Dataset Update
1. Overview
To ensure data timeliness, users need to update datasets. To meet different business scenarios, Guandata BI supports scheduled updates, manual updates, URL trigger updates, and other modes. Users can configure update conditions for datasets to make datasets automatically update under specific conditions. For some datasets (such as Excel, CSV, and account datasets, etc.), Guandata BI also supports users to clean specified data of datasets on demand, controlling dataset size.
After completing data updates, users can understand the specific links, execution status, execution duration, and complete log information of dataset update tasks through "View Update History", improving the problem troubleshooting efficiency of dataset update tasks. This article will provide detailed explanations of the above update configurations.
2. Automatic Update Configuration
The update method of datasets will be affected by the dataset's connection method (direct connection/extraction) and the dataset's type. Users can configure the update method in the dataset integration page and dataset details page (some configuration items have differences), as follows:
Configuration Item | Integration Page | Details Page | Reference | |
General | Scheduling Status | ✅ | ✅ | |
24h Scheduled Update Task Density Map | ✅ | ✅ | ||
Failure Retry | ❌ | ✅ | Introduced below | |
Direct Connection | Cache Validity Period | ✅ | ✅ | |
Real-time Card Data | ✅ | ✅ | ||
Extraction | Data Update Cycle | ✅ | ✅ | |
Deduplication Primary Key | ✅ | ✅ | ||
Incremental Update | ✅ | ✅ | ||
(Incremental Update Mode) Auto Update Data Structure | ❌ | ✅ | Introduced below | |
(Incremental Update Mode) Pre-cleanup Rules | ❌ | ✅ | Introduced below | |
Task Priority | ✅ | ✅ |
2.1. Failure Retry
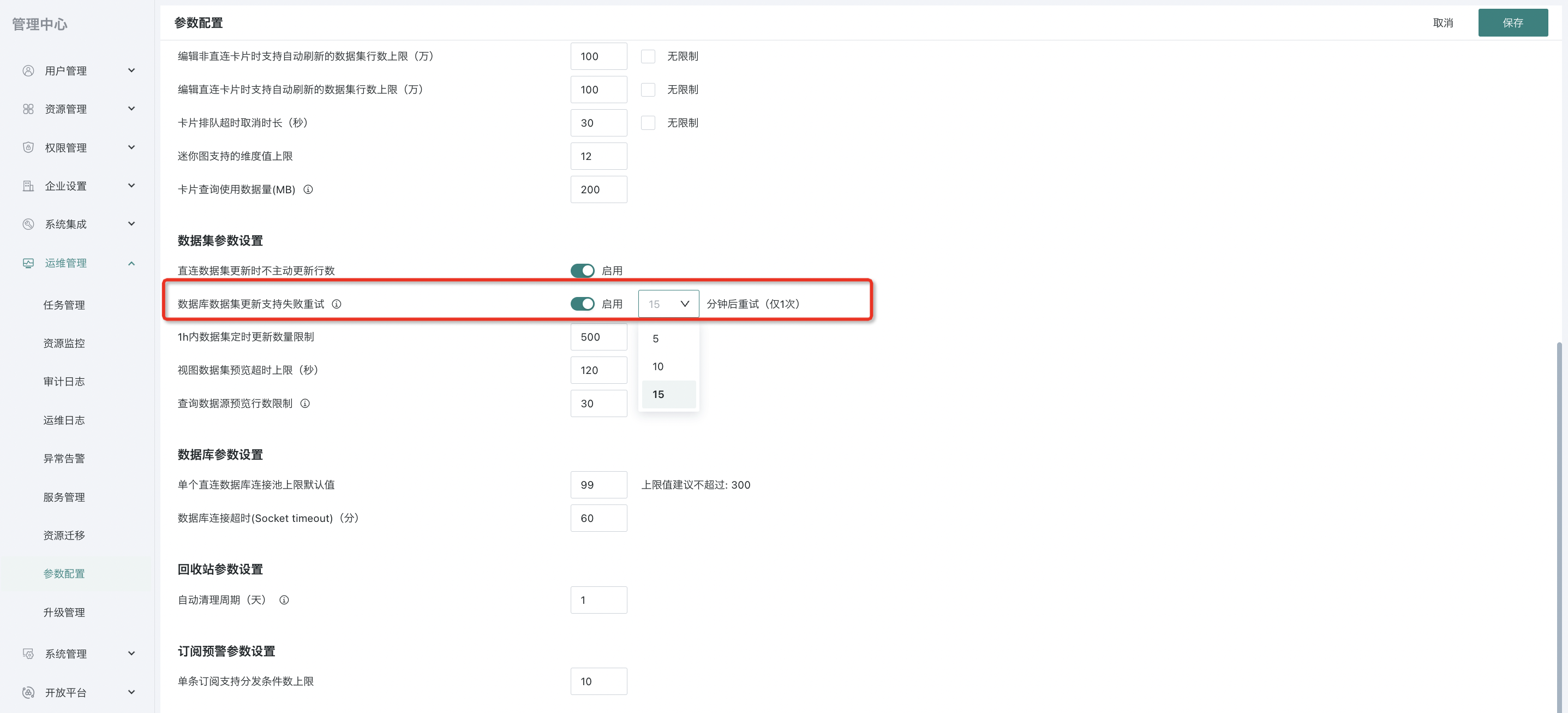
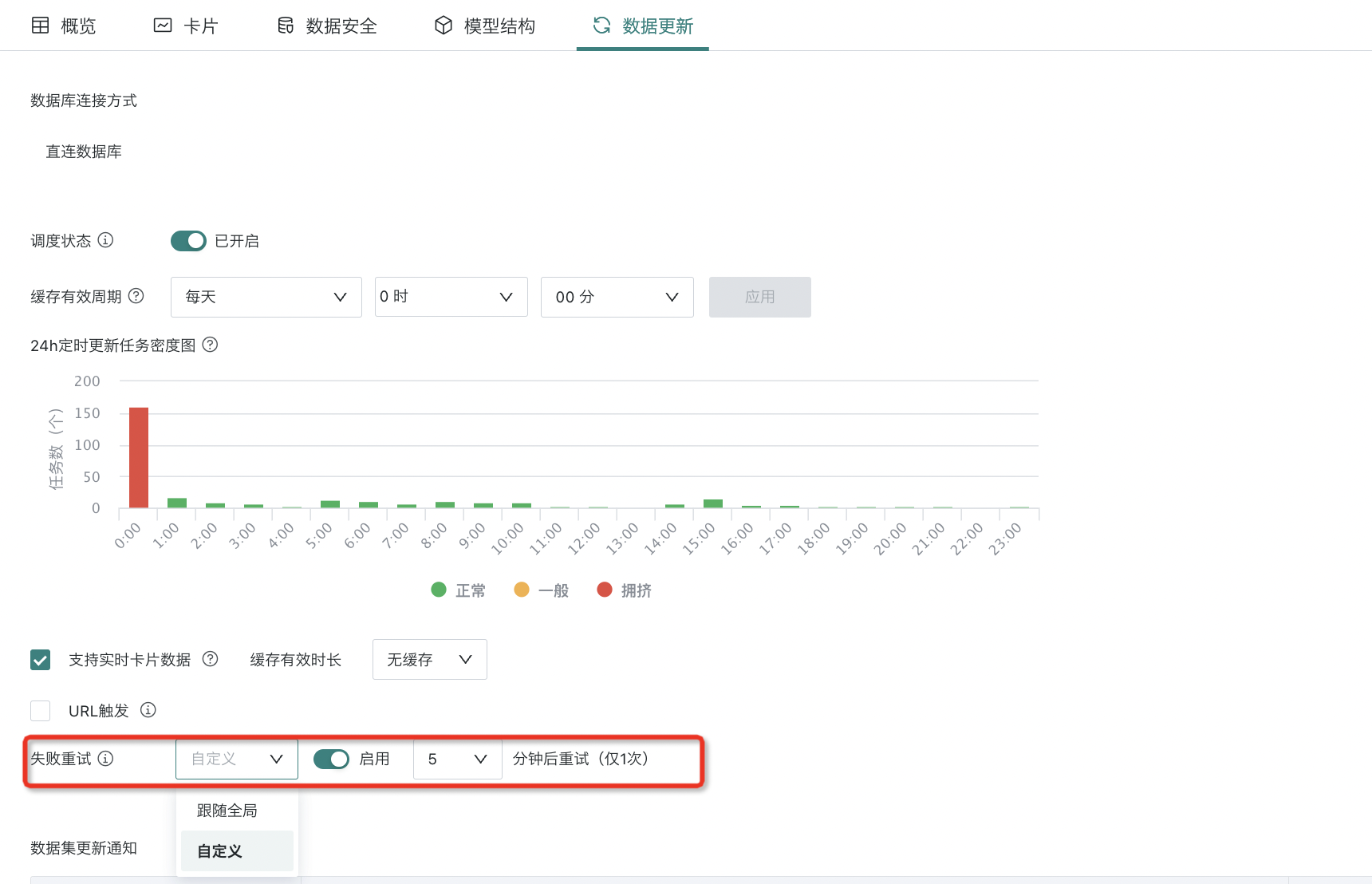
During dataset update, tasks may fail due to task exceptions. Users can enable "Failure Retry" to ensure data timeliness and accuracy, that is, perform task retry at the first time. The retry interval supports two modes: user-defined and follow global configuration. Both modes can set retry intervals at minute level (5/10/15 minutes).
Note:
1. "Failure Retry" only supports automatic updates (including: scheduled updates, URL triggers), and does not support manual updates.
2. Failure retry only supports "1 time".
The "Failure Retry" function has two modes: follow global and custom, which can be configured in the Management Center and dataset details page respectively:
- Follow Global: Users can enable "Failure Retry" in Management Center > Operation & Maintenance Management > Parameter Configuration. After completing the relevant configuration, the system will default all datasets to "Follow Global" settings;
- Custom: If you only need to set "Failure Retry" for a single dataset, users can enable "Failure Retry" on the dataset details page, set the retry interval, and after setting, it will take priority over the global level settings.
2.2. Auto Update Data Structure
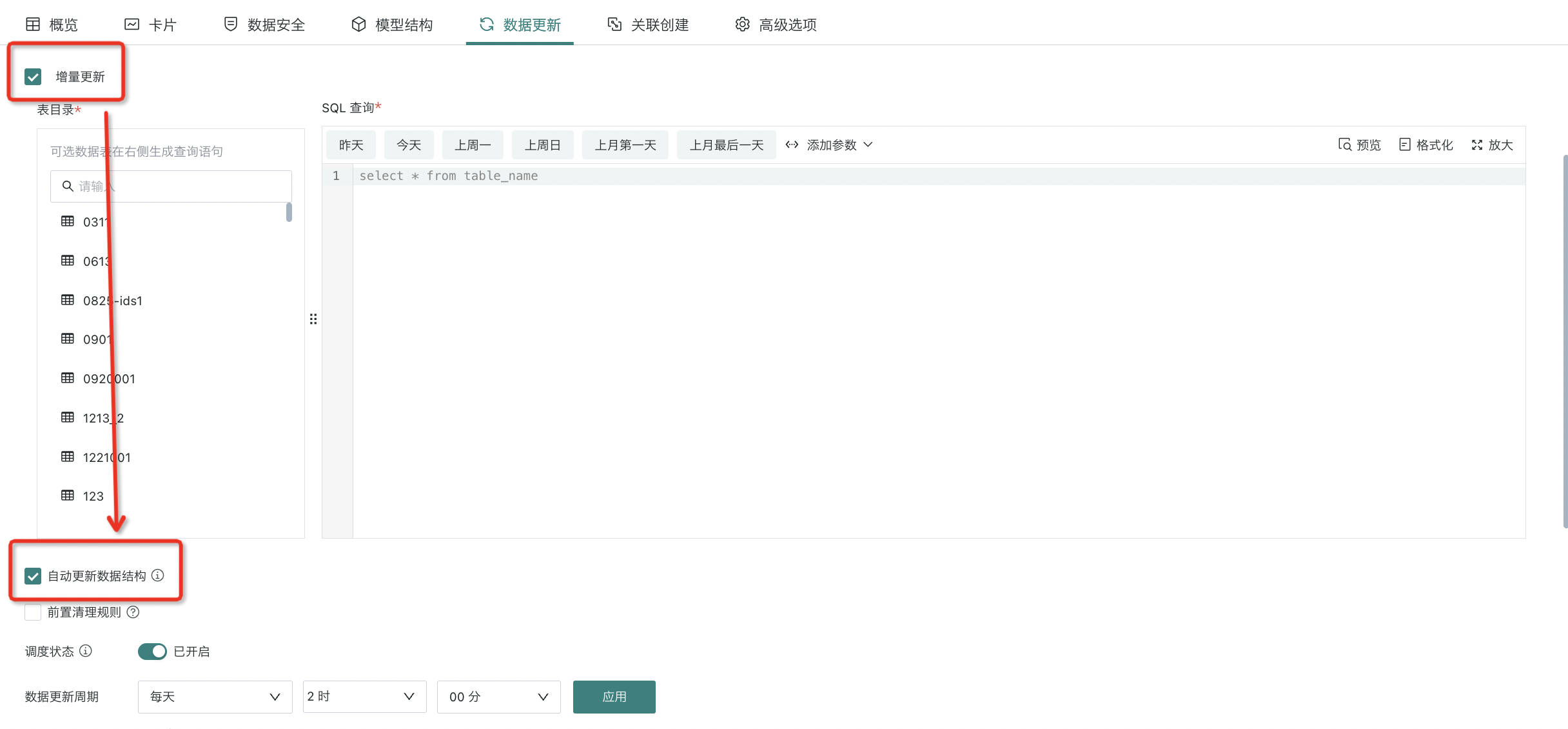
For extraction datasets, you can check whether to enable "Incremental Update". For the definition and explanation of incremental updates, please refer to [Standard Database Connection Guide](../3-Database Data Integration/0-Database/1-Standard Database Connection Guide.md#full-update-incremental-update).
After enabling, you can continue to choose whether to check "Auto Update Data Structure". After checking, the dataset structure can change with the source database structure changes.
Note:
1. Datasets that support "Auto Update Data Structure" need to meet 3 conditions: database source datasets, extraction method, and incremental update enabled;
2. "Auto Update Data Structure" currently only supports adding fields to datasets after source field addition, and does not delete dataset fields after source field deletion.
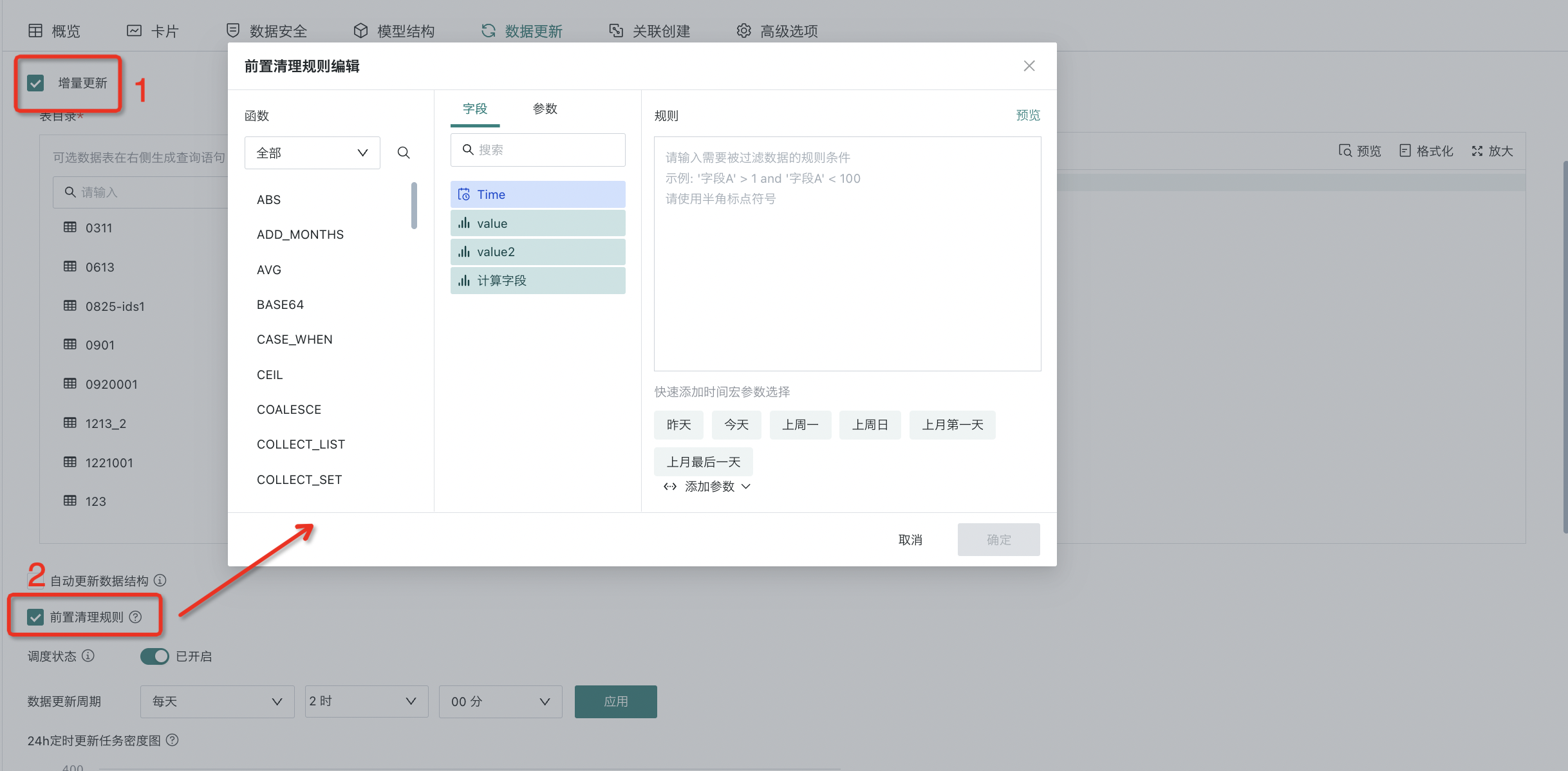
2.3. Pre-cleanup Rules
For extraction datasets, after checking "Incremental Update", you can choose whether to check "Pre-cleanup Rules". After checking, data that meets the rules will be automatically deleted from the dataset before updating.
Note: For system-built incremental update datasets (except builtin_user, builtin_data_source, builtin_data_flow), pre-cleanup rules are also supported.
3. Manual Update Configuration
In addition to configuring update conditions for datasets to achieve automatic dataset updates, users can also manually complete dataset update operations.
For most datasets, clicking the "Update" button on the data details page can achieve instant data updates. For Excel and CSV type file datasets, manual data updates need to be achieved through the "Data Append/Replace" function.
3.1. Data Update (Non-Excel/CSV)
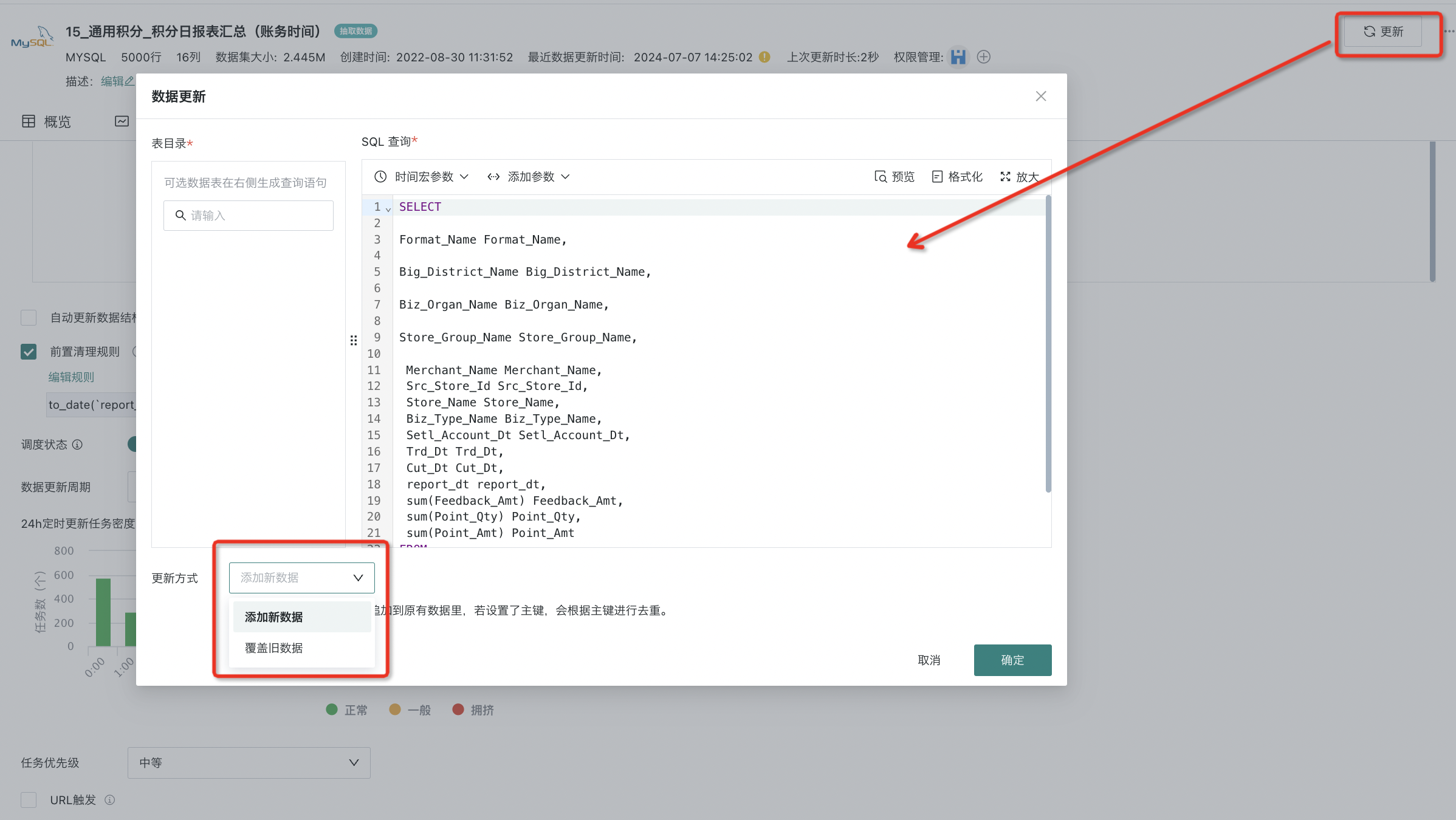
For most data (except Excel/CSV), click the "Update" button in the upper right corner of the dataset details interface to manually trigger instant dataset updates.
For extraction datasets, the update method is divided into two modes: adding new data and overwriting old data.
-
Add New Data: The execution result will be appended to the original data. If a primary key is set, deduplication will be performed according to the primary key.
-
Overwrite Old Data: The execution result will replace the original data, and all historical data will be cleared.
Note:
1. For card dataset types, for example: Dataset A creates Card B, and Card Dataset C is created based on Card B. The specific update situation is:
(1) Regarding the structure of card datasets: If Card B is modified, Card Dataset C will not automatically sync, and Card Dataset C needs to be manually updated to sync.
(2) Regarding the data content of card datasets: When the original Dataset A is updated, it will trigger data updates for Card Dataset C.
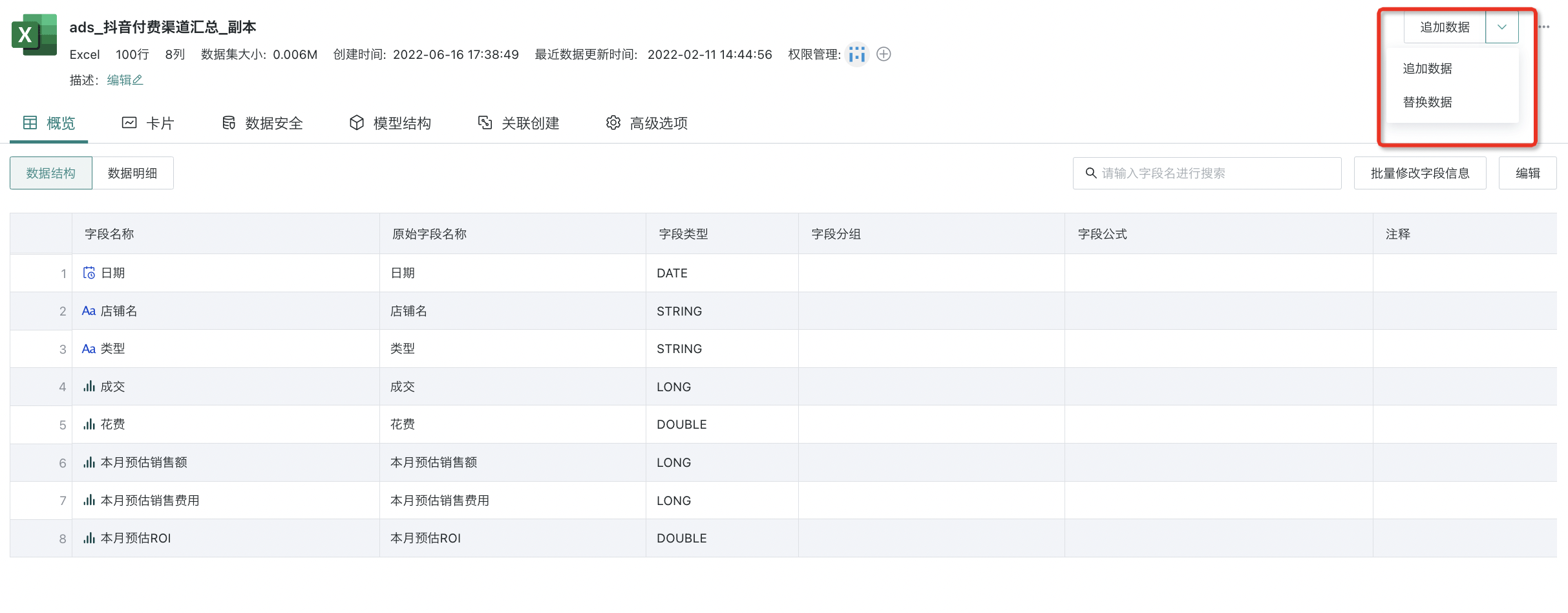
3.2. Data Append/Replace (Excel/CSV)
For datasets imported from files (Excel/CSV), you can select "Append Data" or "Replace Data" in the upper right corner of the dataset details page. For more specific operations, please refer to the relevant documentation for importing data from files. For details, please refer to [Import Data from Files](../2-File Data Integration/0-Local Files.md#25-append-replace-data).
4. URL Trigger Update
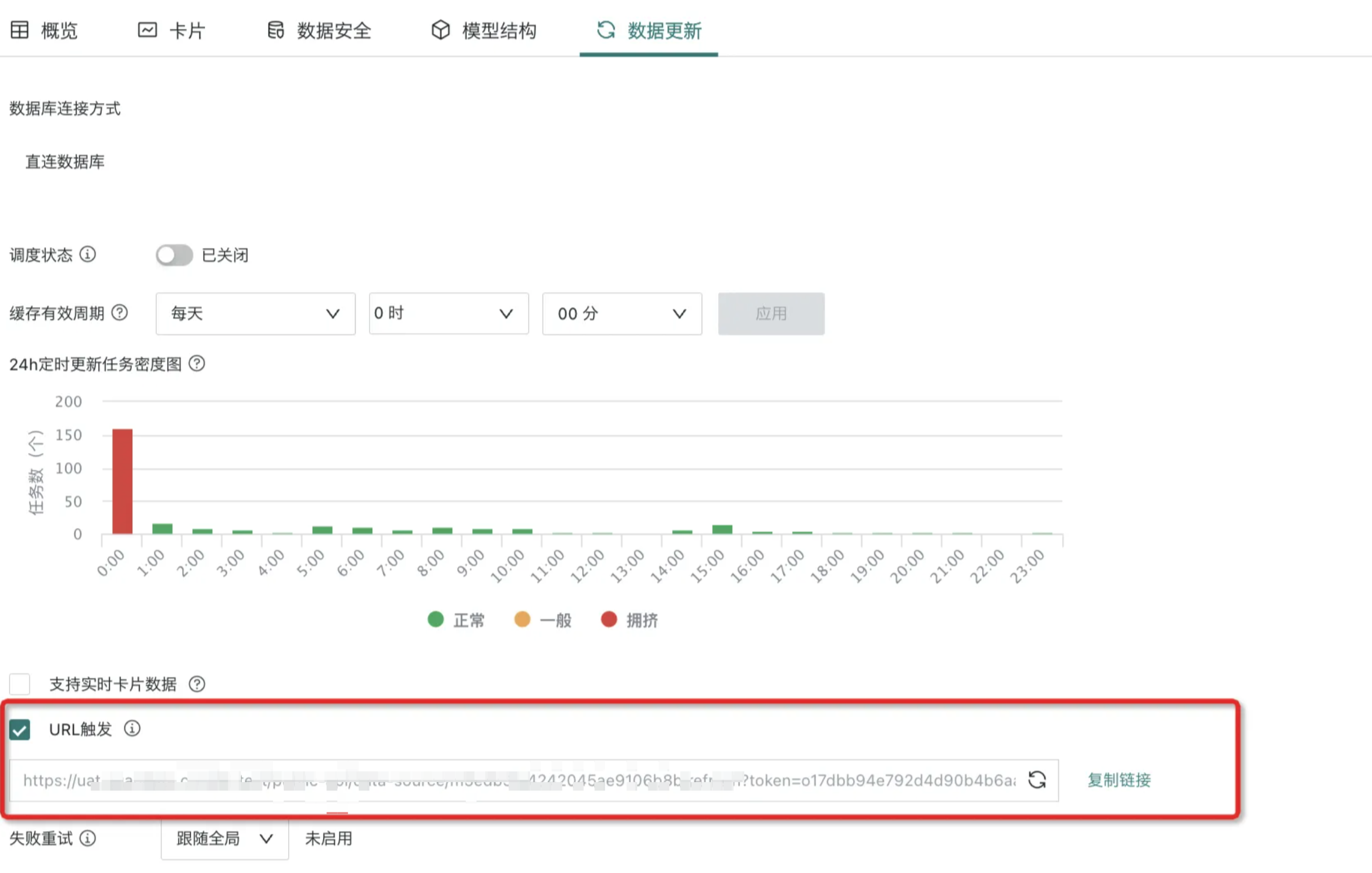
The data update URL trigger mechanism refers to the function of external updates for datasets connected through database connections (such as direct connection datasets, extraction datasets, FTP datasets, etc.) through URL triggers, that is, convenient for external systems to notify the Guandata platform to sync data in a timely manner after data updates are completed.
On the dataset details page, you can choose whether to enable "URL Trigger" updates. After checking, users can directly update the current dataset through the following URL in external systems without user verification. For details, please refer to View Data Update URL Trigger Mechanism.
Note:
1. Dataset updates via URL trigger are not affected by scheduling status (enabled or disabled).
2. For example, you can manually click the update button through the Guandata BI user interface to immediately update the dataset, or trigger the update process by sending a URL request with specific parameters to the system.
5. Data Cleanup
Users can set certain cleanup rules for data in datasets through the "Data Cleanup" function, only retaining data that meets certain rules, filtering out data that does not meet requirements, and efficiently obtaining data that meets requirements.
Note:
1. View datasets and direct connection datasets do not support data cleanup;
2. Other datasets imported from files and connected to databases support data cleanup.
3. Built-in datasets support data cleanup.
- Click the "···" operation bar in the upper right corner, select "Data Cleanup", and the "Data Cleanup" popup will appear on the page. Click the "New" button to enter the "Rule Editor".
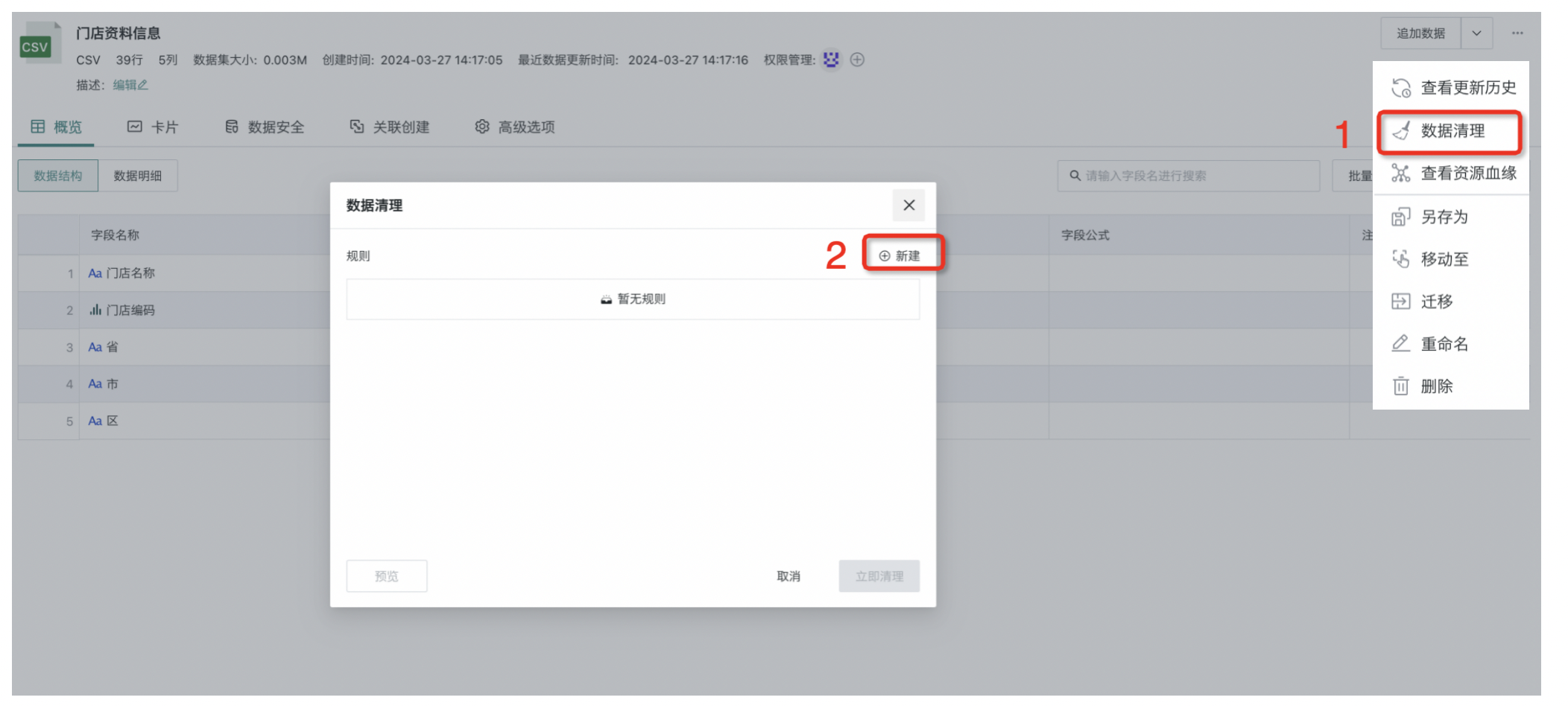
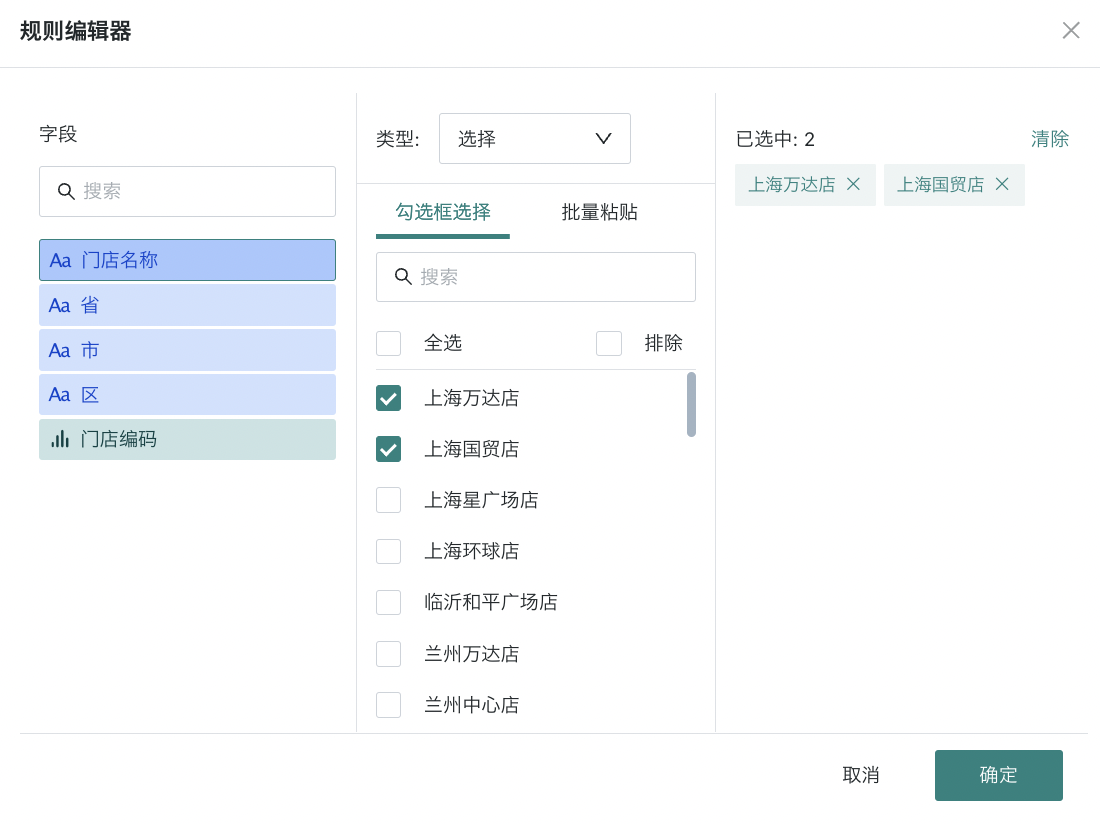
- In the "Rule Editor", select fields, then select rule types, and set cleanup rules. For example, in the figure below, data related to "Shanghai Wanda Store" and "Shanghai Guomao Store" is cleaned up.
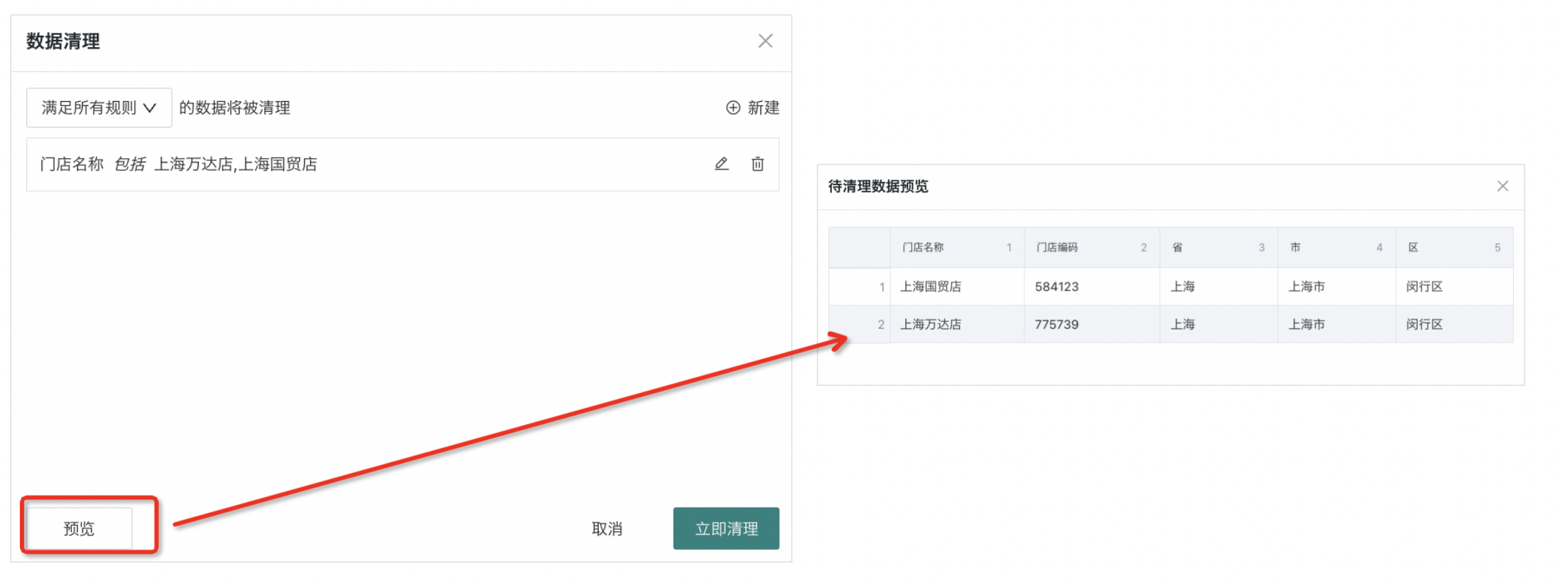
- Click Preview to view the "Data to be Cleaned Preview". After confirming it's correct, click "Clean Immediately" to complete the operation.
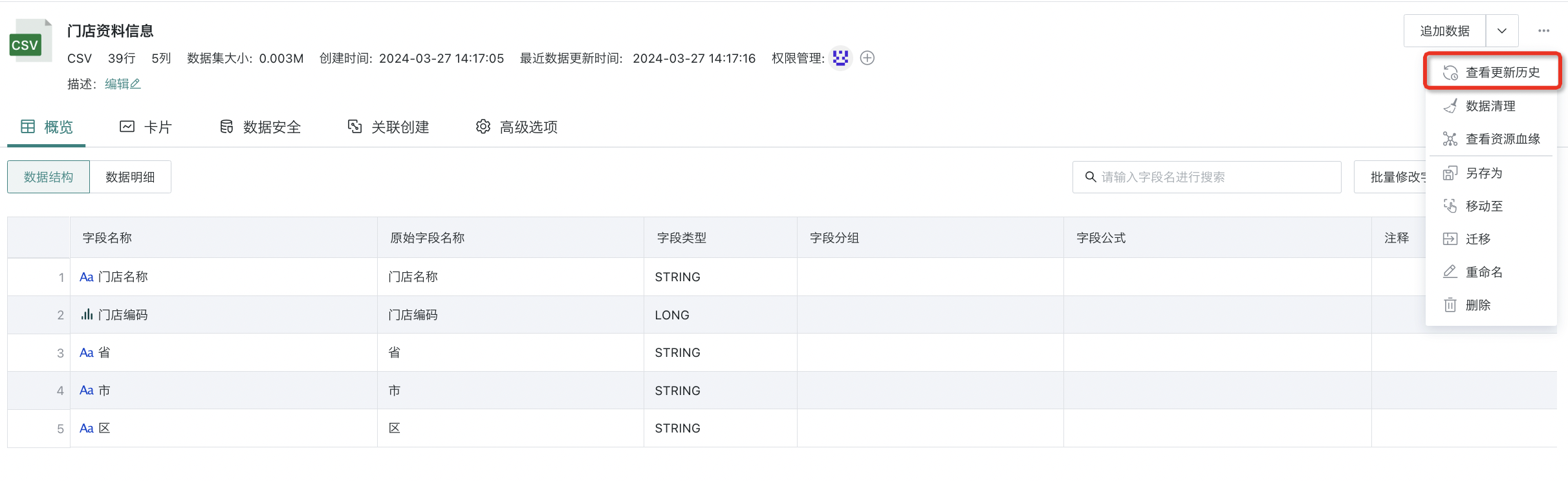
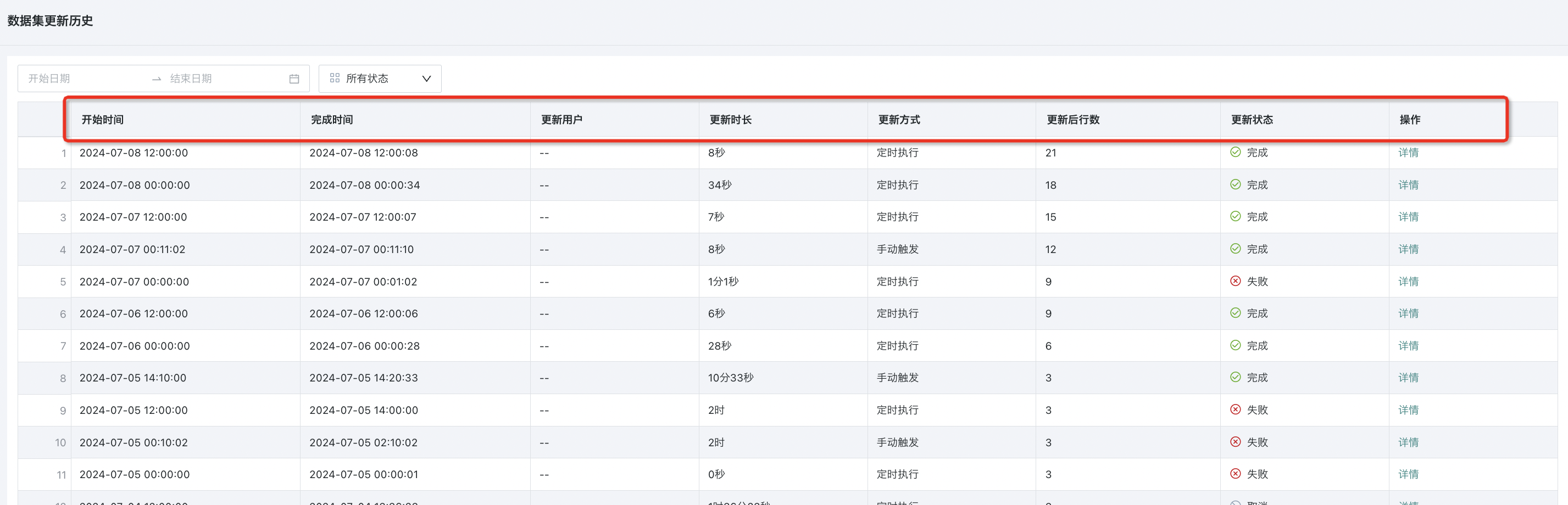
6. View Update History
You can view dataset update history on the dataset details page, supporting viewing specific links, execution status, execution duration, and complete log information, improving the problem troubleshooting efficiency of dataset update tasks. Records are retained for 3 months by default. If you need to save for a longer time, please contact Guandata staff for adjustment.
Note: In version 6.3, the dataset update history monitoring has been restructured for log management. Historical running tasks before the version upgrade time point do not support viewing according to the new logs, and you can jump to Management Center > Task Operation & Maintenance for problem troubleshooting.
The monitoring list supports viewing task information items such as "Update User", "Update Method", and "Operation". The following selects three of them for explanation.
-
Update User: Records the operating user of the dataset update task. The "Update User" for manual triggers is the current operating user, the update user for scheduled and advanced scheduling triggered update tasks is recorded as "-", and the update user for API triggered updates is recorded as the user in the token.
-
Update Method: Includes API, manual trigger, scheduled scheduling, and advanced scheduling trigger.
-
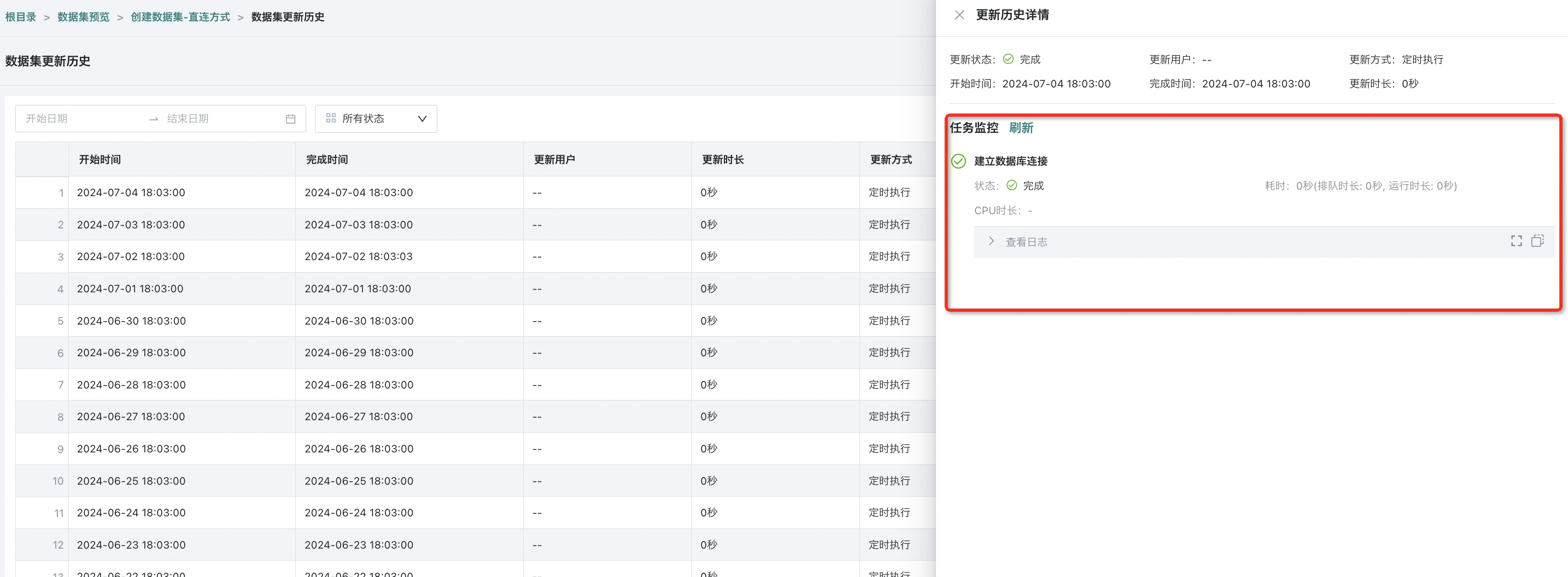
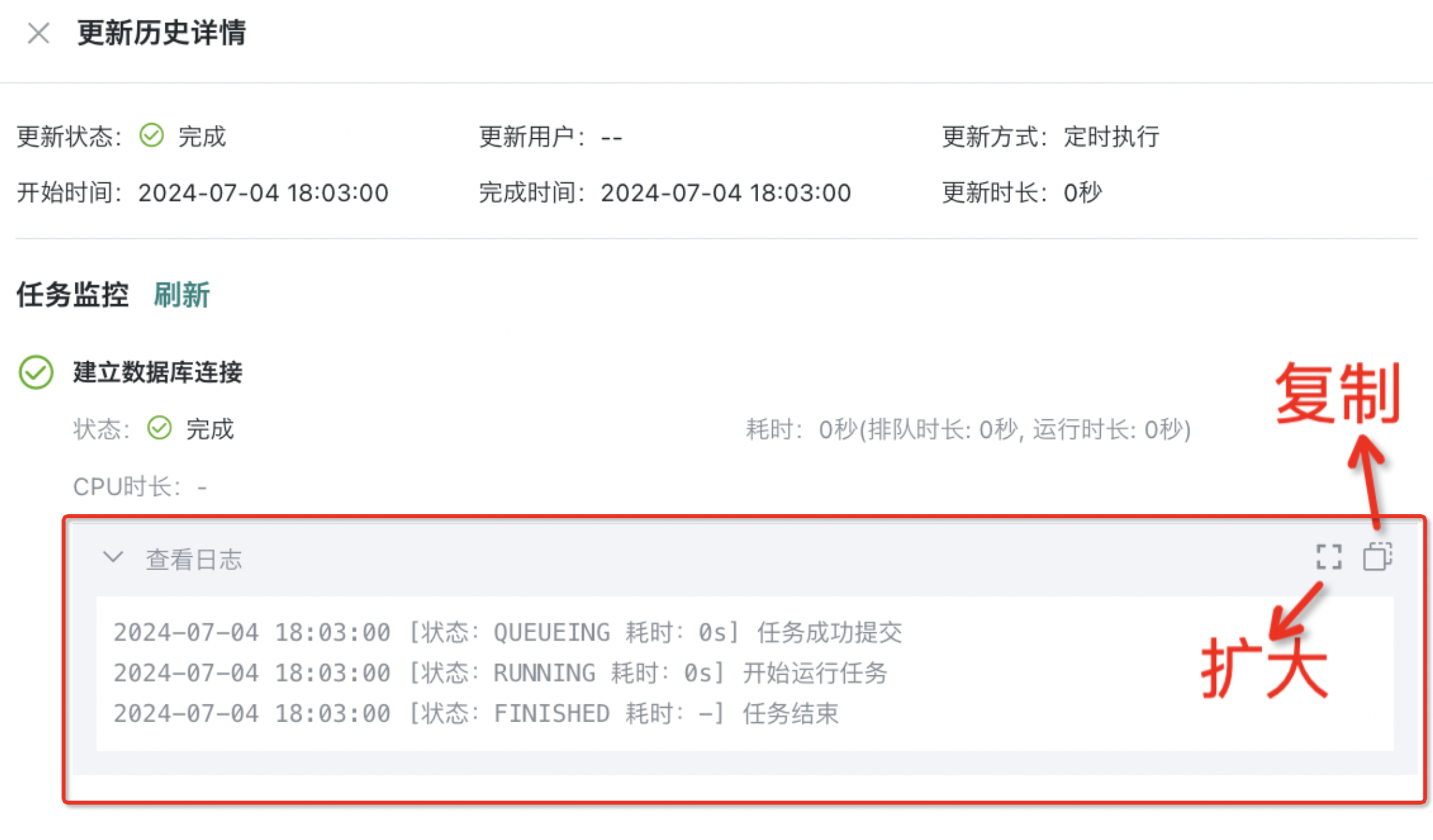
Operation: Click "Details" to view the specific links, execution status, execution duration, and complete log information of the update task. On the update history details page, click "View Log" for each link to display the log in full screen and copy all current logs to the clipboard.
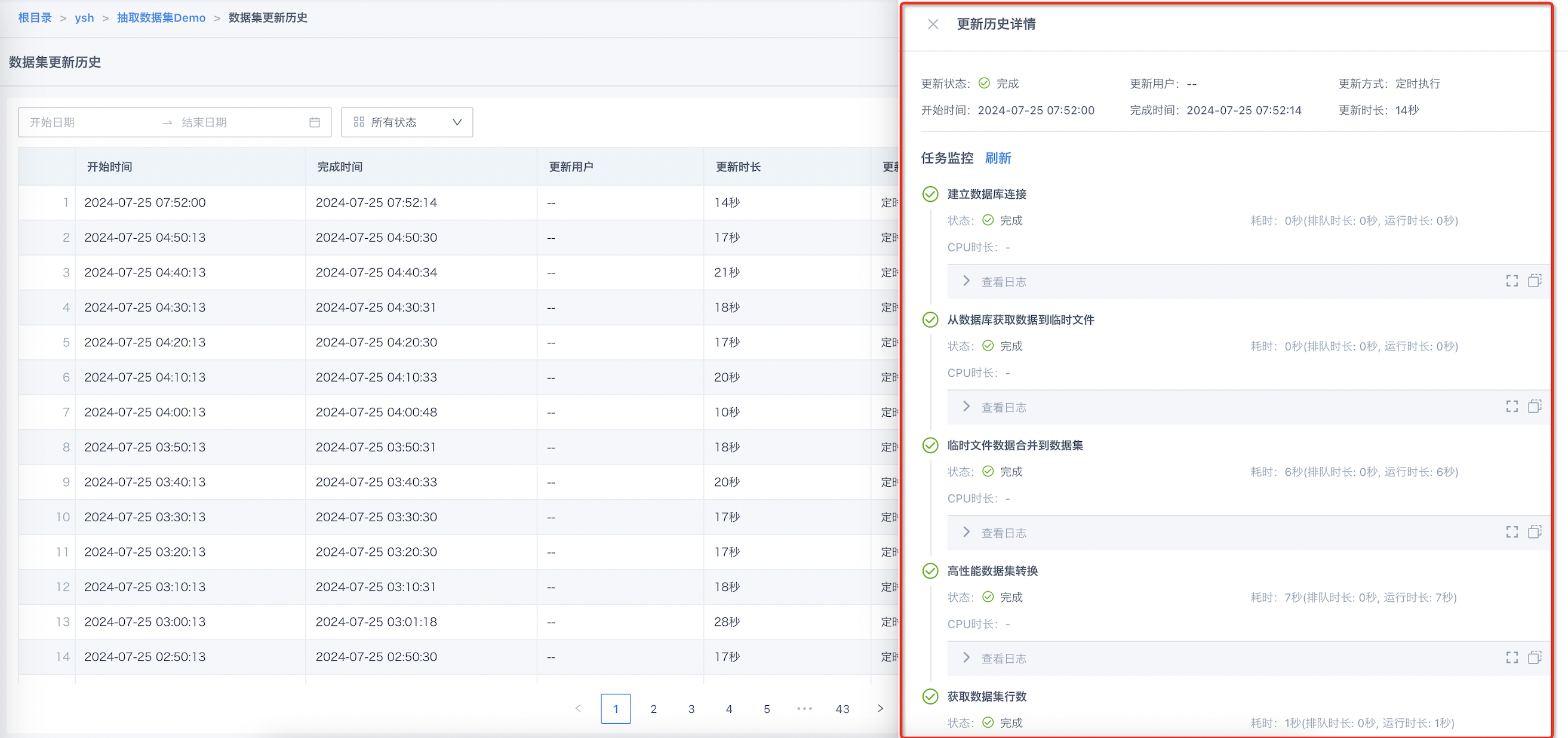
- Extraction Dataset Example: Task links include "Establish Database Connection", "Get Data from Database to Temporary File", "Merge Temporary File Data to Dataset", and "Get Dataset Row Count".
- Direct Connection Dataset Example: Task links include "Establish Database Connection".