Year-over-Year and Month-over-Month
1. Overview
1.1. Application Scenarios
Year-over-year and month-over-month analysis is a common method in data analysis. Combining these analyses can help us more easily discover outliers or abnormal trends in data.
For example, in sales performance analysis, month-over-month analysis can quickly grasp the fluctuations in sales performance over the past few months or weeks.
Year-over-Year (YoY): Usually refers to the change between the nth month of a certain year and the nth month of the previous year, such as comparing data from 2023 with data from 2022.
Month-over-Month (MoM): Refers to the change between two consecutive statistical periods (such as two consecutive days or two consecutive months). For example, comparing data from May 2023 with data from June 2023.
1.2. Feature Introduction
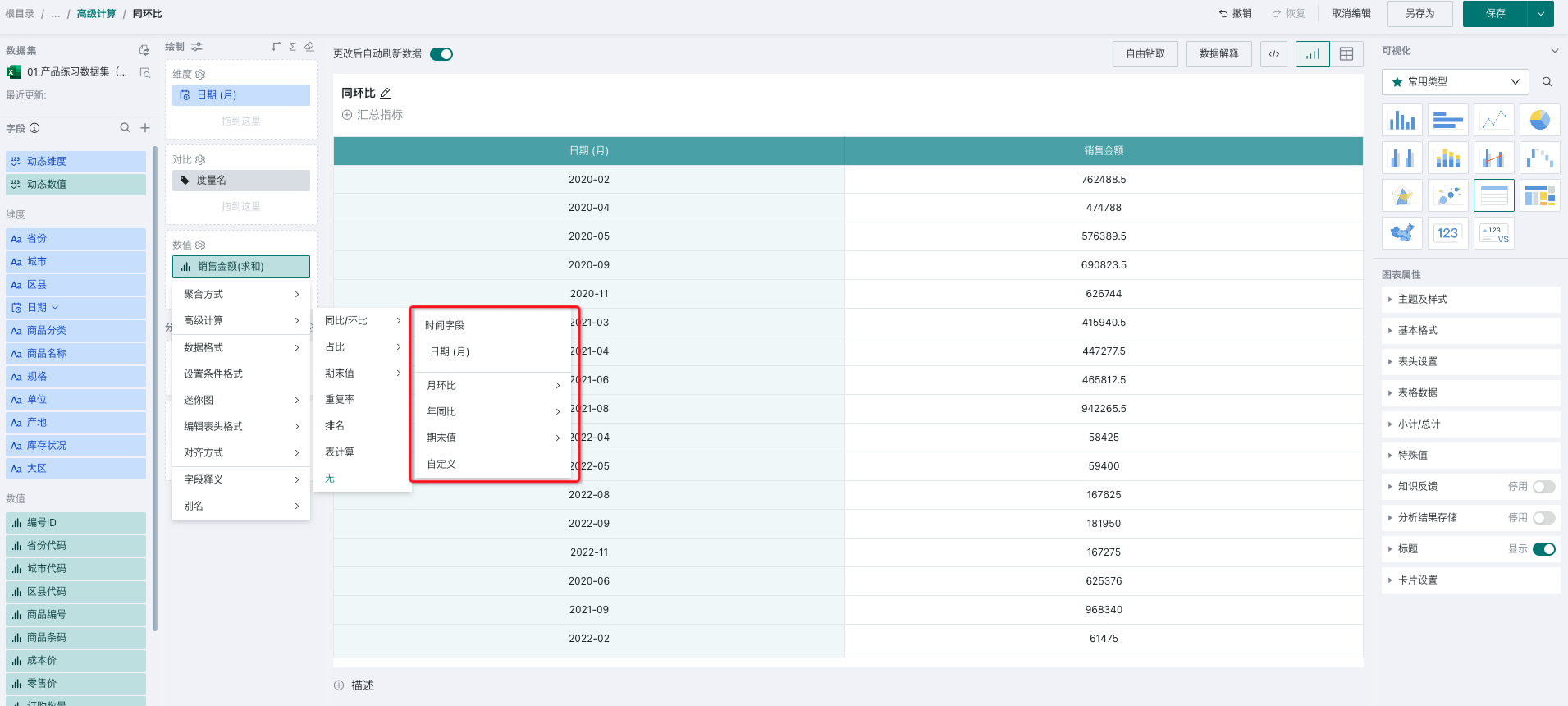
In the value bar, click the field to be calculated for YoY/MoM, and select "Advanced Calculation - YoY/MoM" from the dropdown menu.
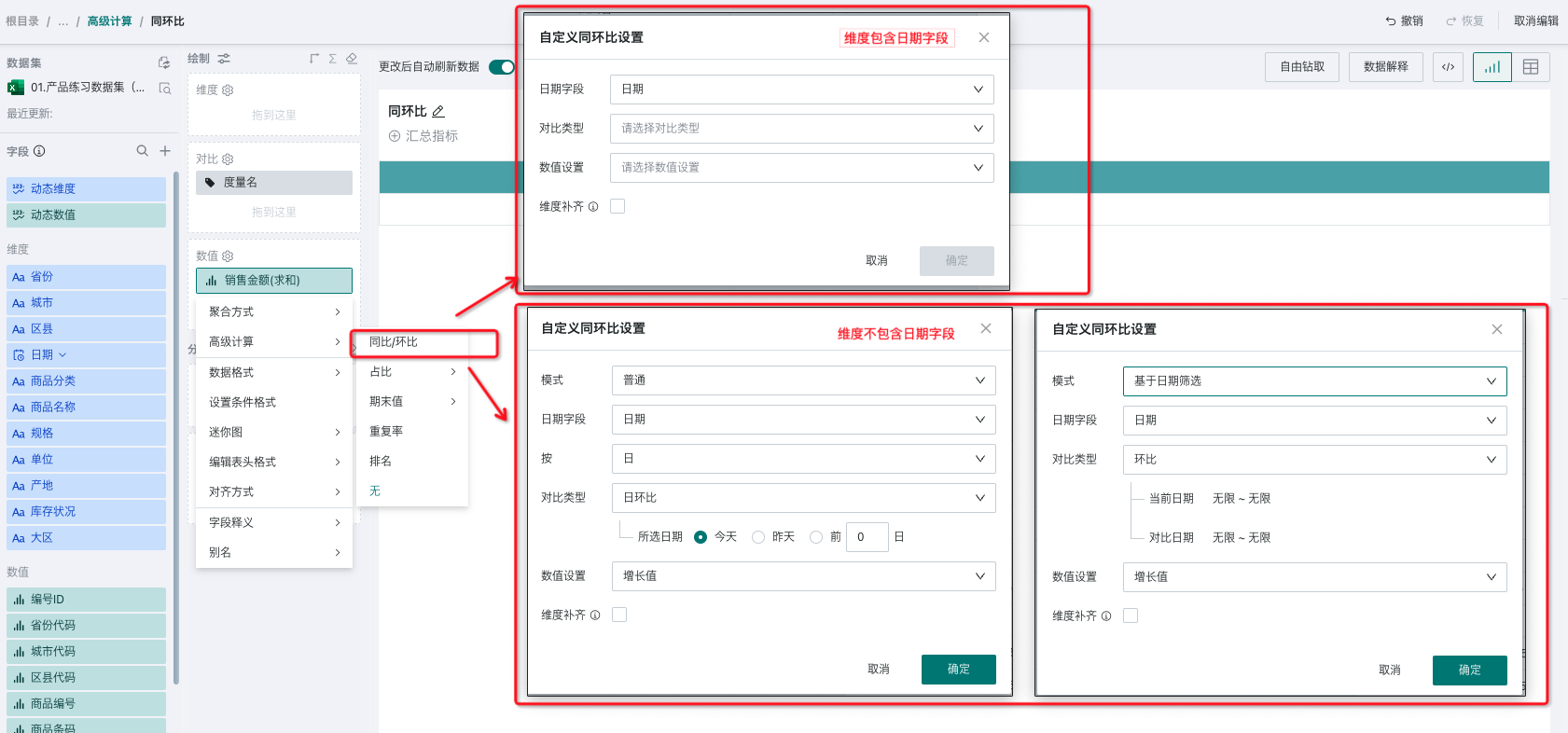
Whether there is a date-type field in the dimension bar of the drawing area will affect the configuration of YoY/MoM. As shown below, users can choose the appropriate method according to the actual scenario.
2. Instructions
The following will introduce the meaning of various configurations of YoY/MoM in detail, including mode, date field, comparison type, value settings, and dimension completion.
2.1. Mode
According to whether there is a date-type field in the dimension bar of the drawing area, there are three types: simple mode, normal mode, and date filter-based mode.
Dimension Field Situation | Dimension Contains Date Field | Dimension Does Not Contain Date Field | |
Mode Type | Simple Mode | Normal Mode | Date Filter-Based Mode |
Specific Performance | No need to select a date field, the first date field in the dimension is used as the basis for YoY/MoM calculation by default. | Need to specify a date field, and the selectable range is all date fields in the dataset. Select the granularity of analysis, such as calculating MoM by month. | Need to specify a date field, and the selectable range is all date fields in the dataset and filter. In this scenario, there must be a date filter on the page, and the date field in the filter must be consistent with the date field configured for YoY/MoM. |
Configuration Screenshot | 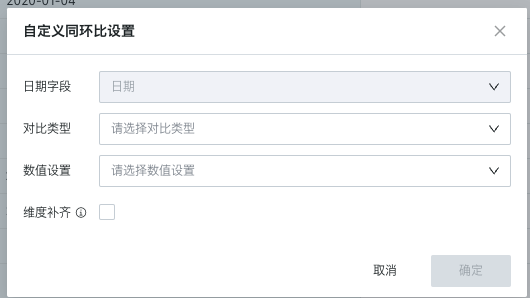 | 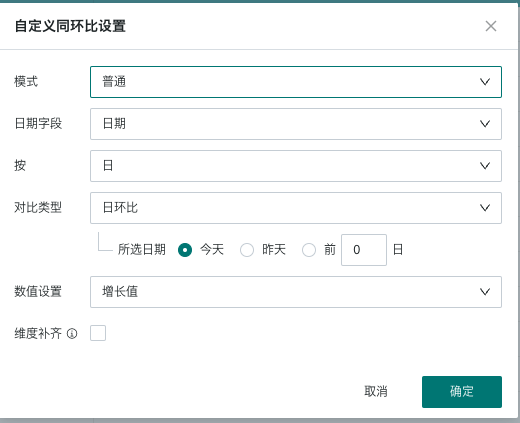 | 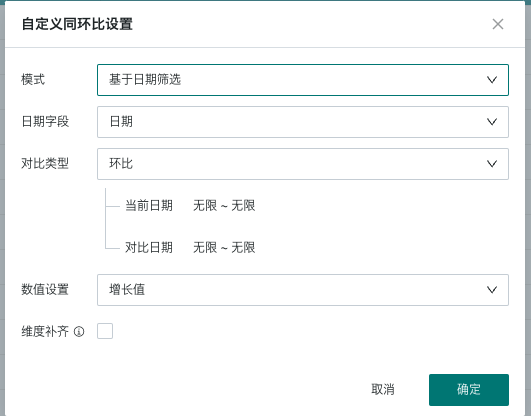 |
2.2. Date Field
YoY/MoM is a calculation based on dates, so a date dimension needs to be specified when calculating YoY/MoM, i.e., the date dimension on which the calculation is based.
The reference date is the time field for calculating YoY/MoM, and only date-type fields are supported.
The selection range is the date fields in the dataset and filter, and the default is the first date field in the dimension.
2.3. Comparison Type
Since the configuration of comparison types varies in different modes, detailed explanations for each scenario are provided in Section 3 of this document.
| Date Field Granularity | YoY/MoM Description |
|---|---|
| Year granularity | Year-over-year: Compare this year with last year, e.g., compare 2024 with 2023. |
| Quarter granularity | Quarter-over-quarter: Compare this quarter with last quarter, e.g., compare Q2 2024 with Q1 2024. Year-over-year: Compare this quarter with the same quarter last year, e.g., compare Q2 2024 with Q2 2023. End-of-period value - Last year-end: Compare this quarter with last year-end, e.g., compare Q2 2024 with Q4 2023, Q1 2024 with Q4 2023. |
| Month granularity | Month-over-month: Compare this month with last month, e.g., compare July 2024 with June 2024. Year-over-year: Compare this month with the same month last year, e.g., compare July 2024 with July 2023. End-of-period value - Last quarter-end: e.g., compare July 2024 with June 2024, August 2024 with June 2024. End-of-period value - Last year-end: e.g., compare July 2024 with December 2023, August 2024 with December 2023. |
| Week granularity | Week-over-week: Compare this week with last week, e.g., compare week 20 of 2024 with week 19 of 2024. Year-over-year: Compare this week with the same week last year, e.g., compare week 20 of 2024 with week 20 of 2023. |
| Day granularity | Day-over-day: Compare today with yesterday, e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with July 7, 2024. Week-over-week: Compare today with the same day last week, e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with July 1, 2024. Month-over-month: Compare today with the same day last month, e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with June 8, 2024. Quarter-over-quarter: Compare today with the same day last quarter, e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with April 8, 2024. Year-over-year: Compare today with the same day last year, e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with July 8, 2023. End-of-period value - Last month-end: e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with June 30, 2024, August 31, 2024 with July 31, 2024. End-of-period value - Last quarter-end: e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with June 30, 2024, August 31, 2024 with June 30, 2024. End-of-period value - Last year-end: e.g., compare July 8, 2024 with December 31, 2023, August 1, 2024 with December 31, 2023. |
| Hour, minute, second, year-month-day-hour-minute-second fields | Custom configuration for YoY/MoM is supported. |
2.4. Value Settings
Guandata provides three calculation types: growth value, growth rate, and comparison value. The following are detailed explanations of the three calculation types:
-
Growth Value: Current period data - Previous period data;
-
Growth Rate: Two calculation methods are provided: (Current period data - Previous period data)/Previous period data% or (Current period data - Previous period data)/abs(Previous period data)%;
-
Comparison Value: Previous period data.
"Current period" refers to the data corresponding to the current cycle or period, and "previous period" refers to the data corresponding to the previous cycle or period.
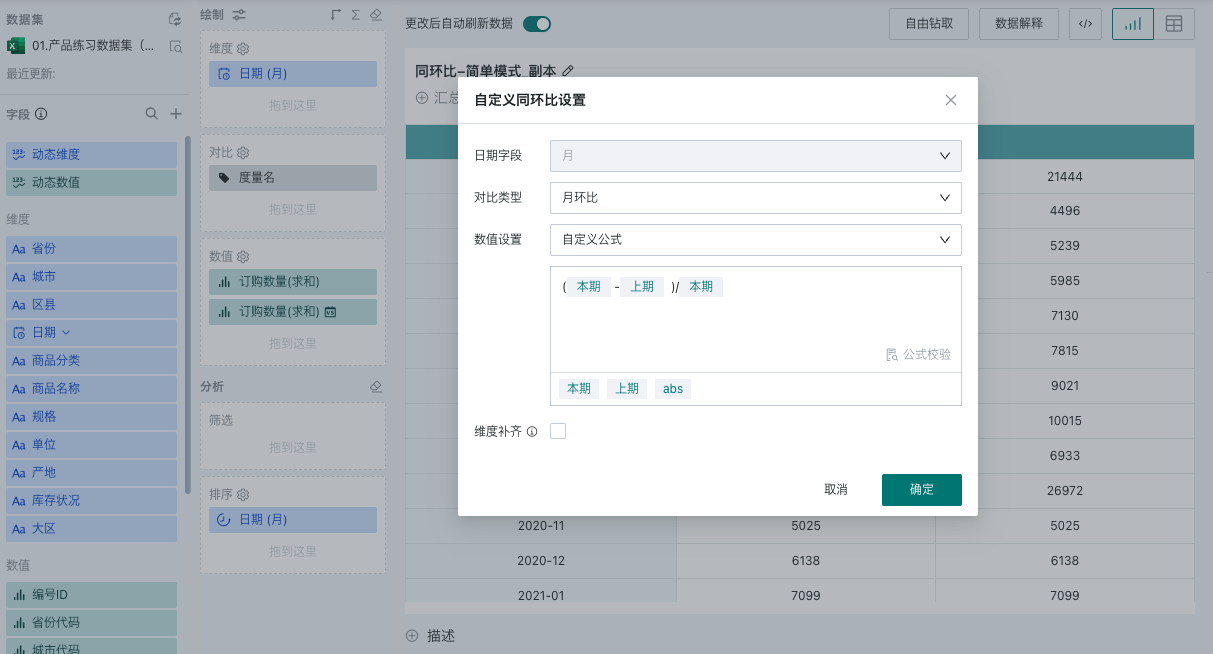
In addition to the above three quick calculation methods, users can also customize YoY/MoM formulas according to actual business scenarios. Free arithmetic operations and absolute value calculations can be performed on current and previous period data, such as "(Current - abs(Previous)/Current) + 1".
2.5. Dimension Completion
In YoY/MoM calculation, when there is no data in the current period but there is data in the previous period, you can use this function to complete the data.
-
Checked: Complete dimension values. That is, when there is no value in the current period but there is a value in the previous period, display the row (outer join);
-
Unchecked: Do not complete dimension values, display according to the actual data. That is, when there is no value in the current period and there is a value in the previous period, do not display the row (default value) (left join).
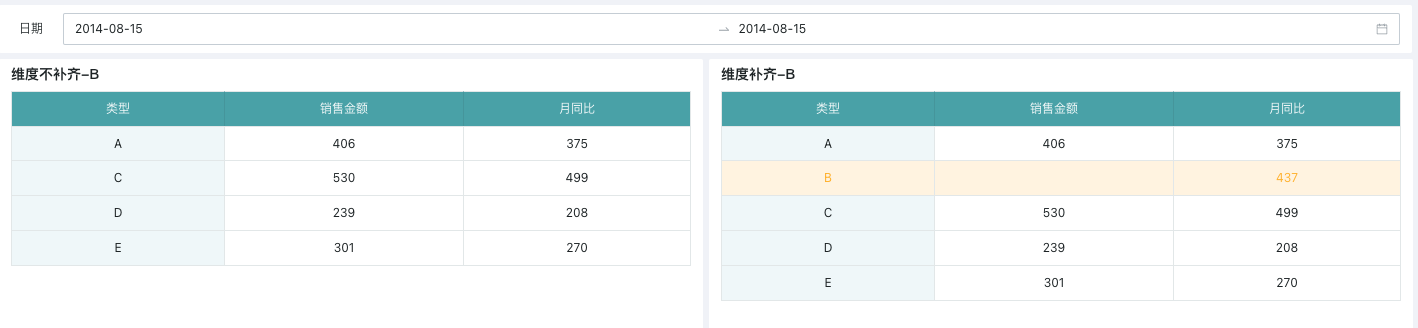
As shown below, on August 15, type B has no data in the current period but has data in the previous period.
-
When dimension completion is not checked, the data for type B on this day is not displayed, as shown on the left;
-
When dimension completion is checked, the data for type B is completed, as shown on the right.
3. YoY/MoM Configuration Examples
3.1. Quick YoY/MoM
When the dimension bar in the drawing area contains a date-type field, you can quickly calculate YoY/MoM in Advanced Calculation > YoY/MoM. The system will automatically provide supported YoY/MoM calculation methods based on the granularity of the date, as detailed below:
| Date Field Granularity | Supported YoY/MoM Calculations |
|---|---|
| Year granularity | Year-over-year |
| Quarter granularity | Quarter-over-quarter, Year-over-year, End-of-period value - Last year-end |
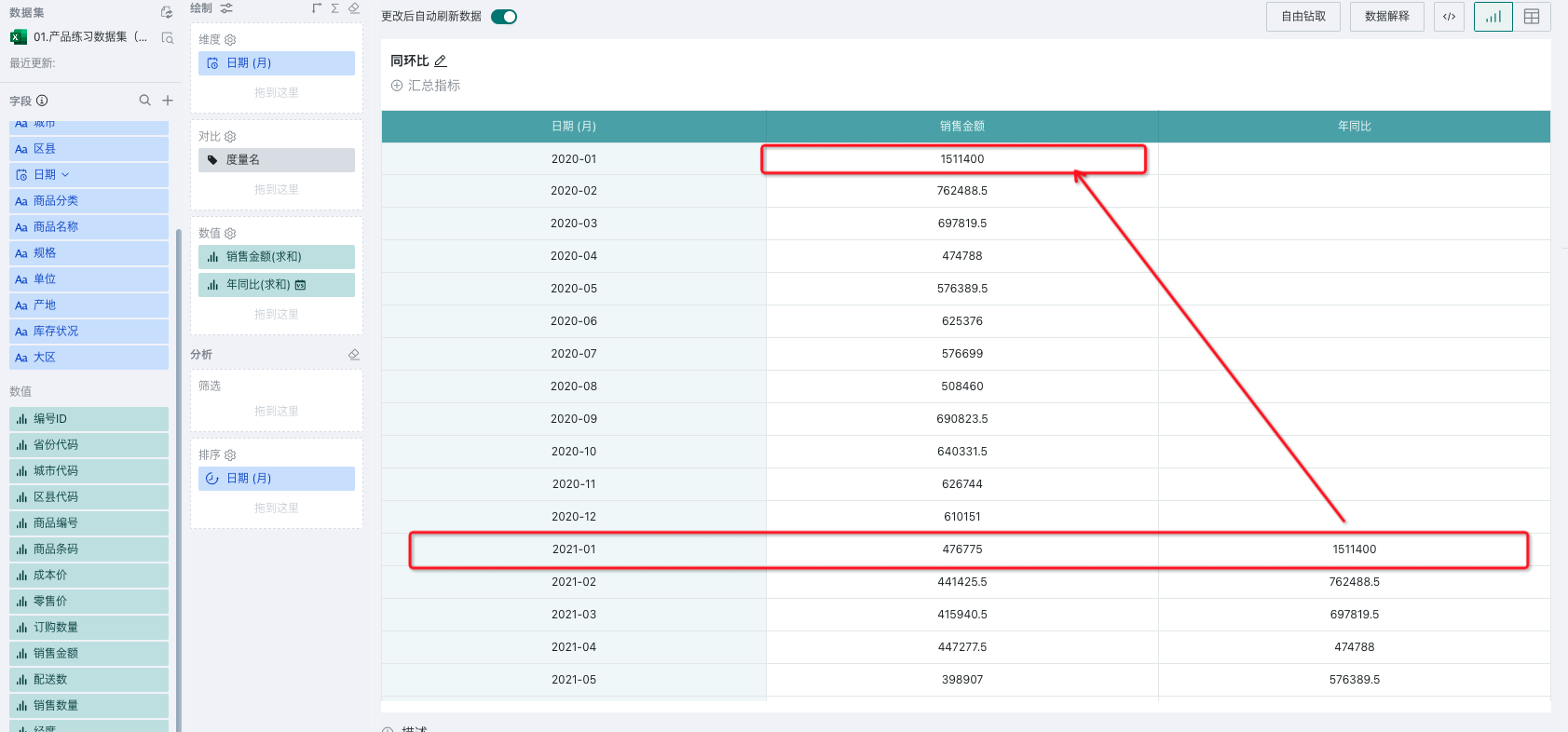
| Month granularity | Month-over-month, Year-over-year, End-of-period value - Last quarter-end, End-of-period value - Last year-end |
| Week granularity | Week-over-week, Year-over-year |
| Day granularity and hour, minute, second | Day-over-day, Week-over-week, Month-over-month, Quarter-over-quarter, Year-over-year, End-of-period value - Last month-end, End-of-period value - Last quarter-end, End-of-period value - Last year-end |
For example, to calculate last year's monthly sales for the same period, as shown below:
3.2. Dimension Contains Date Field
When users want to display YoY/MoM by date field as a dimension, but the quick YoY/MoM calculation cannot meet the needs and want to use custom YoY/MoM formulas or dimension completion, you can use simple mode. As shown below, you can select a custom formula in the value settings, and users can customize the YoY/MoM formula according to actual business scenarios. Here, you can freely perform arithmetic operations and absolute value calculations on current and previous period data.
For example, in the figure below, the date field is used as the dimension, and the month-over-month and year-over-year of monthly sales are calculated. The YoY/MoM formula is (Current - Previous)/Current+1.
3.3. Dimension Does Not Contain Date Field
3.3.1. Normal Mode
When users want to use a text field as a dimension to view the YoY/MoM growth of this month's data by region, you can use normal mode.
-
Supports analysis by day, week, month, quarter, and year, and the comparison type changes dynamically according to the date granularity.
-
Selected date description: The selected date is mainly used to determine the current period data. Since YoY/MoM calculation is a calculation over a period of time, the selected date is equivalent to adding a filter to the reference time field for YoY/MoM. For example, for monthly granularity, if you select this month, it means the current period data is the data for the current month.
As shown below, select a date-type field as the reference time field for YoY/MoM calculation. Since year-over-year analysis with monthly granularity is required, select by month below, comparison type is year-over-year, and selected date is this month. If the current time is July 2024, the current period in the YoY/MoM calculation is the data for July this year, and the previous period is the data for July last year.
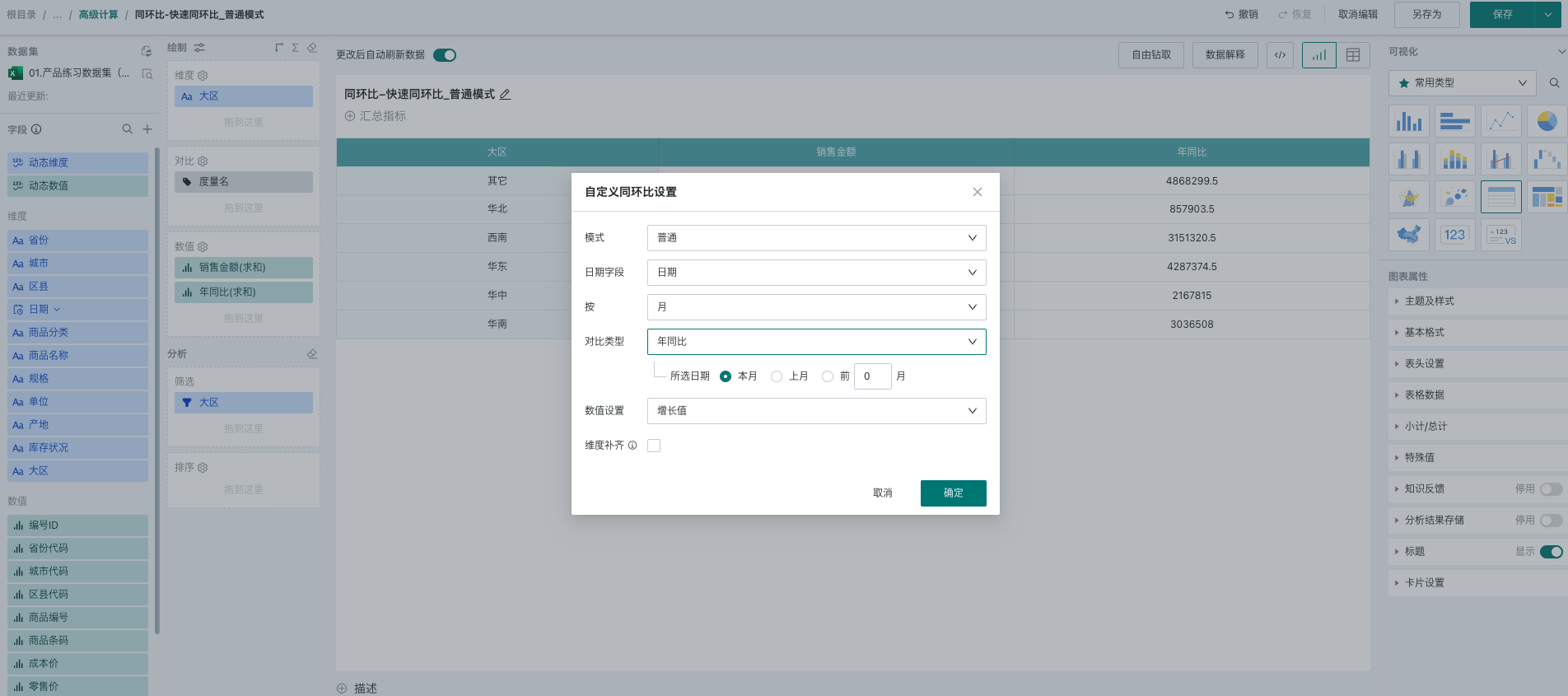
For YoY/MoM analysis with day granularity, this mode also provides richer configurations:
- Selected date: Used to determine the current period data. In addition to selecting today, yesterday, and previous days, interval selection is also supported, that is, selecting a period of time as the current period data;
- Interval selection provides two methods: manual selection in the calendar and custom time macros. For usage of time macros, refer to the document [Dynamic Time Macro](../4-Dynamic Time Macro.md).
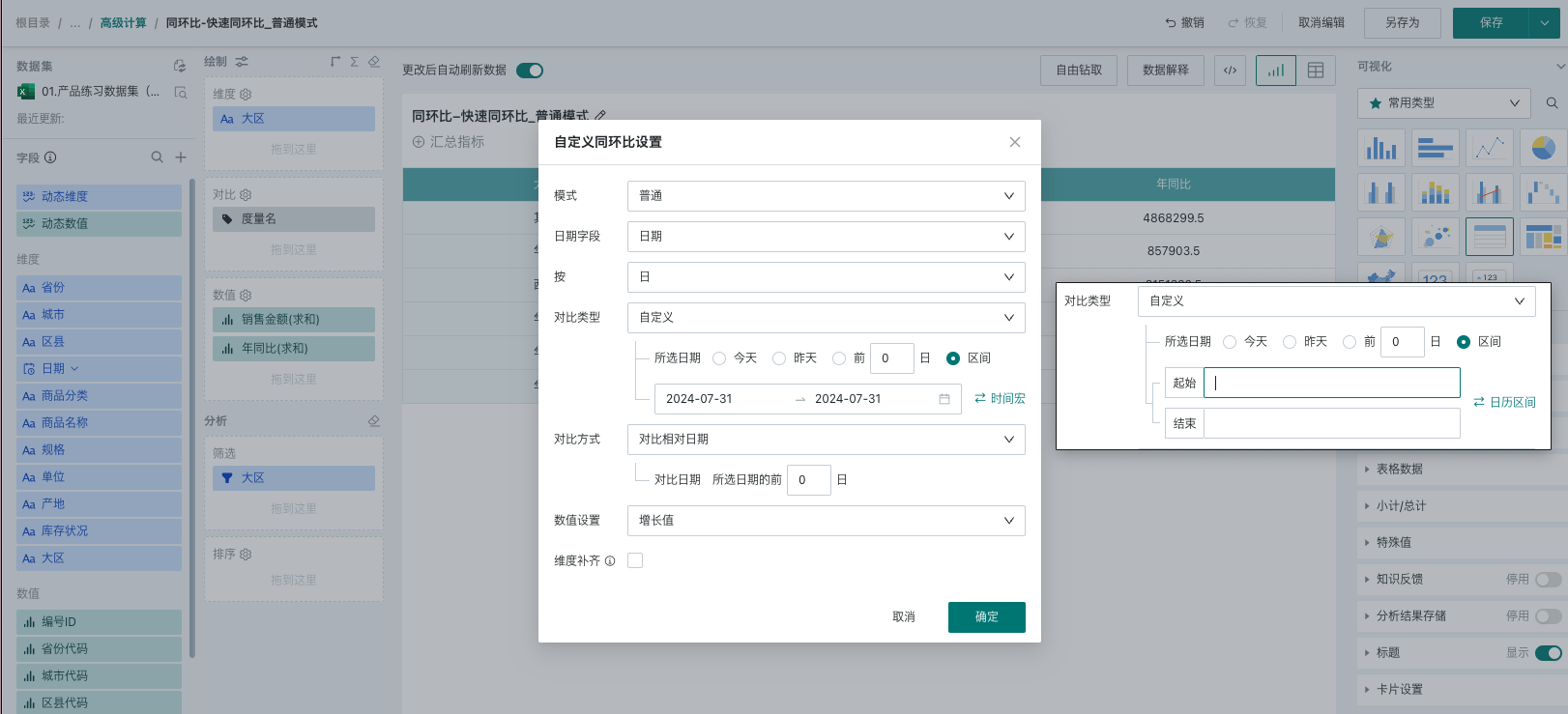
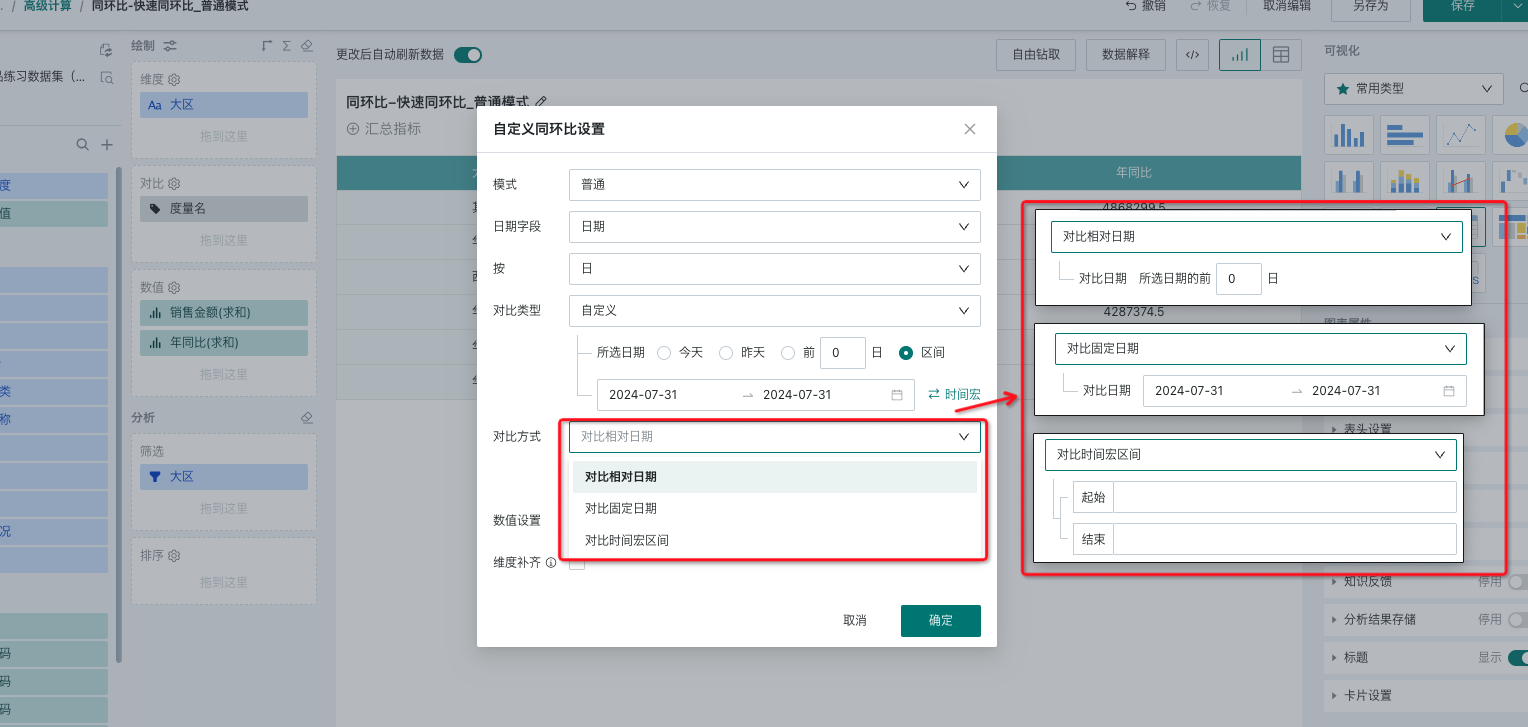
- Comparison method: Provides three methods: compare with relative date, compare with fixed date, and compare with time macro interval. The selected date is used to determine the current period data, and the comparison date is used to determine the previous period data. Details are as follows (taking July 10, 2024 as an example):
-
Compare with relative date: Customize the dynamic date as the previous period data by manual input;
- If the relative date is set to [3 days before the selected date] and the selected date is [yesterday], the previous period data is offset by 3 days from the selected date. The current period data is July 9, and the previous period data is July 6.
- If the relative date is set to [3 days before the selected date] and the selected date is an interval [July 10, 2024 ~ July 15, 2024], the previous period data is offset by 3 days from the start and end of the selected date, also forming an interval. The current period data is [July 10, 2024 ~ July 15, 2024], and the previous period data is [July 7, 2024 ~ July 12, 2024].
-
Compare with fixed date: Select a fixed date interval as the previous period data;
- If the fixed date is set to [July 10, 2024 ~ July 15, 2024] and the selected date is [yesterday], the current period data is July 9, and the previous period data is [July 10, 2024 ~ July 15, 2024].
-
Compare with time macro interval: Determine the previous period data by customizing the time macro. For usage of custom time macros, refer to the document [Dynamic Time Macro](../4-Dynamic Time Macro.md).
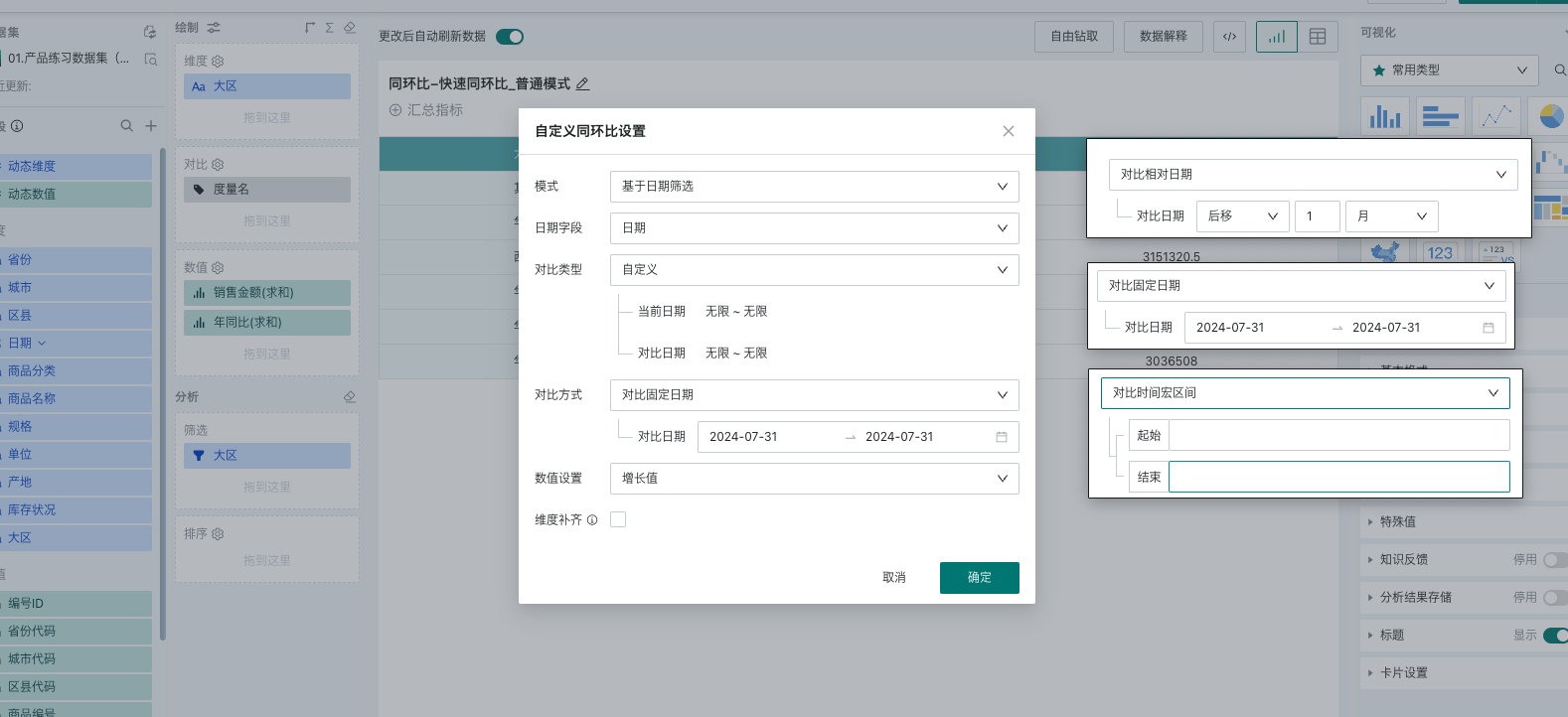
3.3.2. Date Filter-Based Mode
When users want to use text as a dimension and compare current and previous period data through a filter, you can use the date filter-based mode.
The comparison type changes dynamically according to the date granularity, supporting analysis by year, quarter, month, week, and day. For details, refer to the scenarios listed in the comparison type table in this document.
When the comparison type is custom, it means you can arbitrarily select a period as the current and previous period. The configuration details are as follows:
Comparison method: Provides three methods: compare with relative date, compare with fixed date, and compare with time macro interval. The date range selected by the filter determines the current period data, and the comparison date is used to determine the previous period data. Details are as follows (taking the date filter selection [July 10, 2024 - July 31, 2024] as an example):
-
Compare with relative date: Customize the dynamic date as the previous period data by manual input, supporting both forward and backward shifts to determine the direction of the offset. Various granularities (year, month, week, day, not supporting quarter) are also provided to determine the length of the offset;
- If the relative date is set to [move forward 1 month] and the selected date is the current filter's date range, the previous period data is offset by 1 month from the selected date. The current period data is [July 10, 2024 - July 31, 2024], and the previous period data is [August 10, 2024 - August 31, 2024].
-
Compare with fixed date: Select a fixed date interval as the previous period data;
- If the fixed date is set to [July 10, 2024 ~ July 15, 2024] and the selected date is the current filter's date range, the current period data is [July 10, 2024 - July 31, 2024], and the previous period data is [July 10, 2024 ~ July 15, 2024].
-
Compare with time macro interval: Determine the previous period data by customizing the time macro. For usage of custom time macros, refer to the document [Dynamic Time Macro](../4-Dynamic Time Macro.md).
4. Usage Restrictions
-
Only supported when there is a date field in the dataset (newly created date-type calculated fields are also supported);
-
Not supported for detail tables.