Duplication Rate
1. Overview
1.1. Application Scenarios
Duplication rate can be used in calculation scenarios such as repeat purchase rate, repurchase rate, etc., for example, to calculate the number of repeat purchases/repeat purchase rate of consumers for products or services, so as to analyze consumer loyalty to the brand.
1.2. Feature Introduction
In the value bar, click the field to be calculated for duplication rate, and select "Advanced Calculation - Duplication Rate" from the dropdown menu to pop up the setting box.
Duplication count is used to indicate the number of indicators or events that meet specific duplication conditions within a specific time period. It can help us understand the proportion of repeated indicators or events, so as to evaluate the characteristics or trends of the data.
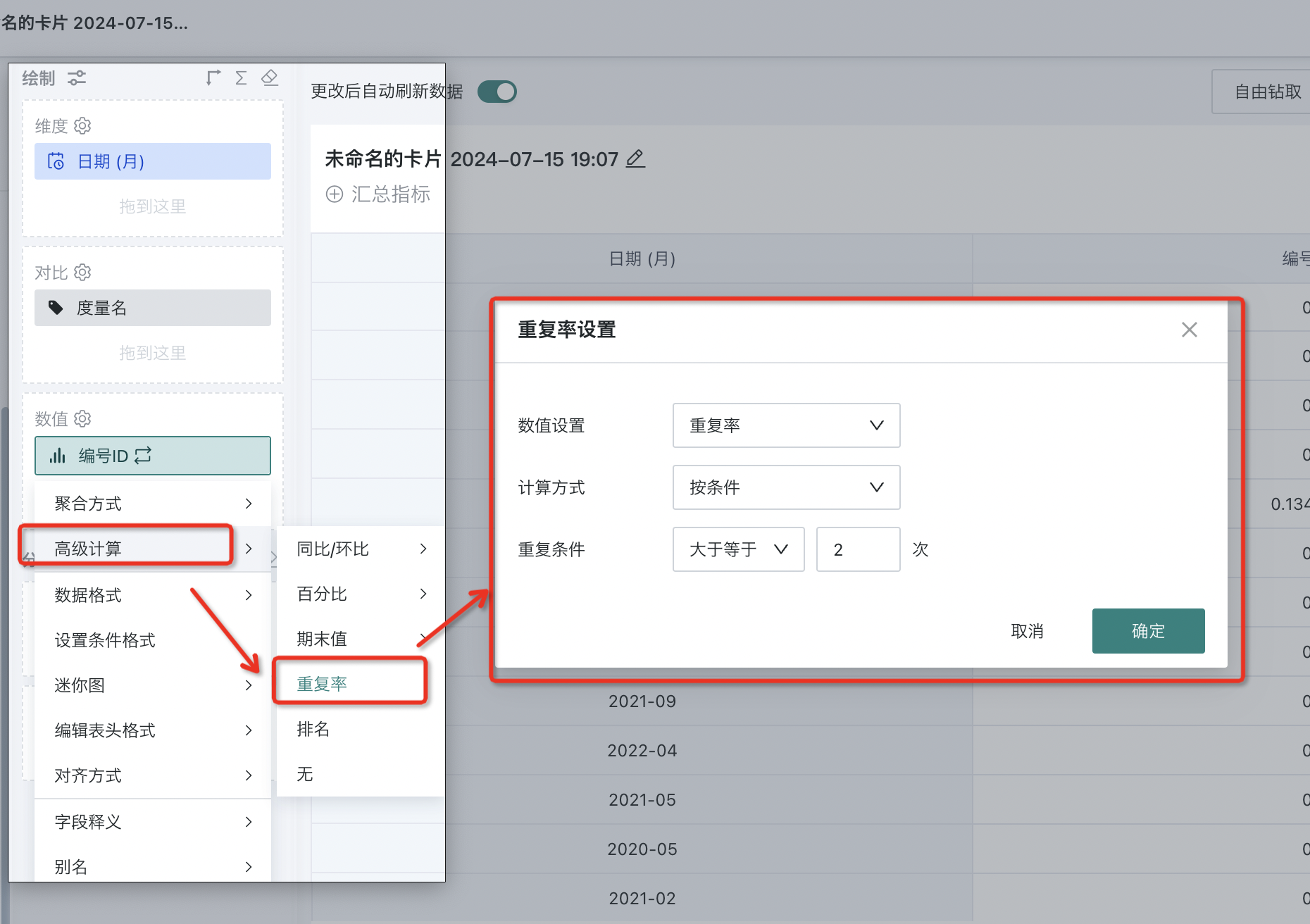
2. Quick Start
There are two calculation methods for duplication rate: by condition and by count.
Supports calculation of duplication count and duplication rate. Duplication count indicates the number of indicators or events that meet specific duplication conditions within a specific time period.
Duplication rate = duplication count / total number of indicators * 100%
At the same time, the calculation of duplication rate requires a time range, so there must be a date field in the dataset, divided into two scenarios:
-
When there is a date field in the dimension bar, the date field is used as the basis for analysis, and no additional date field configuration is required.
-
When there is no date field in the dimension bar: you need to configure the basis date field, and also determine the time range by configuring the calculation period.
- The time range supports three methods: date filter, fixed date, time macro
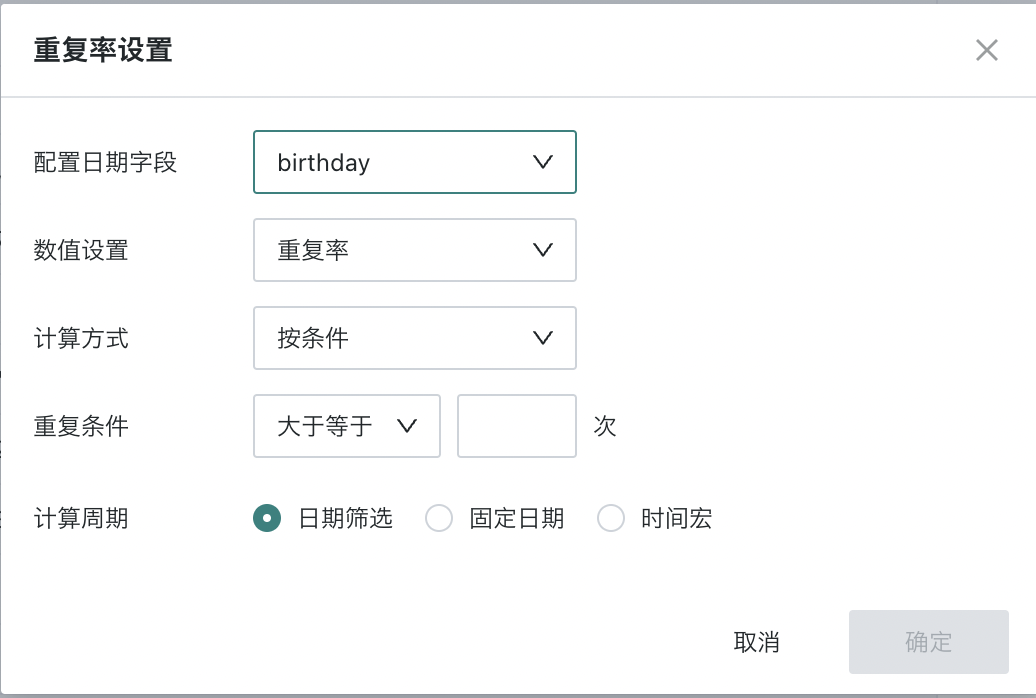
In addition, duplication rate can be calculated by condition and by count. The following will introduce the two calculation methods in detail.
2.1. By Condition
Meaning: Judged by condition, the number of times the indicator value that meets the condition appears is the duplication count. For example, in the analysis of member repurchase rate consumption data, define consumption times ≥ 2 as repeat purchase customers.
For example: In September 2022, 10 customers made purchases, of which 3 customers made more than 2 purchases, that is, repeat purchases. There were 10 purchase behaviors in total, so the total number of indicators is 10. Users A, B, and C each made repeat purchases, the duplication count is 3, and the duplication rate = duplication count / total number of indicators = (3/100)*100% = 3%.
Step 1: Drag the dimension you want to analyze into the dimension bar, such as consumption time - month;
Step 2: Drag the member code into the value bar, select the aggregation method as distinct count, and calculate the number of members per month;
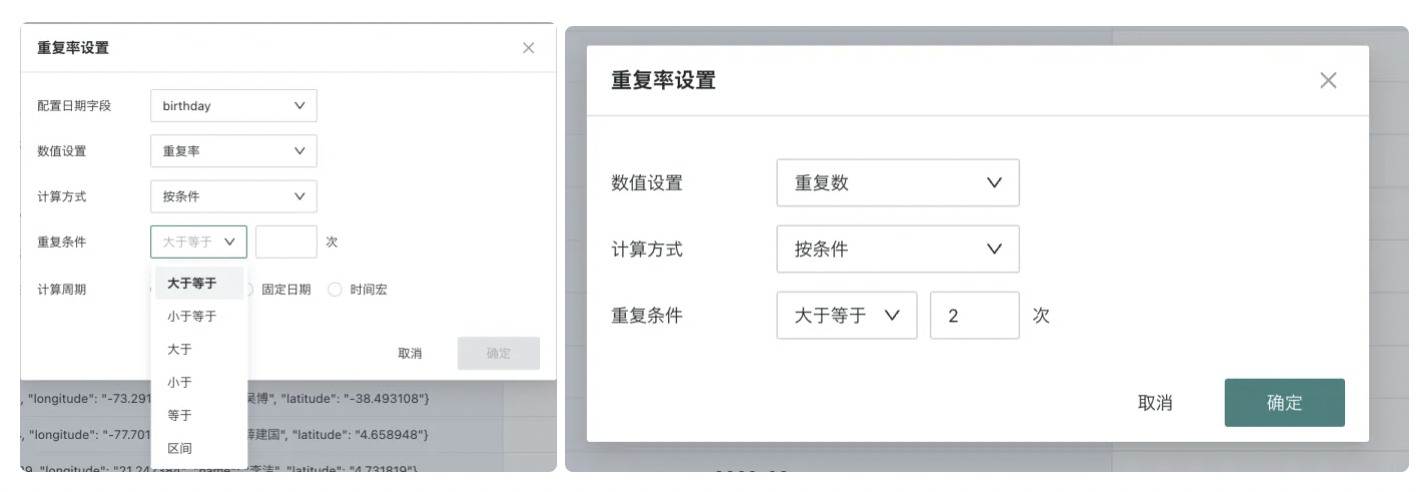
Step 3: For the field generated in step 2, set Advanced Calculation - Duplication Rate. The specific settings are as follows: set the value to duplication count, calculation method to by condition, and define ≥ 2 times as repeat purchase. The calculation result is the duplication count, i.e., the number of repurchasing members (number of members with consumption times ≥ 2).
Value settings and duplication conditions are supported here.
-
Value settings: Support selection of duplication count and duplication rate. Repurchase rate = number of repurchasing members / number of members.
-
Duplication condition: Support selection of greater than or equal to, less than or equal to, greater than, less than, equal to, interval.
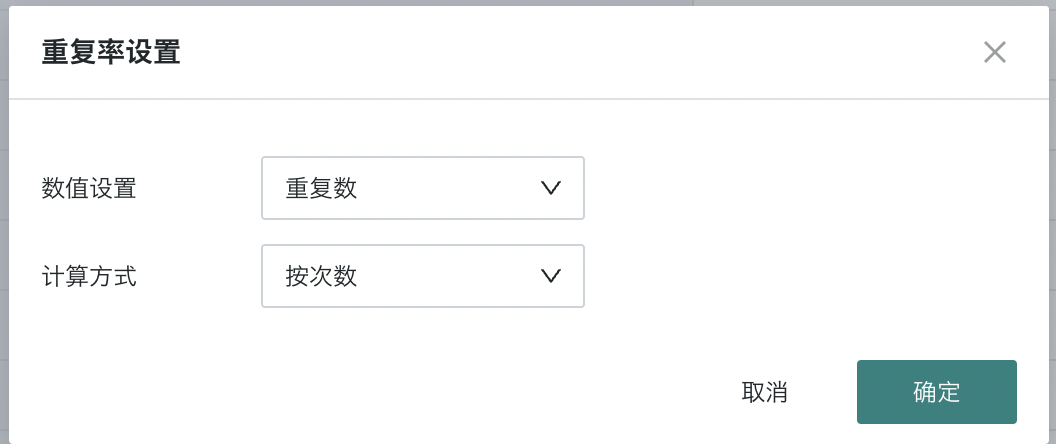
2.2. By Count
Meaning: Within a time period, duplication count = number of repeated indicators, duplication rate = duplication count / total number.
Duplication count = COUNT([indicator]) - COUNT(DISTINCT([indicator])), duplication rate = duplication count / COUNT([indicator]).
For example, in September 2022, 30 customers made 100 purchases, so the number of repeat purchases is 70, and the duplication rate is 70%.
Step 1: Drag the dimension you want to analyze into the dimension bar, such as consumption time - month;
Step 2: Drag the member code into the value bar, select the aggregation method as count, select Advanced Calculation > Duplication Rate, and set the value to duplication count, calculation method to by count;
The calculation result is the number of repeat purchases. To verify the calculation result, the number of repeat purchases = total number of purchases - number of customers. The total number of purchases can be obtained by counting the member code, and the number of customers can be obtained by distinct counting the member code.
Step 3: Repeat the previous step, set the value to duplication rate. The calculation result is the repurchase rate. Repurchase rate = number of repeat purchases / total number of purchases.
3. Usage Restrictions
-
Not supported for detail tables;
-
Only supported for extraction data, not for direct connection yet;
-
Only supported when there is a date field in the dataset (newly created date-type calculated fields are also supported).