View Dataset
1. Overview
1.1. Function Description
View dataset, formerly known as dynamic dataset, refers to the Spark SQL-based parameterizable executable dynamic dataset provided by Guandata. It can dynamically associate and calculate non-direct connection datasets, providing more flexible data analysis methods. It is a query calculation function that solves complex analysis problems in ad-hoc analysis scenarios through Spark SQL.
Through view datasets, users can integrate 1 or more non-direct connection datasets (excluding real-time datasets) through Spark SQL to reorganize datasets and create new datasets. With the help of Spark SQL's rich data processing functions, users can complete complex association queries, data preprocessing, etc. In addition, dynamic parameters can be added to Spark SQL query statements to complete dynamic calculation requirements.
1.2. Application Scenarios
- PSD Calculation for Chain Retail Enterprises
When calculating PSD, the numerator sales amount is at the date, store, and SKU dimensions, and the statistics are obtained through aggregation calculations on the sales amount table; while the denominator operating days are at the date and store dimensions, and the statistics need to be aggregated on the store operating table. It does not need to be accumulated at the product (SKU) dimension. If you choose any method of direct association on the original table, either the data volume will expand dramatically, or the aggregated results will be inaccurate. Only by associating the aggregation results of the two tables and then calculating PSD is the simplest and most accurate way. Guandata's view dataset supports automatic association of multiple datasets. Through custom SQL, parameters are injected into the SQL, hierarchical aggregation is performed on the two original tables, and the result sets are associated to calculate PSD values.
- Other Scenarios
-
Calculate year-over-year and month-over-month percentages of enterprise-related business data;
-
Analyze consumer consumption frequency distribution issues within dynamic time ranges.
2. Usage Guide
2.1. Creating View Dataset
Function entry: Data Preparation > Datasets > New Dataset > Application > View Dataset.
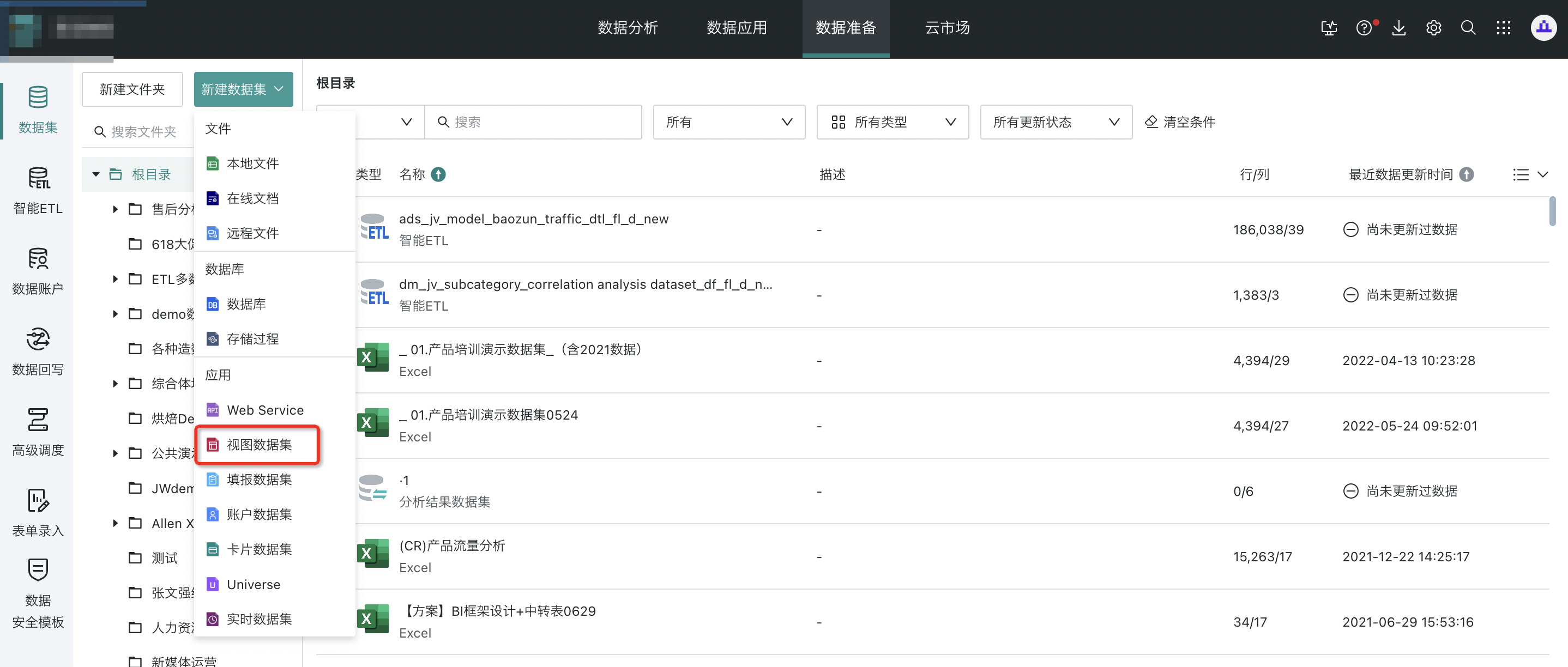
2.2. Selecting Data Tables
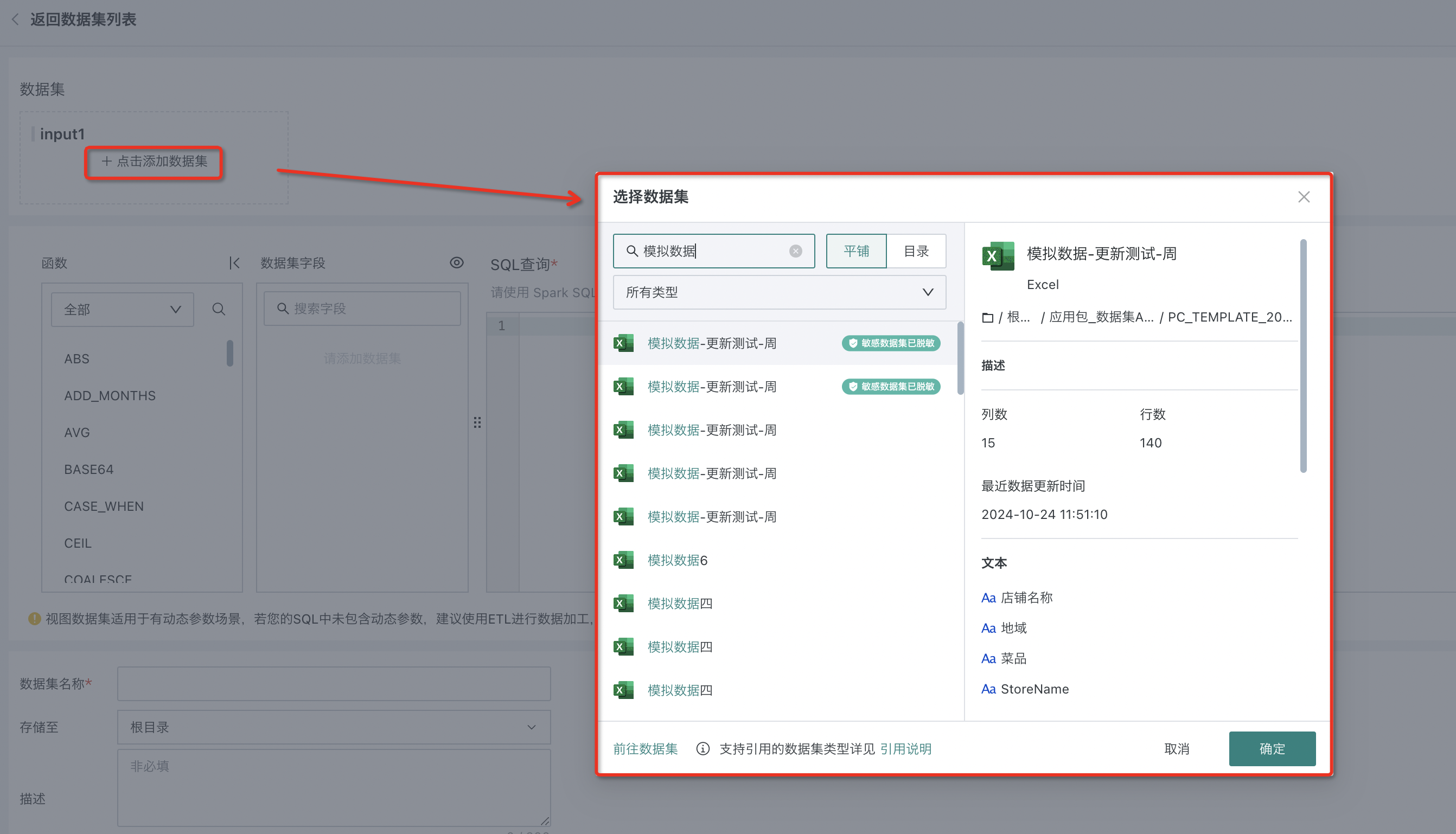
Enter the view dataset configuration page, click Add Dataset, and select 1 or more data tables.
Note: To ensure calculation performance, please try to select 2 or fewer datasets.
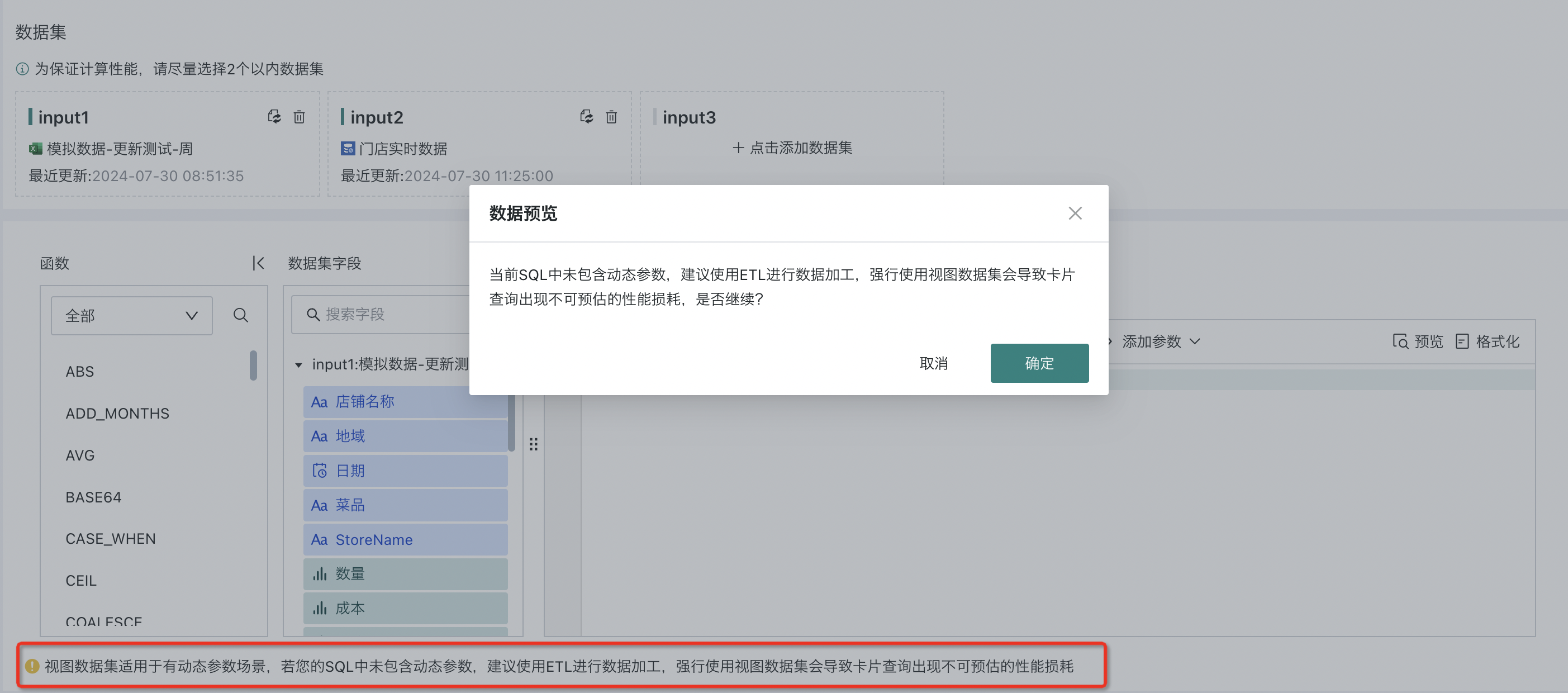
2.3. Inputting Dynamic Query SQL
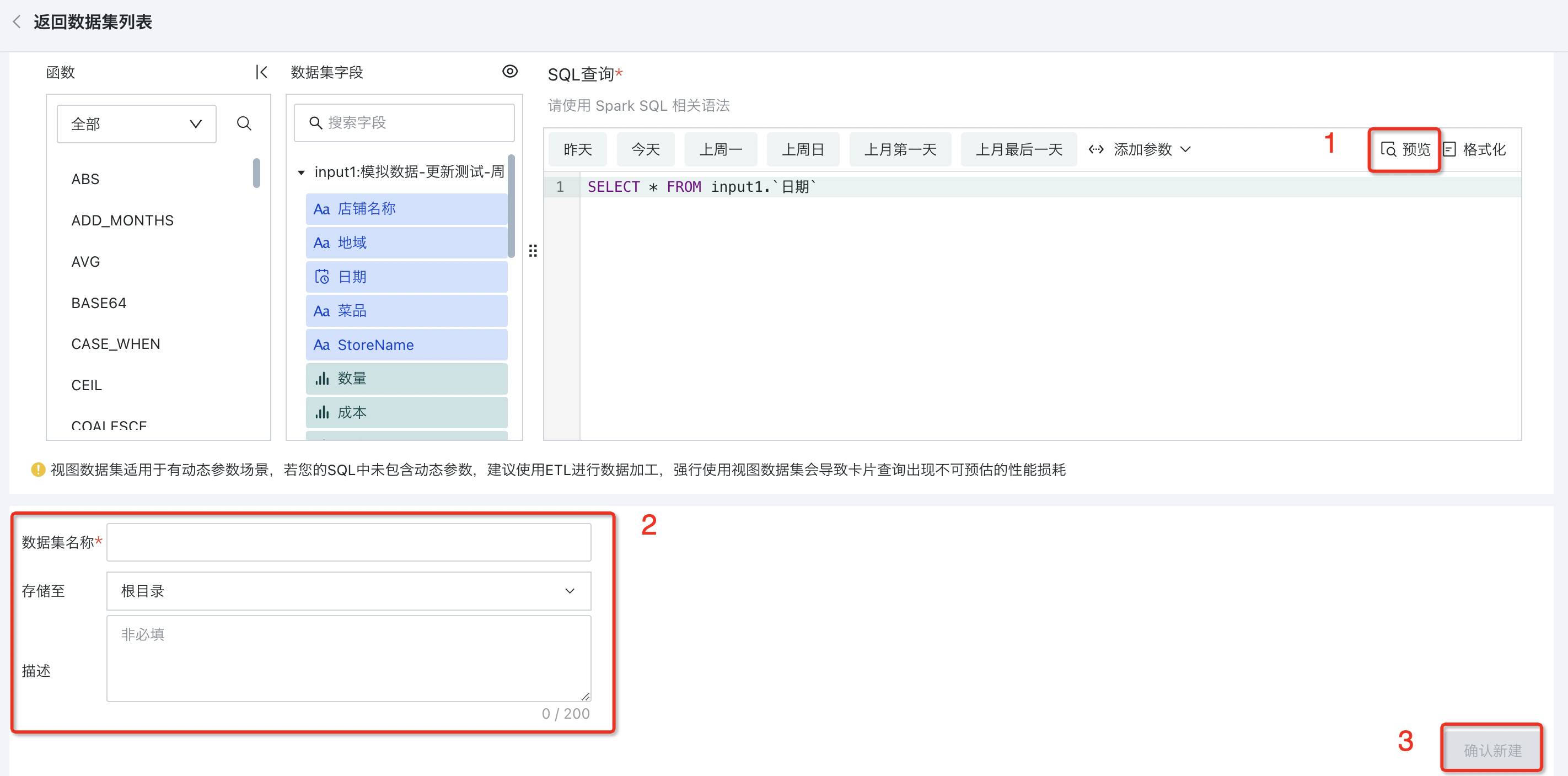
After selecting the relevant datasets, when users input "Dynamic Query SQL", they can select "Dataset Fields" and "Dynamic Parameters (Optional)" on the left as needed to achieve flexible parameter passing and query actions in dynamic parameter scenarios. After completing the SQL writing, click the "Preview" button to confirm data accuracy.
Users can choose to use system default table names or dataset names. After switching to dataset names, they cannot switch back to system default table names.
- Using system default table names: The system will automatically generate INPUT as the table name
Note: Currently uses system default table names by default
- Using dataset names: Datasets will directly use their original table names or dataset aliases
Note:
View datasets are suitable for dynamic parameter scenarios. If your SQL does not contain dynamic parameters, it is recommended to use ETL for data processing. Forcing the use of view datasets will cause unpredictable performance loss in card queries.
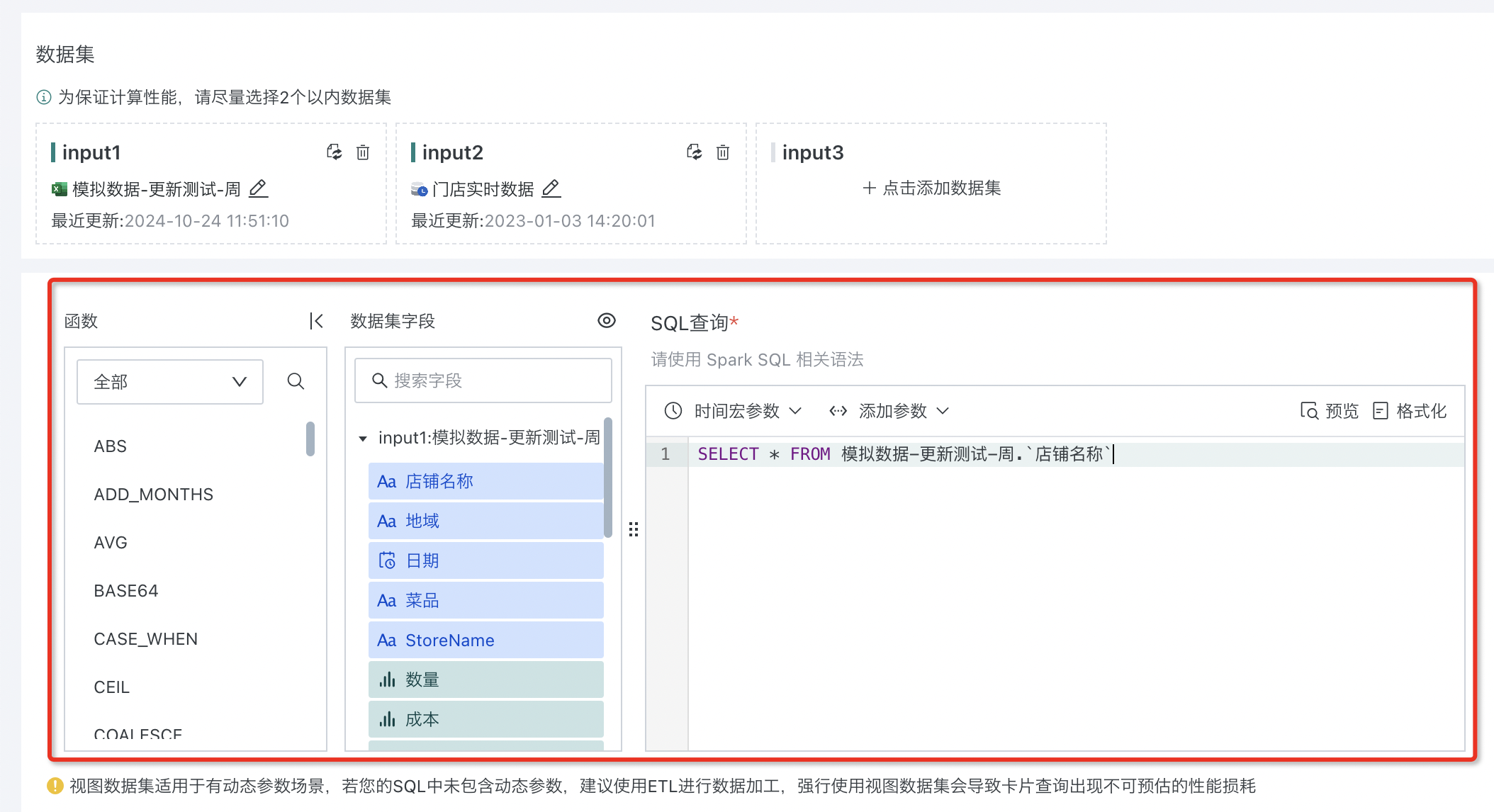
To facilitate understanding of the business meaning of the view, you can set an alias for the view name.
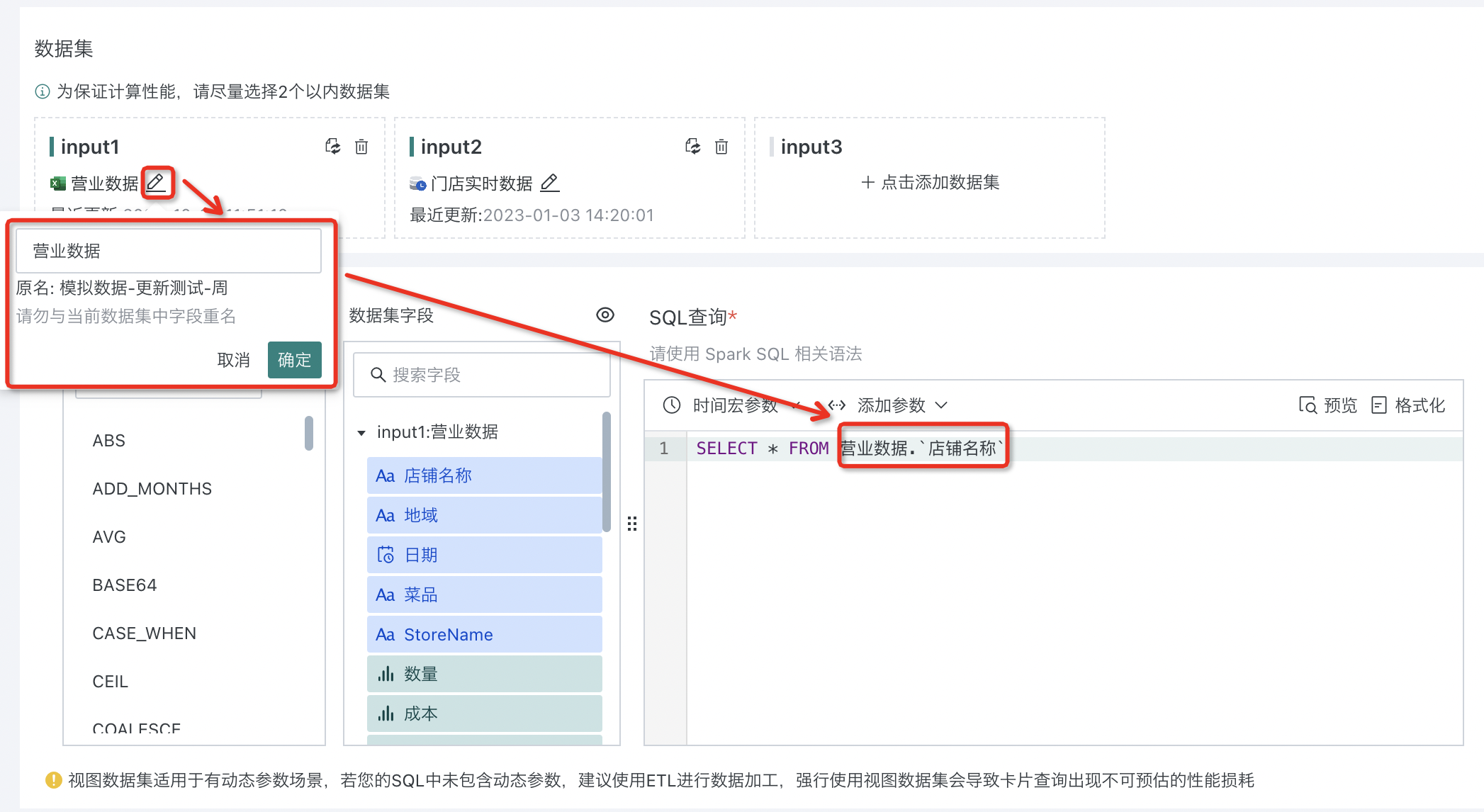
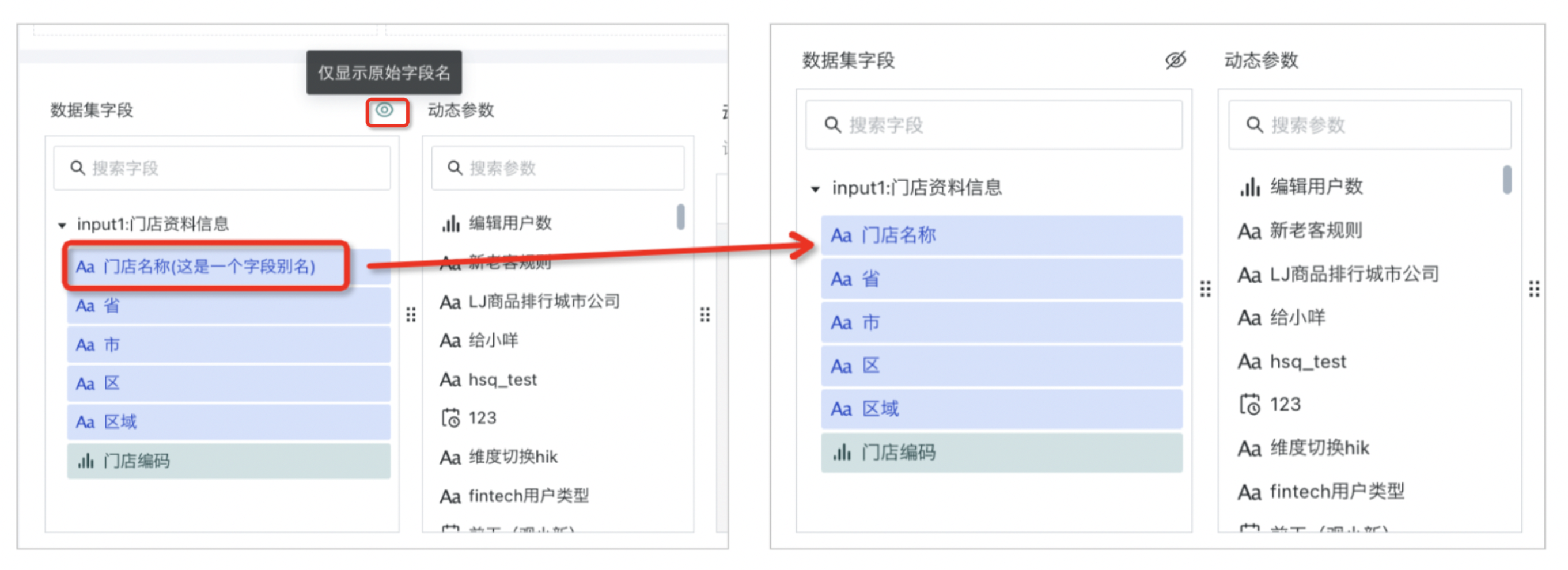
Sometimes users will set field aliases for certain fields in datasets. If you want to hide these field aliases in dataset fields, click "Show Only Original Field Names" to hide field aliases.
2.4. Filling Dataset Information
After successful data preview, specify the dataset name and storage location, add dataset description as needed, click "Confirm New" to complete dataset creation.
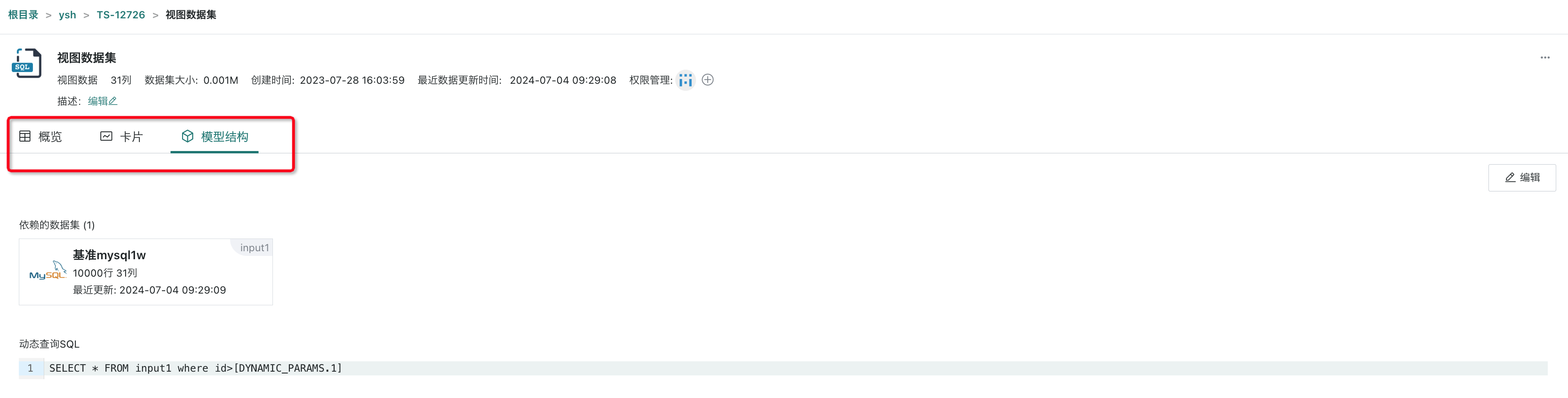
2.5. Creating Completed Dataset
After successful creation of the view dataset, you can find the dataset in the corresponding folder directory. Click on the dataset to enter the dataset details page, where you can view the dataset overview, related cards, and model structure, and modify configuration items in various interfaces.
2.6. Setting Preview Timeout Limit
Users can set the preview timeout limit for view datasets in the Management Center, and guide users to use view datasets in recommended scenarios to reduce performance loss.
In Management Center > Operation & Maintenance Management > Parameter Configuration, you can set the view dataset preview timeout limit, default is 60 s.
After setting, it will not affect historically created view datasets.