Cell Dynamic Attributes-Range Attributes
1. Overview
This article will详细介绍模板单元格中的"范围"功能及其配置使用方法。我们将通过一个具体的范围属性案例来展示如何有效实践。
本教程所使用的案例数据集如下:出货单.xlsx
范围的视频讲解,详见动态属性-范围。
1.1. Application Scenarios
For the following scenarios, it's suitable to use the cell R attribute (Range):
- Need to batch set parent cells for a region.
- Parent cells are located to the right or below child cells, and parent cell setting cannot be achieved through C attribute.
1.2. Function Introduction
The R attribute allows specifying a matrix range of cells as child cells of the current cell to achieve batch parent cell setting effect, currently only supports manual input setting.
Compared to C attributes and default parent cells, the R attribute has different functional characteristics and priority, suitable for more complex layout requirements.
The following is a comparison of differences between three types of parent cells:
| Parent Cell | Priority | Functional Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C Attribute | High | Can set 2 parent cells (one left, one above), can inherit when multiple dimensions are adjacent | Parent-child relationship is simple and clear | Need to set one by one, troublesome when there are many cells |
| Default Parent Cell | Medium | Left and upper adjacent template cells automatically become parent cells | Automatically effective, convenient and efficient | Small coverage, easily overlooked |
| R Attribute | Low | 1. Range allows nesting (complete containment). 2. Cells with the same expansion direction cannot intersect in Range. 3. If a cell is located in multiple Ranges, it's divided into two groups by direction, and the smallest Range in each group takes effect on it. | Only need to set for some header cells to achieve batch parent cell setting effect, high efficiency. | Range intersection is complex and needs to be careful about conflicts; low priority, not recommended to mix with C attributes. |
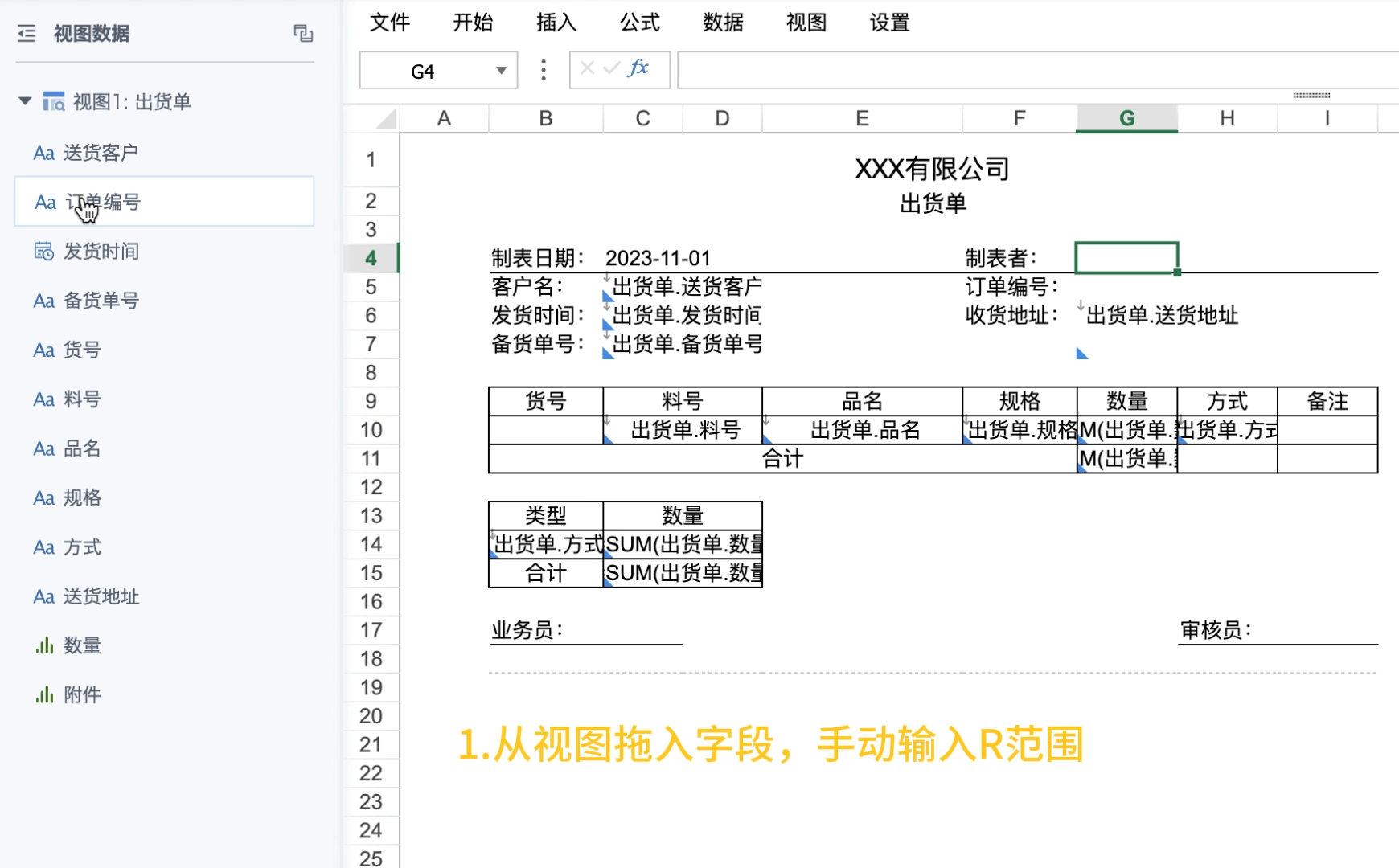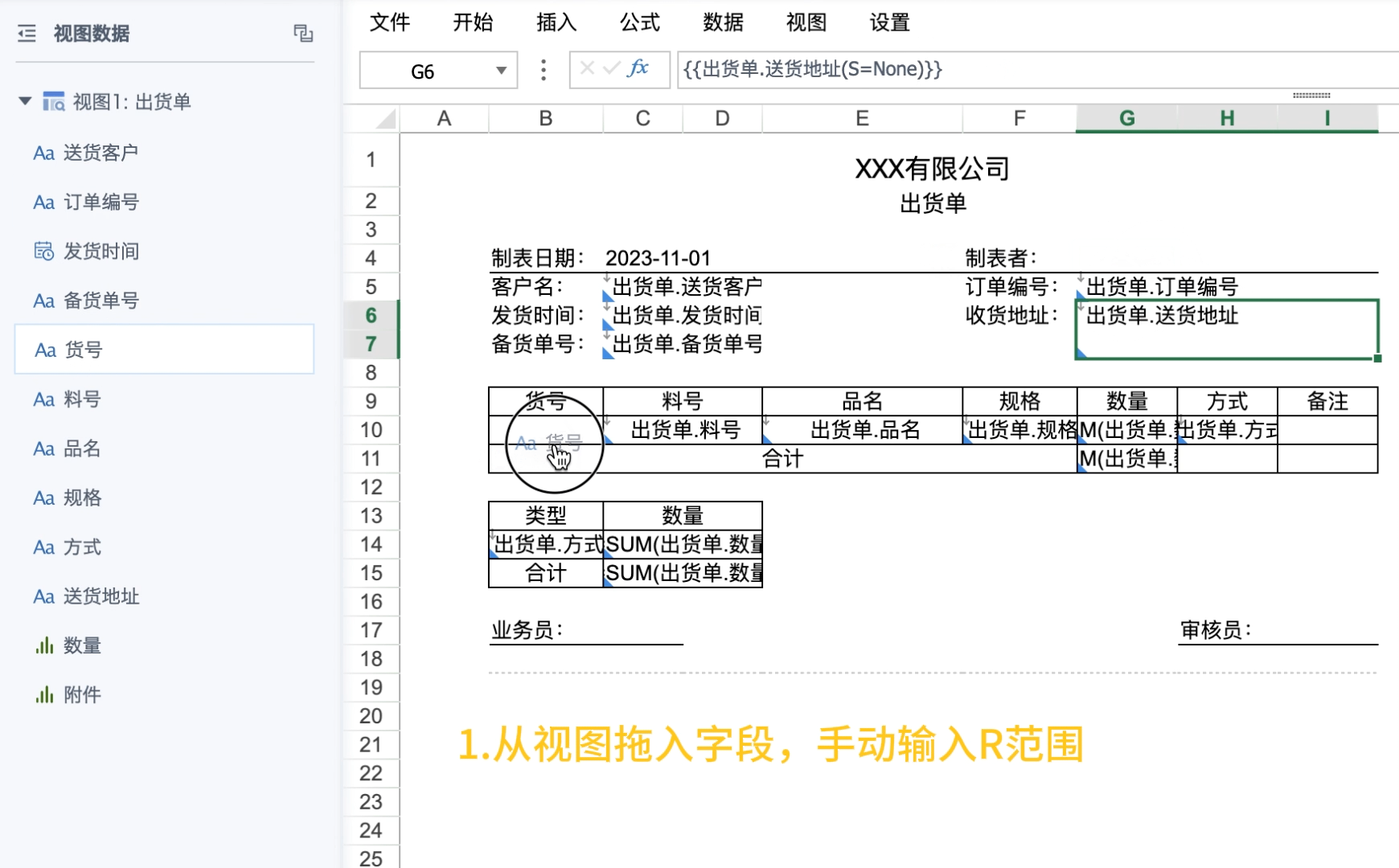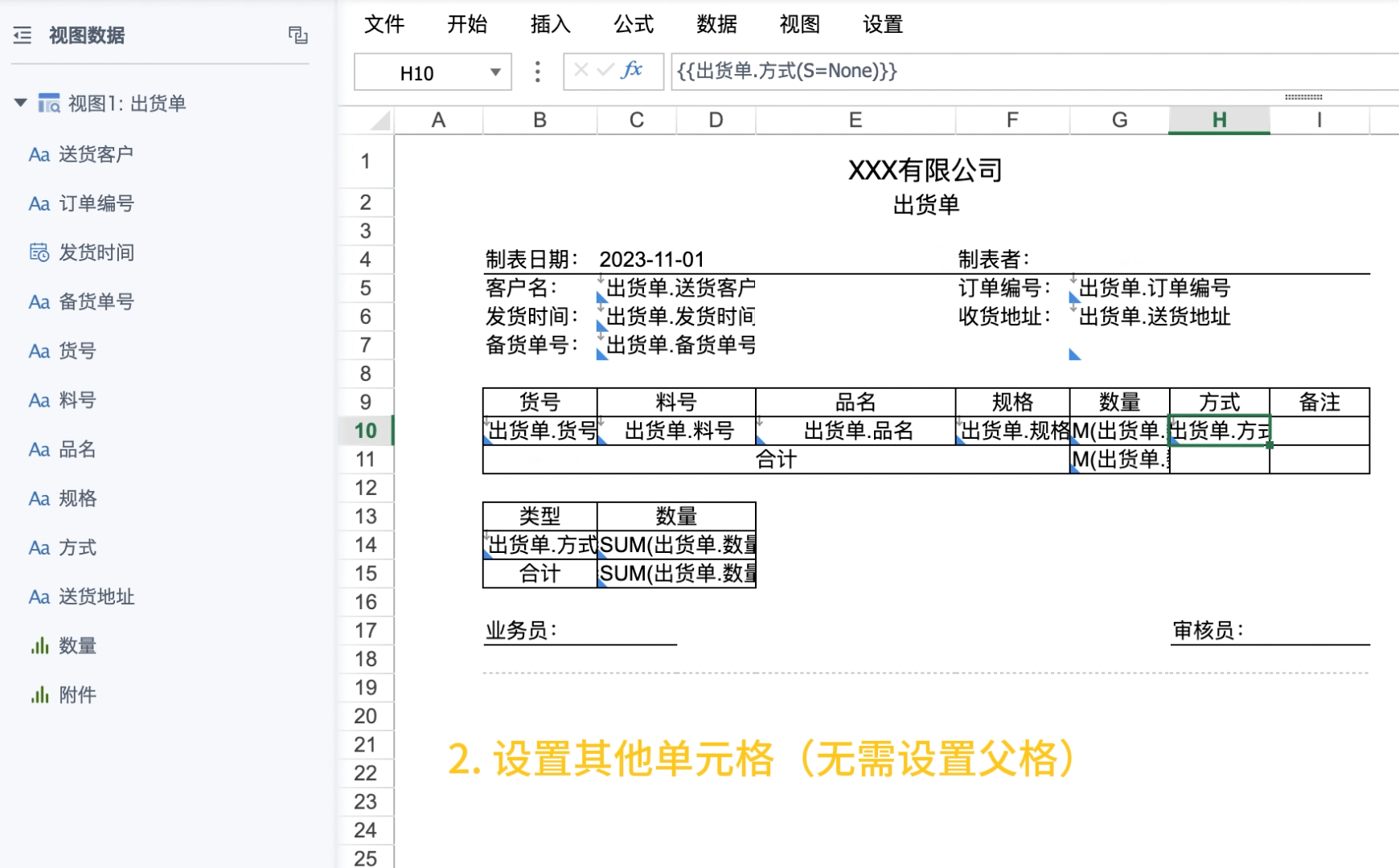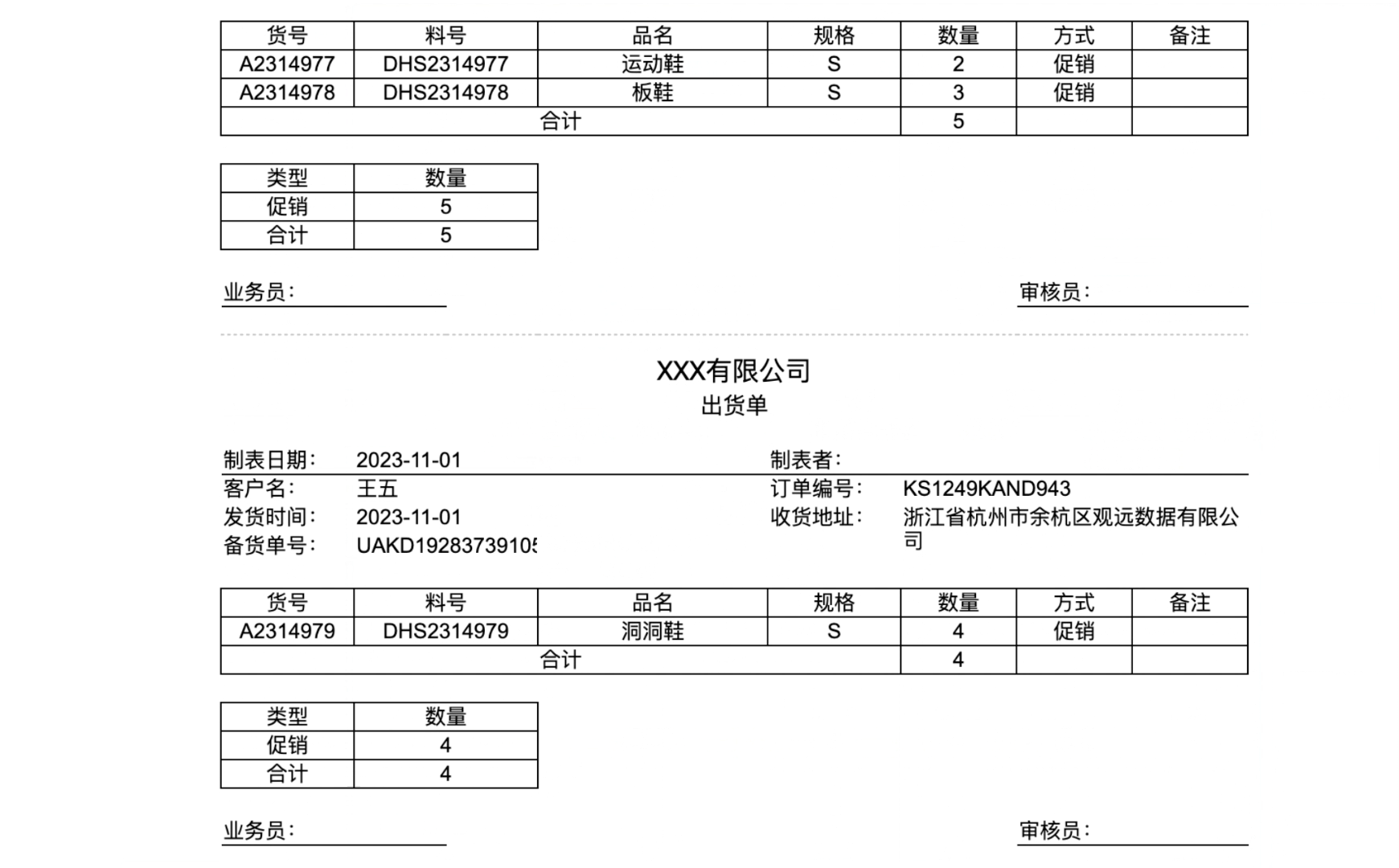
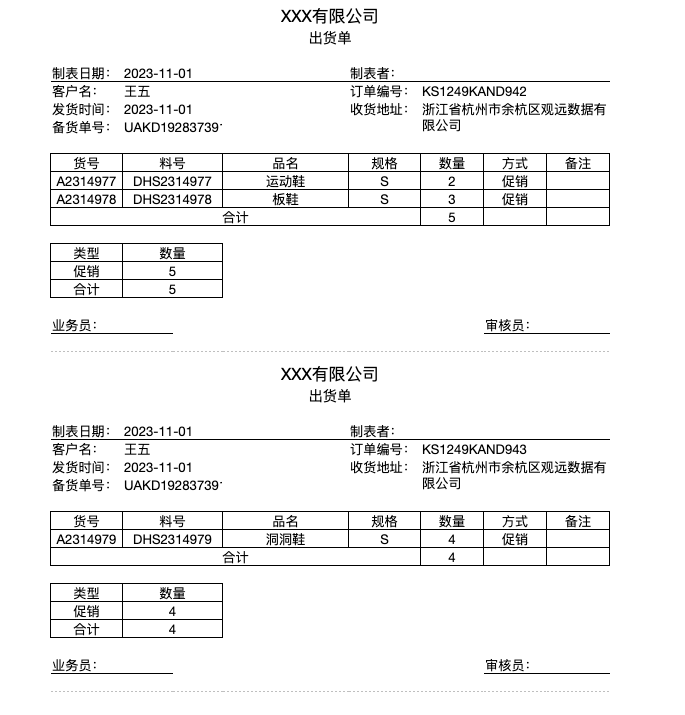
1.3. Case Effects
Using "Order Number" as the primary key, generate multiple delivery orders based on order numbers (i.e., generate as many delivery orders as there are order numbers).
Each order contains multiple product codes, and each product code data occupies one row.
2. Implementation Approach
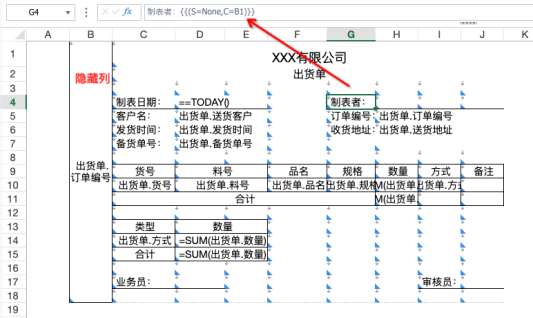
-
If using C attribute to set parent cells, since C attribute parent cells can only be to the left or above child cells, and the primary key "Order Number" is located in the middle-right of the entire report, preview will report errors and cannot save. You can only insert a hidden column at the front, drag "Order Number" into this column as parent cell, then convert all cells in the form range behind (including blank cells) to template cells and set parent cells to achieve this. The implementation steps are troublesome and easy to miss settings.
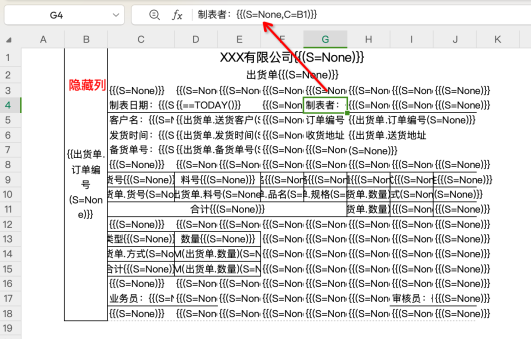
-
If using R attribute, the steps are simplified to: static headers + drag and drop view fields + 2 cells set R attribute.

3. Operation Steps
-
Prepare static headers (need to first build the general table structure style, enter text as static headers by position, merge cells horizontally or vertically as needed);
-
Drag the primary key field (dimension field used as parent cell) from the view, manually enter R attribute, note to separate from other attributes with half-width commas.