Dataset Preview and Edit
1. Overview
To help users better understand and use data, Guandata BI supports users to preview the specific data and various information of datasets, and on this basis, perform a certain degree of editing on datasets. This article will provide detailed explanations for this.
2. Operation Guide
2.1. Preview
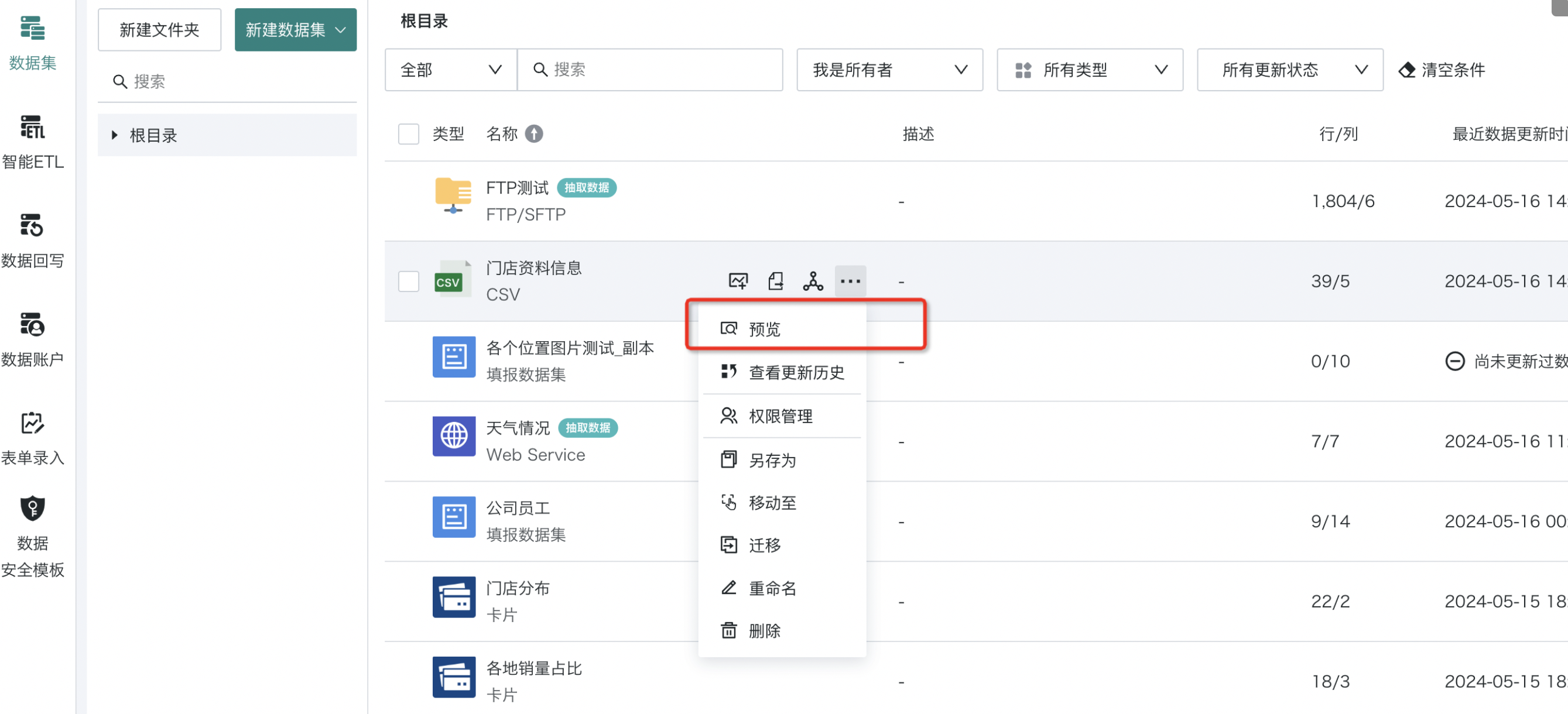
On the dataset list page, click the "..." button of any dataset and select "Preview" to view the data of the current dataset (up to 30 rows of data can be previewed). In addition to using the "Preview" function, you can also go to the "Overview > Data Details" interface on the dataset details page to view dataset data. For related operations, please refer to [Data Details](2-Dataset Preview and Edit.md#data-details) below.
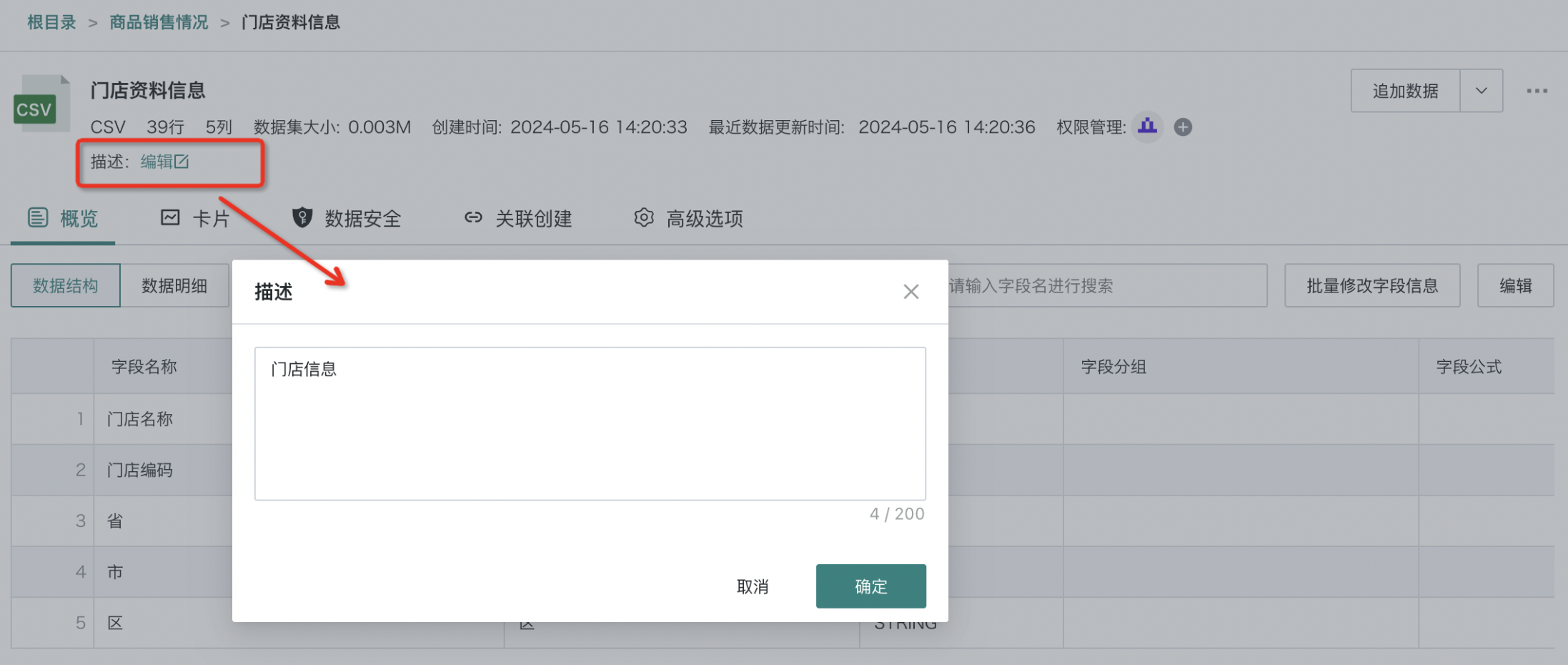
2.2. Description
When creating a dataset, you can add description information when confirming the data table information; on the dataset details page, you can see the added description information and also edit it.
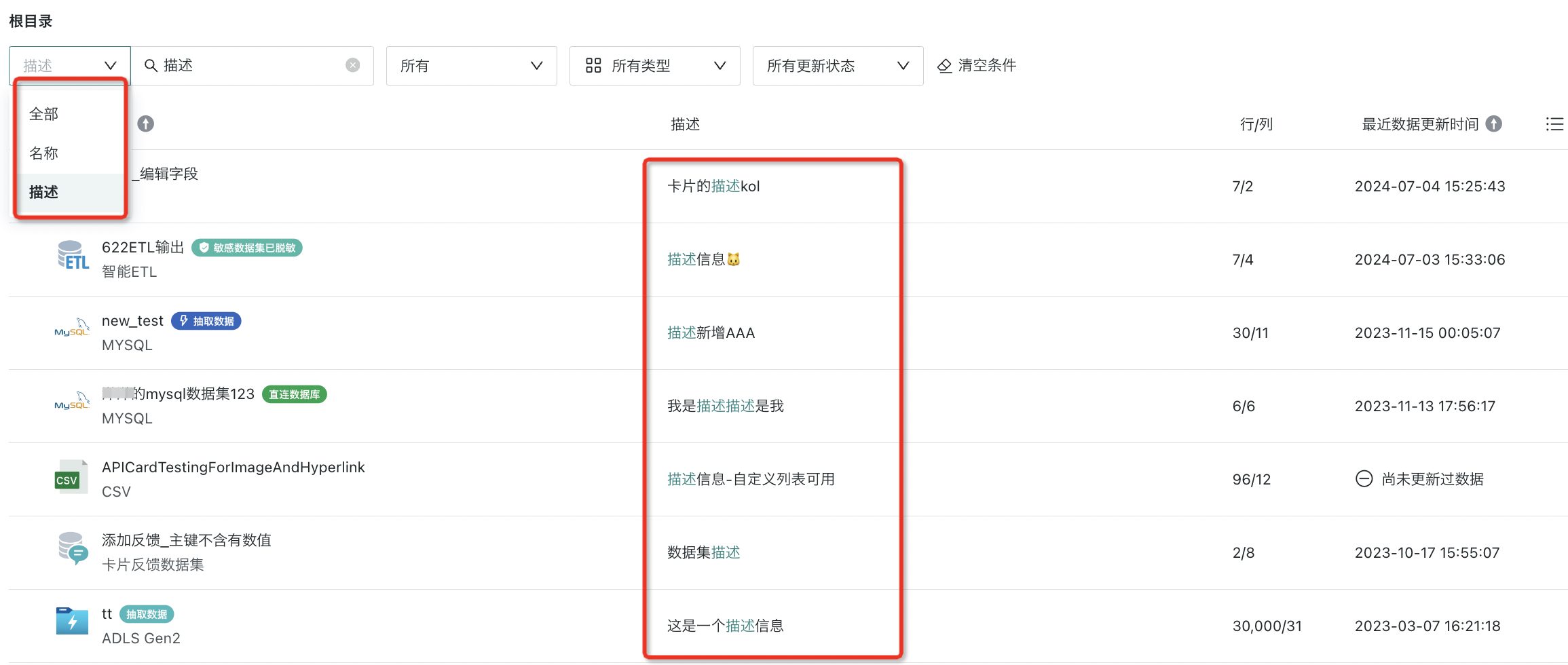
After adding description information to the dataset, a description information column is added to the data center list page. When using the search bar in the upper left corner of the page, you can switch to search by name/description/all, and search keywords will be highlighted in the results.
2.3. Overview
In the "Overview" interface of the dataset details page, you can view detailed information of the dataset, including "Data Structure" and "Data Details", and you can also perform a series of editing operations on the dataset.
Data Structure
After clicking "Data Structure", you can view the description information and field information of the dataset, and perform editing and batch modification operations on the dataset fields.
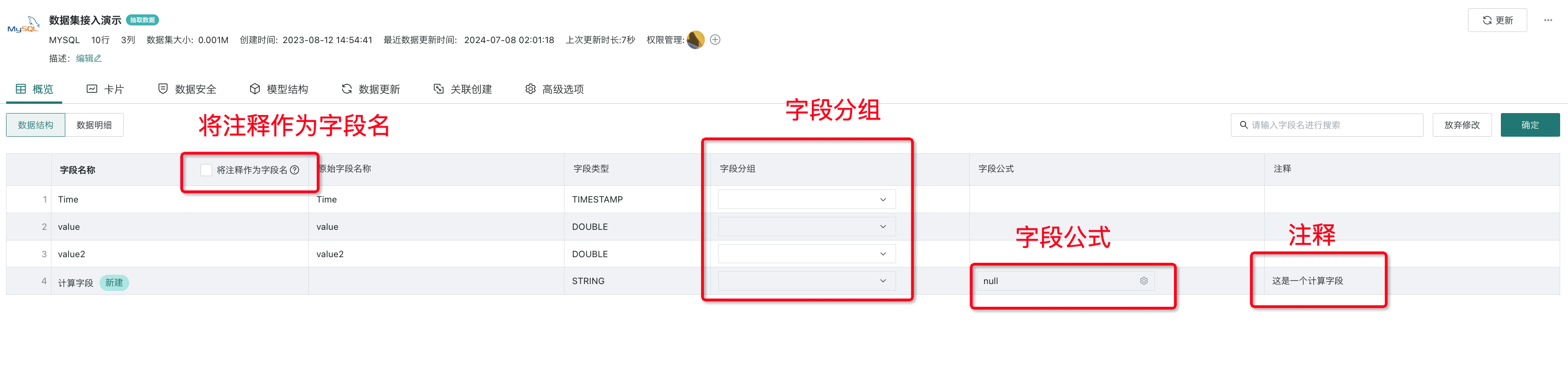
Edit
Click the "Edit" button in the upper right corner of the interface to configure as follows:
-
Use comments as field names (only for database datasets): Checking "Use comments as field names" can use field comments as dataset field names. After checking, field names will automatically sync to the field comments already set in the database.
-
Field grouping: You can select grouping for fields.
-
Field formula: The "Field formula" column for newly created calculated fields or grouped fields will have an operation box with a settings icon. Click to edit the calculation formula or grouping.
-
Comments: Add comments to various fields of the dataset.
Note:
1. Non-newly created calculated fields or grouped fields have no input box and cannot be edited.
2. The "Use comments as field names" here is not to use the "Comments" manually added by users in "Overview" as dataset field names, but to automatically sync field names to the field comments already set in the database.
Batch Modify Field Information
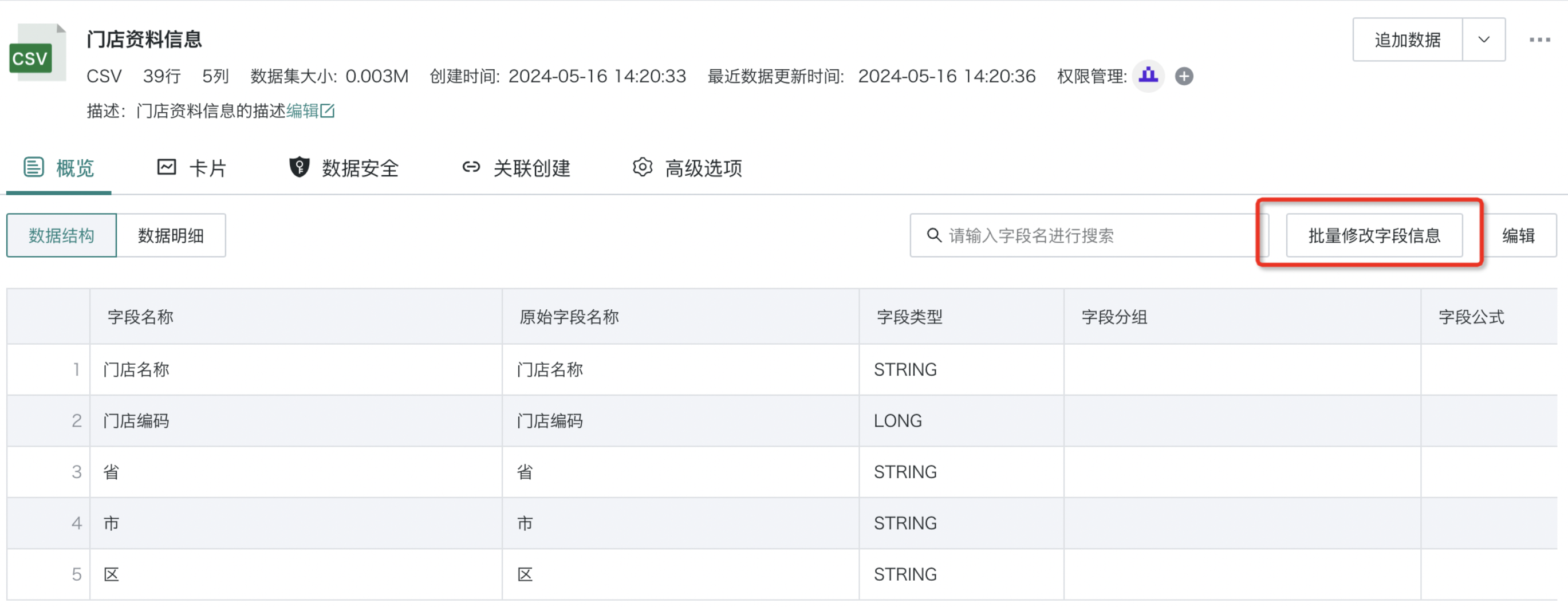
Supports batch modification of field information. The operation steps are as follows.
-
Click the "Batch Modify Field Information" button.
-
Click the green highlighted "Download Template" button in the popup to download the Excel document.
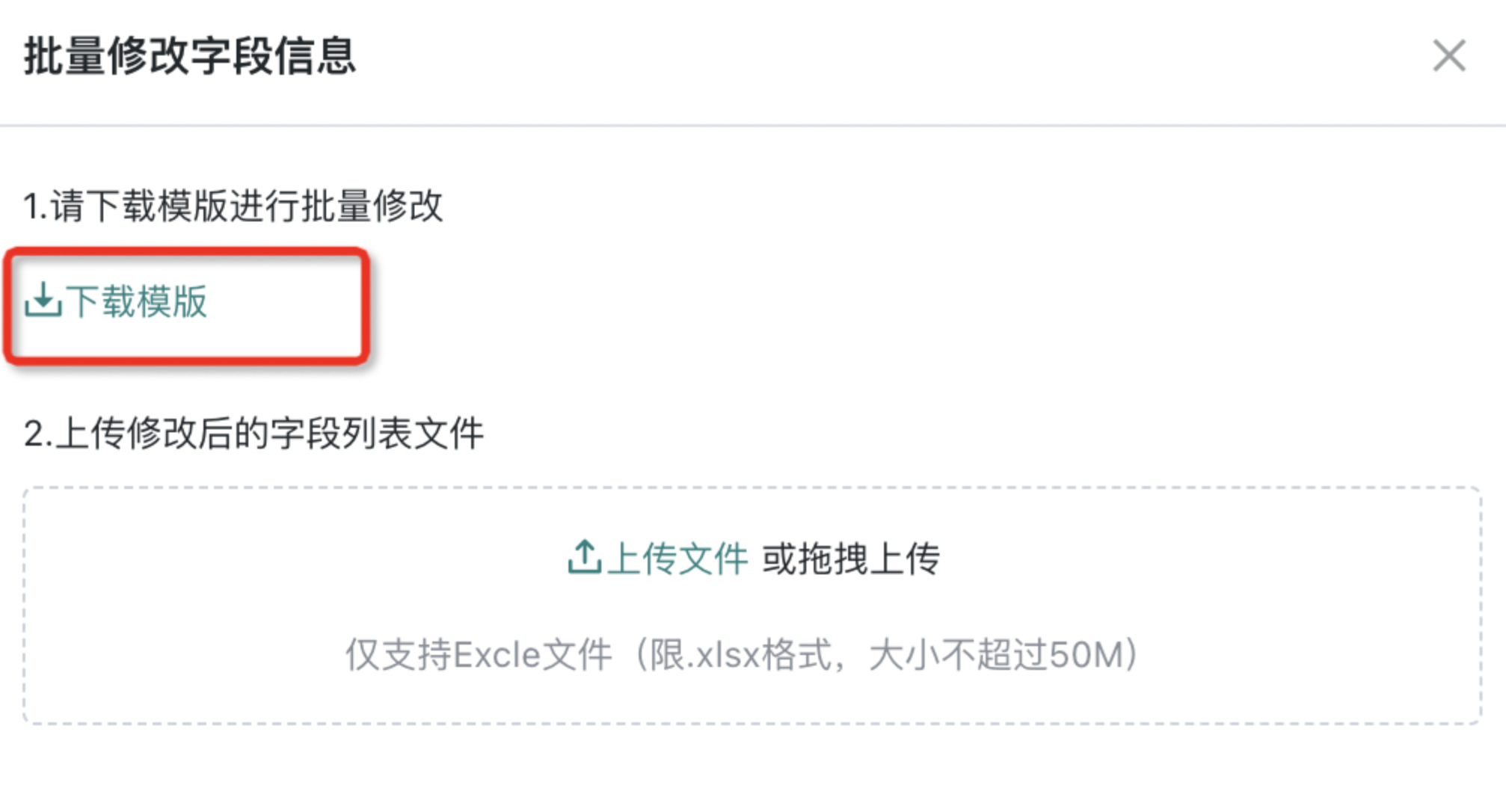
- After completing the template content according to modification requirements, upload to complete the corresponding field information batch modification. Calculation fields and ETL nodes downstream that reference this dataset will automatically inherit the modified field names.
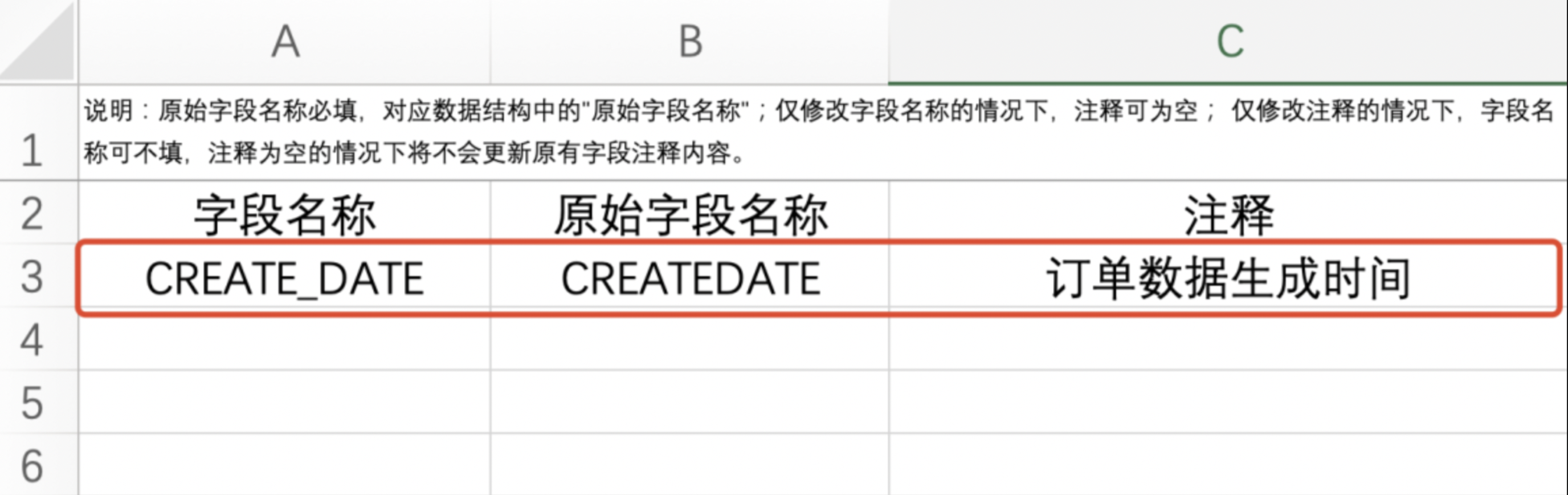
Note:
1. When "Download Template" gets the input template for information to be modified, the original field name is required, corresponding to "Original Field Name" in the data structure;
2. When only modifying field names, comments can be empty;
3. When only modifying comments, field names can be left unfilled. When comments are empty, the original field comment content will not be updated.
Data Details
Users can preview the specific data of the dataset in the "Data Details" interface, providing 1000 rows of data preview. On this basis, you can perform data filtering, create new calculated/grouped fields, and export dataset operations.
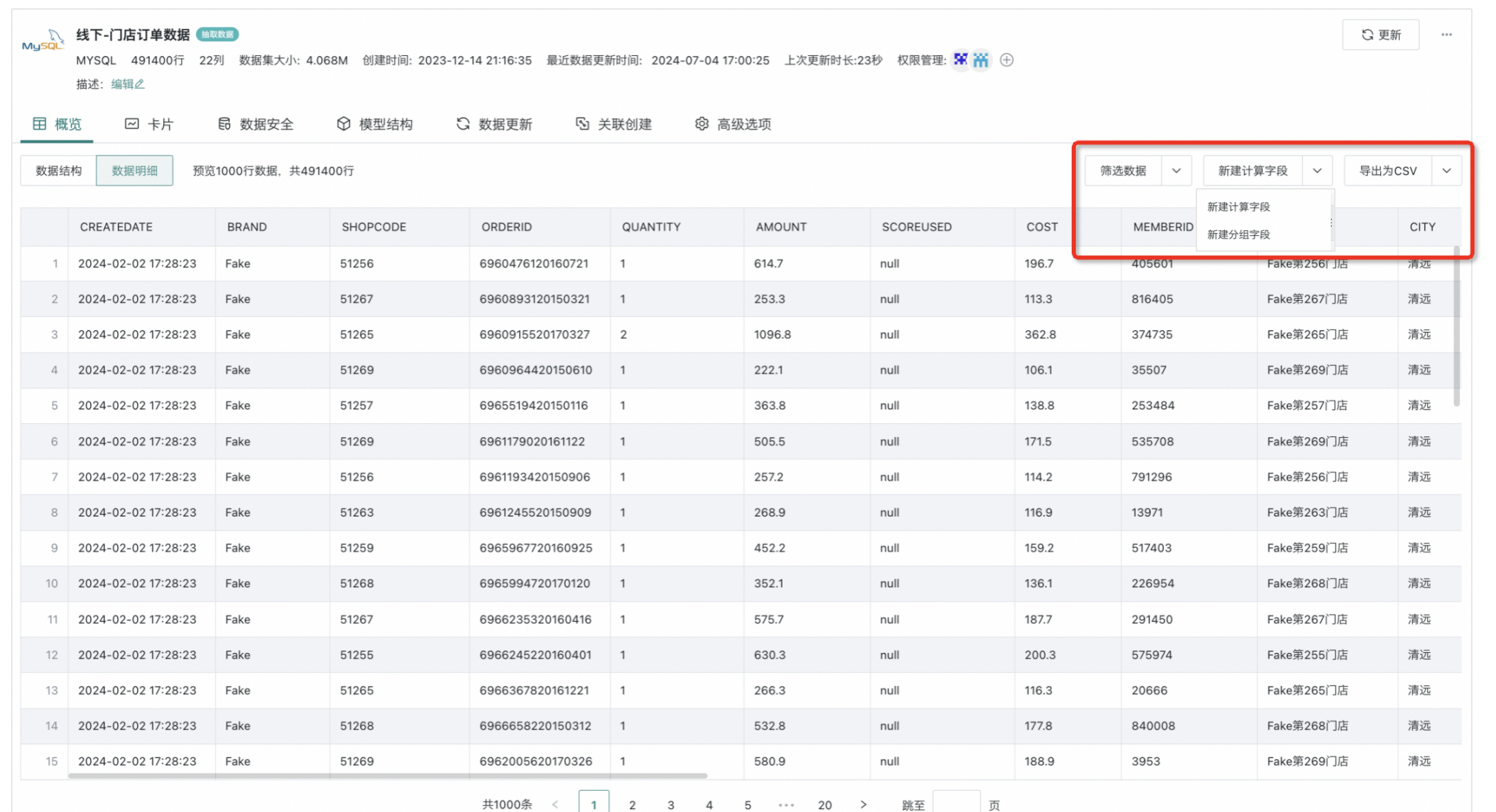
Filter Data
You can filter the preview data, supporting two methods: setting filter rules and selecting columns.
- Method One: Set Filter Rules
- Click "Filter Data" in the upper right corner to enter the "Filter Rules" editing popup, and click "New";
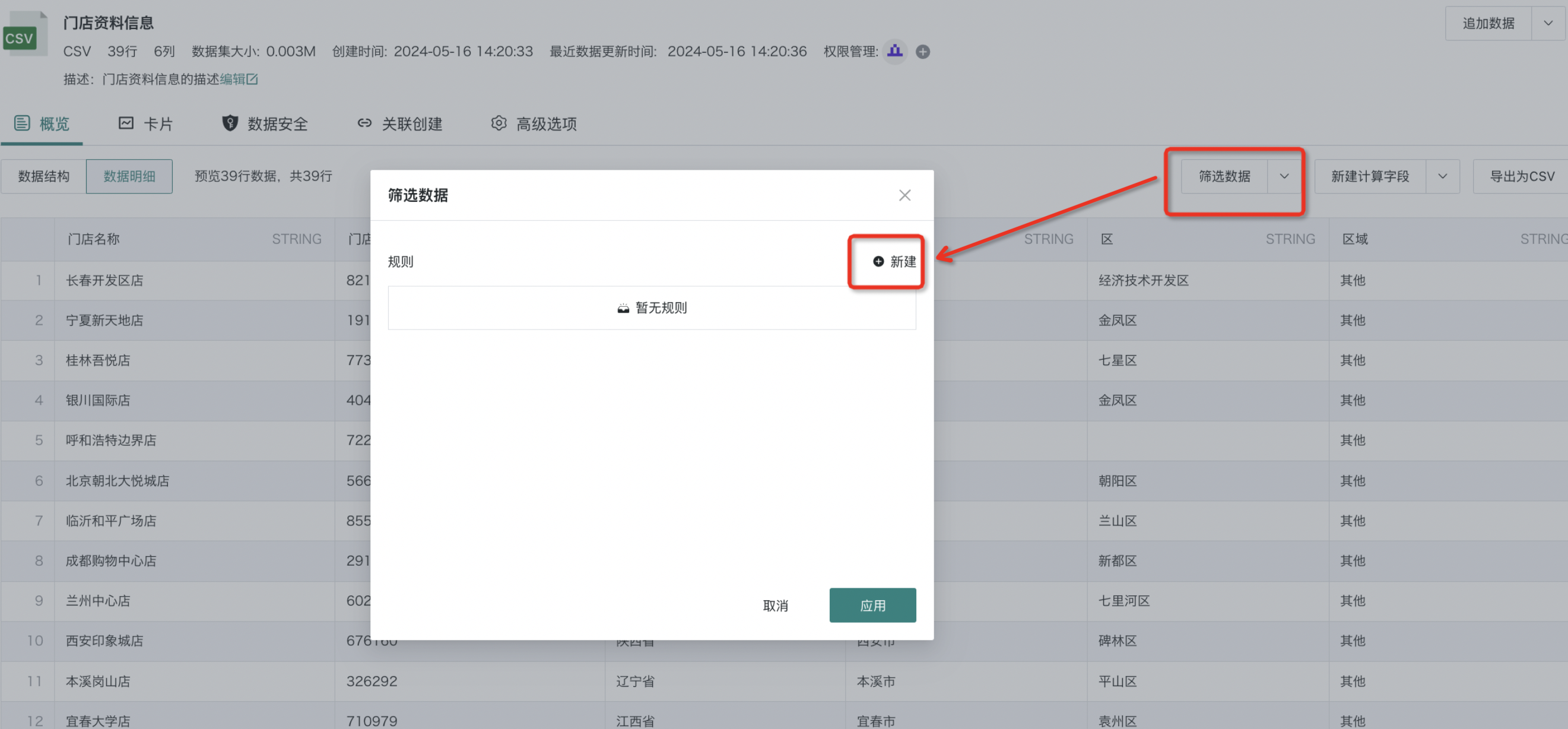
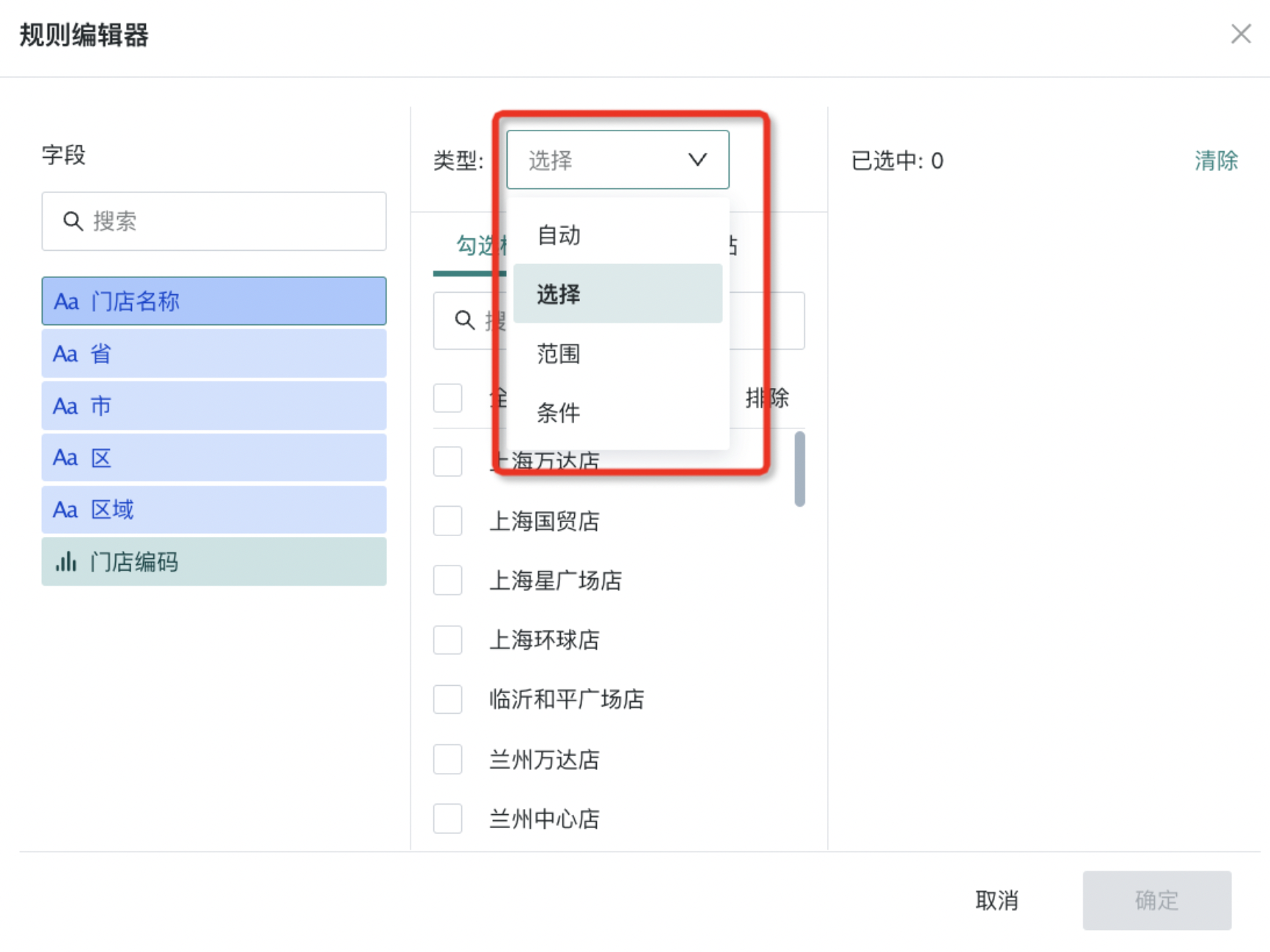
- Enter the "Rule Editor", select fields; then according to page prompts, set the filter type (3 types in total: automatic, selection, range).
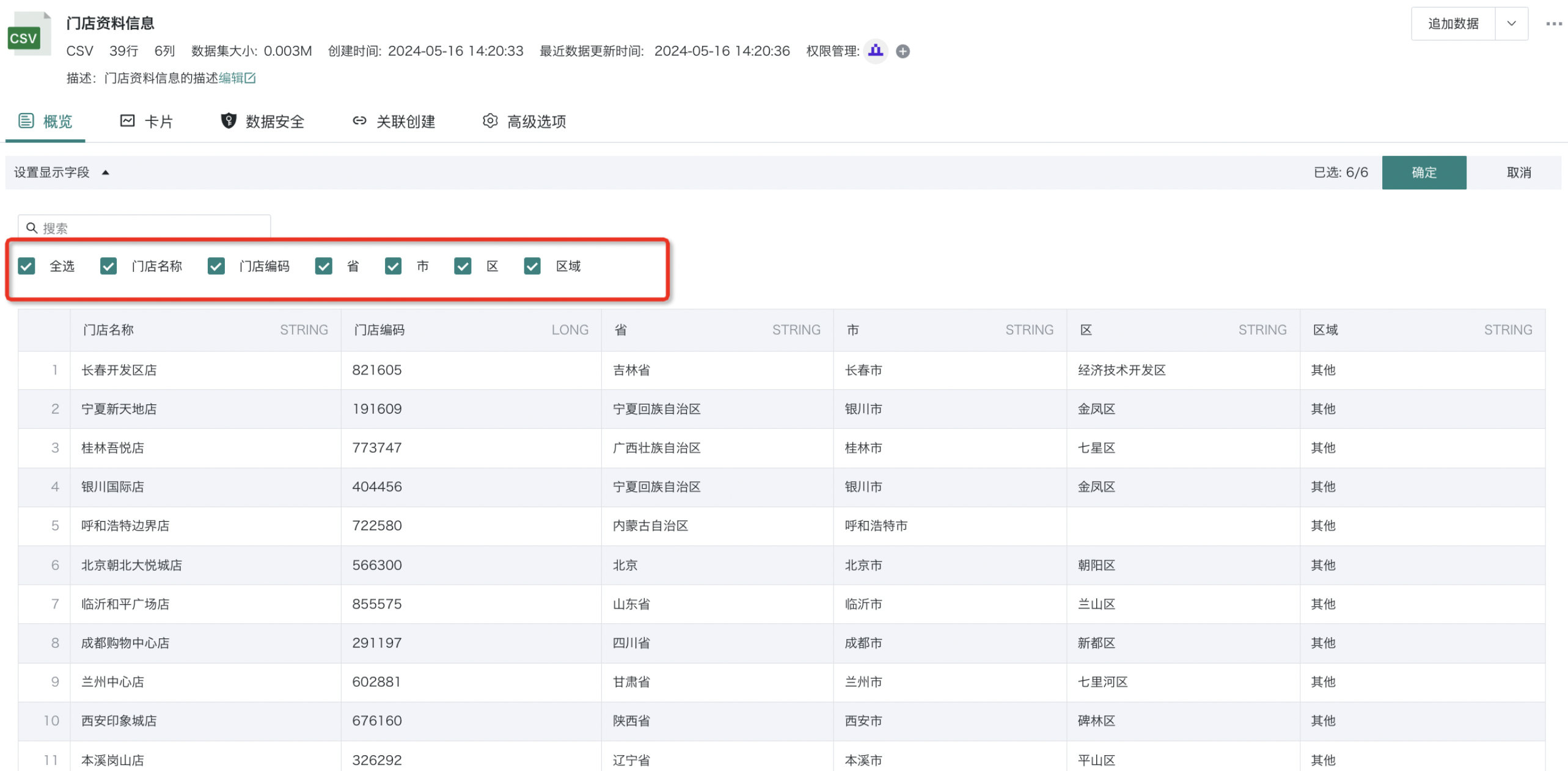
- Method Two: Select Columns
Click the small arrow to the right of "Filter Data", select "Select Columns", and you can check the columns you want to filter.
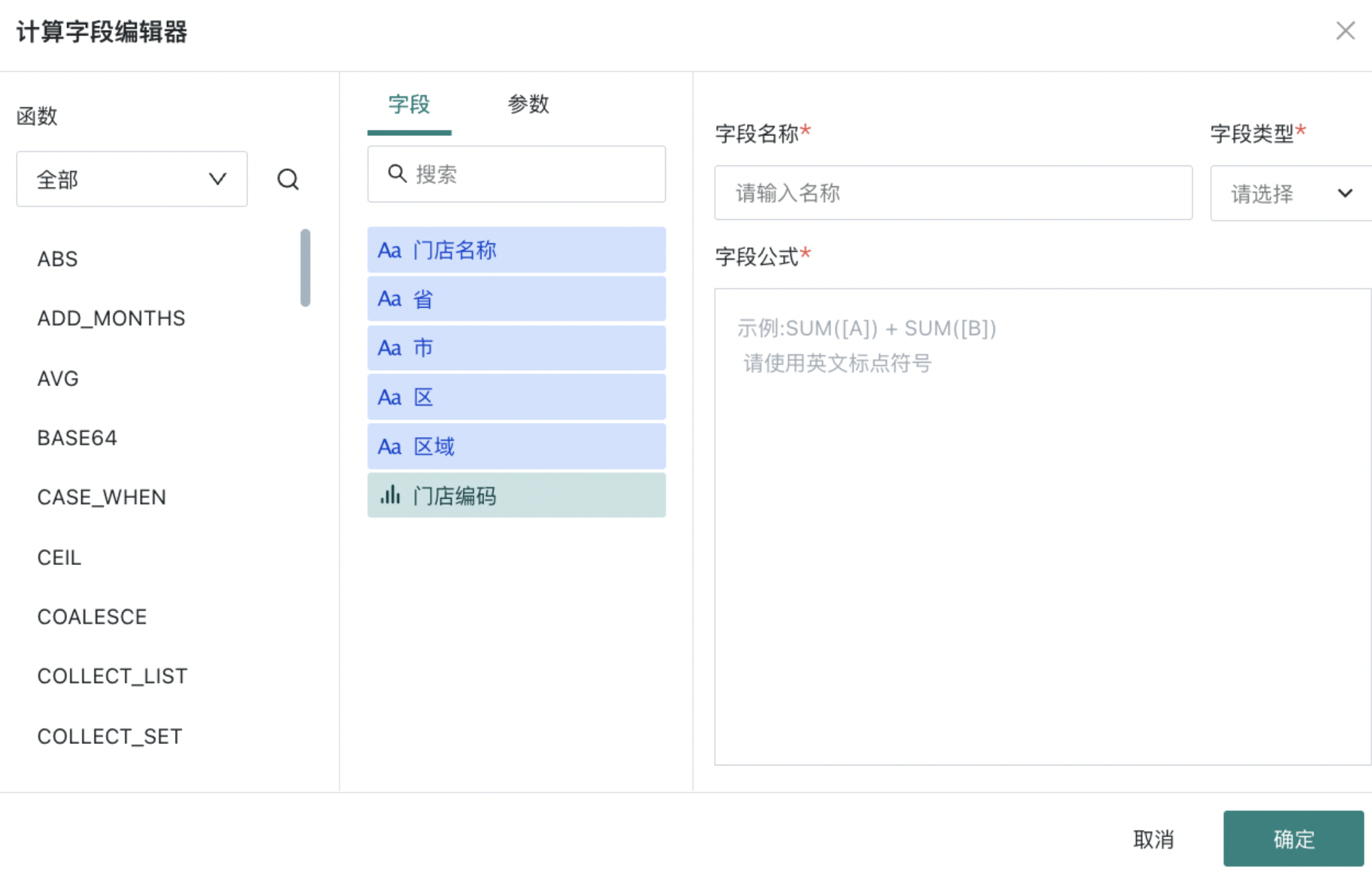
Create New Calculated Field
Click "Create New Calculated Field" in the upper right to open the "Calculated Field Editor", select functions, fields/parameters, and set a new "Field Name". For more details about creating new calculated fields, please refer to Create New Field.
Create New Grouped Field
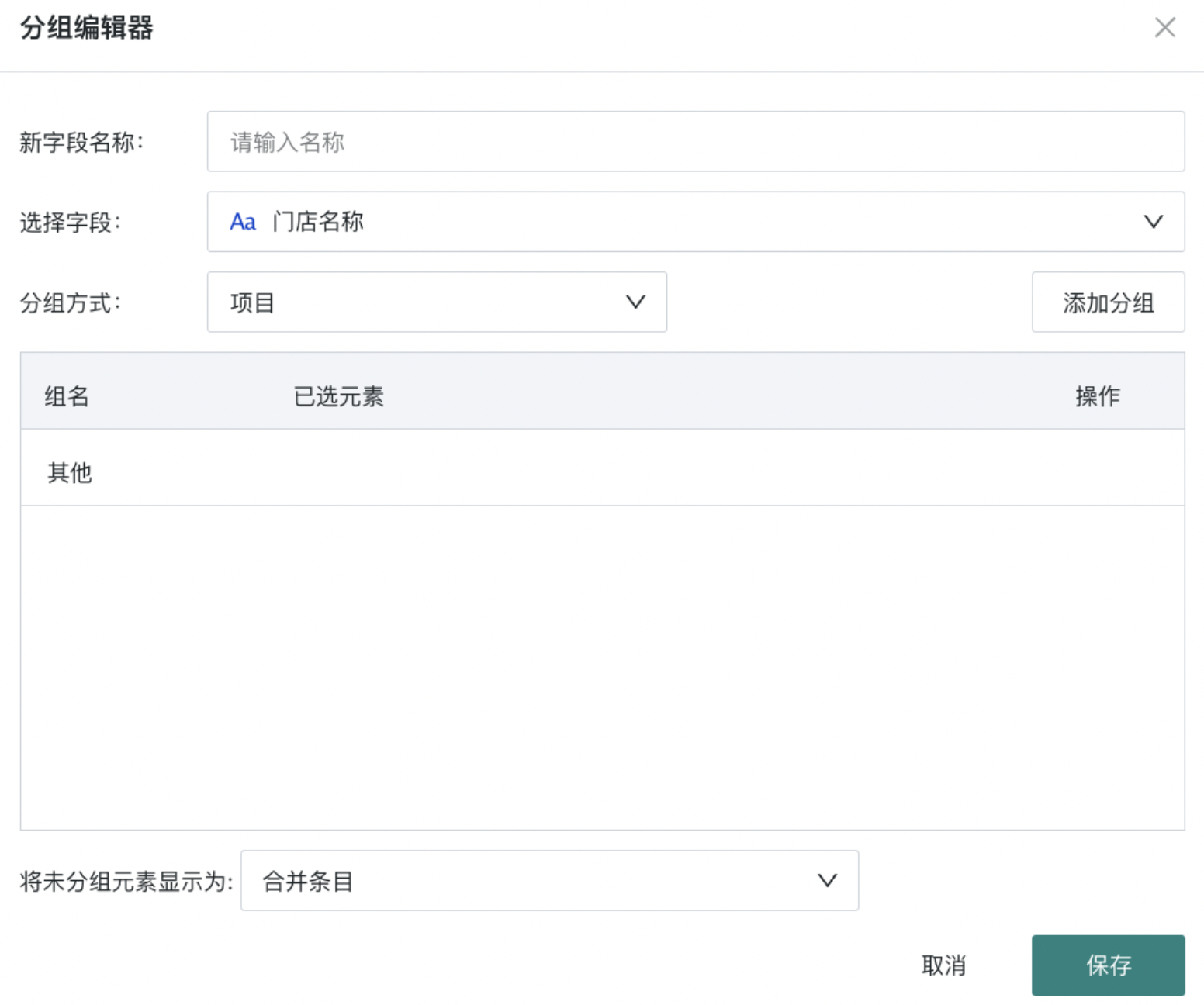
Click the small arrow to the right of "Create New Calculated Field" in the upper right corner of the overview, select "Create New Grouped Field", in the "Grouping Editor" popup, name the new field you want to create, select the fields you want to group and summarize and the grouping method. Set ungrouped elements to display as "Merge Entries" or "Separate Entries", and finally click "Save". For more details about creating new grouped fields, please refer to Create New Field.
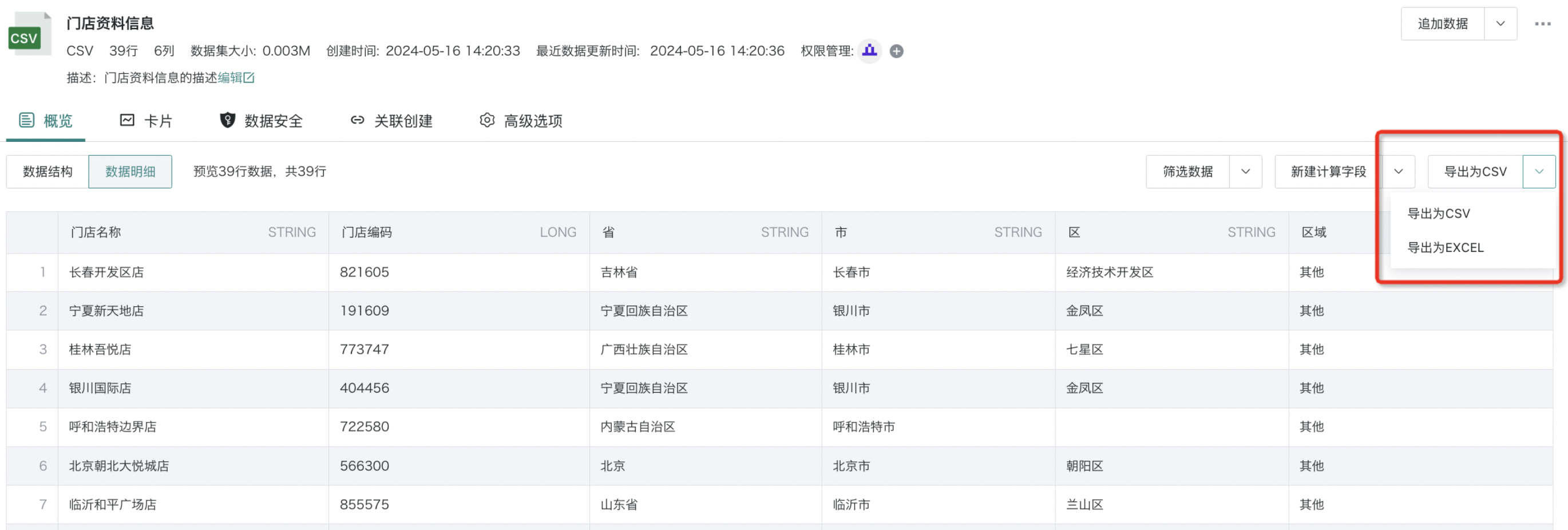
Export Data
Supports two export methods: CSV format or EXCEL format. For details, please refer to [Basic Common Operations](1-Basic Common Operations.md).
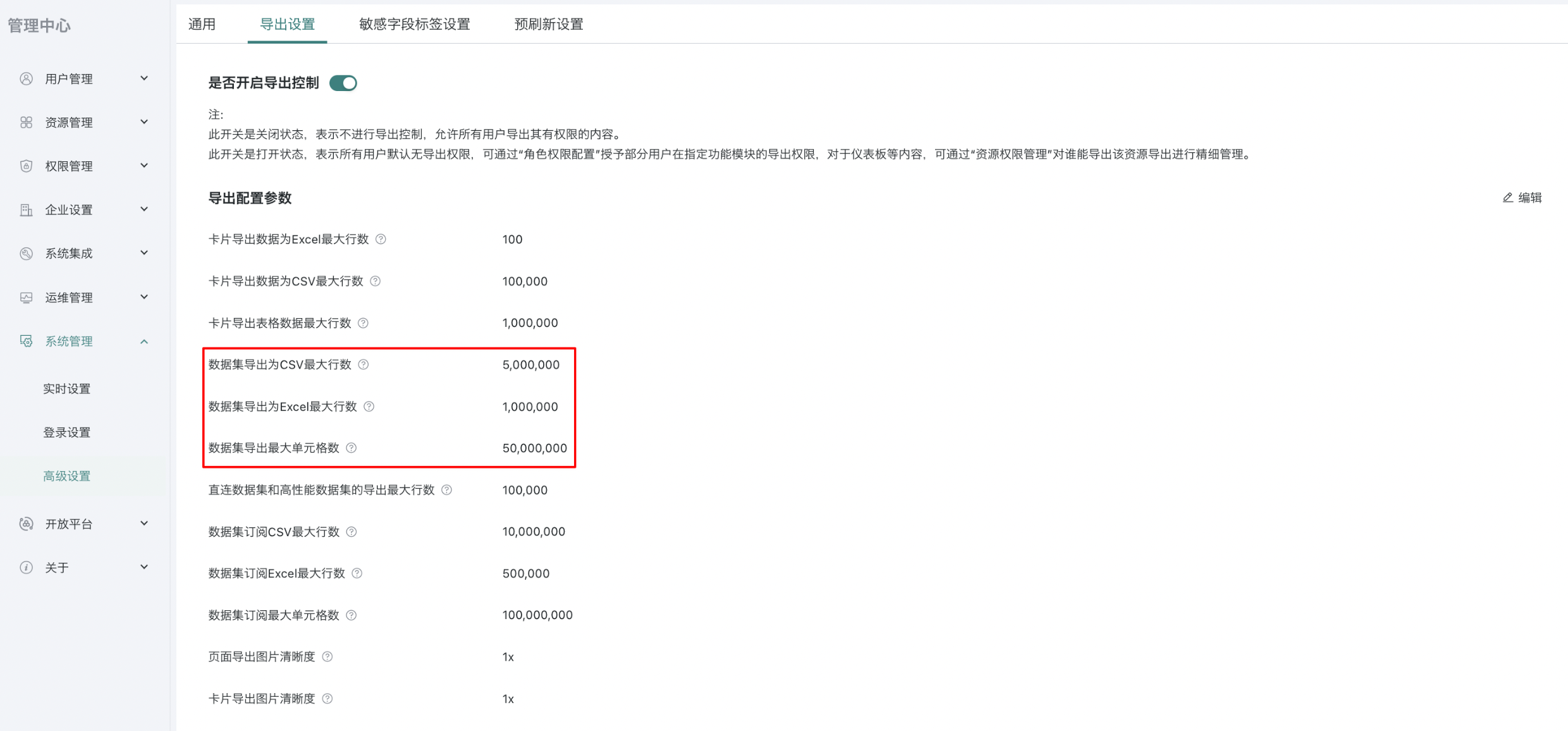
The dataset export data volume is controlled by the row count configuration item in Management Center - System Management - Advanced Settings - Export Settings.
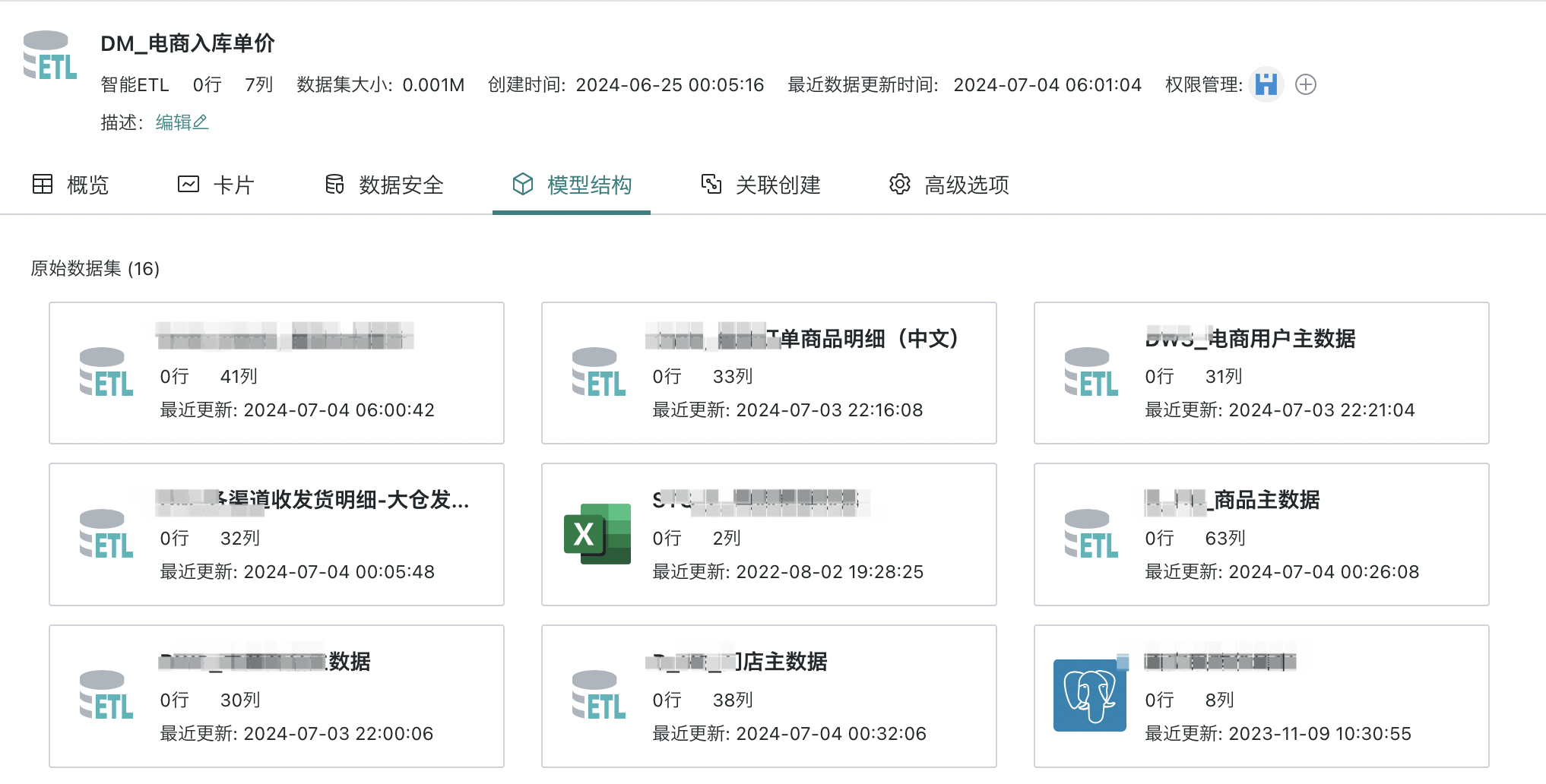
2.4. Model Structure
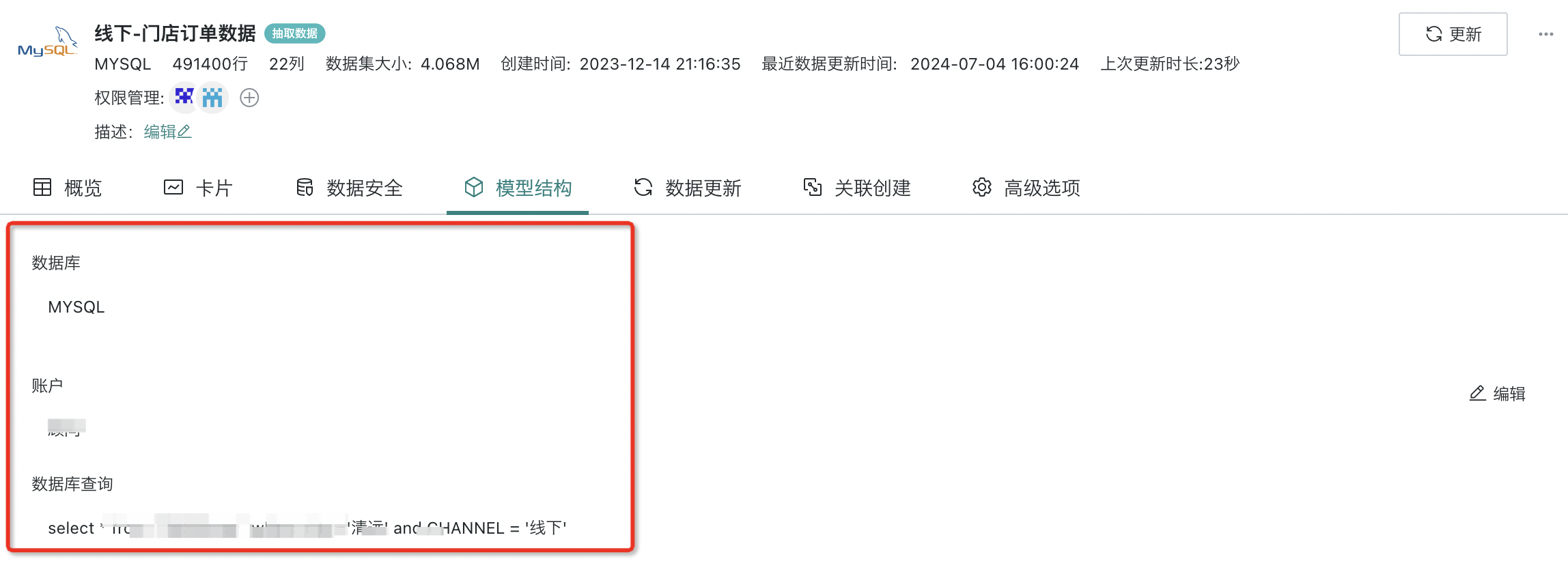
Model structure refers to the data hierarchical relationships and data flow logical structure of the dataset. Different types of datasets have different model structures. After entering the dataset details interface, you will see the model structure of the dataset. Click "Model Structure" to see the model structure information such as data source, data account, ETL, database query SQL, dynamic indicators, etc. of the dataset.
- Taking a database dataset as an example, you can view the database query SQL.
- Taking an ETL dataset as an example, you can view its original dataset, and in the ETL details module, you can also go to view its ETL model information.
-
Taking a direct connection Hive dataset (dataset created through direct database connection) as an example, click "Edit" in the upper right corner to enter the model structure update process (the core is data source change):
-
(Optional) Select account: You can choose another data account, or create a new data account.
-
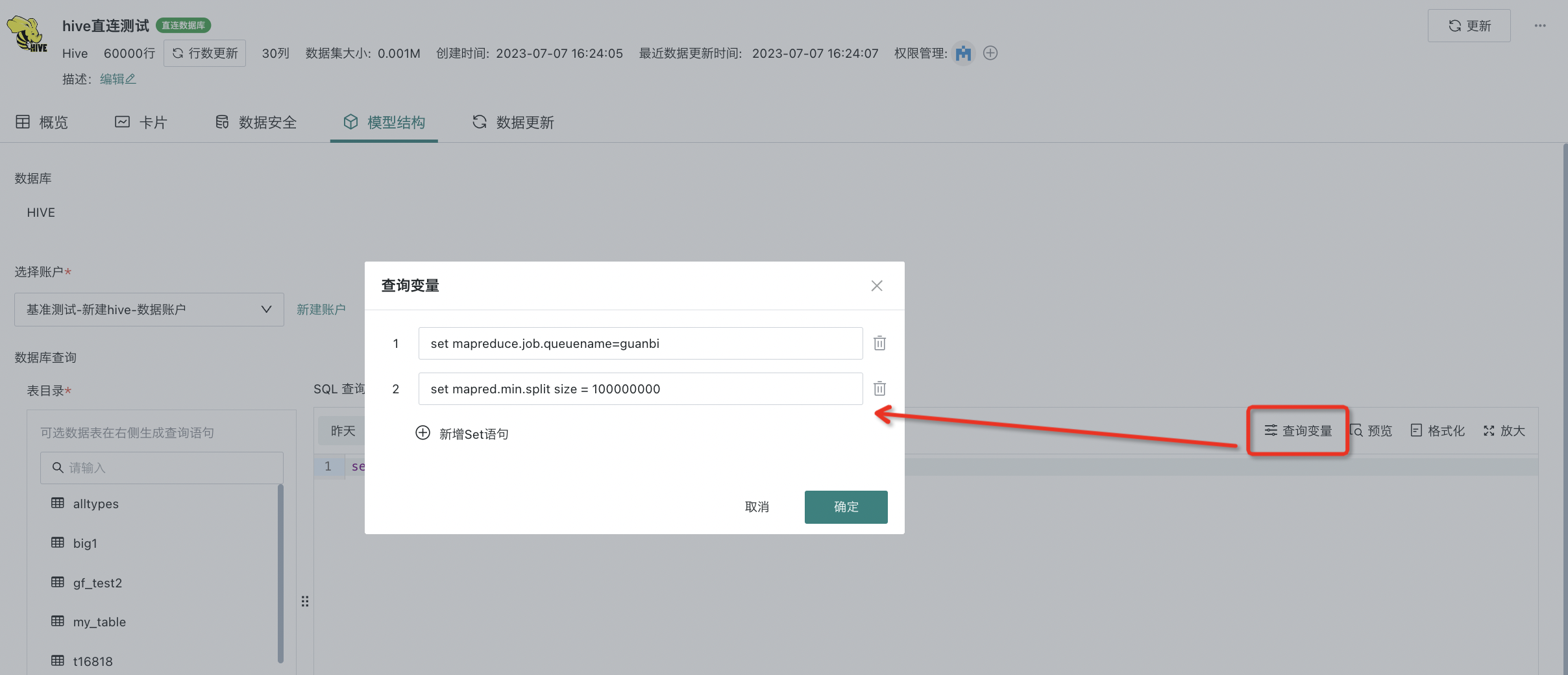
(Optional) Query variables: Query variables support multiple entries and are executed before the query SQL is submitted. Dataset creation also supports setting query variables, which are executed before extraction.
-
Note:
1. Query variables currently support MaxCompute, Impala, and Hive. For other database engines, please contact Guandata support personnel for evaluation.
2. Since query variables are pushed down to the underlying data platform for execution, the parameter scope and writing specifications need to comply with the underlying data platform specifications.
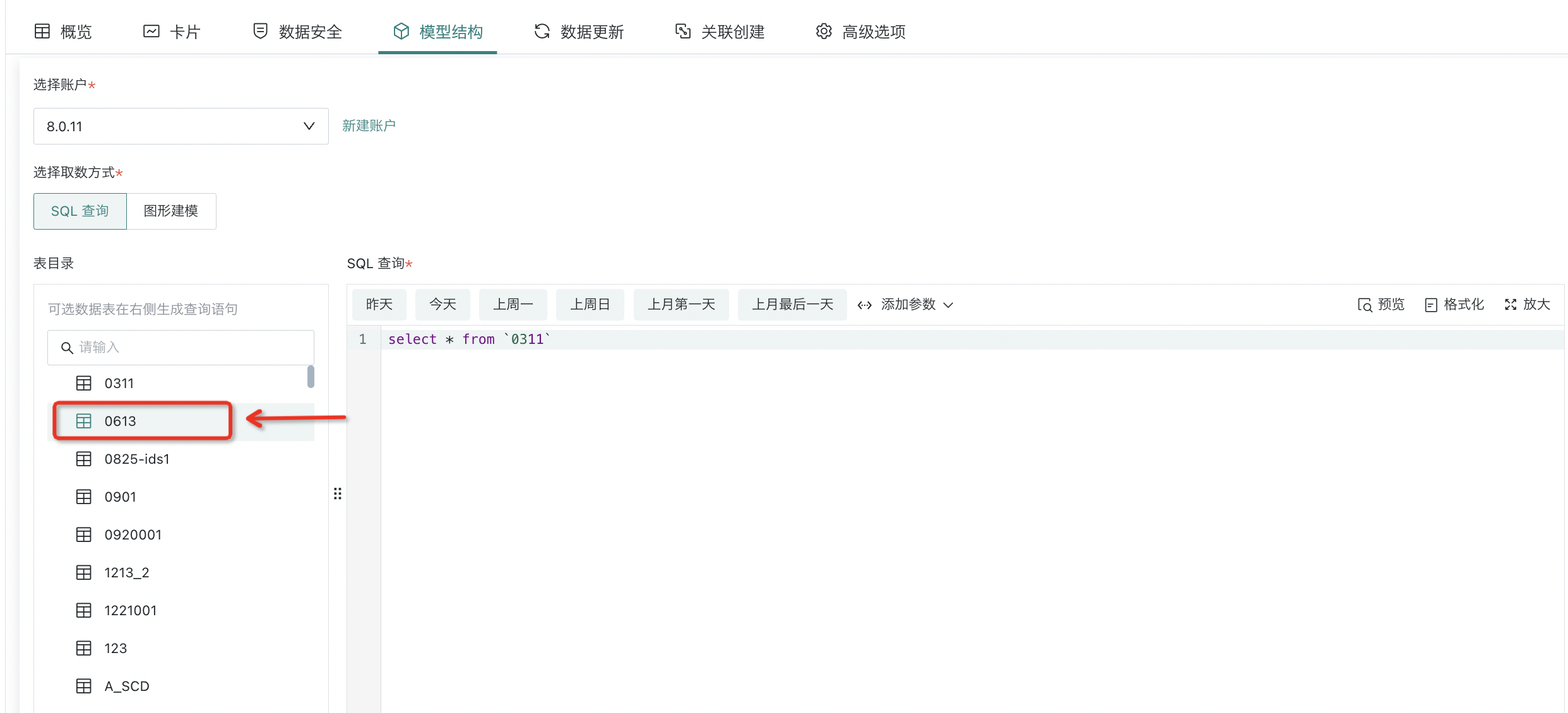
- (Required) Select query table: You can input or select the data table SQL query you want to query, or perform graphical modeling (for graphical modeling, please refer to [Standard Database Connection Guide - Graphical Modeling](../3-Database Data Integration/0-Database/1-Standard Database Connection Guide.md#graphical-modeling)). The specific operation method is consistent with the creation process of the dataset.
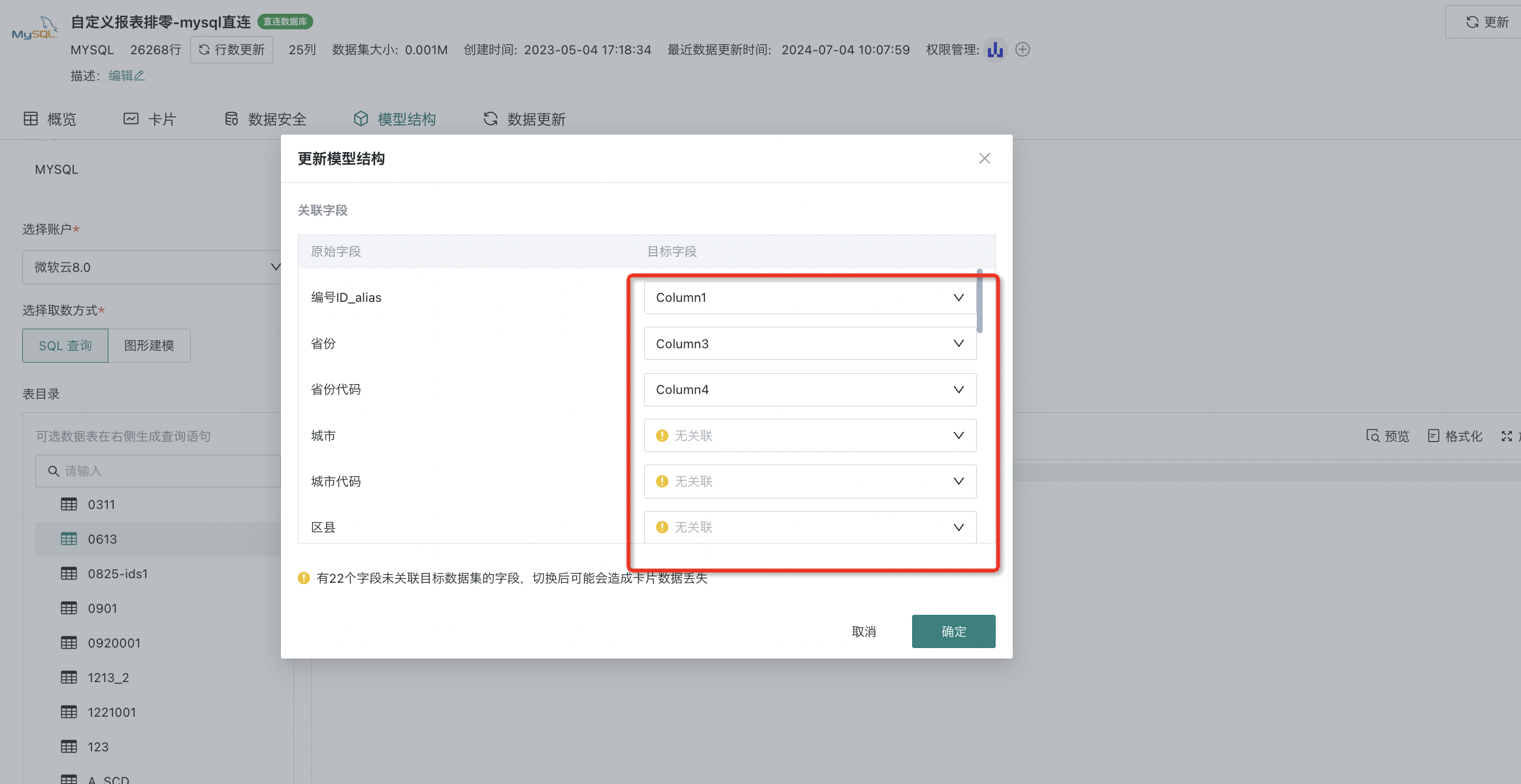
Confirm the update method for updating the model structure, supporting "Update Structure Only" and "Reset Dataset" two options. After selecting as needed, you can complete the model structure update.
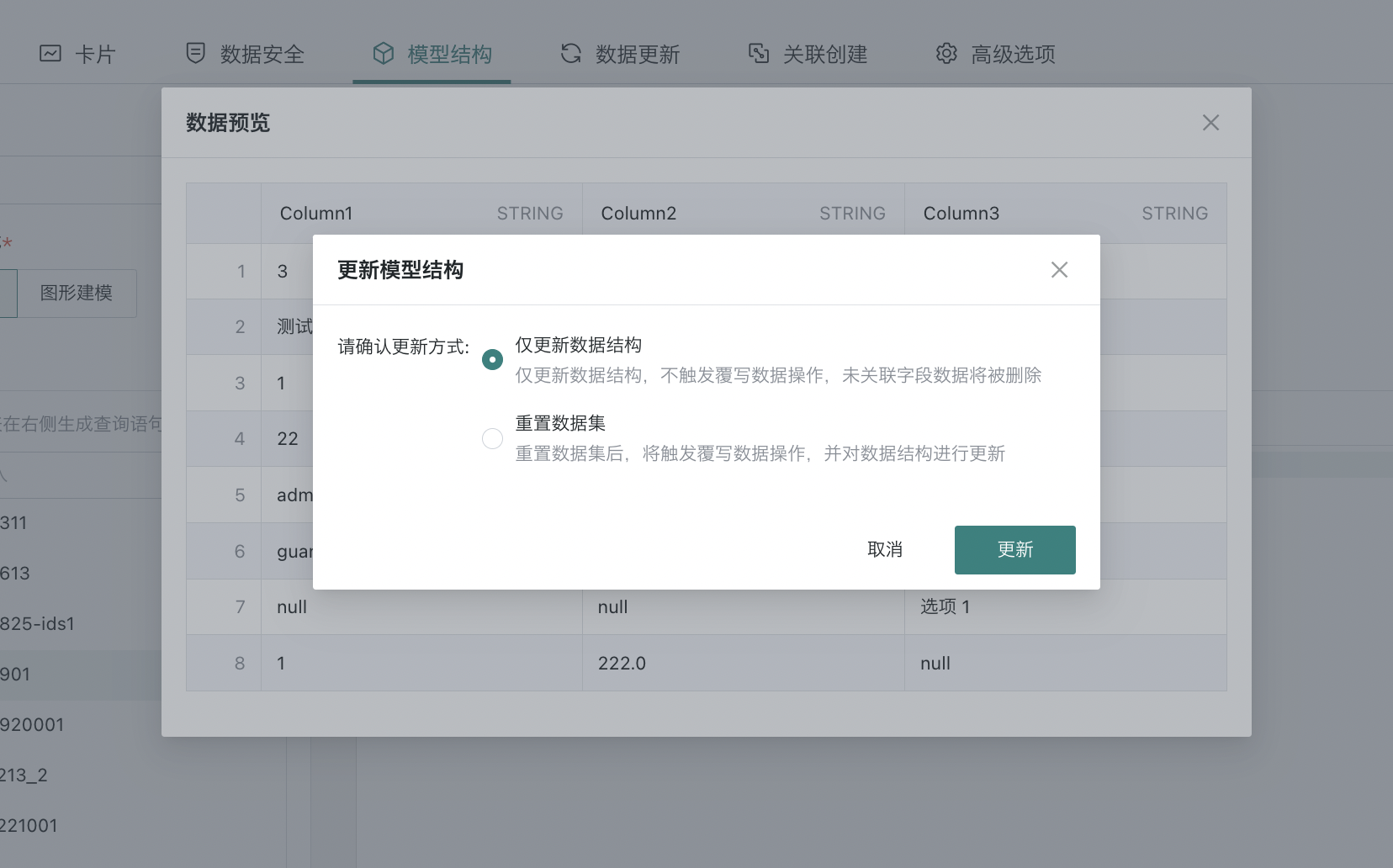
Note:
1. When "Update Data Structure Only" is checked and "Confirm" is clicked, only the target dataset data structure needs to be updated according to the schema parsed by the model structure SQL, without performing a full update operation on the dataset;
After update performance:
(1) New columns on the source side (compared to the target side): Dataset automatically adds new columns, new columns have no historical data, other data unchanged;
(2) Source side schema consistent with target side schema: Data structure & data unchanged;
(3) Missing columns on the source side (compared to the target side): Corresponding columns and data in the dataset are deleted, other data unchanged;
(4) Column name modification: Corresponding column names in the dataset are modified, data unchanged.
2. When the "Update Data Structure Only" option is not checked, follow existing logic, perform full data update and modify schema.