ETL Governance Practice
1. Overview
This article introduces ETL governance, aiming to help users troubleshoot and optimize issues when ETL encounters queue delays.
The article covers the importance of ETL scheduling in the data processing workflow, and how to effectively manage ETL scheduling through monitoring, alerting, and problem localization to ensure the timeliness and accuracy of business data.
1.1. Application Scenarios
You can refer to this article in the following scenarios:
- Abnormal data output time, such as finding that the ETL output efficiency is slower than usual on a certain day;
- Severe ETL queuing, for example, there was no ETL queue before, but now there are a large number of queued tasks;
- From the perspective of resource control, etc.
1.2. Practical Cases
Note: In big data processing workflows, the stability and efficiency of ETL scheduling are crucial to ensuring the timeliness and accuracy of business data. Recently, there have been abnormal phenomena such as significant delays in ETL output time and a surge in the number of queued tasks, which may seriously affect our data analysis and decision support capabilities.
This document aims to use the existing intelligent cloud inspection, task management, operation and maintenance management, and global control functions in the Guandata BI platform to effectively monitor, alert, and locate problems in ETL scheduling.
2. Example Steps
2.1. Determine if there is a service exception
Idea: When ETL queuing is severe, it may be caused by multiple factors, but you can first check whether the Spark service is running normally.
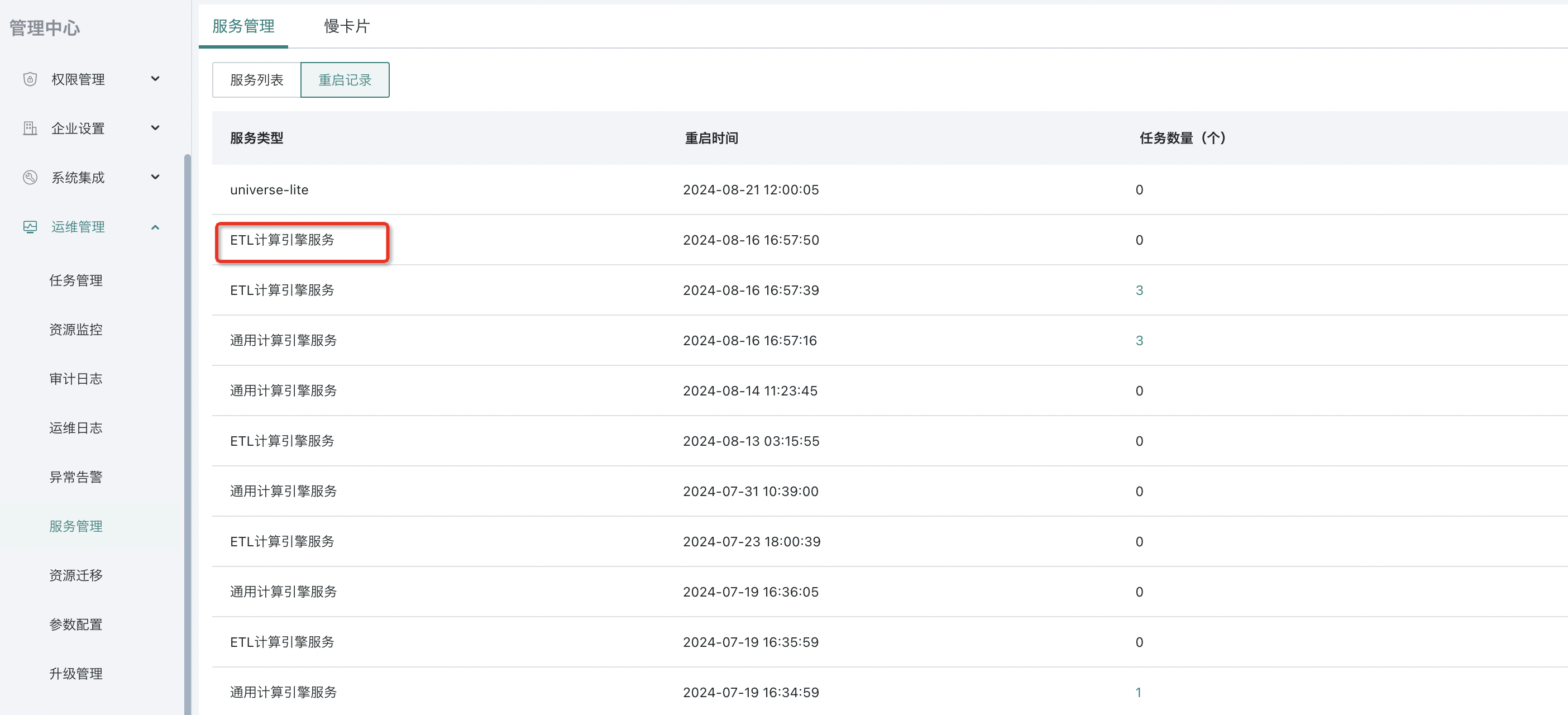
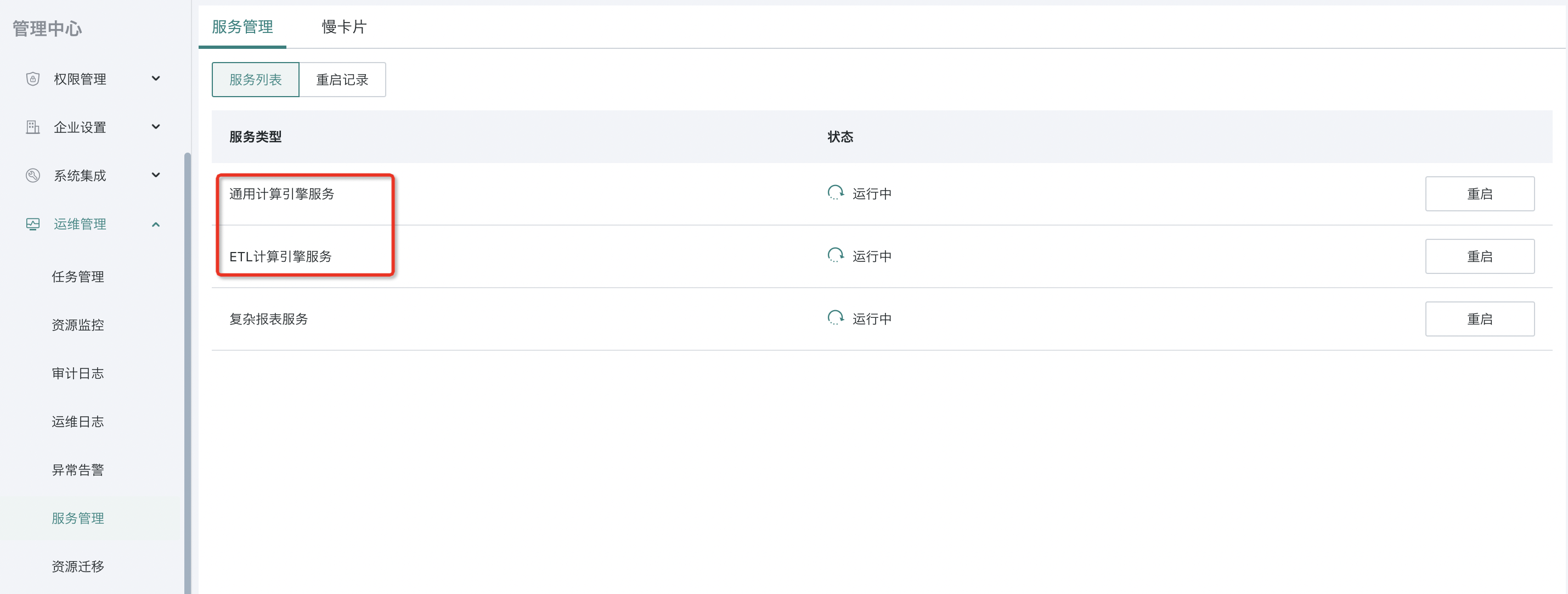
Entry: You can check the Management Center - O&M Settings - Service Management to see if there are any restart records.
If you find that the Spark service has been restarted, it is likely that the queuing problem is caused by a service exception. In this case, it is recommended to contact Guandata O&M/technical support immediately to investigate the cause of this Spark restart, so as to avoid recurrence of subsequent problems and prevent ETL task scheduling from being blocked.
2.2. Determine whether the business growth is the cause
1. View the cloud inspection report: First, check the cloud inspection report and pay attention to whether the number of ETL schedules has increased significantly compared to before.
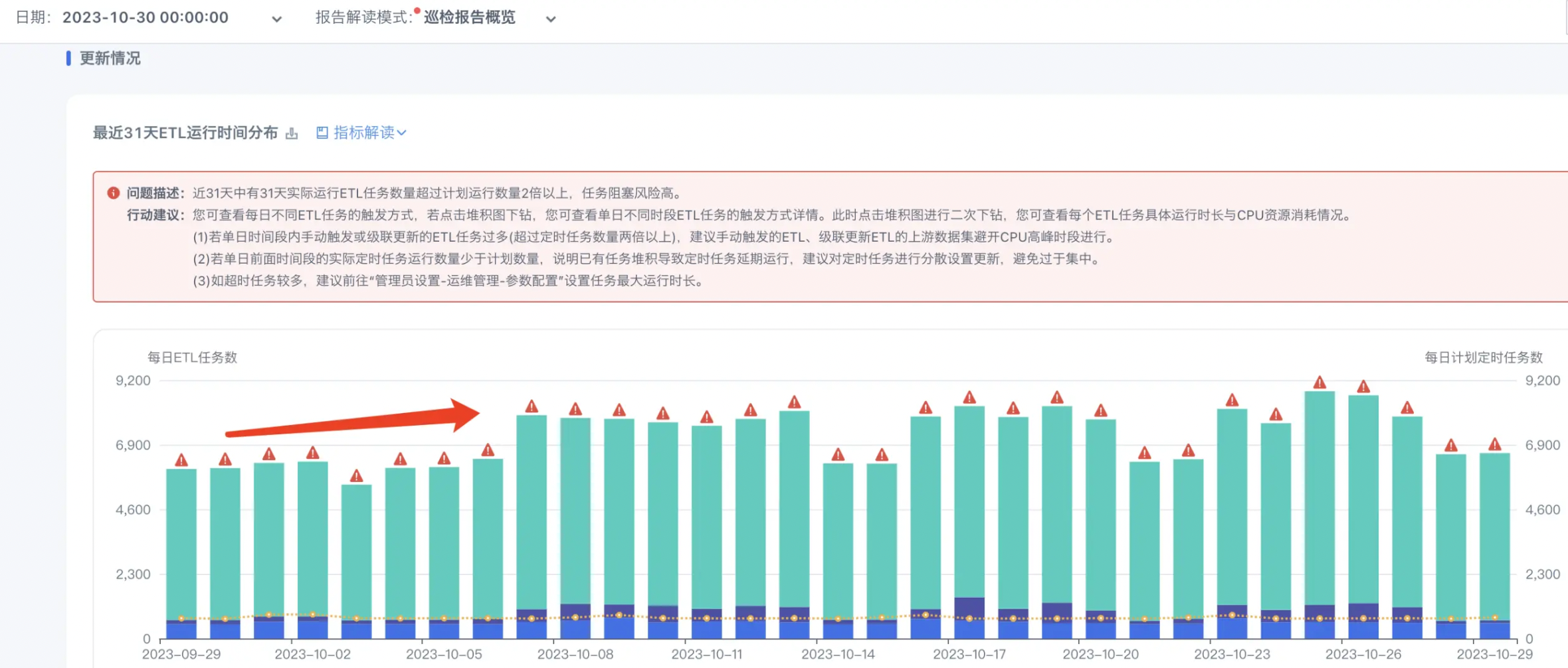
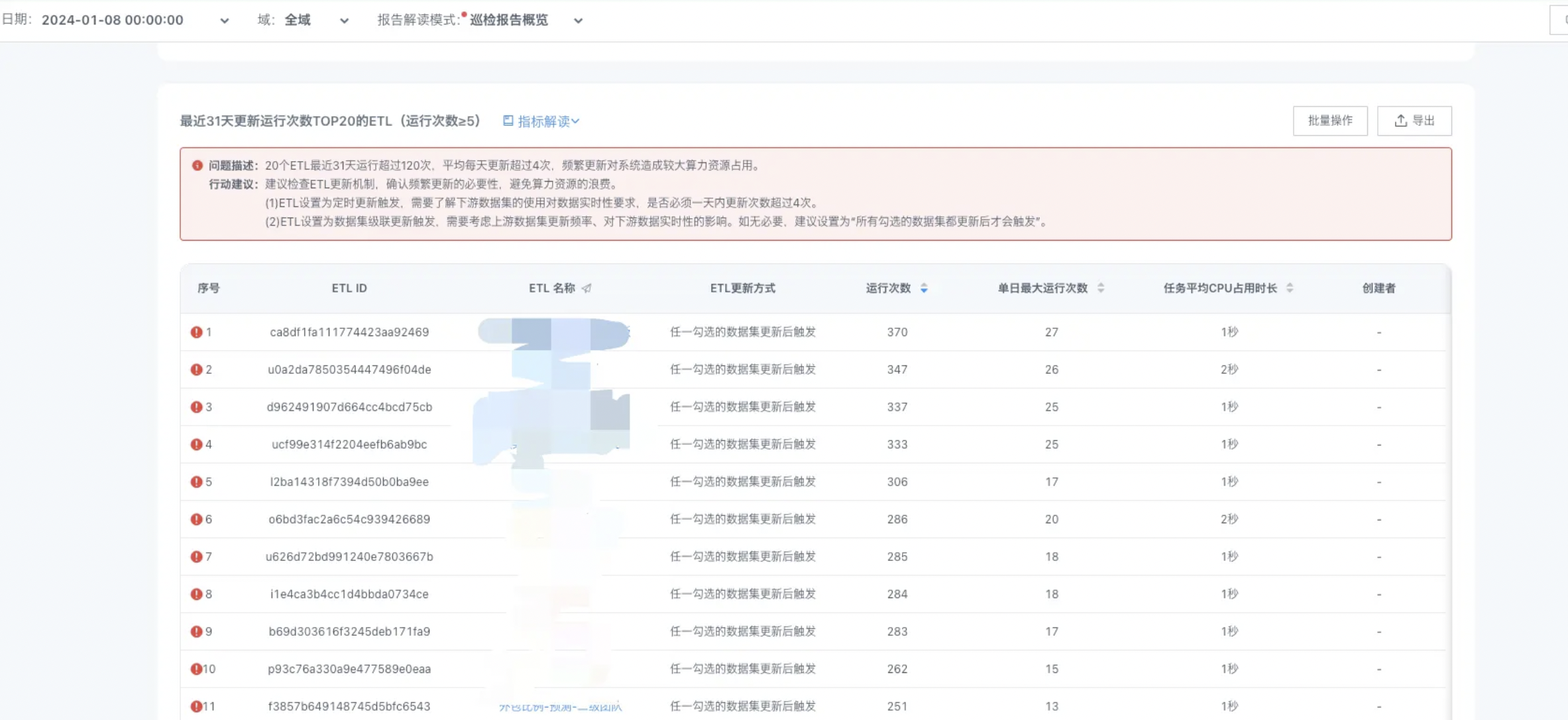
2. Check scheduling rationality: If you find a large increase in ETL task scheduling, you need to first evaluate whether these schedules are reasonable.
In the cloud inspection report, find the "Top 20 ETLs by update runs in the last 31 days" and check whether there are ETLs with abnormally high scheduling times that do not conform to business scheduling logic.
Relevant adjustments need to be made. Excessive scheduling not only occupies the concurrency of ETL scheduled updates, but may also occupy too much CPU resources. Therefore, reasonable scheduling is crucial to the stability of BI.
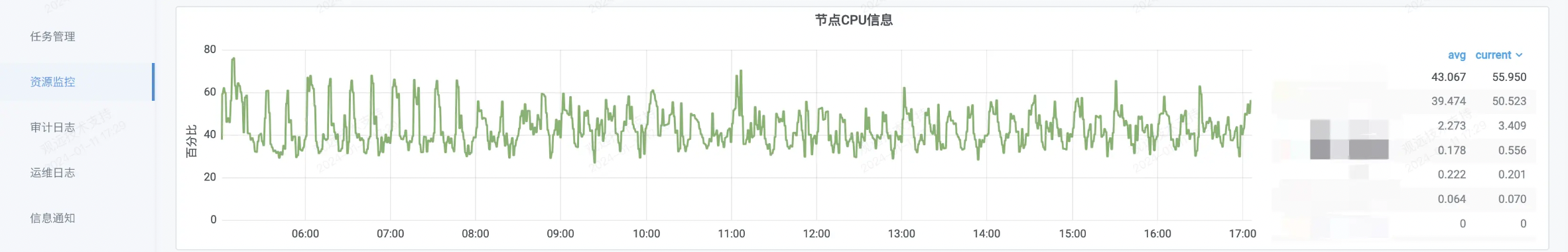
3. Handling ETL scheduling growth caused by normal business growth: If the growth in ETL scheduling is due to normal business growth, and the CPU usage remains at a high level (e.g., above 80%), this may indicate that resources are insufficient to support business growth. In this case, it is recommended to contact Guandata O&M/technical support to evaluate expansion matters to ensure sufficient resources to support business growth.
2.3. Optimization Directions
Optimize ETL tasks with high CPU consumption
Check the "Top 20 ETLs by CPU usage duration in the last 31 days" in the cloud inspection report to see if there are tasks with CPU usage duration exceeding 1 hour.
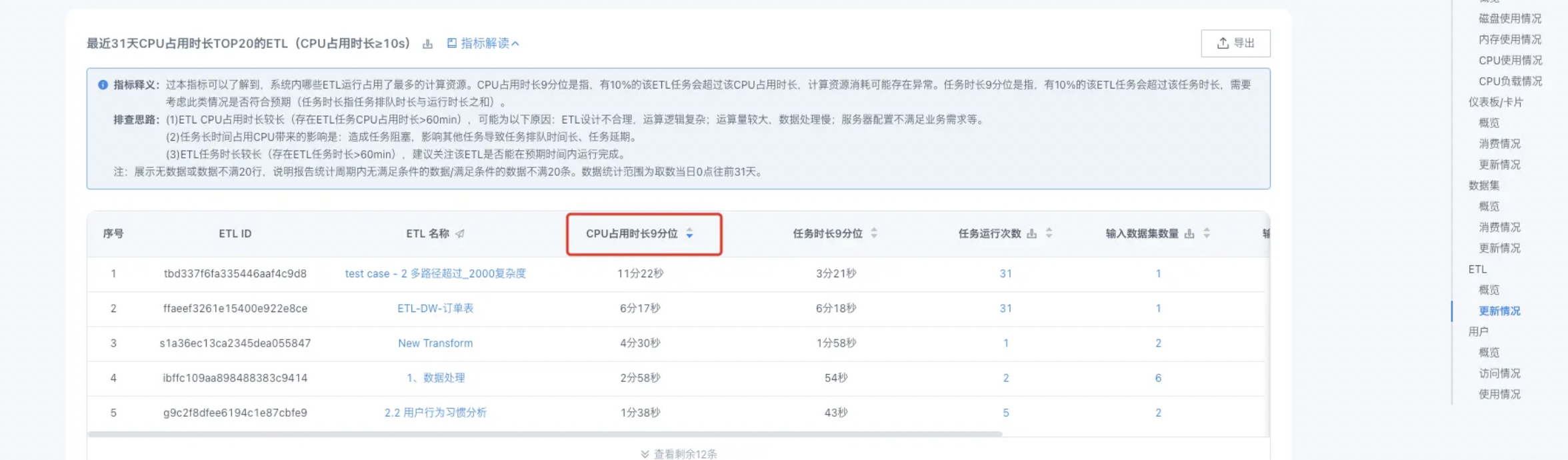
For ETL tasks that consume a lot of CPU resources, you can refer to the document [ETL Optimization Suggestions](../../10-Tips and Best Practices/1-ETL/8-ETL Optimization Suggestions.md) for optimization, reduce unnecessary resource consumption, and prevent long-term resource occupation from causing ETL scheduling blockage.
Distribute ETL scheduling time
Method 1: Analyze the "ETL run time distribution in the last 31 days" in the cloud inspection report to check whether there are too many ETL runs in a certain time period. It is recommended to distribute the execution to each time period as much as possible without affecting the business, or execute it during idle time at night to avoid running at the same time and causing blockage.
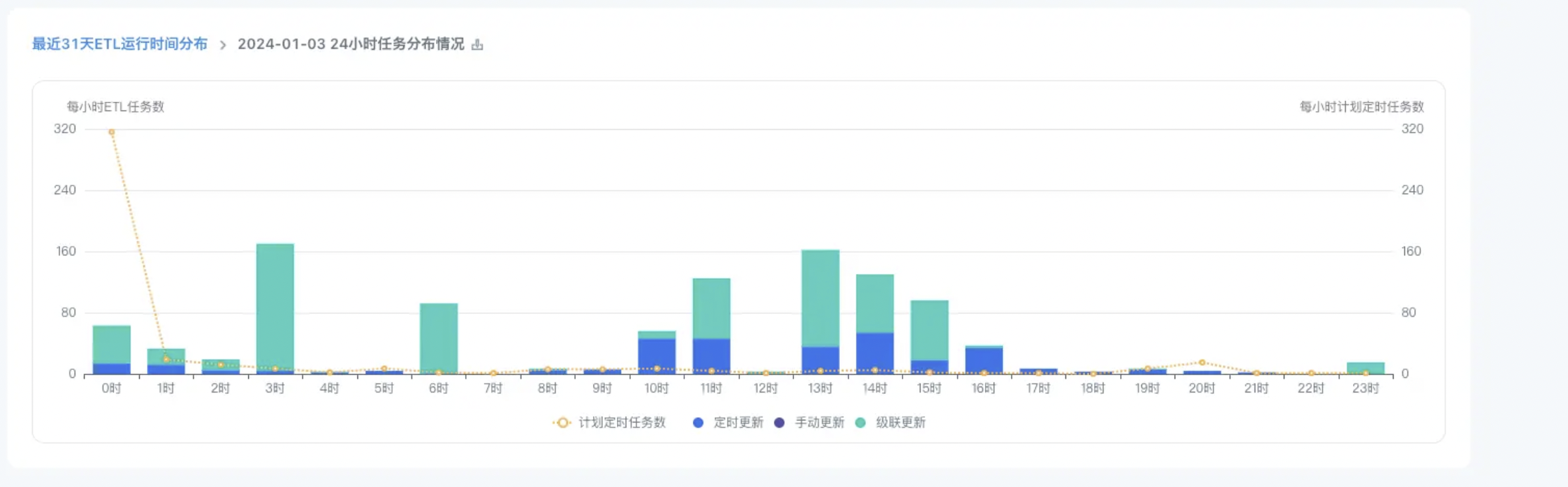
Method 2: For some customers who use Spark resource isolation (cards and ETL are deployed with separate job engines), ETL scheduling is concentrated at midnight, causing queuing.
If there is no need to view data at midnight, it is recommended to communicate with Guandata technical support/O&M to configure dynamic switching of job engine deployment. At night, the card's job engine can also be provided for ETL use to ensure that ETL has more computing resources available at midnight, improve resource utilization, and alleviate ETL queuing.
How to check if dual jobs are deployed? Go to Management Center - O&M Management - Service Management to check the General Computing Engine Service and ETL Computing Engine Service.
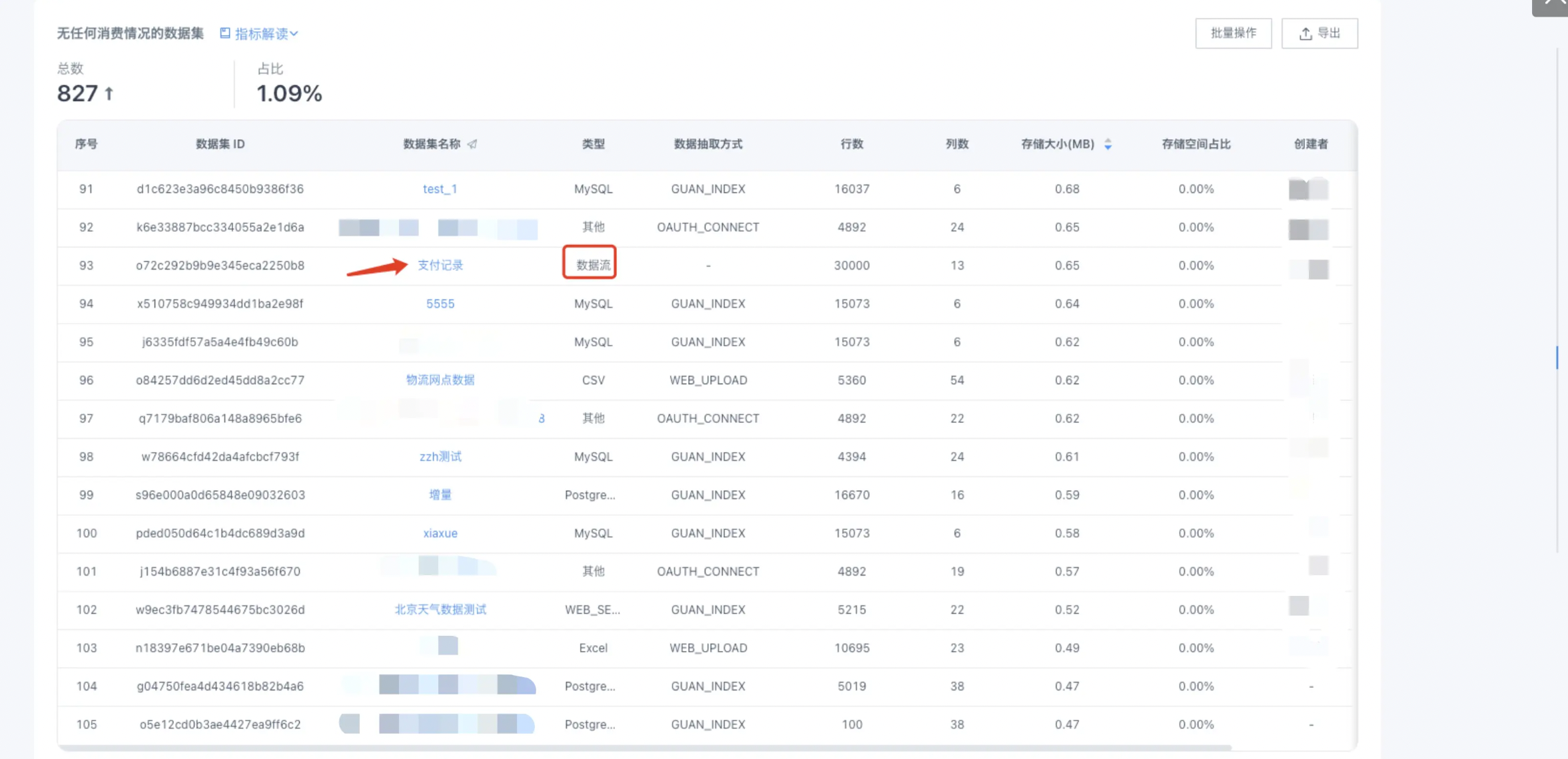
Clean up invalid ETL resources
In the cloud inspection - ETL section, check the ETL datasets of type [Data Stream] in the "Datasets with no consumption". Check whether the ETL schedule to which it belongs has other output datasets, and whether other output datasets have subsequent usage. If not, it is recommended to clean up the relevant ETL schedule to avoid resource waste.
Limit ETL global parameter configuration
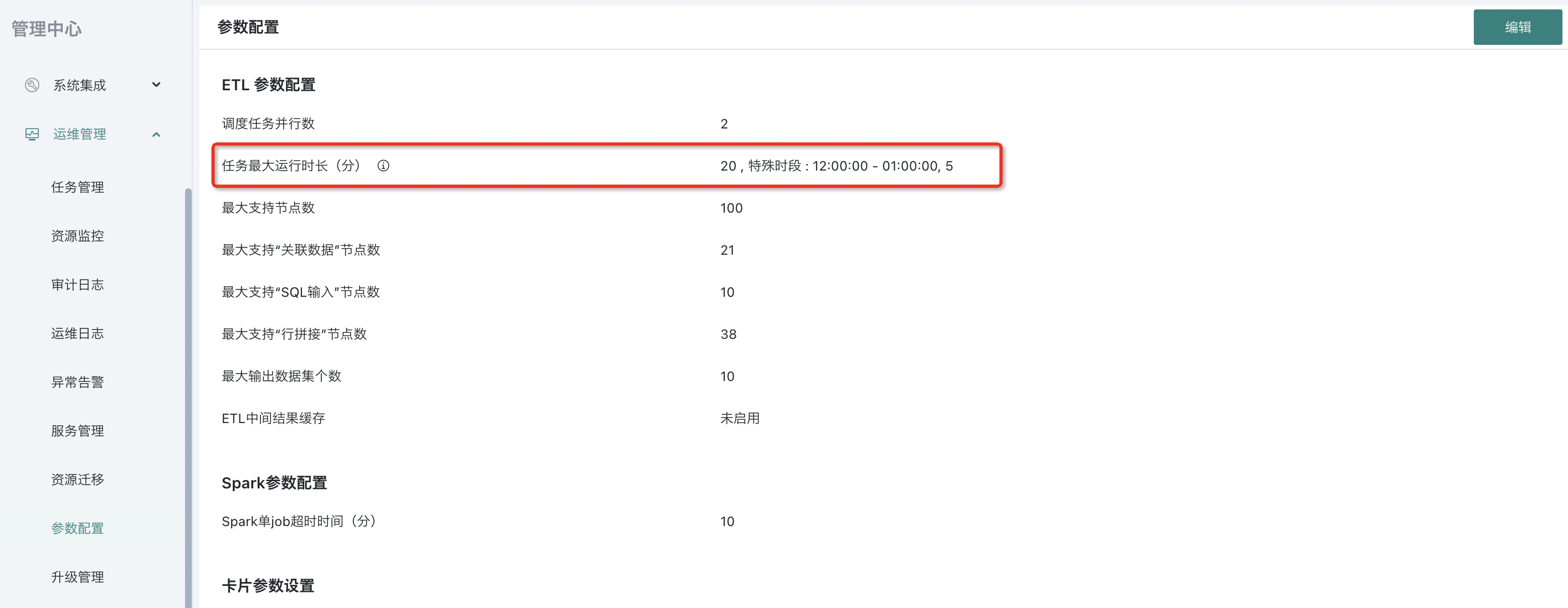
Entry: On the Management Center - O&M Management - Parameter Configuration page.
- You can limit the maximum running time of tasks. For example:
· Set the maximum running time of tasks to control the maximum running time of ETL and avoid abnormal ETL task scheduling blocking for a long time.
· Or set the running time for different time periods, such as no more than 30 minutes during the day and no more than 1 hour during other periods for global control.
- Adjust the number of concurrent tasks. This configuration is mainly for scheduled updates and secondary cascade updates of ETL tasks. Generally, it is configured according to the machine configuration and the size of its own ETL tasks. For example, with 16C128G, if a large number of ETL tasks run in less than 10 minutes, the concurrency can be set to 4-6. If most ETL tasks run for more than 30 minutes, the concurrency is recommended to be set below 4.
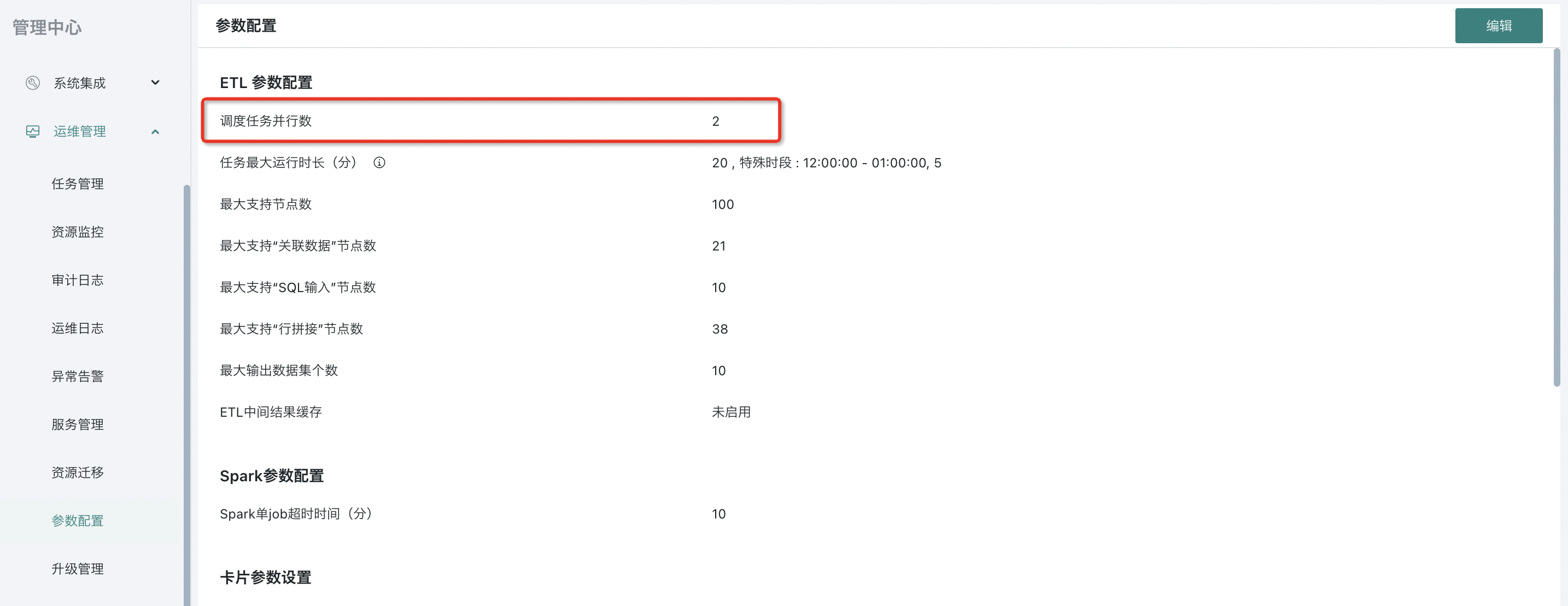
Note: The above information is for reference only. For details, it is recommended to contact Guandata technical support/O&M for evaluation before making adjustments. Excessive concurrency may cause ETL tasks running at the same time to be inefficient due to insufficient CPU resources, so adjustments should be made with caution.
- The remaining configurations can be set according to your own needs, but it is not recommended to set them too high. Complex ETLs consume a lot of performance. Try to reduce the generation of overly complex ETLs (for complex logic ETLs, you can consider splitting them into multiple ETLs and using advanced scheduling functions for sequential scheduling);

Use advanced scheduling to improve ETL scheduling efficiency
For ETL tasks that process data by date growth and historical data does not change, you can use the advanced scheduling function for incremental updates to improve efficiency and reduce resource consumption.
Related reference document: [Practice of ETL and Advanced Scheduling - Guandata BI - Guandata Help Center](../3-Advanced Scheduling (Complex Task Orchestration)/1-Promotion Performance Analysis (Quasi-real-time Incremental Update).md)