LDAP Account Dataset
1. Overview
Guandata BI supports automatically obtaining data from LDAP and achieving seamless integration of account data between enterprise LDAP systems and Guandata BI analysis platform through account synchronization. This feature was launched in version 5.4.0. The difference from the original LDAP account association function is that LDAP account association requires manual account creation and cannot automatically update accounts. However, LDAP account dataset can rely on the account synchronization function to automatically create and update accounts, keeping them consistent with LDAP node status.
This section will use an example to completely describe the entire process of LDAP account dataset from creating LDAP connection to completing account synchronization.
1.1. Prerequisites
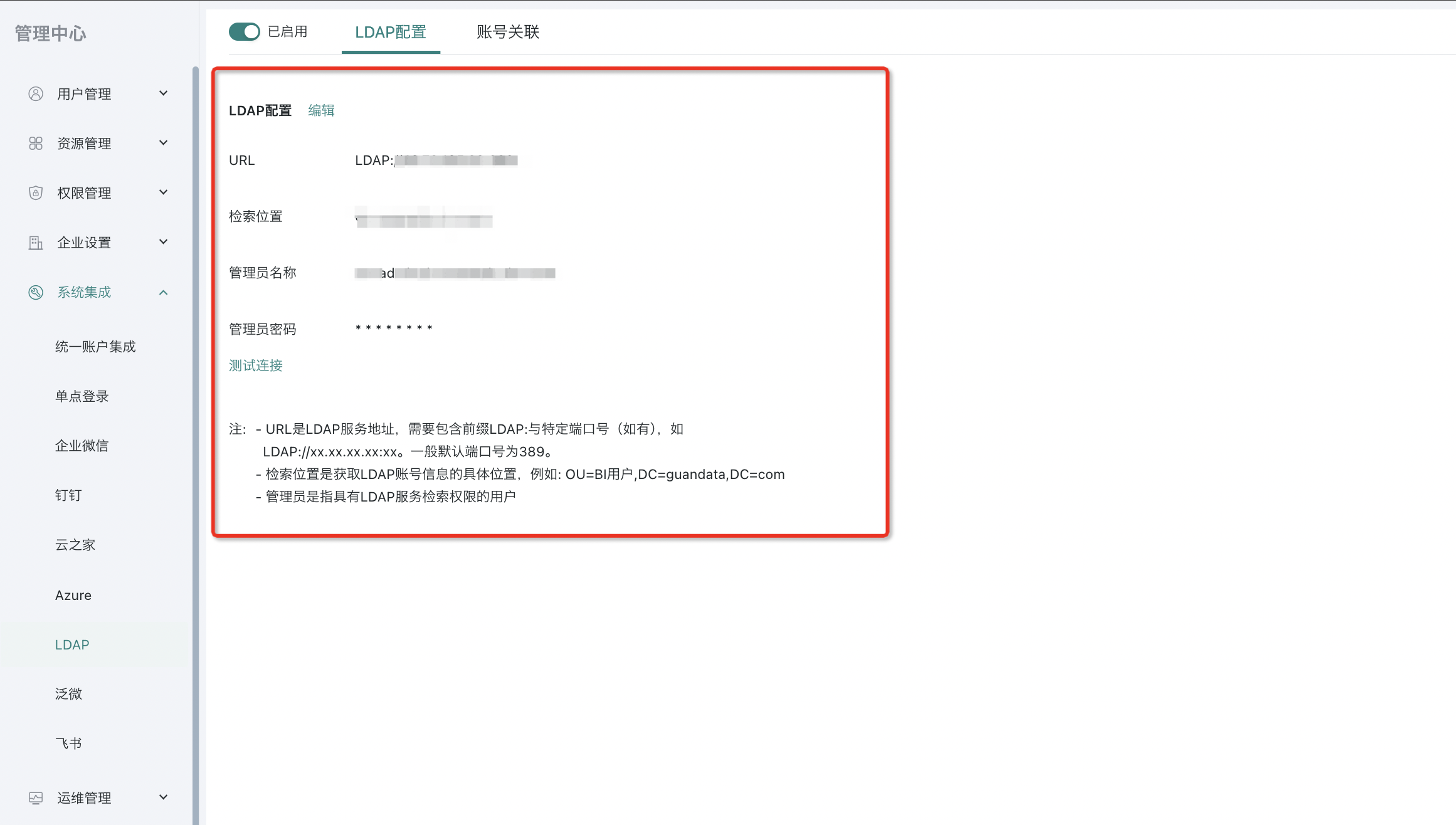
Configuring LDAP Connection
Function entry: Management Center > System Integration > LDAP.
Among them, URL is the LDAP server address, and search location means only synchronizing node information under this directory.
Organizing Account Synchronization Fields
-
Account synchronization required fields (required): Skip this step if not used for account synchronization.
Please check the sources and corresponding fields for account synchronization required fields including but not limited to the following:
Table | Field | Description | Recommended Source | Example Source |
User | Name | Name | LDAP Field | LDAP Field |
Account | Unique Account | Use cnname | Use cnname | |
Account Type | participant corresponds to read-only user admin corresponds to administrator editor corresponds to regular user | ETL Processing | ETL Processing | |
User Group ID | Department/User Group ID | ETL Processing, If LDAP has no such field, you can use the user group's built-in objectGUID | ETL Processing | |
User Group | User Group ID | Department/User Group ID | Priority use LDAP field, If LDAP has no such field, you can use the user group's built-in objectGUID | Built-in Field |
User Group Name | Department/User Group Name | LDAP Field | LDAP Field | |
Parent User Group ID | Parent Department/User Group ID | Priority use LDAP field, If LDAP has no such field, you can use the user group's built-in parentGUID | Built-in Field |
2. Operation Steps
2.1. Selecting Connector
Function entry: Data Preparation > Datasets > New Dataset > Application > Account Dataset > LDAP Dataset.
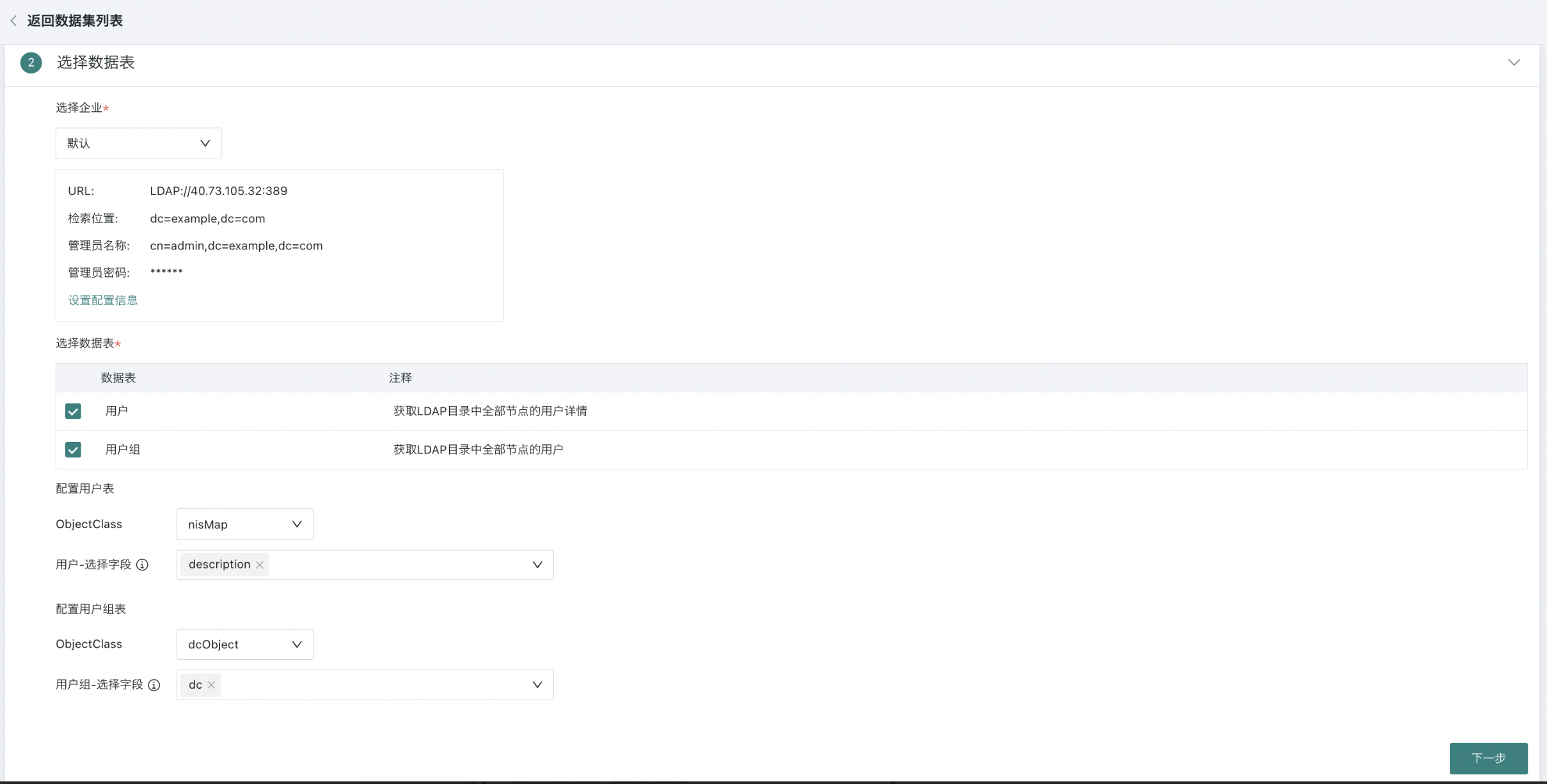
2.2. Selecting Data Tables
After selecting the default enterprise, LDAP configuration information will be automatically populated. After selecting the ObjectClass that stores users and user groups in LDAP, the attributes of that Class will be populated as available fields for selection.
Note: If the required fields are not found in the selectable range, you need to determine which class the field is inherited from, and select that class to see the field.
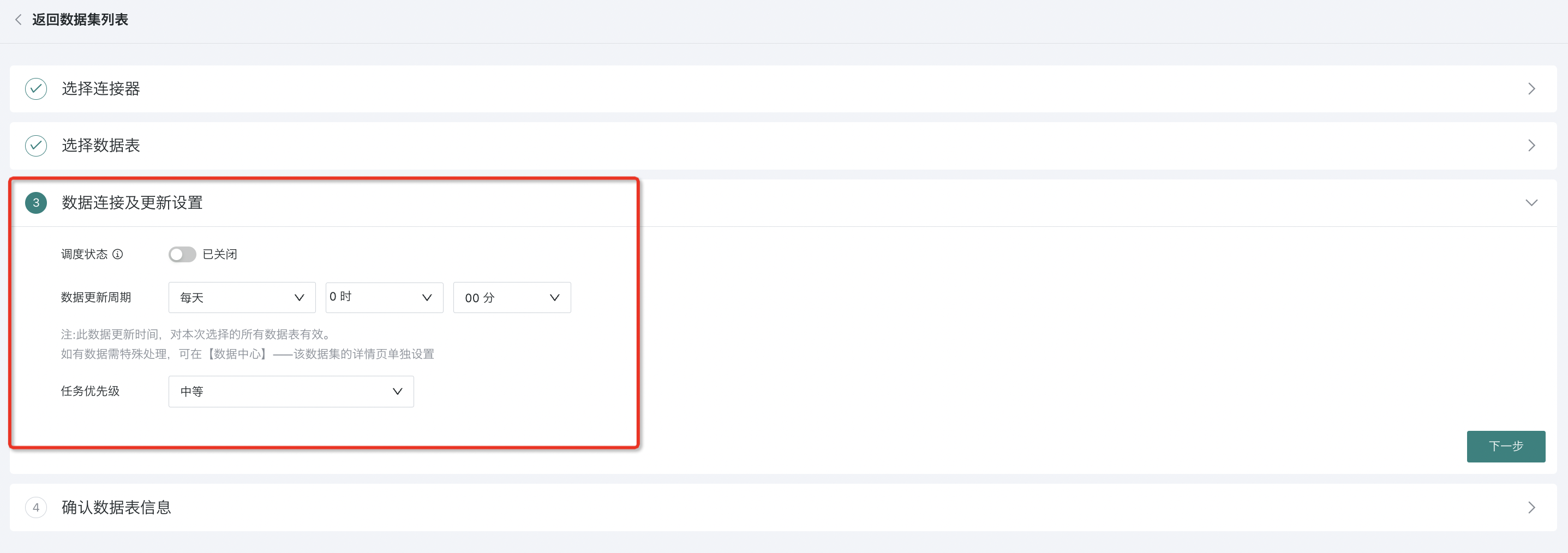
2.3. Setting Data Update Method
Configure data update settings. Users need to configure scheduling status, dataset update cycle, and task priority here. The specific configuration process is not expanded. For details, please refer to [Standard Database Connection Guide](../3-Database Data Integration/0-Database/1-Standard Database Connection Guide.md#22-data-connection-and-update-configuration).
2.4. Confirming Data Table Information
Specify a convenient and identifiable name for the account dataset, and specify the save location. After clicking "Confirm New", the dataset creation is successful. You can find the corresponding account dataset in the corresponding folder directory in the dataset management interface.
The fields in user and user group account datasets consist of built-in fields and selected fields. The built-in fields are as follows:
| Field Name | Required Data | Description | Example |
| userid | No | - | - |
| rdnld | Yes | Current node name & type | |
| dn | Yes | Current node directory path | |
| cnname | Yes | K8S's default field sAMAccountName is used as LDAP account field, otherwise LDAP login cannot be used | - |
| parent | Yes | Parent node directory path | OU=财务部,O=分公司A,DC=guandata,DC=com |
| objectSID | No | Object's security identifier; if LDAP itself has no id field, it can be used as user/user group id | 69441024fffdafffd1b7e4252fffd |
| objectGUID | No | Object unique identifier; if LDAP itself has no id field, it can be used as user/user group id | 4bfffdfffdfffd2436d49fffd7f4a4a831 |