Standard Database Connection Guide
1. Overview
Guandata provides data integration services from various databases, currently supporting database integration through two approaches.
-
Support for 40+ standard database integrations: including but not limited to MySQL, PostgreSQL, Greenplum, SQL Server, Oracle, Presto, Amazon Redshift, MaxCompute, SAP HANA, Teradata, BW, TiDB, Doris, Vertica, Netsuite, ClickHouse, Hive, IBM DB2, HAWQ, AnalyticDB, Gbase 8t, Informix, Kylin, Impala, Sybase, MangoDB, Druid, Trino, DAMENG, Snowflake, StarRocks, CirroData, Access, etc.
-
Self-service external database integration: Supports users to self-service integrate various external databases including cloud vendors and domestic databases. For details, please refer to [Self-service External Database Integration](3-Self-service External Database Integration.md).
2. Single Database Creation
Function entry: Data Preparation > Dataset > New Dataset > Database.
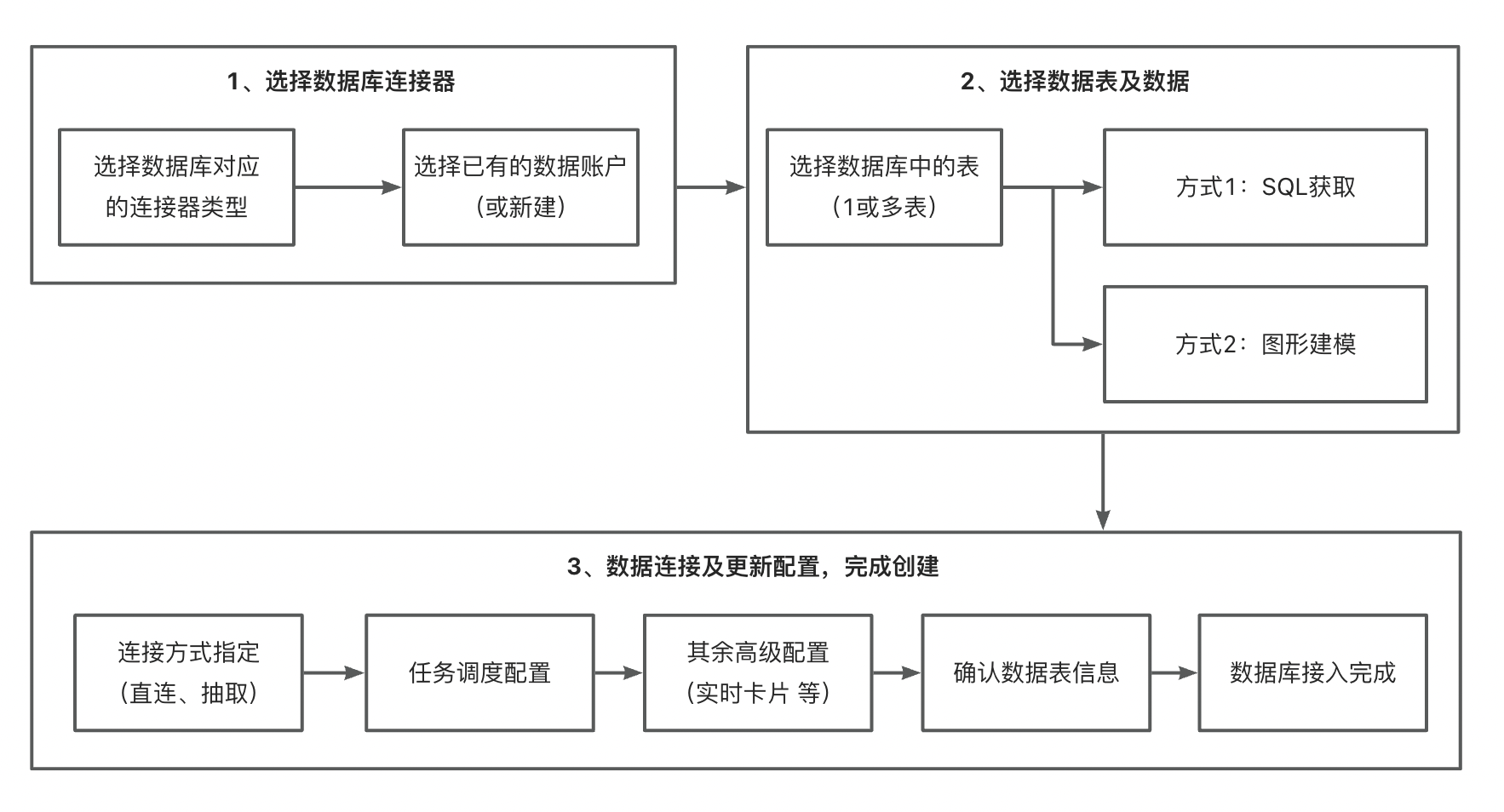
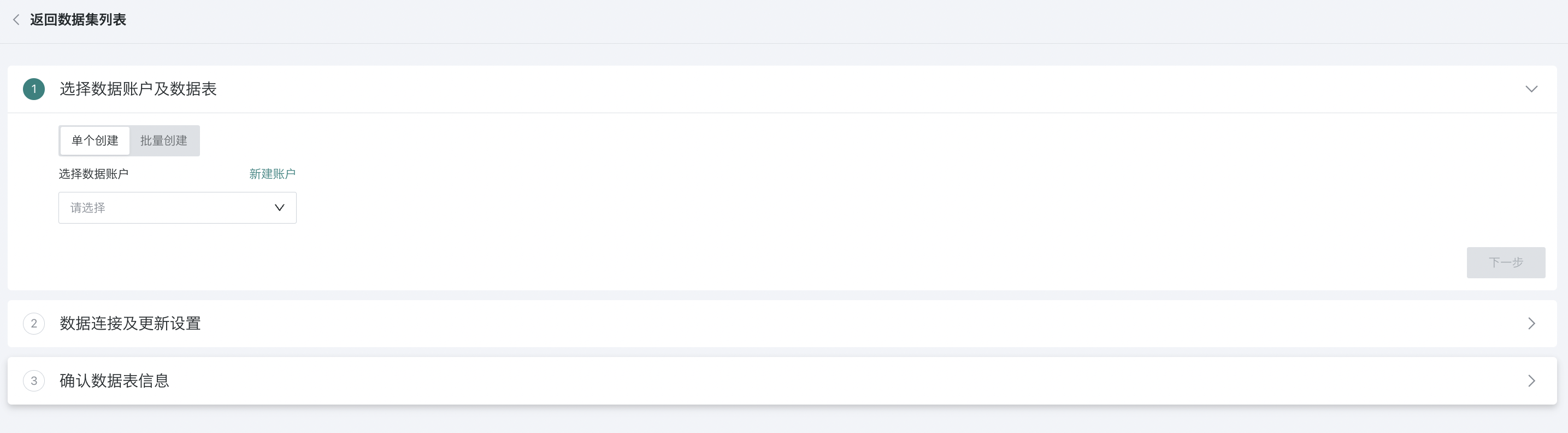
2.1. Select Data Account and Data Table
Select "Single Creation" and choose or create a new database account. For details, please refer to [Data Account](../../1-Data Account.md).
During the data connection configuration process, Guandata BI supports users to perform SQL queries and graphical modeling operations on one or more tables in the database.
-
SQL Query: A traditional query method open to IT or technical personnel, where users can perform complex SQL query operations on one or more tables in the database.
-
Graphical Modeling: An interface-based operation method for business personnel. Through a graphical interface, users can perform operations between tables, reducing the complexity and operational barriers of data integration, enabling non-technical personnel to easily perform data modeling.
Note:
1. Currently, only MySQL and Impala databases support graphical modeling operations.
2. Due to the different data structures and query characteristics of MongoDB and SAP BW databases, the configuration process when integrating with Guandata BI will have corresponding differences. Users are advised to refer to the "MongoDB/SAP BW Connection Guide".
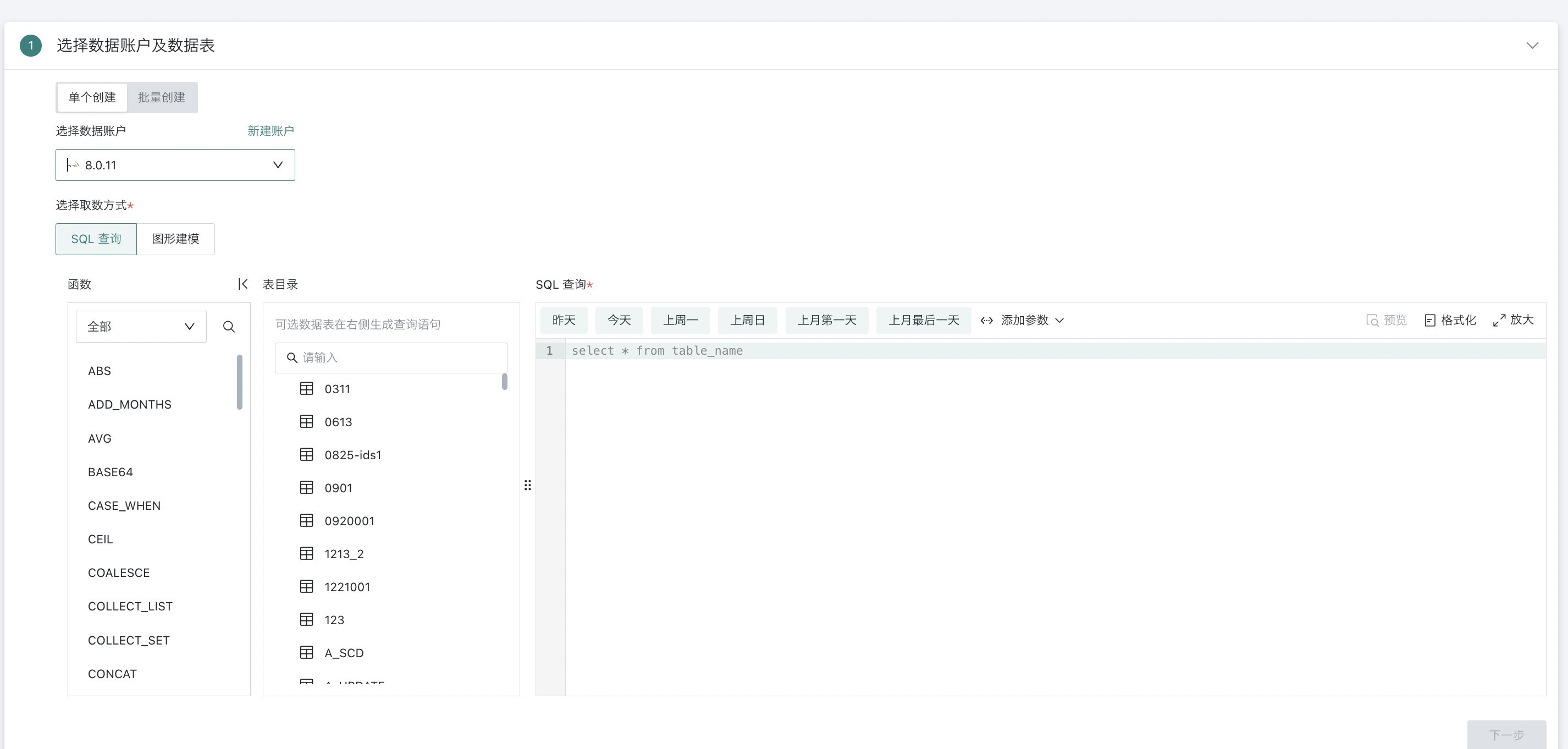
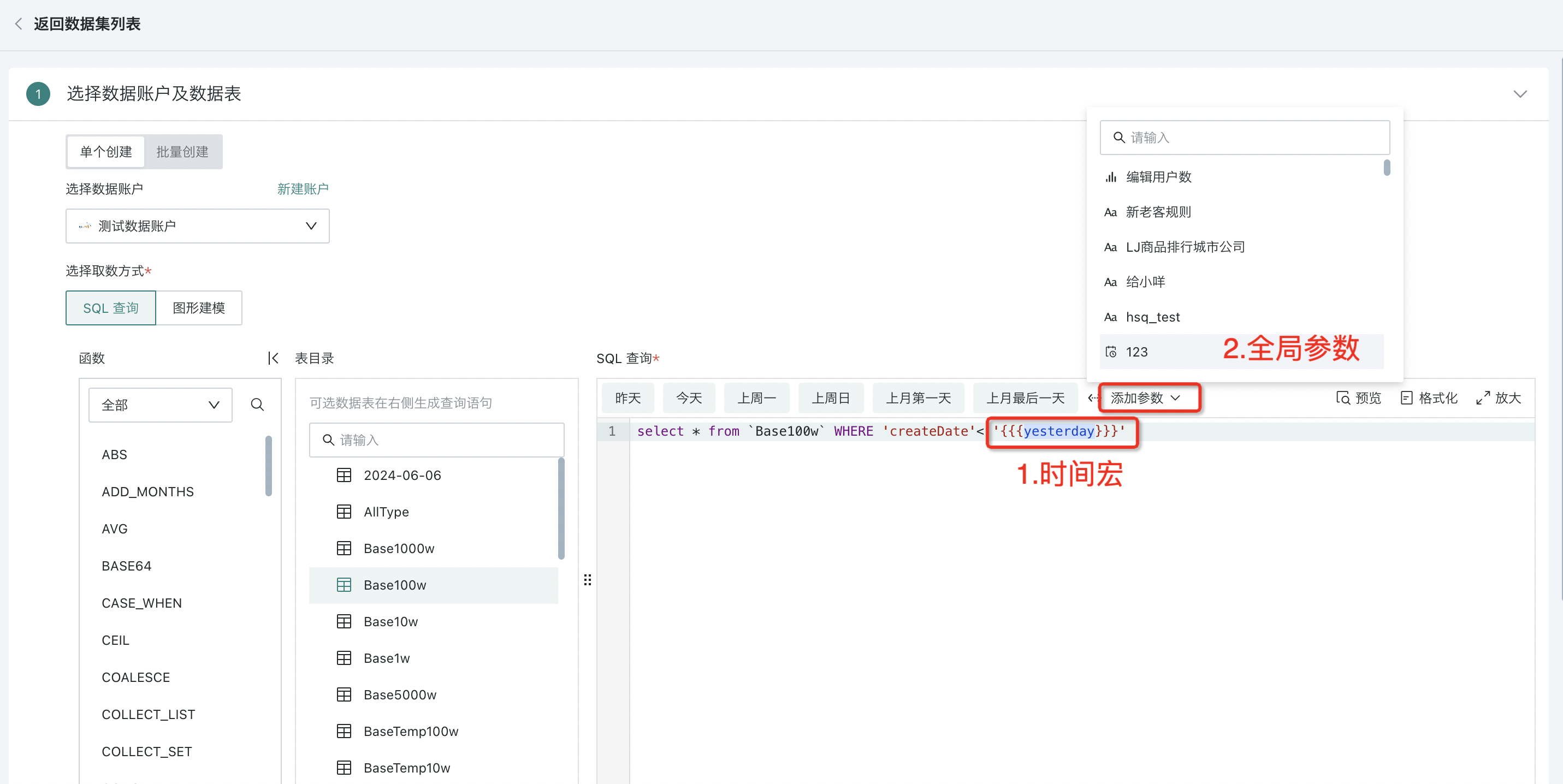
SQL Query
Select one or more tables from the database table directory on the left, and enter SQL in the editing area on the right to complete the specified data retrieval.
Additionally, during the data table configuration process, support is provided for introducing time macro parameters, global parameters, etc. During actual calculation, the values of dynamic parameters will be substituted into the query statement to achieve complex data analysis dimension switching and flexible queries, without the need to manually modify parameters each time.
For example, in time macro parameter scenarios, it can help users generate dynamic SQL based on the current date, set time range requirements for data updates and dynamic analysis, and achieve scheduled data refresh and incremental updates. Input:
select date, cost, revenue from table_name where date >='{{{yesterday}}}'
For more details, please refer to Dynamic Time Macro, Global Parameters.
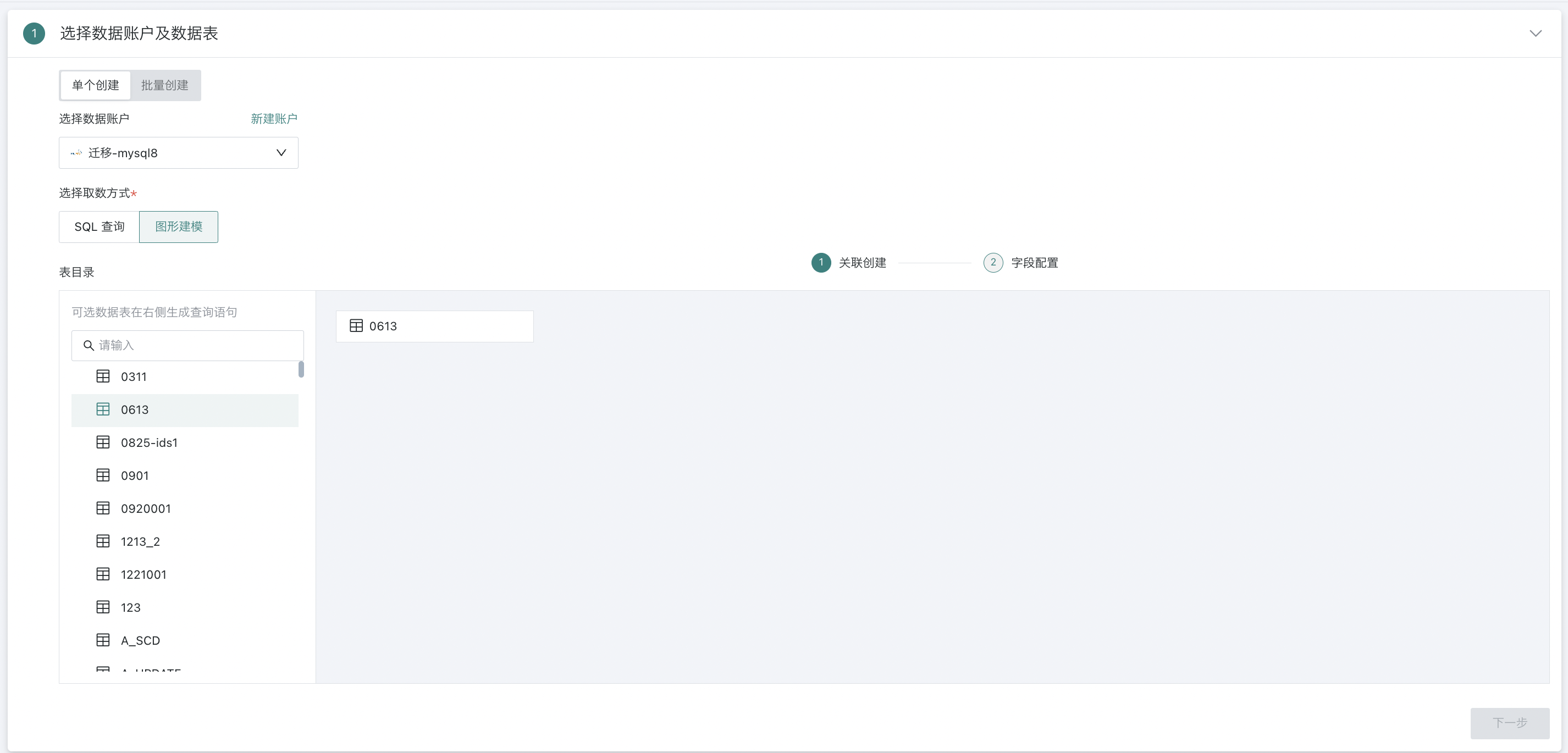
Graphical Modeling
Graphical modeling is a function provided by Guandata to reduce operational barriers during the data integration process, making it easier for non-technical colleagues to perform data connection work more quickly and better. It allows for association operations between tables. When creating a dataset, after selecting MySQL or Impala, you can choose the "Graphical Modeling" method in the database query section.
Note: Currently, only MySQL and Impala databases support graphical modeling operations.
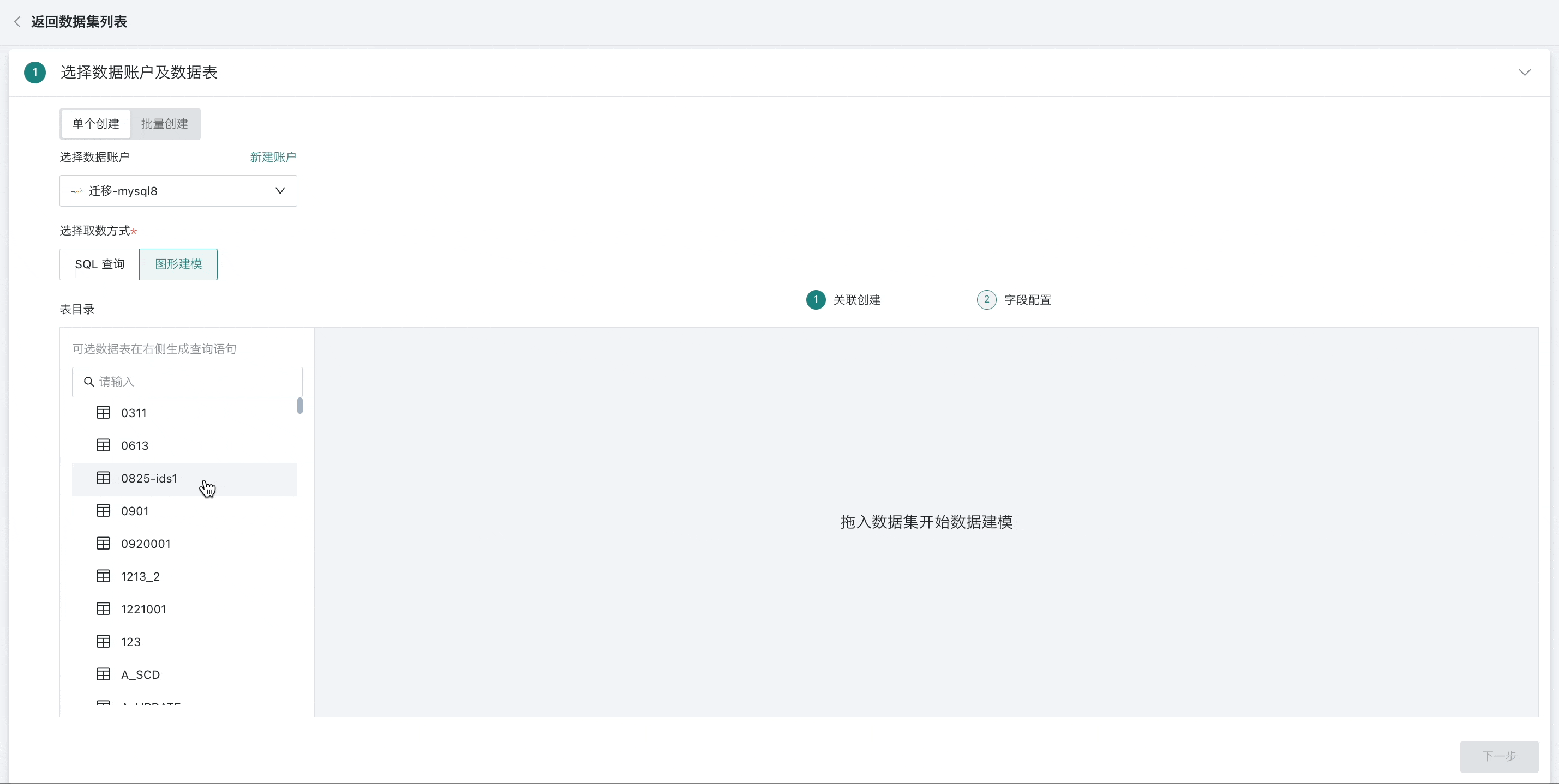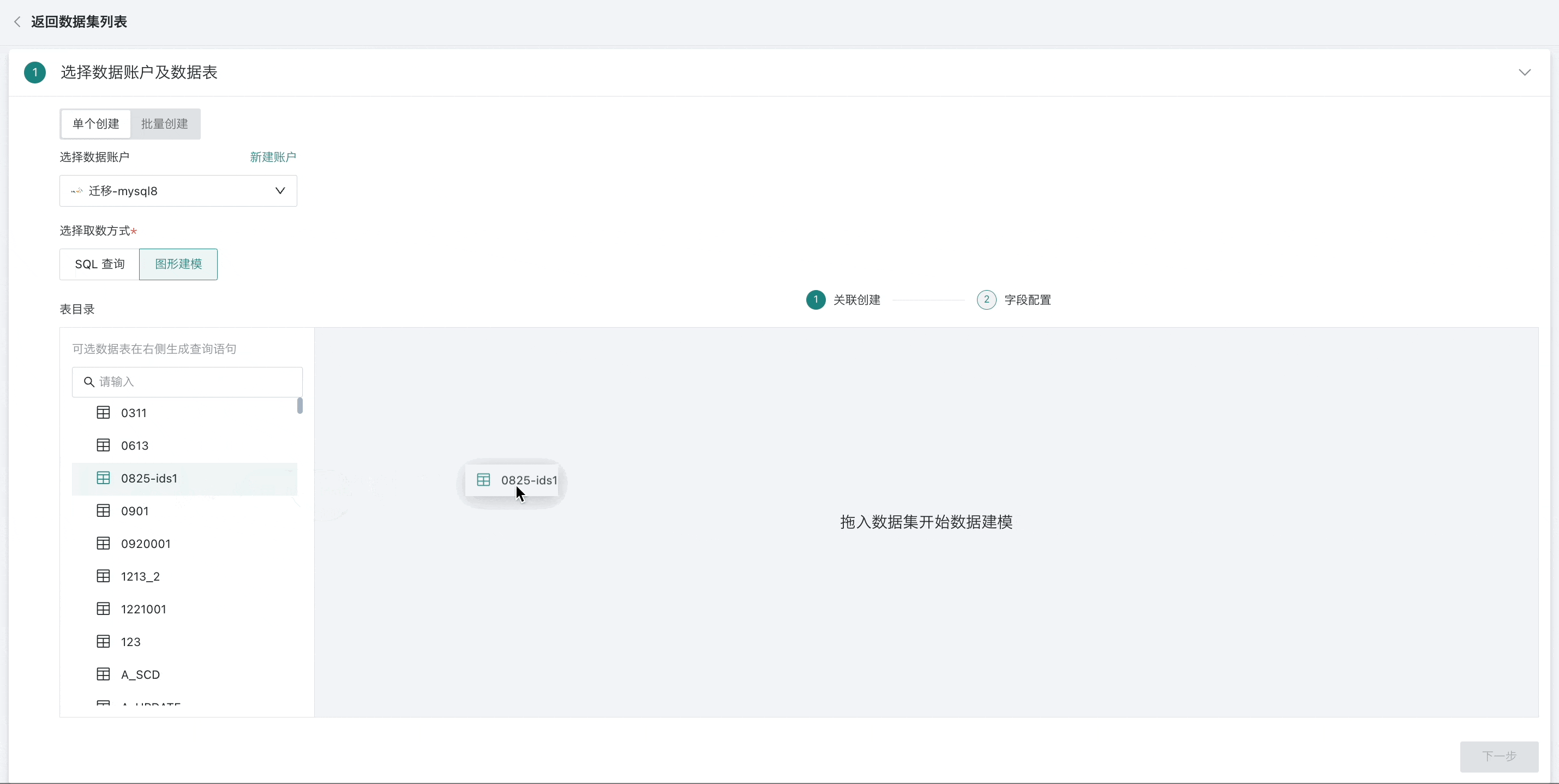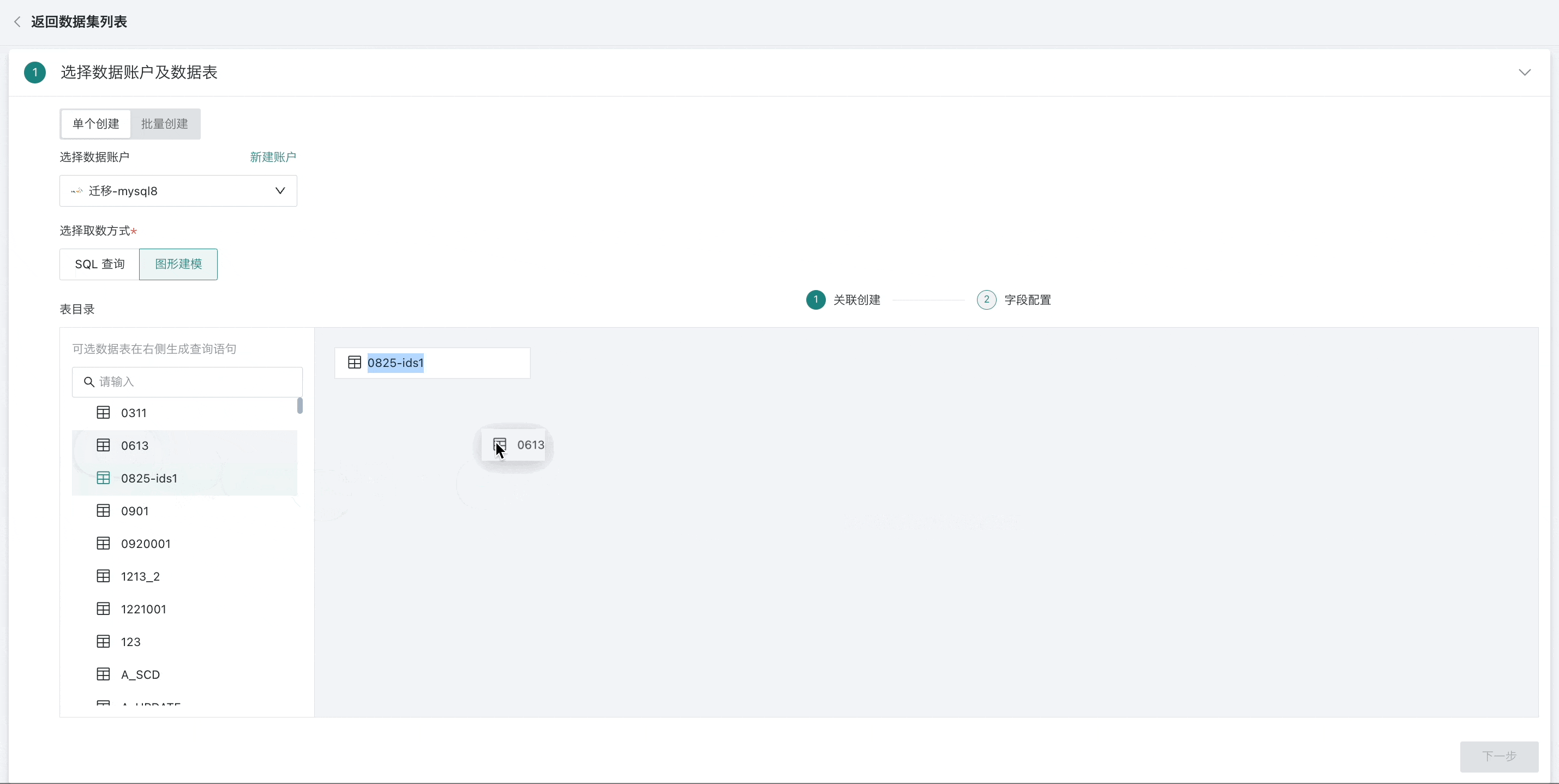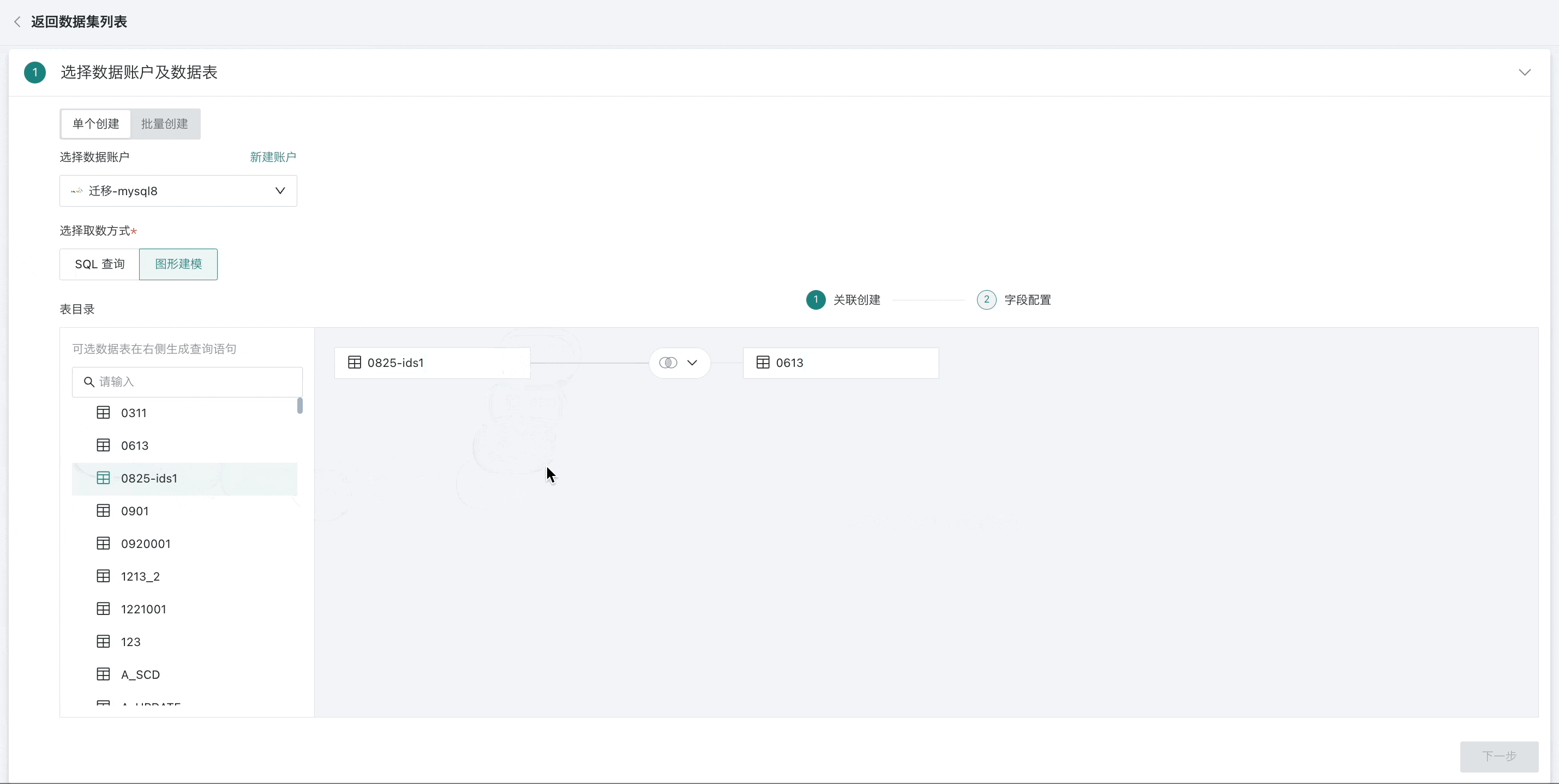
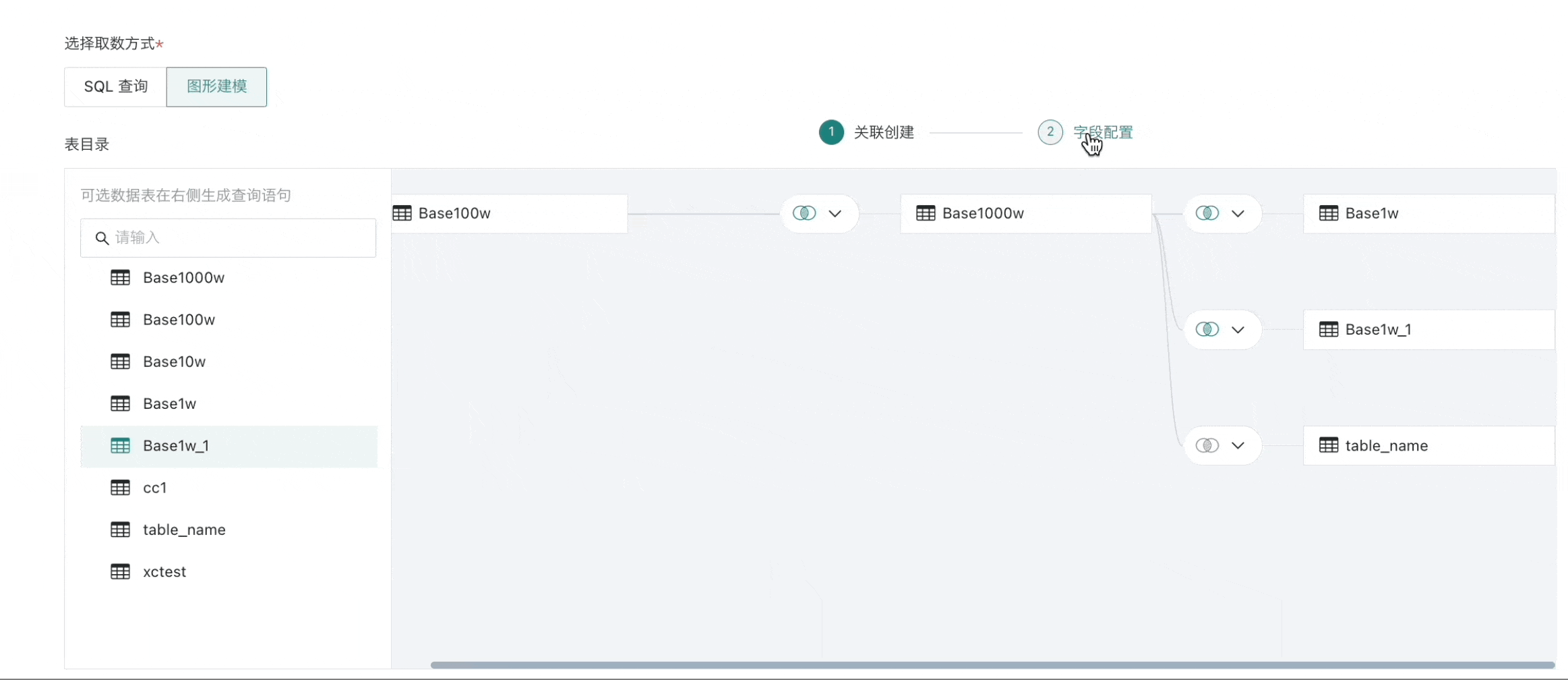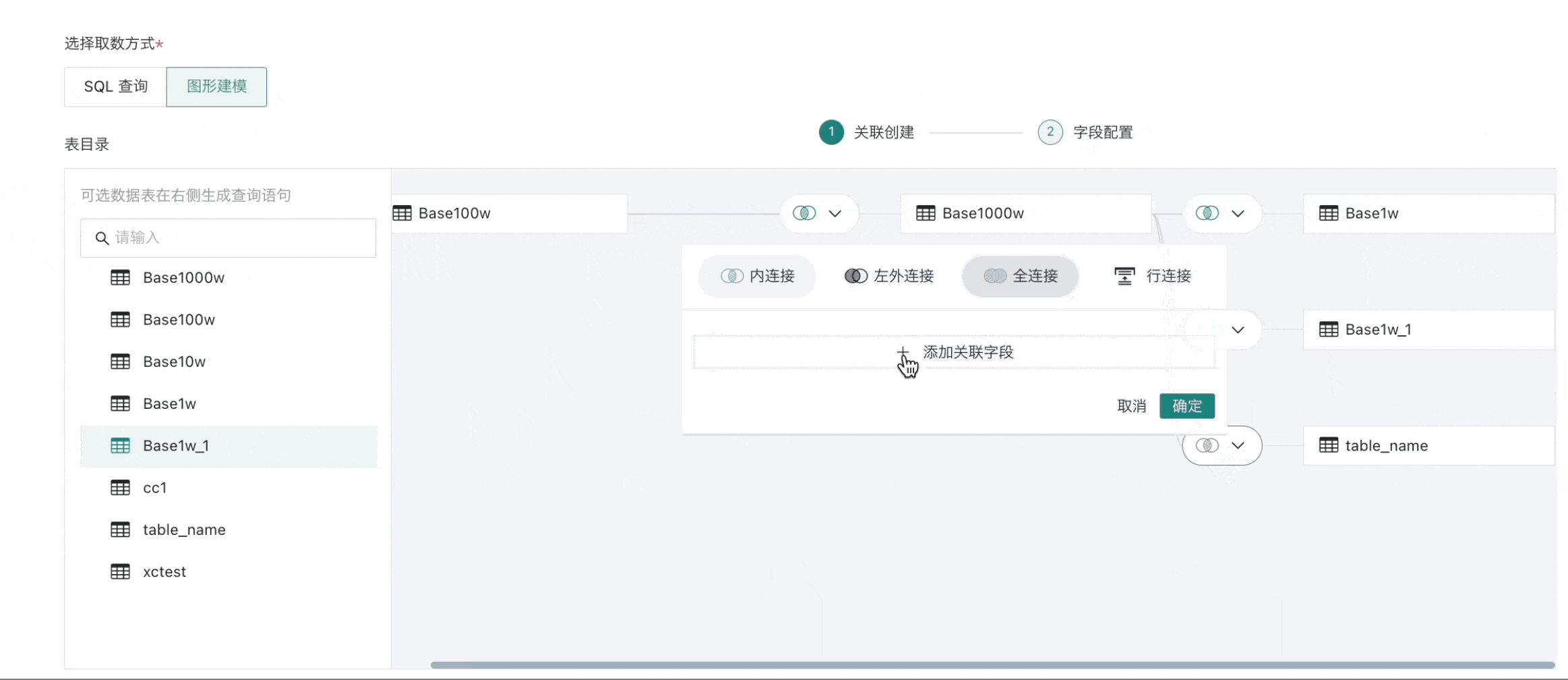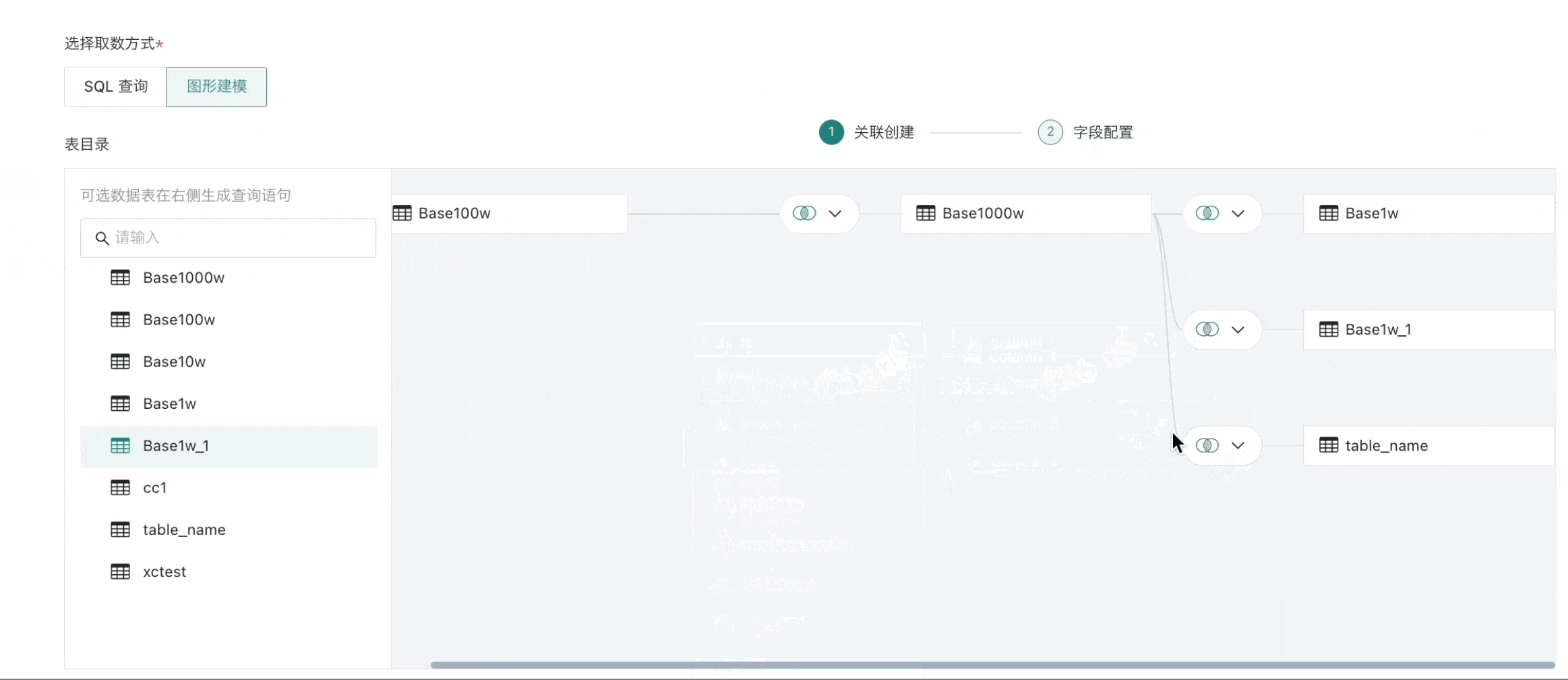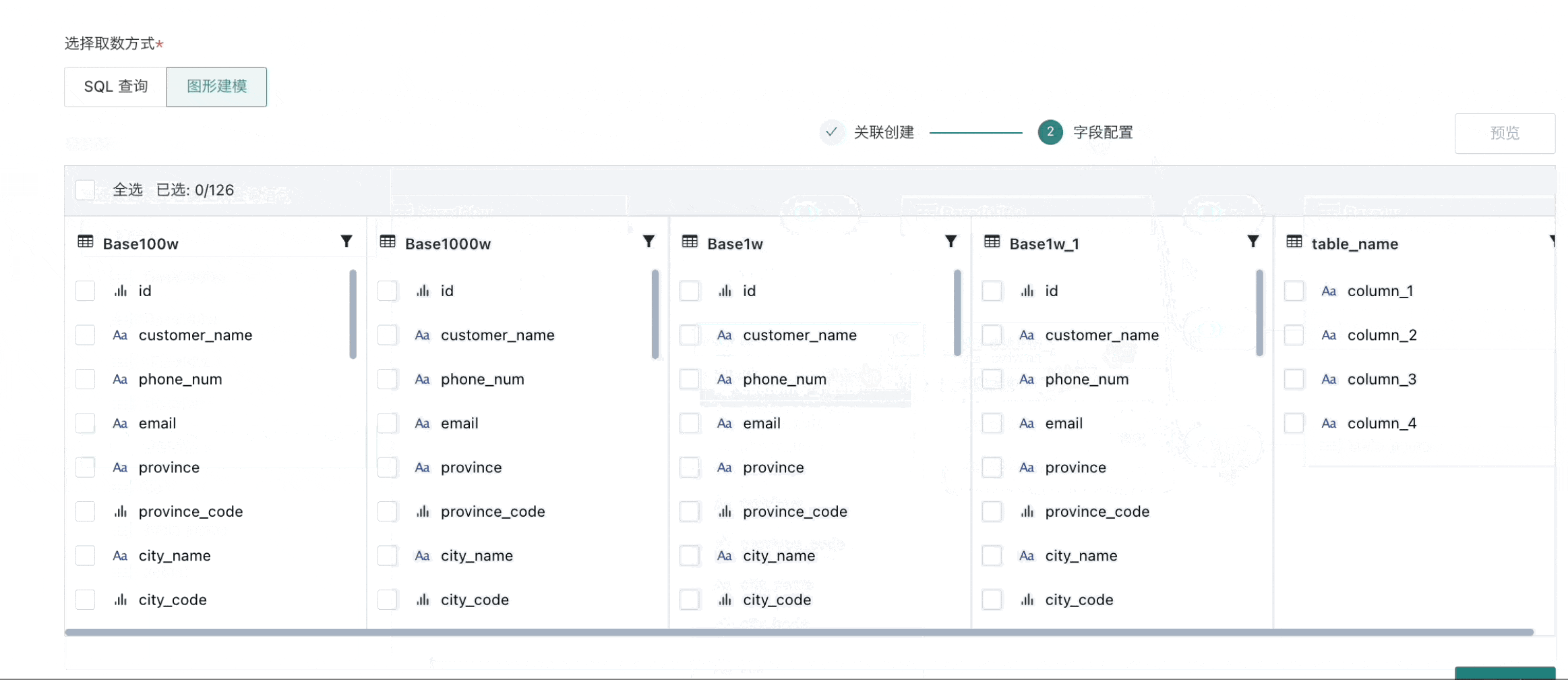
Association Creation
For already created datasets, when modifying the model structure, graphical modeling is also supported. The operation method remains the same, as follows:
- In the database table directory on the left, drag one or more data tables to the "Association Creation" canvas.
-
When selecting a single data table, you can directly enter the field configuration step, complete the selection of one or more fields, and preview the results.
-
When selecting multiple data tables, you need to drag the next data table to the end of the previous data table, forming a wide data table through table association or row concatenation;
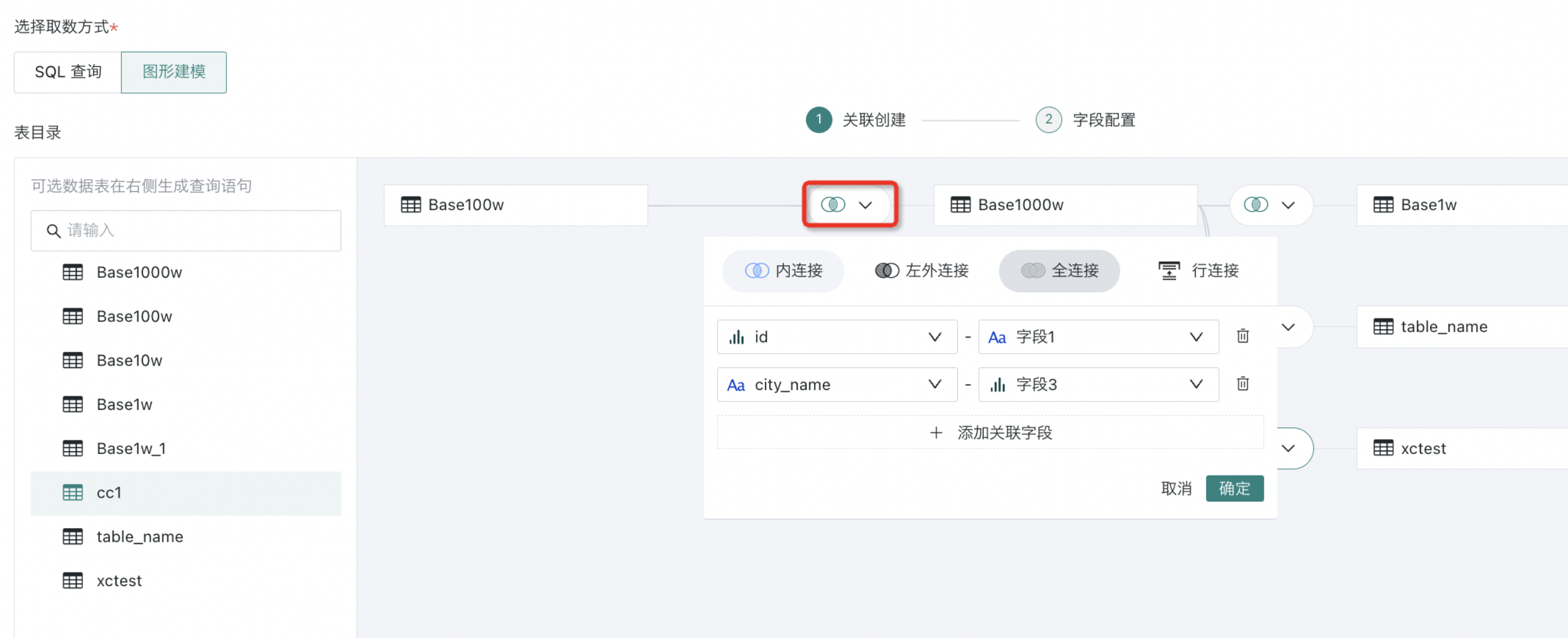
- When dragging in multiple tables, four operations are supported between tables: inner join (default), left outer join, full join, and row concatenation, and set association fields as needed.
Note:
1. Supported operations will coordinate with the database itself. For example, MySQL itself does not support full join, so full join is also not supported in the association creation of graphical modeling.
2. If two tables have fields with the same name, fields with the same name will be automatically prioritized as foreign keys for association;
3. Users can also manually add, remove, and set association conditions.
When the current dataset is no longer needed, right-click on the current node to invoke the delete operation, and click delete.
Note: This operation will simultaneously remove all child nodes. Please handle with caution.
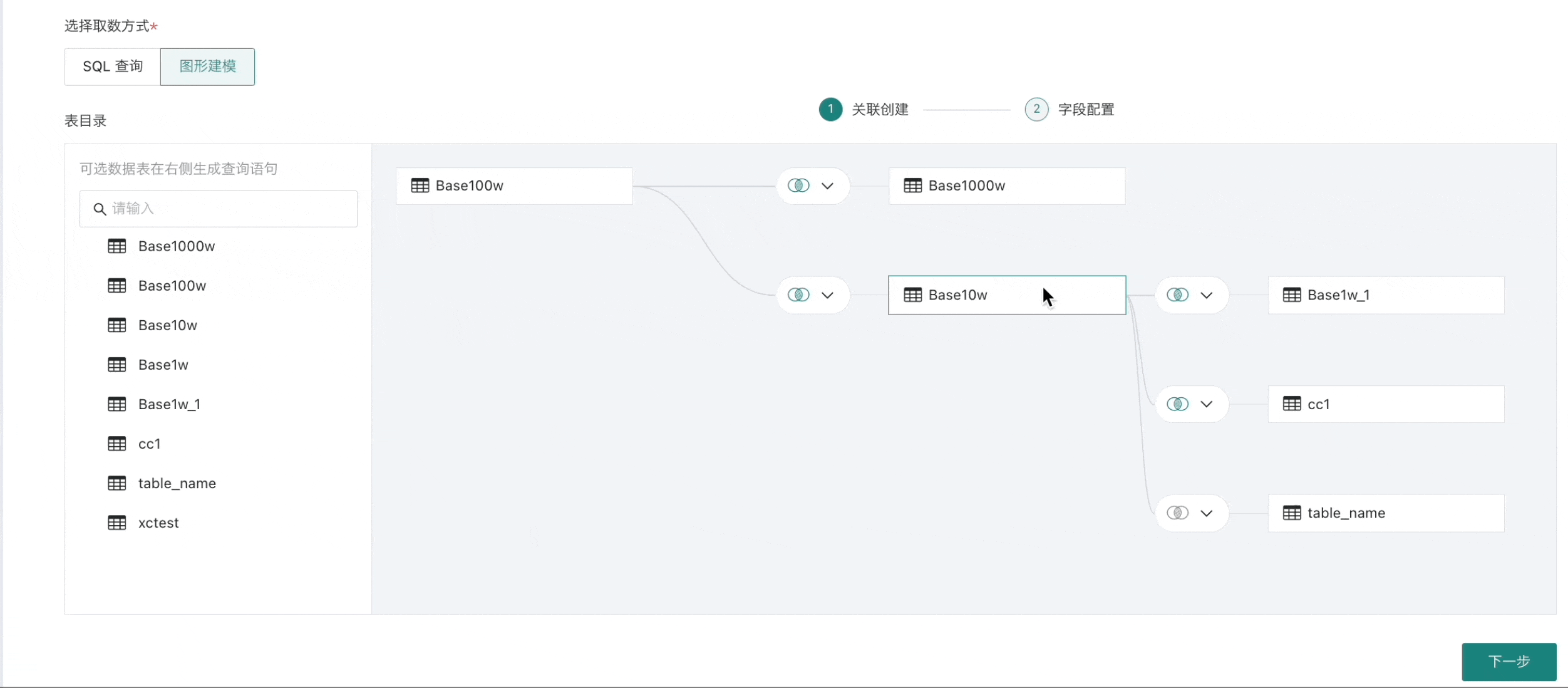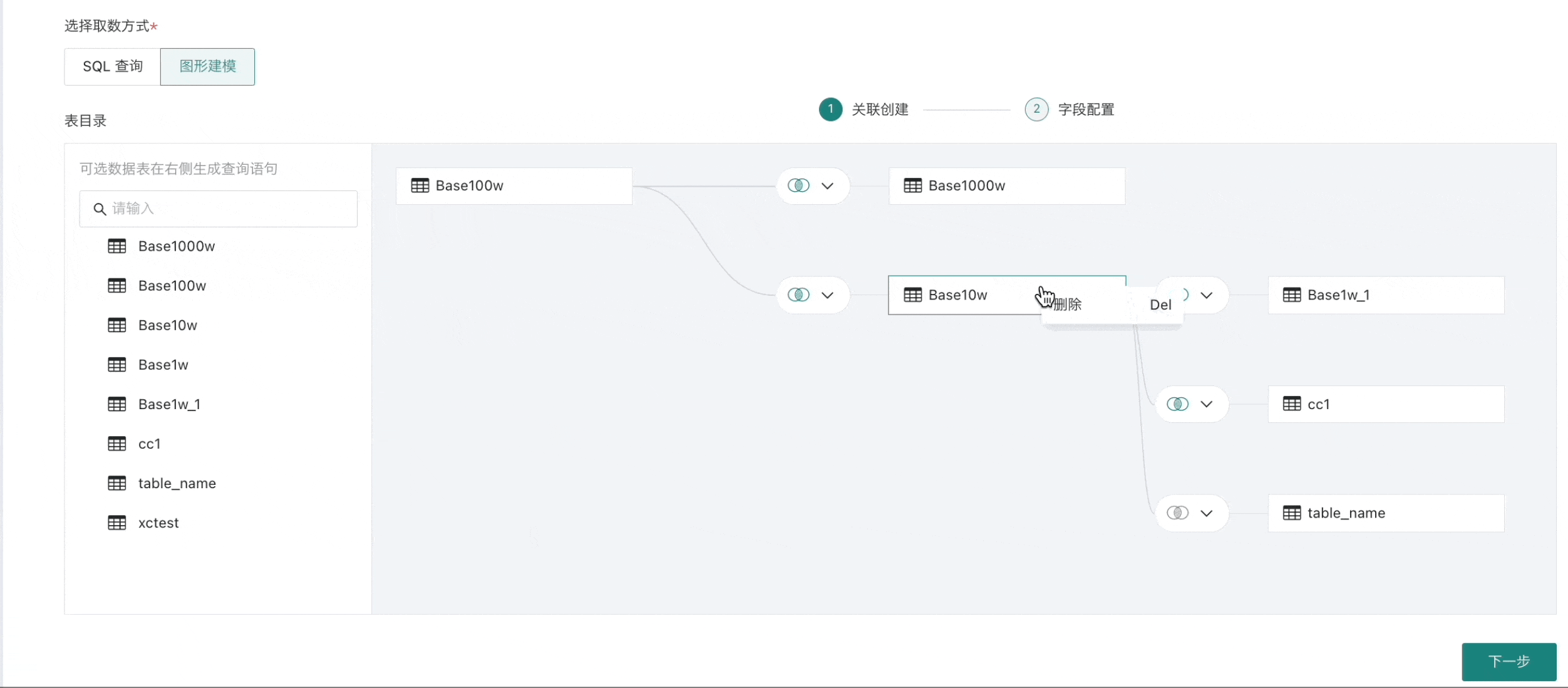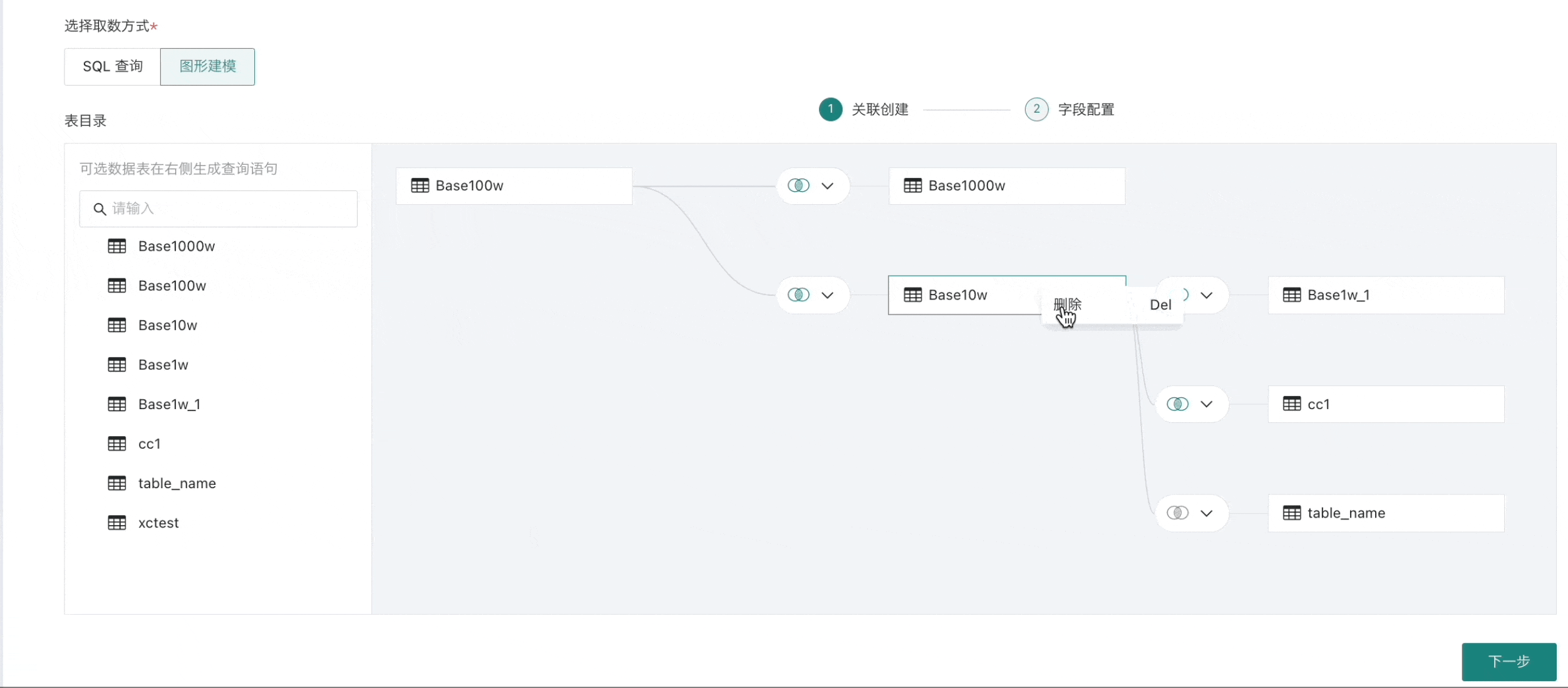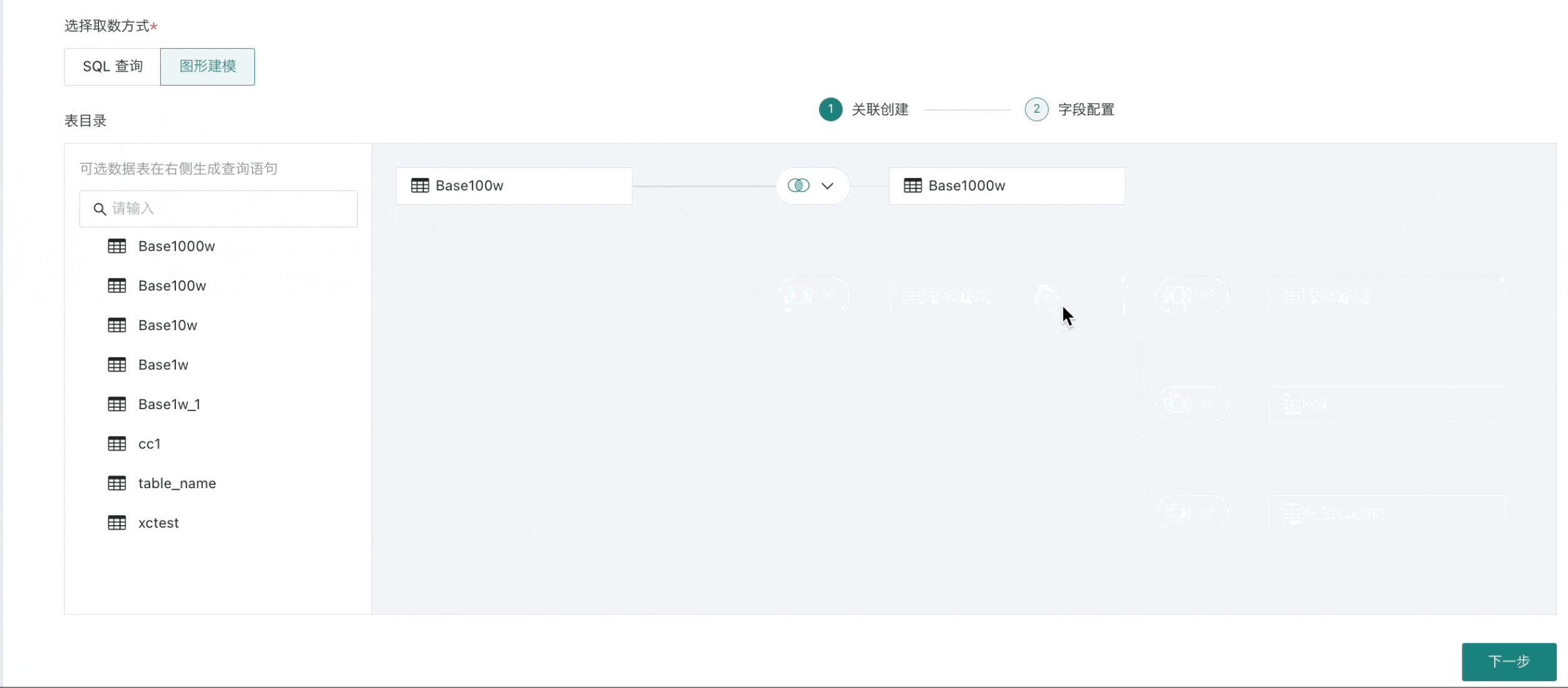
- All association relationships need to be set up before proceeding to step two "Field Configuration";
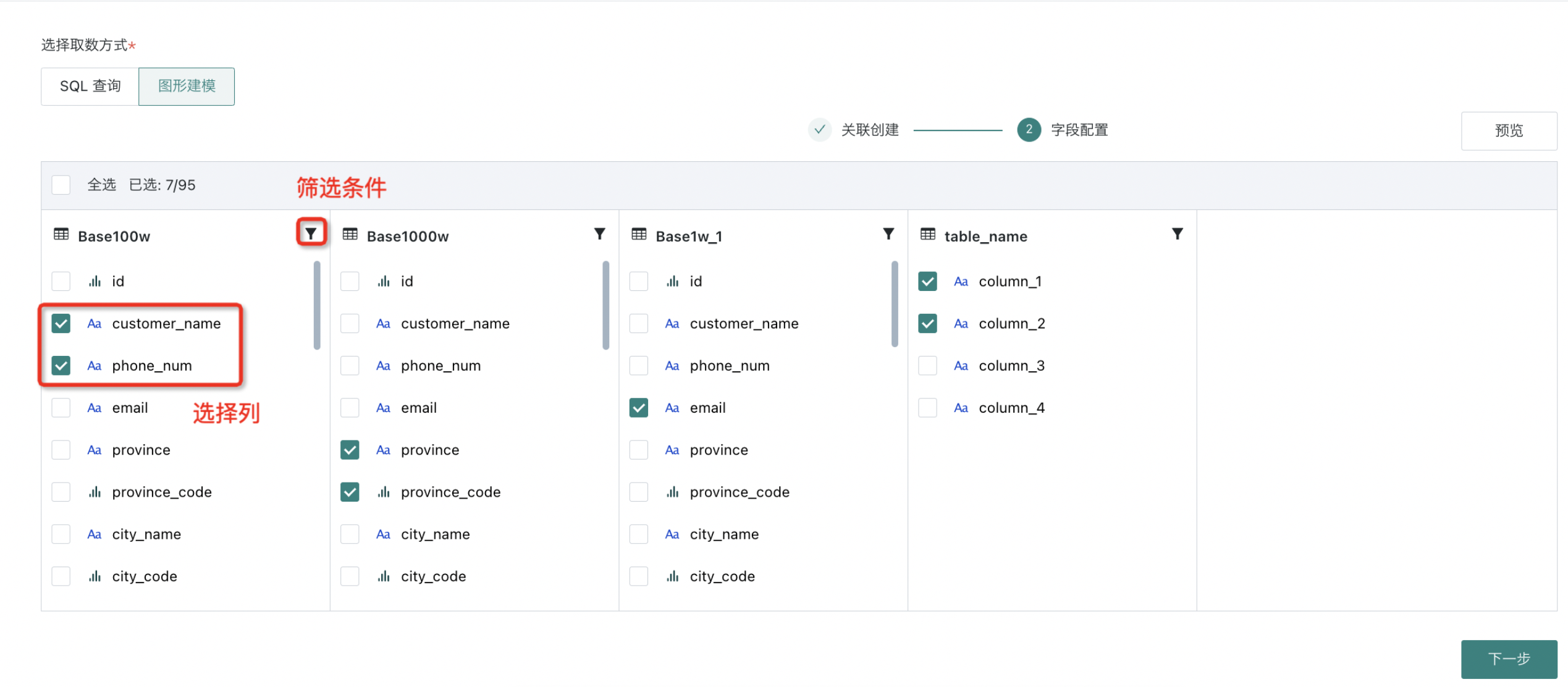
Field Configuration
-
After completing association creation, proceed to field configuration for column selection and condition filtering;
-
After previewing the dataset without issues, you can proceed to the next step.
2.2. Data Connection and Update Configuration
General Configuration
Database Connection Method
| Connection Method | Description | Applicable Scenarios |
| Direct Connection | Directly connect to the user's database for data query and calculation, BI obtains the database returned results for visualization display. | Enterprises prohibit data landing to other systems due to data security considerations; business data changes frequently and requires seeing real-time latest data; large data volume and the customer's own database query performance is good. |
| Extraction | Data needs to be extracted and saved to Guandata BI for calculation, extraction can be full/incremental extraction. | Customers have no data middle platform/data warehouse, building lightweight data warehouse based on Guandata BI |
Scheduling Status
Scheduling status controls whether the dataset automatically updates according to the preset update strategy. When scheduling is enabled, the system will automatically trigger the dataset update process according to the configuration;
When scheduling is disabled, the system will stop automatic updates, but users can still update the dataset through other methods (such as manual update or URL trigger). It is not affected by the scheduling status (enabled or disabled), such as manually clicking the update button through the Guandata BI user interface to immediately update the dataset, or triggering the update process by sending a URL request with specific parameters to the system.
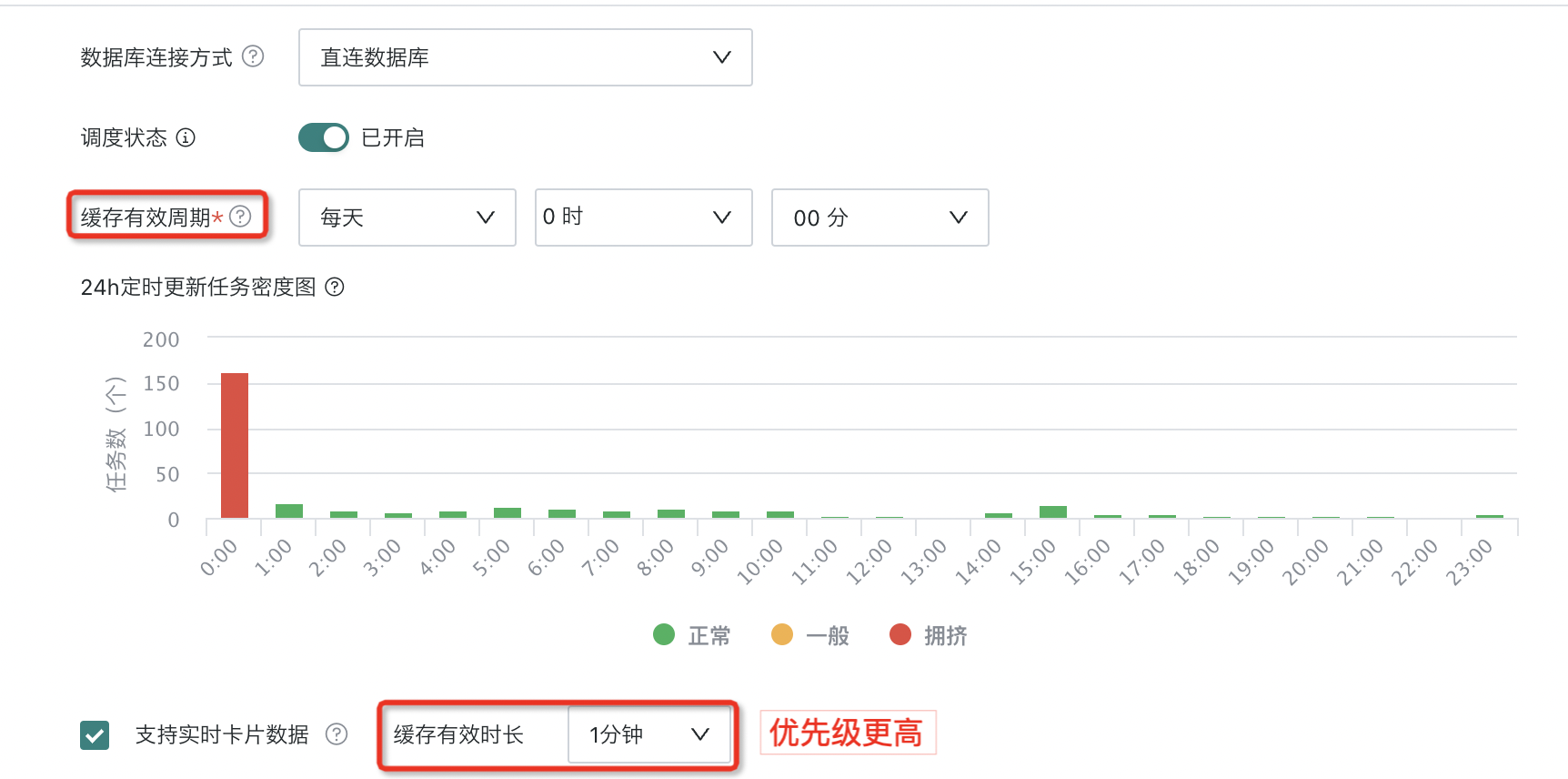
Direct Connection Configuration
Cache Validity Period
In direct connection mode, setting the cache validity period can optimize query performance, reduce database burden, while ensuring users obtain relatively fresh data.
Note:
1. To reduce database pressure, the same query SQL will prioritize using cache, and cache can set validity period.
2. When cache expires, the system will re-query data from the database and update the cache.
Example: If cache validity period is set to 10 AM daily, then the query cache generated by the first access to the card after 10 AM yesterday will be valid until 10 AM today, and the same query for that card during this period will use the same cache. Similarly, after 10 AM today, accessing that card again will re-query from the database and generate new cache, valid until 10 AM tomorrow.
Real-time Card Data/Cache Validity Duration
To meet the demand for real-time analysis, Guandata BI supports real-time refresh functionality for visualization dashboards/cards created based on datasets. This function is implemented through the "Real-time Card Data/Cache Validity Duration" configuration item, allowing users to finely control data update frequency to meet different business scenario data viewing needs. By default, the real-time card data update cycle is set to 1 minute ~ 30 minutes, or no cache mode.
For example, when set to 1 minute, it means that every minute, the relevant cards will automatically obtain the latest data from the data source and update the display, ensuring users see the latest near real-time data.
Note:
1. Dependency configuration: To achieve the effect of real-time data refresh on dashboards/data screens, not only need to check this item, but also need to simultaneously turn on the "Auto Refresh" switch on the relevant dashboard/data screen; only when both conditions are met can users see continuously, real-time updated data on the dashboard or data screen.
2. Priority: After configuring "Cache Validity Duration" in real-time card data, the priority > the cache validity period above.
Extraction Configuration
Data Update Cycle
In extraction mode, the data update cycle is directly related to the trigger time of scheduled extraction tasks. Users can set scheduled tasks according to business needs, specifying when (such as daily midnight, weekly Monday, etc.) to trigger the data extraction process. Extraction can be full extraction or incremental extraction, depending on data change conditions and business requirements. By setting the trigger time of extraction tasks, users can flexibly control data update frequency, ensuring the data in the dataset remains up-to-date.
Note: A single dataset cannot be updated more than 4 times per day.
Deduplication Primary Key
"Deduplication Primary Key" can be understood as using the table's primary key to prevent or remove duplicate data (duplicate records or rows) in the database, ensuring the uniqueness of each row of data in the table, avoiding data analysis errors and inaccurate results due to duplicate records. Its configuration mainly involves primary key definition and deduplication strategy:
Primary Key Definition: A field (or index) in a database table that can uniquely determine a row of data, ensuring the uniqueness of each row of data in the table.
Deduplication Strategy: One or more fields can be configured as the basis for deduplication.
Note:
1. Similar concepts are involved in the "Data Deduplication Operator" in Smart ETL, which can be referenced for learning "Data Deduplication".
2. When performing deduplication operations, carefully choose the deduplication fields to ensure important data is not accidentally deleted.
3. For tables with large data volumes, deduplication operations may consume more computing resources and time, so they need to be handled carefully.
Full Update/Incremental Update
Guandata BI supports two modes in the data extraction and update process: full update and incremental update.
By default, if the incremental update option is not checked, the system will automatically execute full update. The following is a detailed explanation of these two update modes and applicable scenarios, helping users make the best choice based on specific needs and business scenarios to ensure data accuracy and processing efficiency.
| Type | Description | Applicable Scenarios |
| Full Update | Full update refers to extracting all data from the data source into Guandata BI, overwriting previously existing dataset data. | Applicable to scenarios where data table structure changes, data needs to be reset, or large-scale data migration is performed. |
| Incremental Update | According to the set primary key, the obtained incremental data is updated or inserted into the dataset. | Applicable to tables with frequent updates or large data volumes. Such as: data source tables frequently change data, such as real-time transaction data, user behavior logs, etc. |
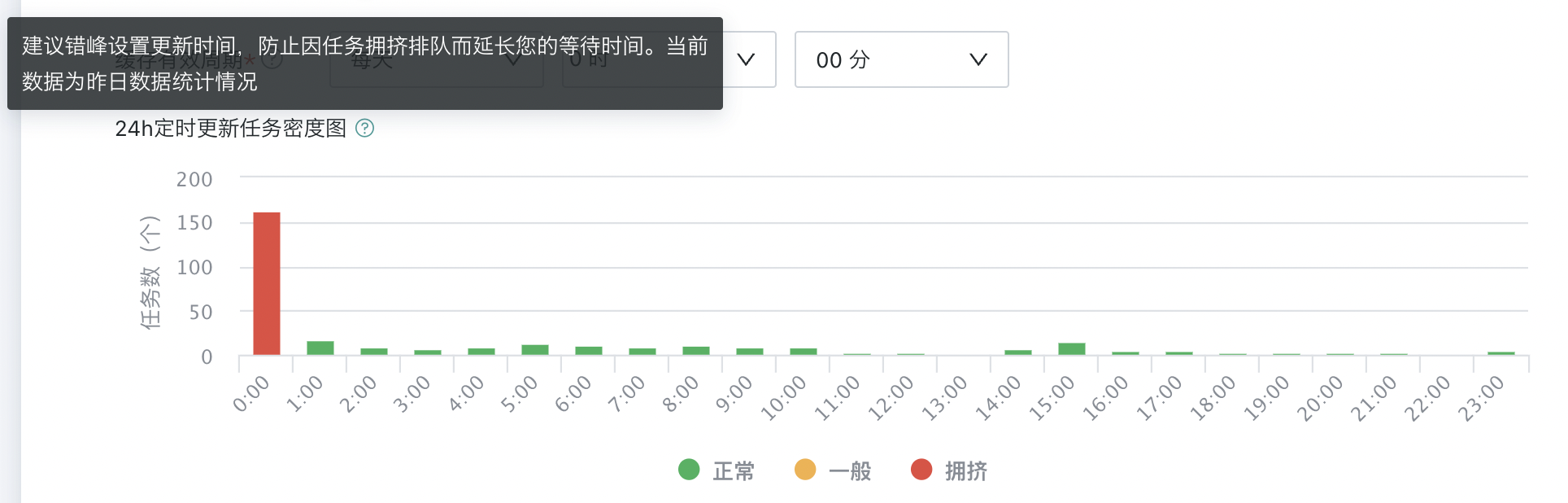
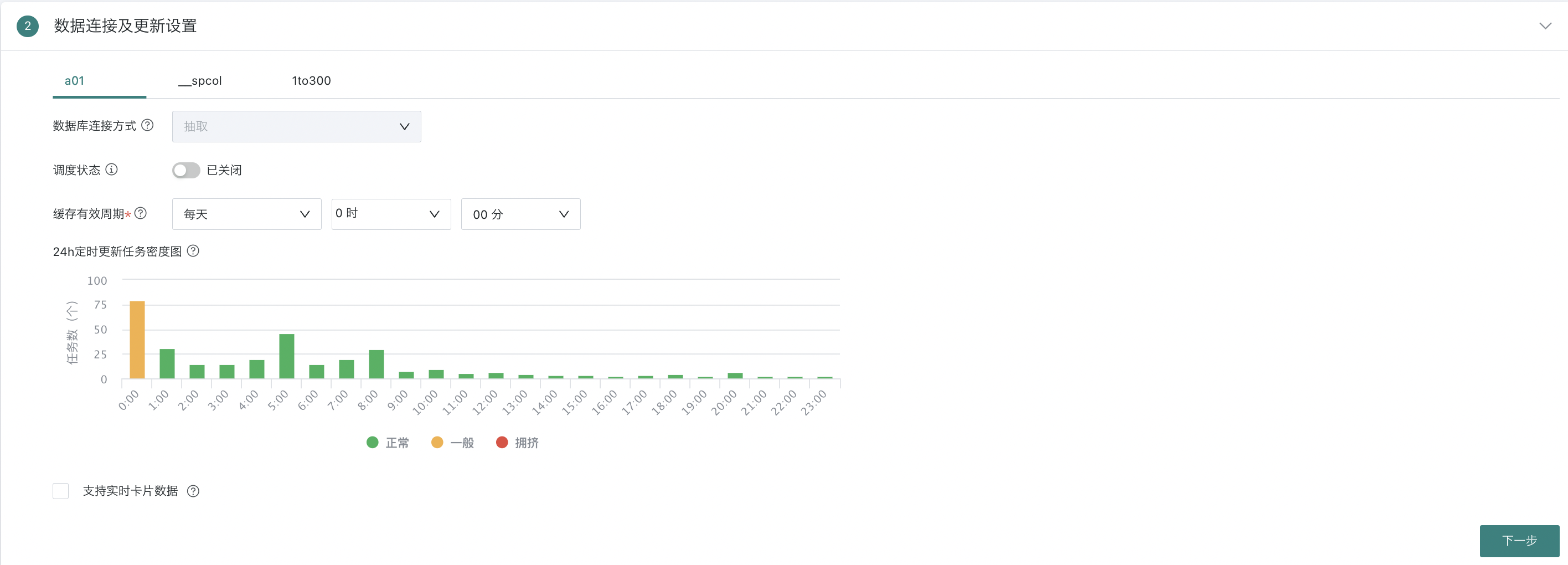
24h Scheduled Update Task Density Map
Reference the number of scheduled update dataset tasks and congestion level within the time period, choose relatively idle time as the current dataset update time, avoid task queuing, and reduce system pressure. Data is only used as a reference for setting update time and may have slight deviations from actual running tasks. Please do not use for statistics.
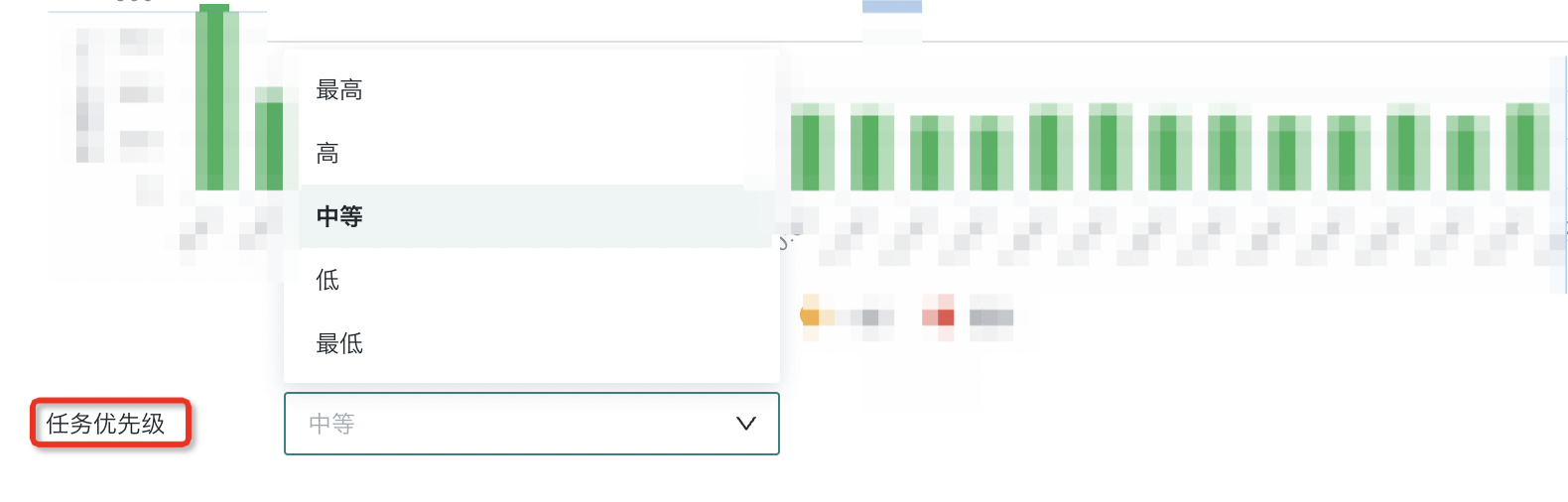
Task Priority
You can set the task priority for dataset extraction to ensure that business high-attention tasks that are scheduled at the same time can be executed with priority. It is divided into five levels: highest, high, medium, low, and lowest, with medium as the default. When the dataset update task is triggered, it will be inserted into the task queue according to the currently configured priority.
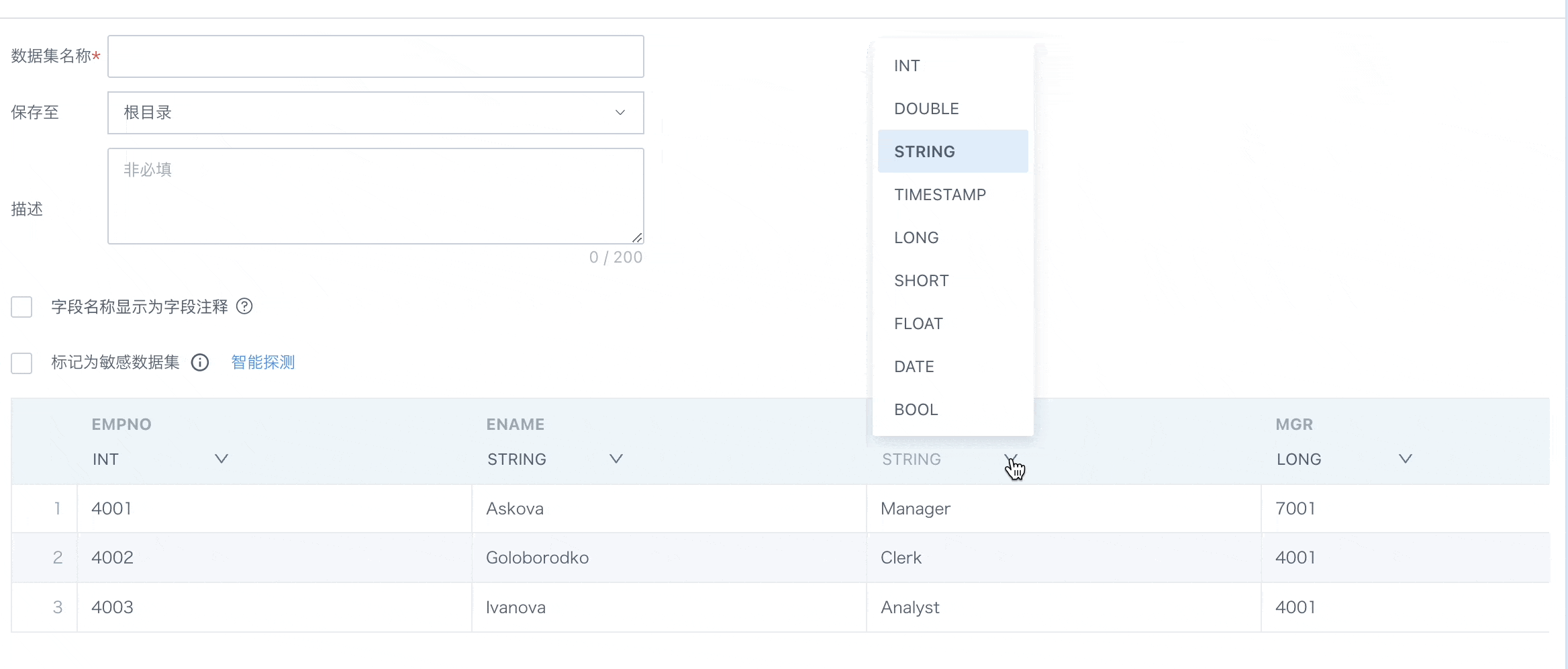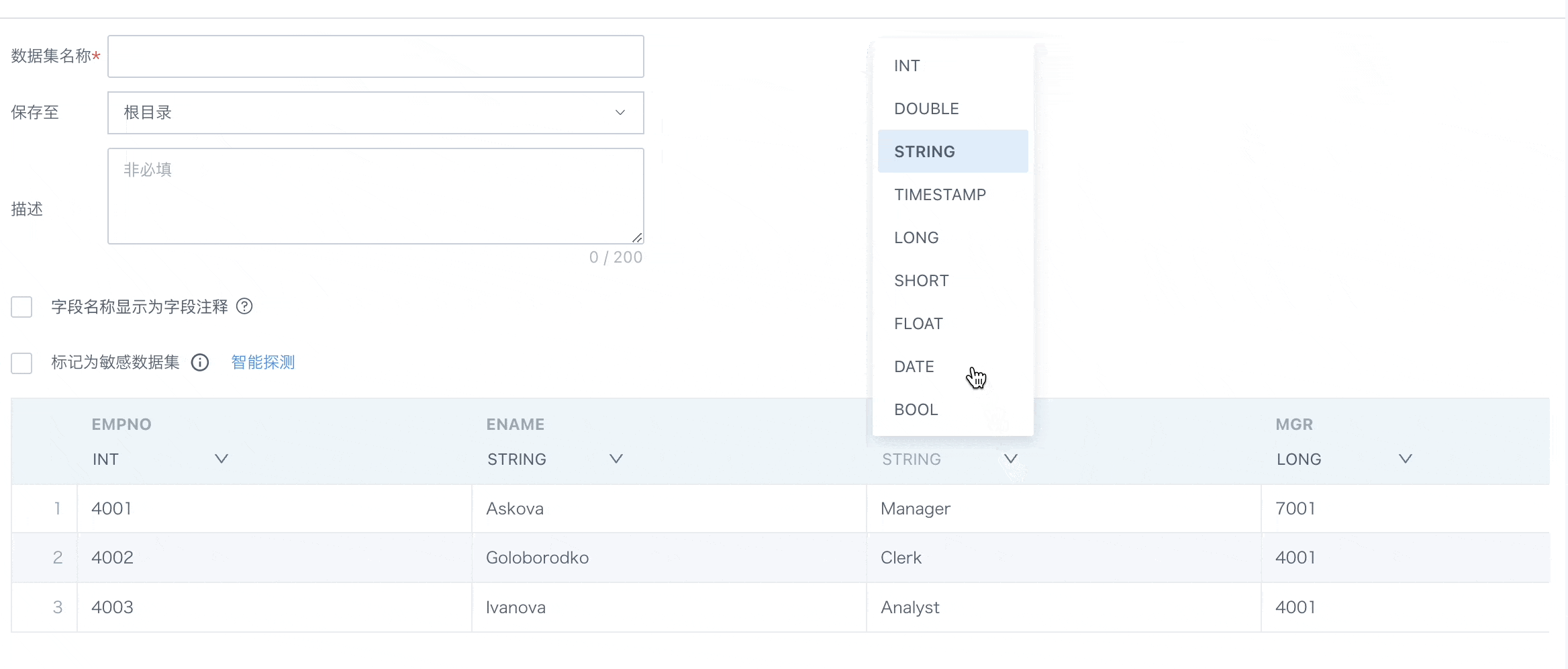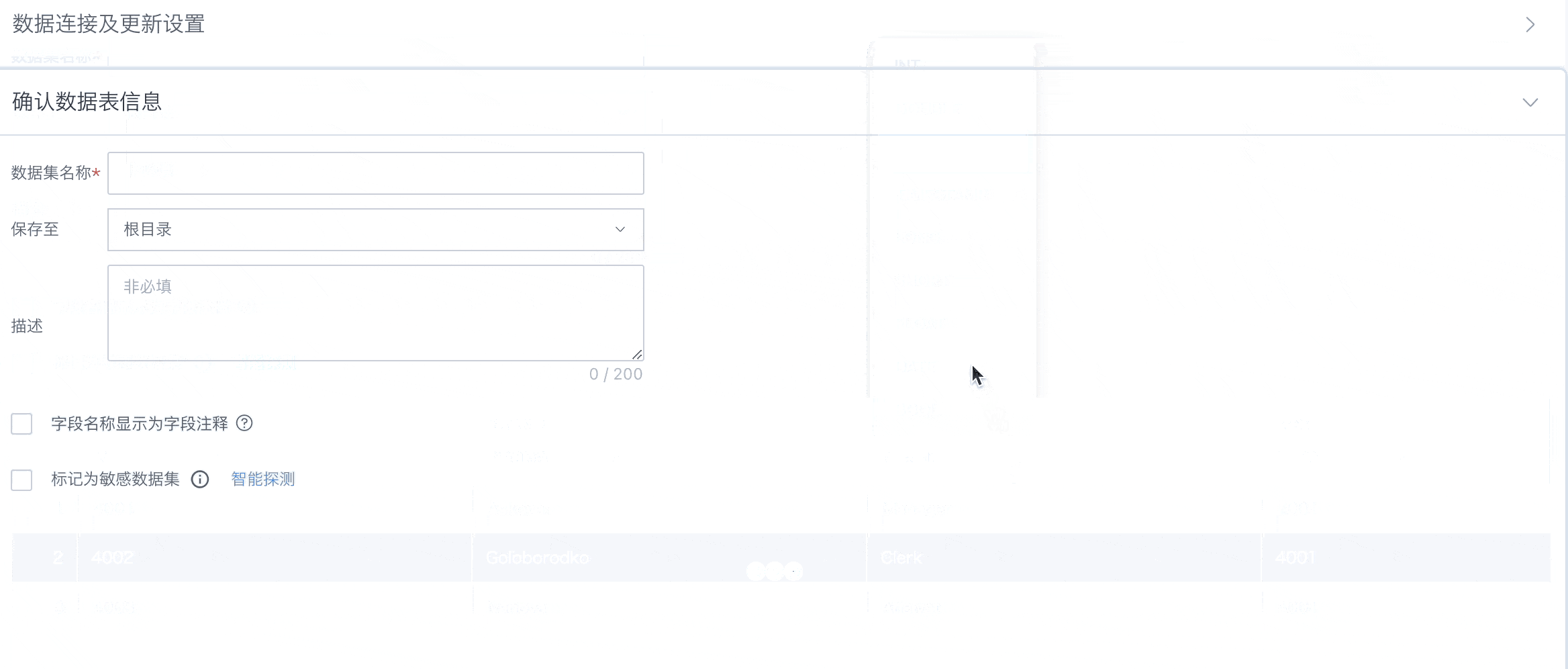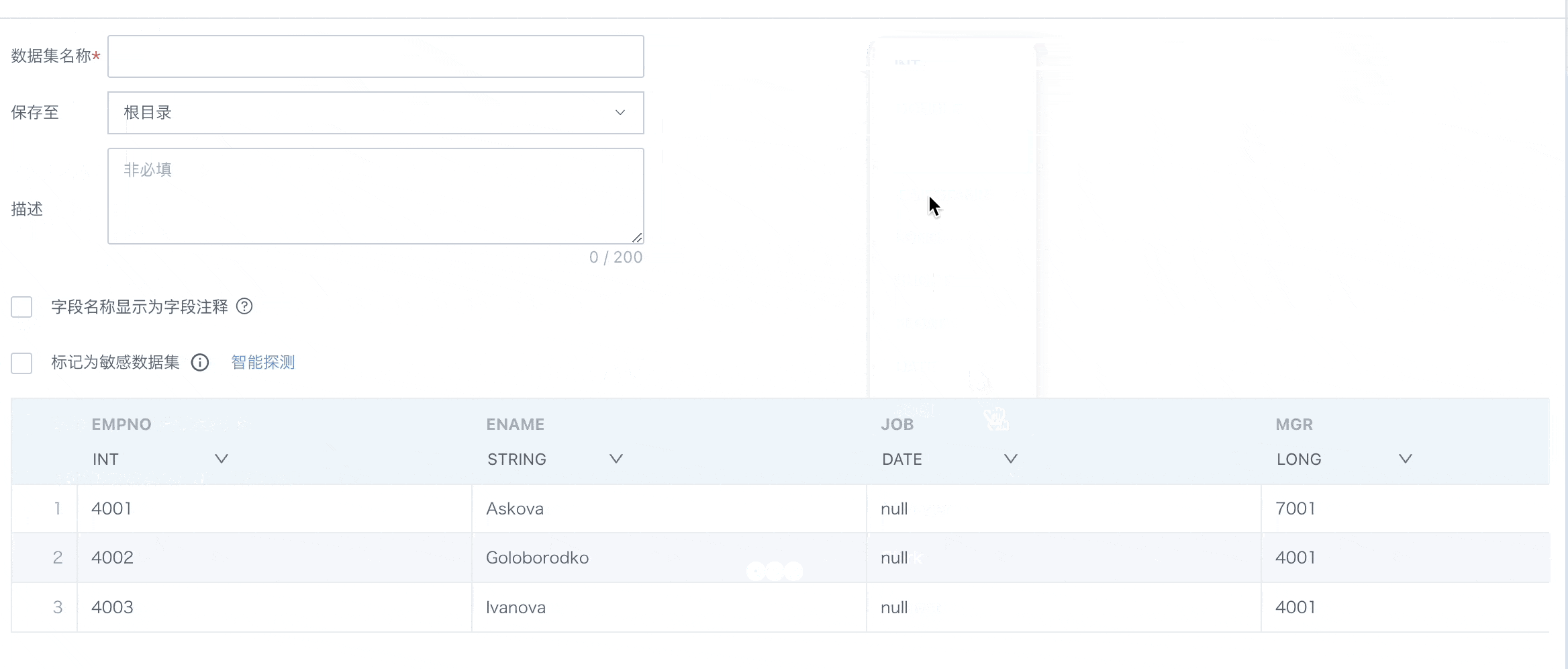
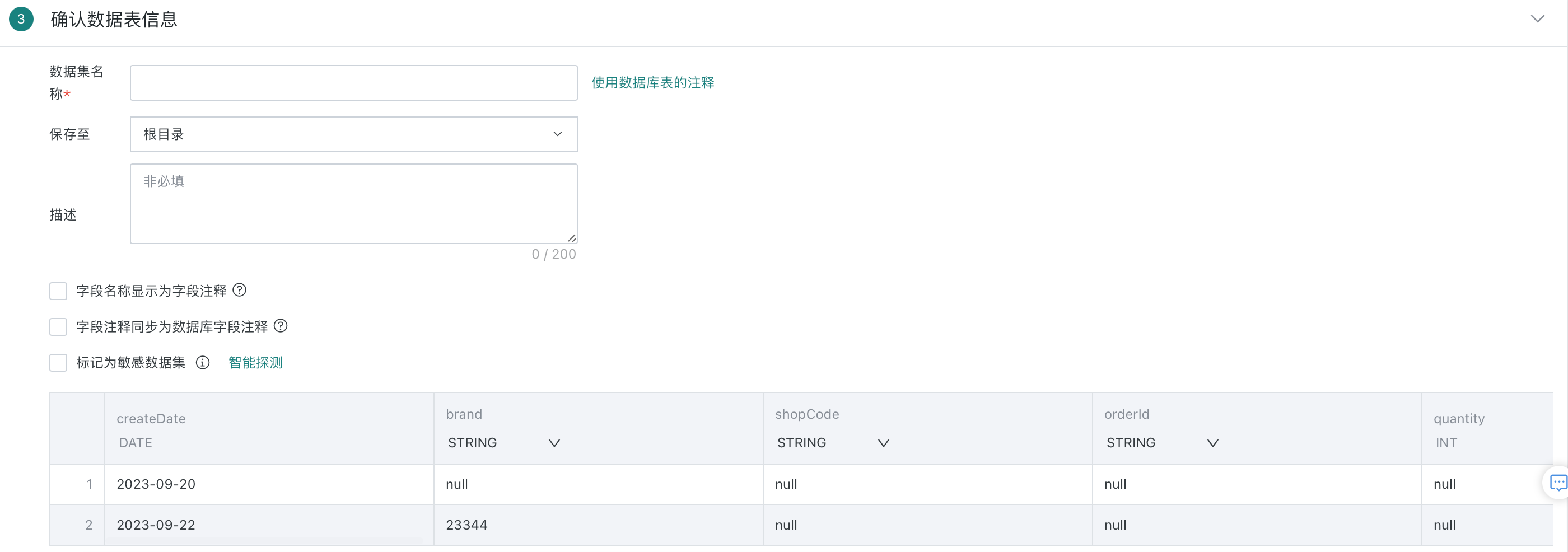
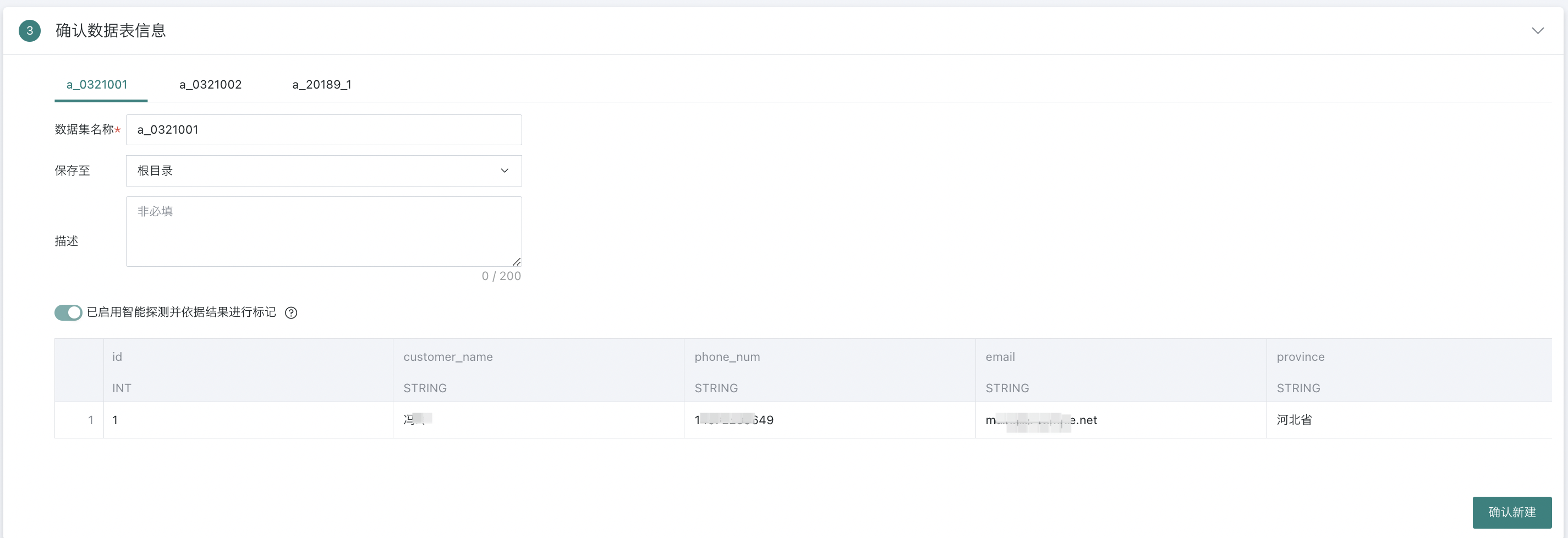
2.3. Confirm Data Table Information
This chapter will详细介绍 confirm data table information, including dataset storage, flexible handling of field comments, sensitive dataset marking, dataset preview and field attribute adjustments, etc., to ensure data consistency and accuracy in subsequent analysis, processing, and display processes.
| 序号 | 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dataset Name | 1. Supports manual entry of dataset name. 2. Supports directly obtaining database table comments as dataset name. If the input SQL contains multiple tables, users will be reminded to choose one to obtain comments. 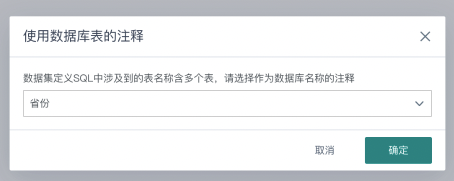 |
| 2 | Save To | Choose save path. |
| 3 | Description | Custom description content, optional. |
| 4 | Field Name Display as Field Comment | After checking, the field name will automatically sync to the field comments already set in the database. When IT departments build application layer wide tables, they usually annotate the Chinese names of dataset fields in the table structure comments in the data warehouse or database environment. When BI integrates with wide tables, this function can directly overwrite the field comments in the original table comments as field names, reducing repetitive manual modification work. (*Note: This function currently only supports single table datasets, and the currently supported databases include: MySQL, Hive, Impala, Presto, ADB, ClickHouse, MaxCompute, GaussDB, StarRocks, GBase). |
| 5 | Field Comment Sync to Database Field Comment | After checking, the field comment will automatically sync to the existing comments of database fields. |
| 6 | Mark as Sensitive Data | Supports marking the current dataset as "Sensitive Dataset". After enabling, sensitive datasets cannot be directly used to create cards. You need to go to the dataset details - Data Security page to configure sensitive fields and masking rules, effectively preventing unauthorized access and leakage of sensitive data. For details, please refer to Data Masking. |
| 7 | Dataset Information |
|
Note:
1. Field type switching is only supported in extraction mode.
2. During dataset extraction, if a column type is inconsistent, the task will not fail.
3. Batch Database Creation
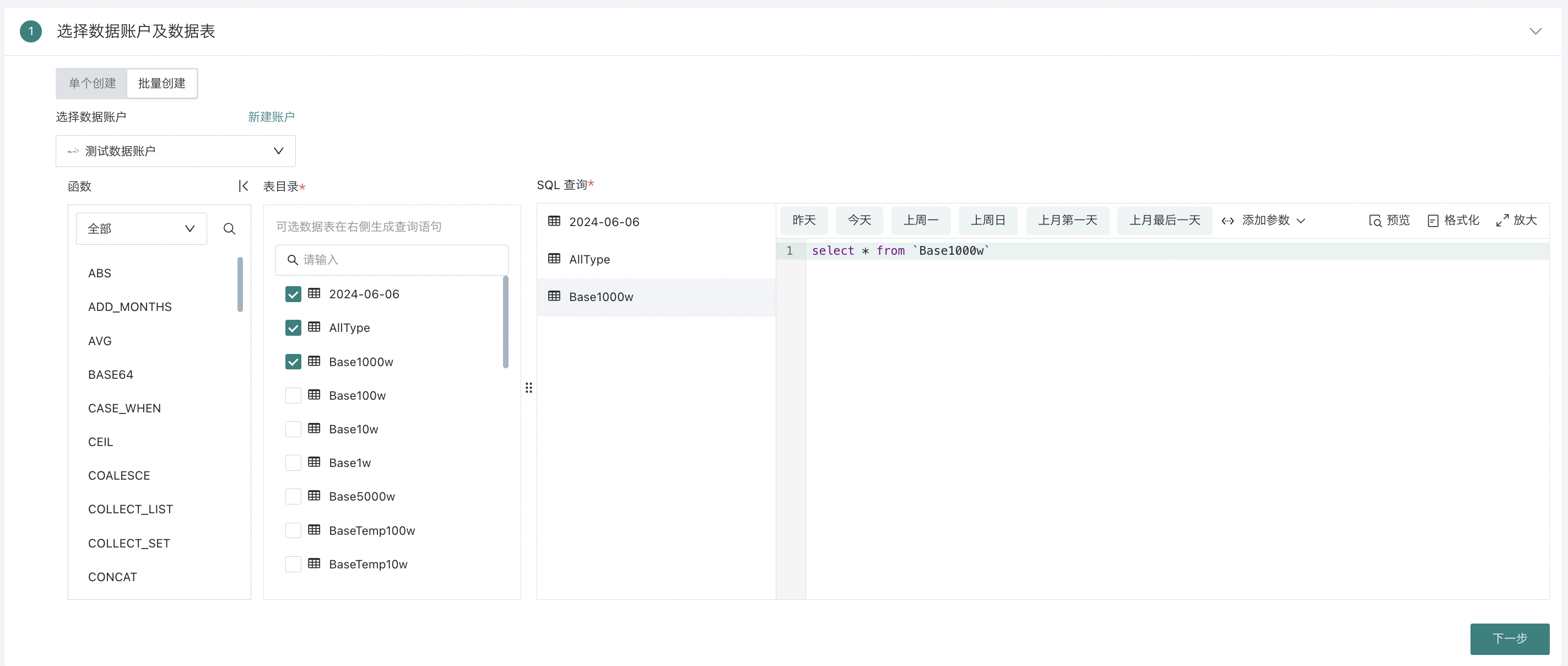
The same data account database tables support batch creation. When users need to batch extract all data tables from a single database to BI, this function can be used to achieve this.
- When creating a database and selecting batch creation, you can check multiple data tables in the database and select different tables for SQL editing below the SQL query. After all SQL editing is completed, click Next.
- In the data connection and update settings, configure the connection method and update method for each dataset.
- Finally, confirm the table information for each dataset one by one, and click Confirm to create the dataset.
Note: MongoDB and SAP BW type databases do not support batch creation.