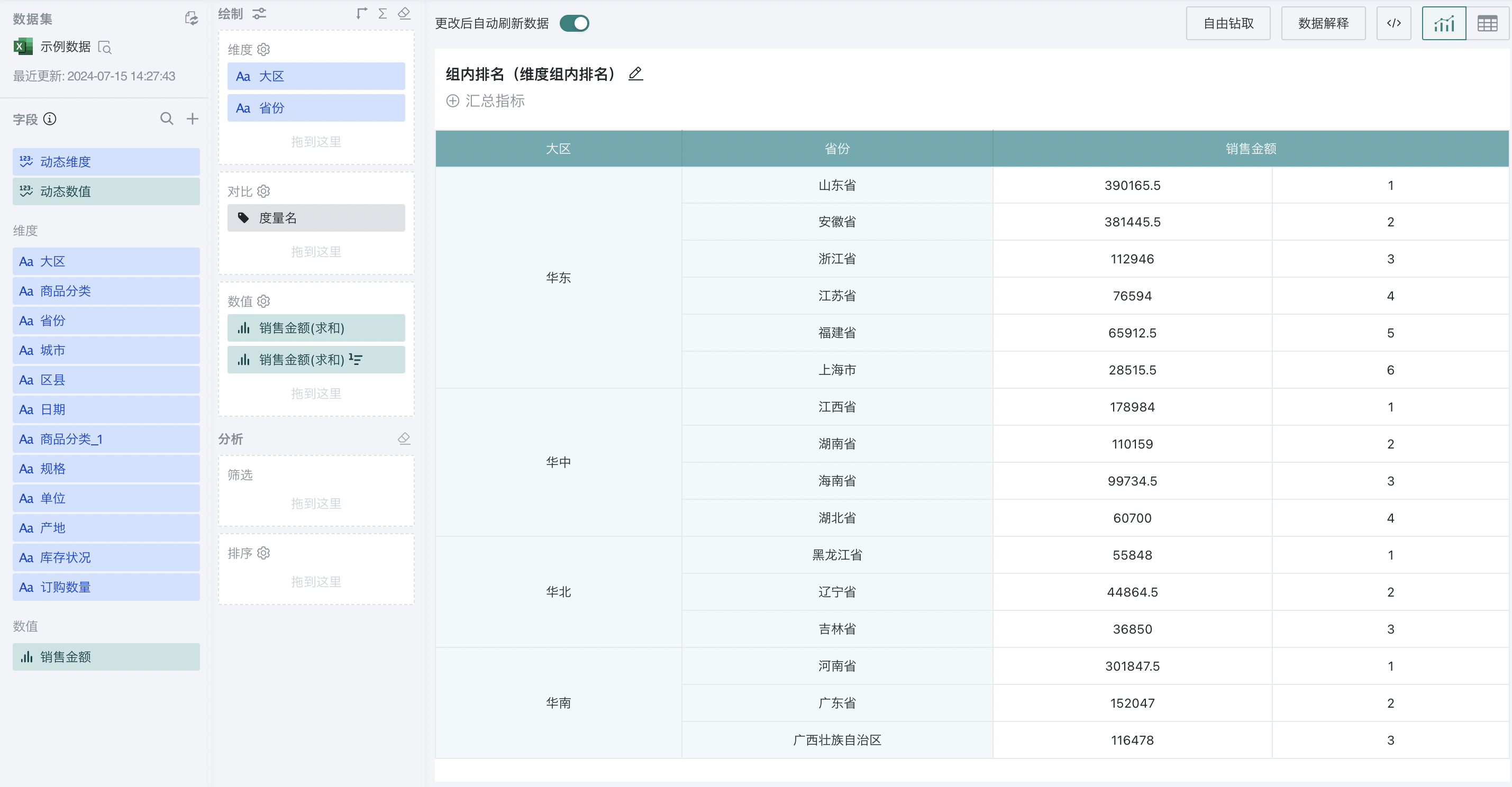
2.2. Group Ranking
Group ranking is achieved by setting the ranking type to "dimension group ranking". For example, to analyze the ranking of sales amount of different provinces in each region:
Step 1. Create a normal table, drag "Region" and "Province" into the dimension bar, and "Sales Amount" into the value bar, as shown below:
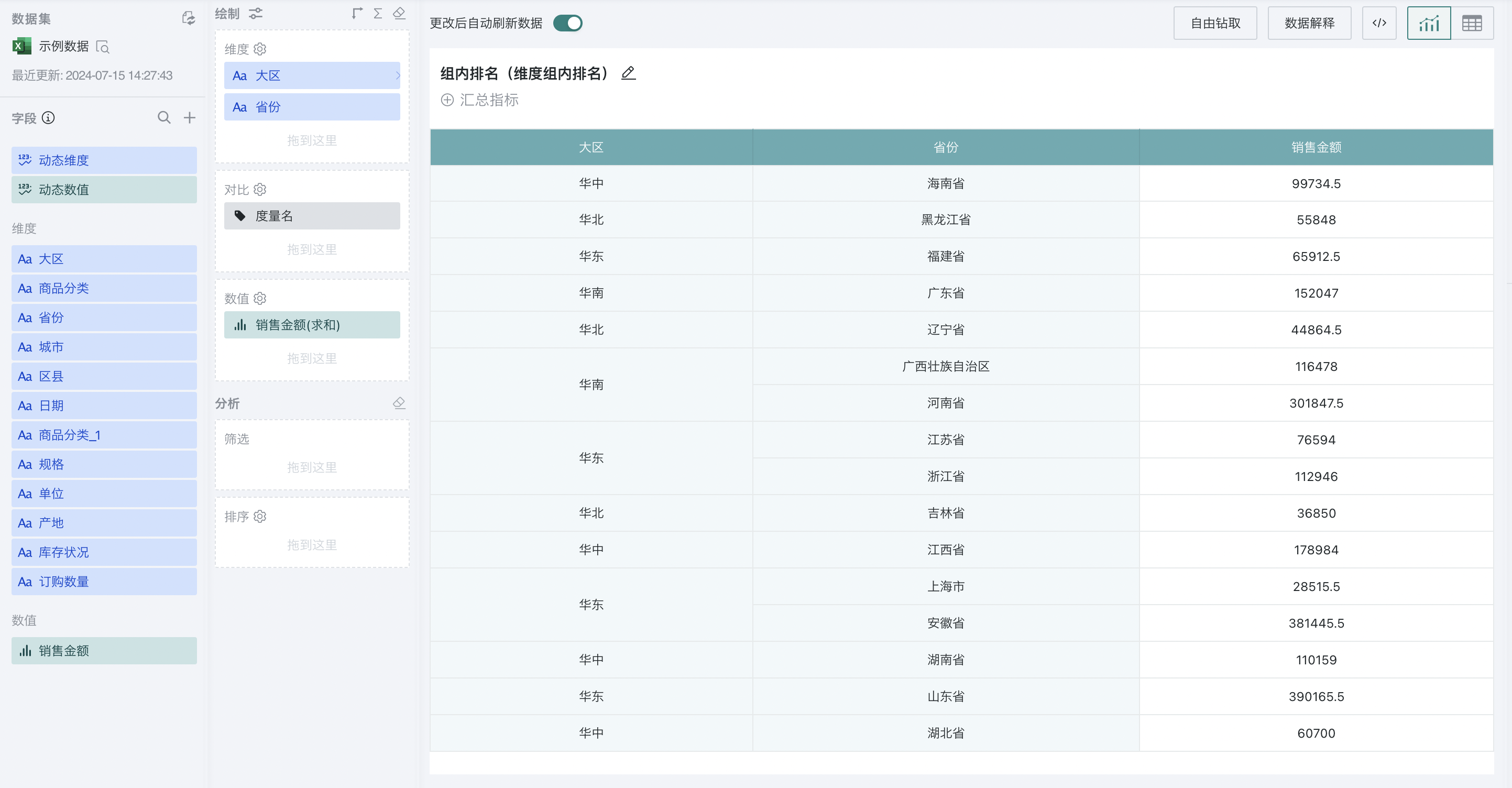
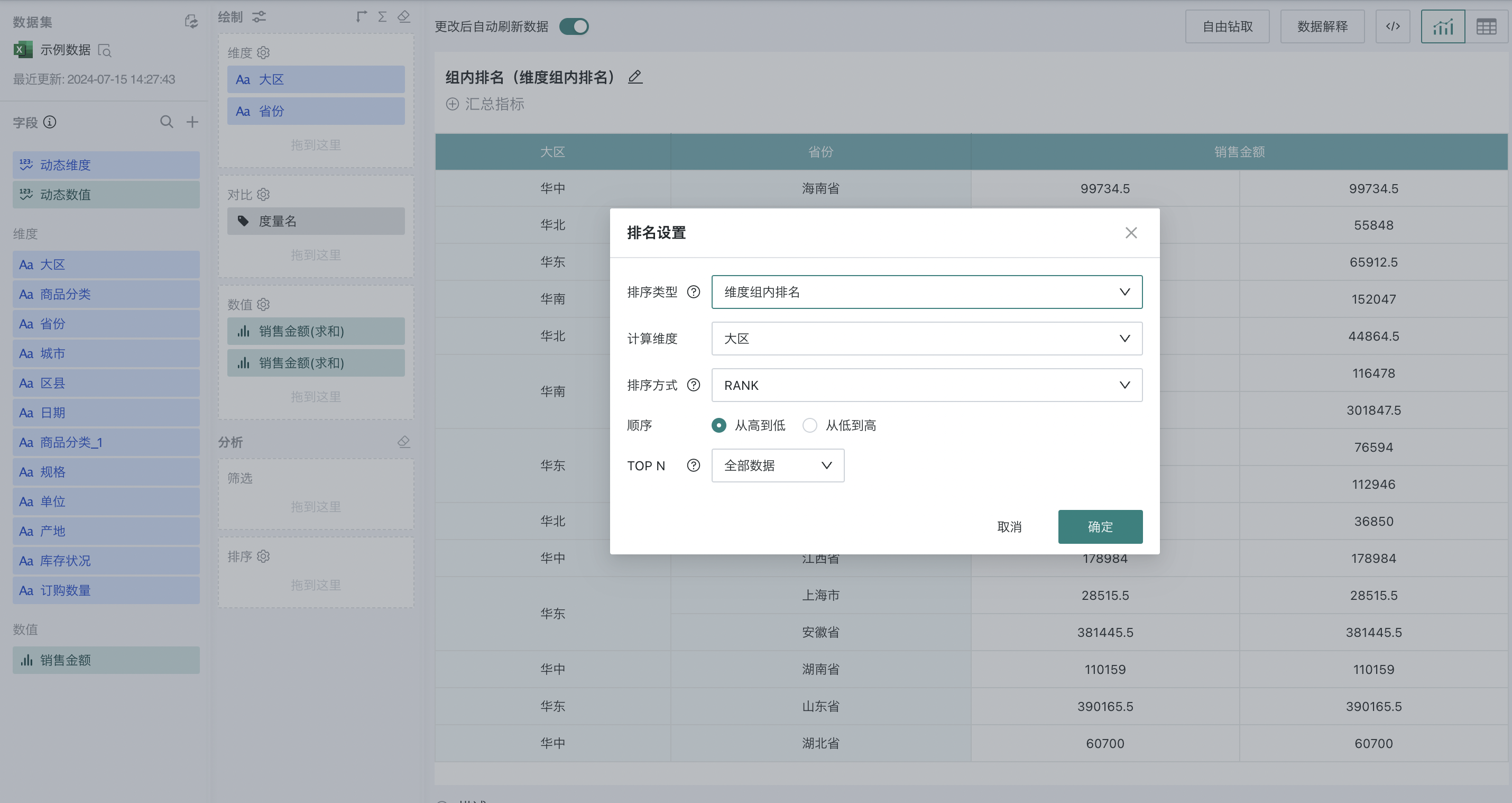
Step 2. Click "Sales Amount" and select "Advanced Calculation - Ranking". The ranking configuration popup appears. Select "dimension group ranking" as the ranking type, and select "Region" as the calculation dimension, and "from high to low" as the order.
Explanation of the selection range for calculation dimensions: When there are N dimensions, for the last dimension, there is no finer dimension, and the ranking value is always 1, which is meaningless. Therefore, only the first N-1 dimensions can be selected here. For example, when there are 3 dimensions, any of the first two can be selected; when there are 2 dimensions, the first one can be selected.
At this point, each region will be grouped, and the sales amount of different provinces in each region will be ranked from high to low, as shown below:
2.3. TOP N
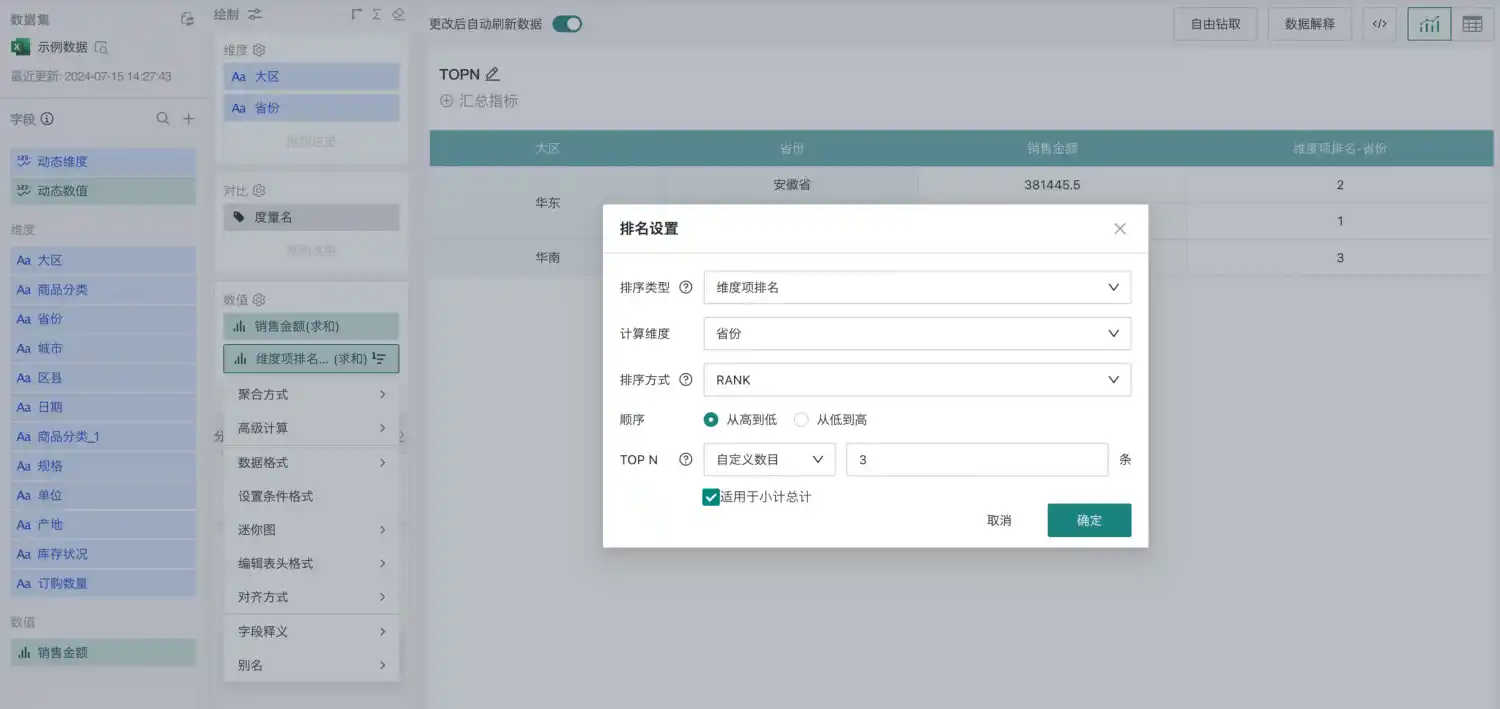
In addition to group and global ranking, TOPN filtering and analysis of ranking results is also supported.
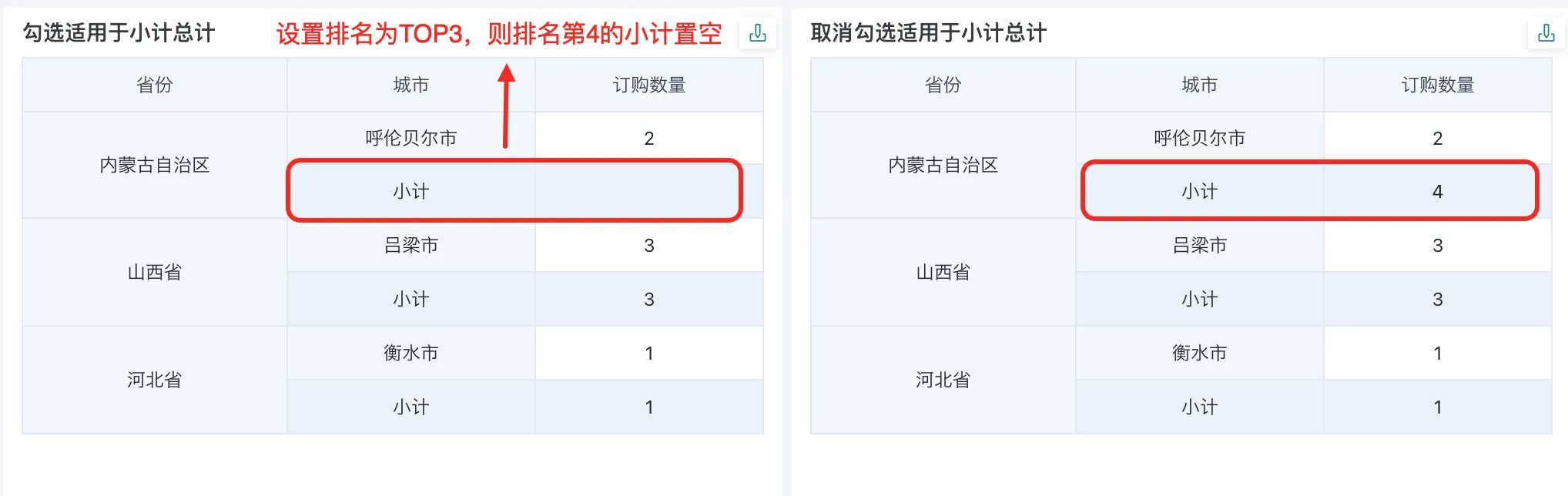
After setting the ranking, set a custom number in TOPN. The custom number must be a natural number between 1 and 100.
For example: If the user wants to see the top three provinces in national sales, select "Custom Number" in TOP N and enter "3".
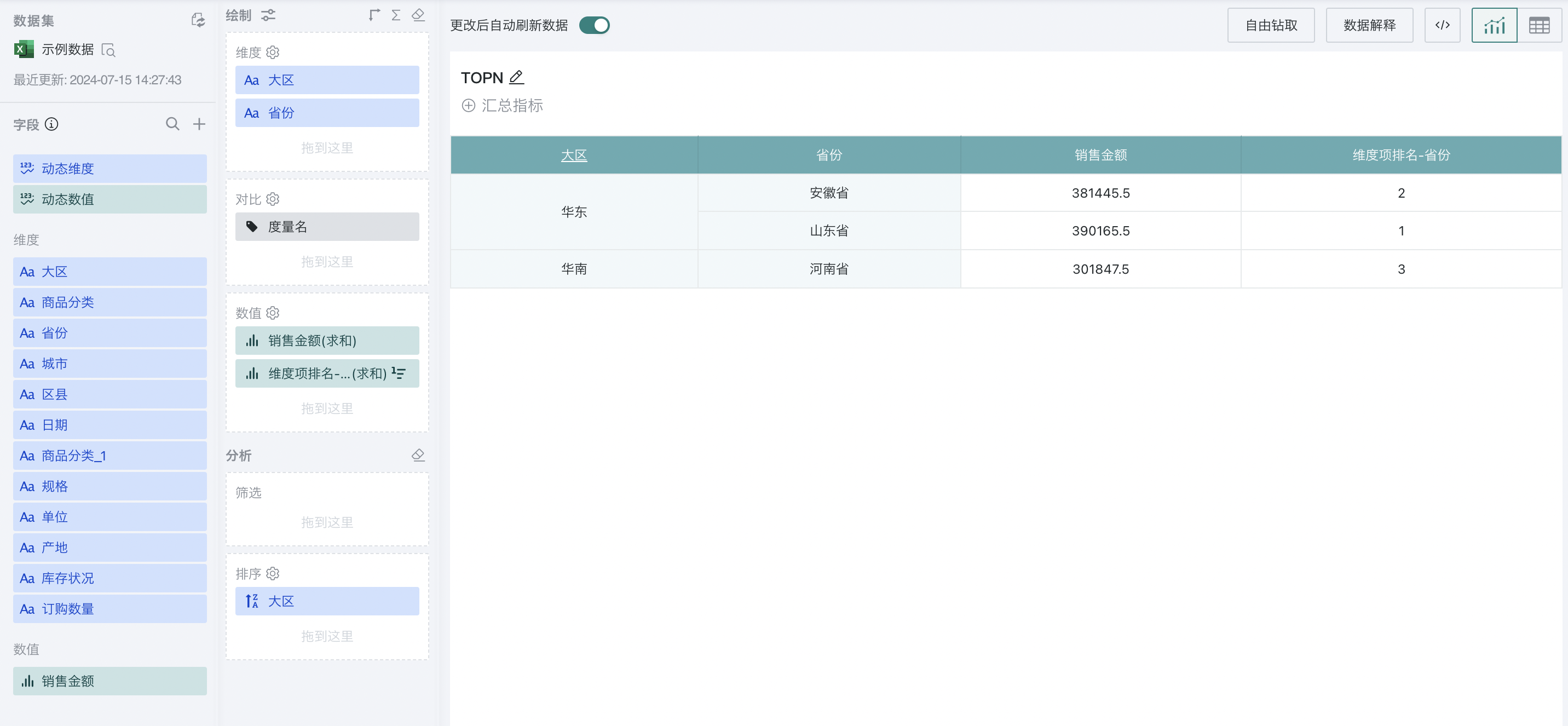
At this point, you can filter out the top three provinces in national sales.
Note:
For subtotals, ranking is also supported.
In the TOP N ranking settings, you can check "Apply to subtotal and total". When checked, the ranking value is displayed for subtotals that meet the TOP N requirements, and empty values are displayed for those that do not. When unchecked, the ranking of all subtotals is displayed.
3. Usage Restrictions
- Not supported for detail tables