Stored Procedure
1. Overview
1.1. Function Description
Stored procedure refers to the function of creating through parameterized extraction and being able to initiate parameterized dynamic data queries on stored procedure datasets on the page side.
Currently, Guandata supports MySQL, SQLServer, and Oracle stored procedures.
1.2. Application Scenarios
In enterprises, there are often situations where traditional reports need to use stored procedures to implement complex calculation logic. When enterprises have built many stored procedures in Oracle data warehouses, they need to execute stored procedures through parameterized methods to obtain result data. Guandata's stored procedure related functions can integrate with Oracle stored procedures, create stored procedure datasets, and support parameterized queries initiated on the page side.
1.3. Prerequisites
When integrating stored procedure datasets, you need to select a data account.
Users who have already created data accounts can ignore this step. Users who have not created data accounts can go to [Data Account](../1-Data Account.md) for more information.
2. Usage Guide
Function entry and main steps are as follows:
-
Enter the data preparation page and click the Dataset module in the left navigation;
-
Click the New Dataset button and select Database > Stored Procedure;
-
Select the corresponding connector and stored procedure, and configure related items as needed;
-
After confirming that the data table information is correct, click Confirm New to complete the integration.
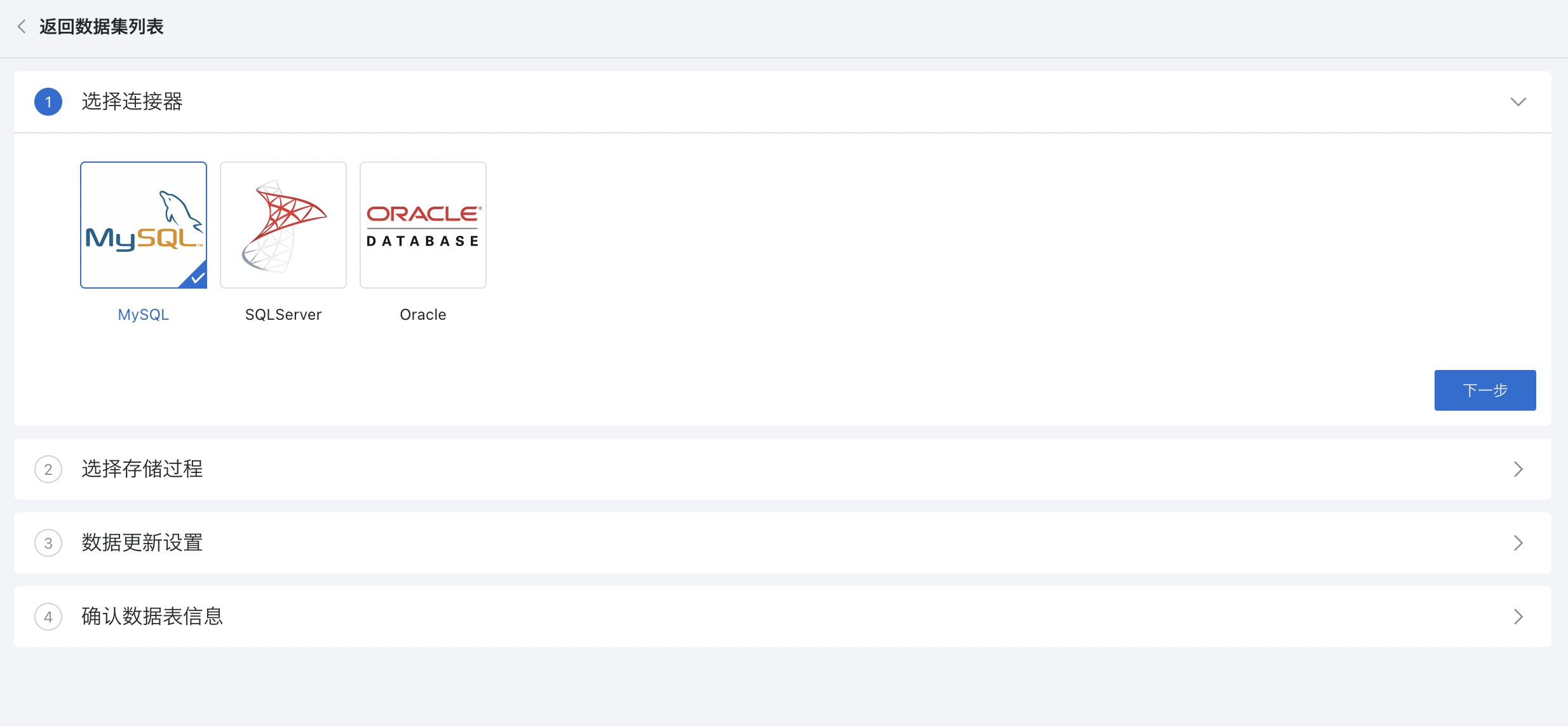
2.1. Select Connector
Function entry: Data Preparation page > Dataset module > New Dataset > Stored Procedure > Select Connector.
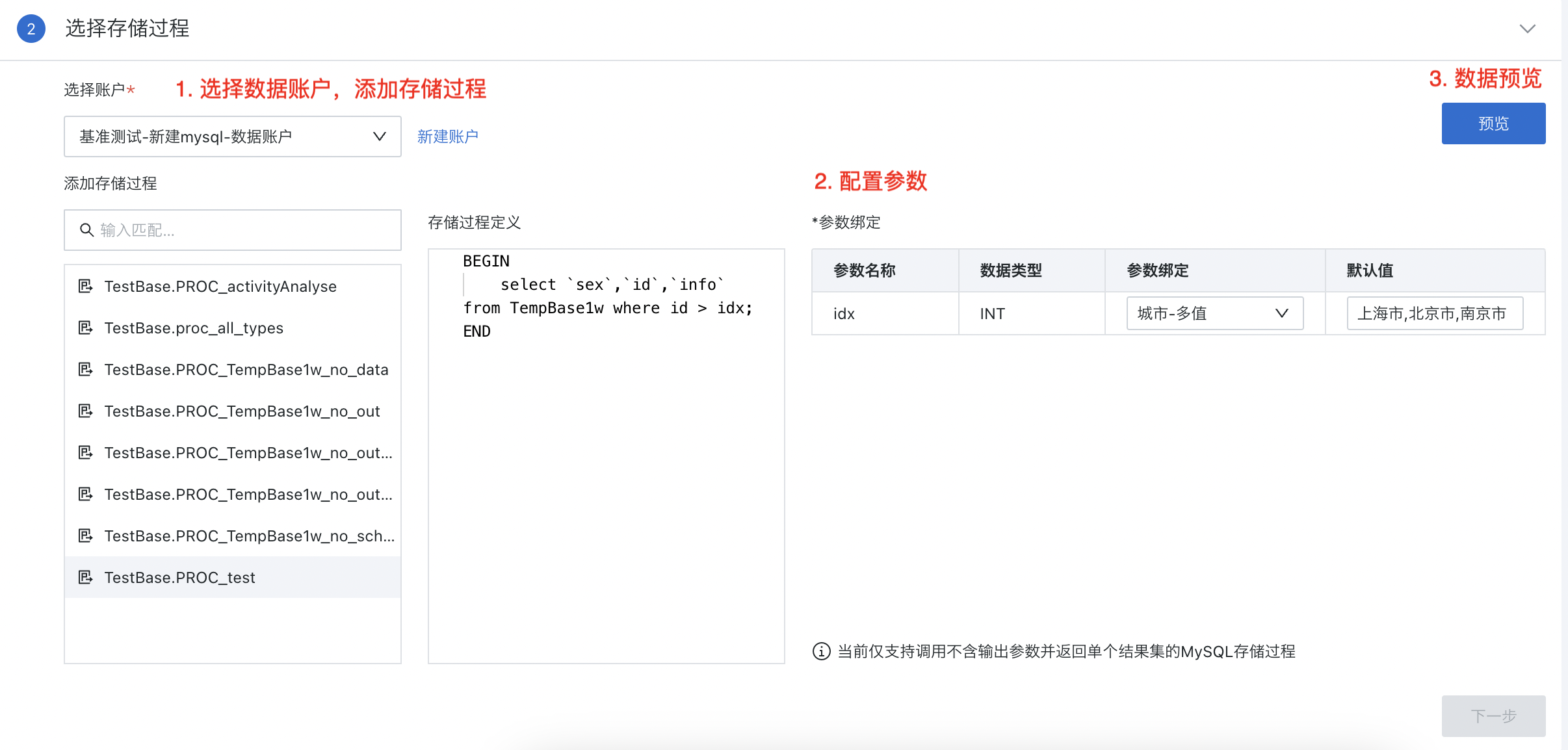
2.2. Select Stored Procedure
-
Select a data account and add a stored procedure;
-
Configure parameters:
-
Input parameters: Users can map the input parameters in the stored procedure definition to Guandata's global parameters, and also support custom default values;
-
Output parameters: For Oracle stored procedures, if there are output parameters in their definition, you need to select the output parameters; if there are multiple output parameters, only one cursor-type output parameter can be selected.
Note:
1. MySQL and SQLServer only support integration of stored procedures that return a single "result set" and have no output parameters;
2. Oracle supports integration of stored procedures that return multiple "result sets" and have output parameters.
- Click "Preview", confirm the data is correct, and then click Next.
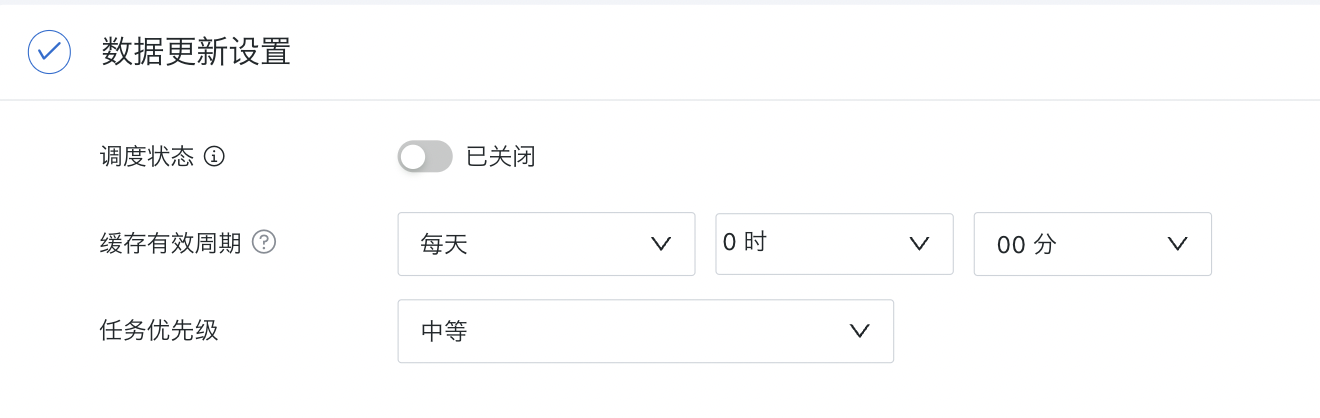
2.3. Set Data Update Method
When integrating stored procedures, you can configure scheduling status, cache validity period, and task priority.
You can refer to the data update configuration of standard database integration. For details, please refer to [Standard Database Connection Guide](0-Database/1-Standard Database Connection Guide.md).
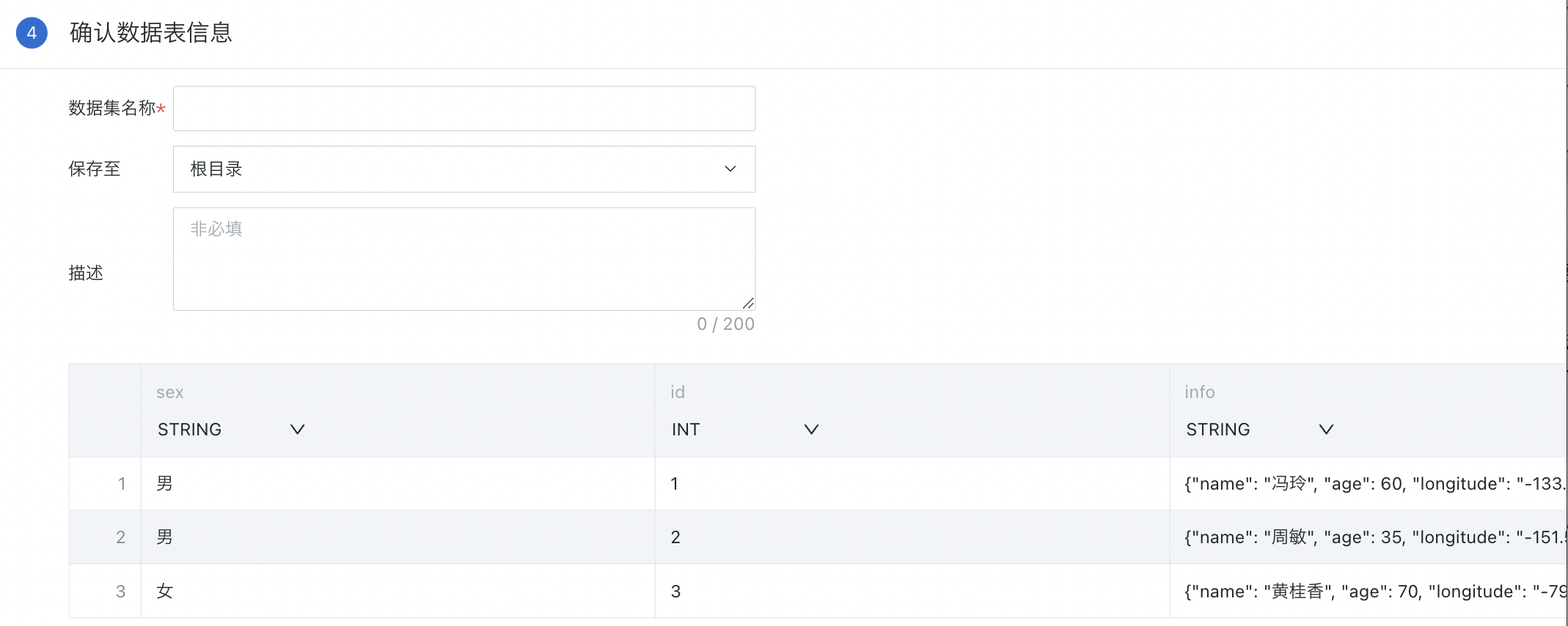
2.4. Confirm Data Table Information
-
Fill in the dataset name, storage path, description information and confirm. The storage path defaults to the system root directory;
-
Confirm whether to modify field names and types. You can refer to the data update configuration of standard database integration. For details, please refer to [Standard Database Connection Guide](0-Database/1-Standard Database Connection Guide.md#22-data-connection-and-update-configuration).
-
Field name: Click on the field position to rename the field;
-
Field type: Click the downward arrow next to the field type to adjust the field type.
- Finally, click "Confirm New" to complete the dataset creation.