Remove Duplicates
1. Overview
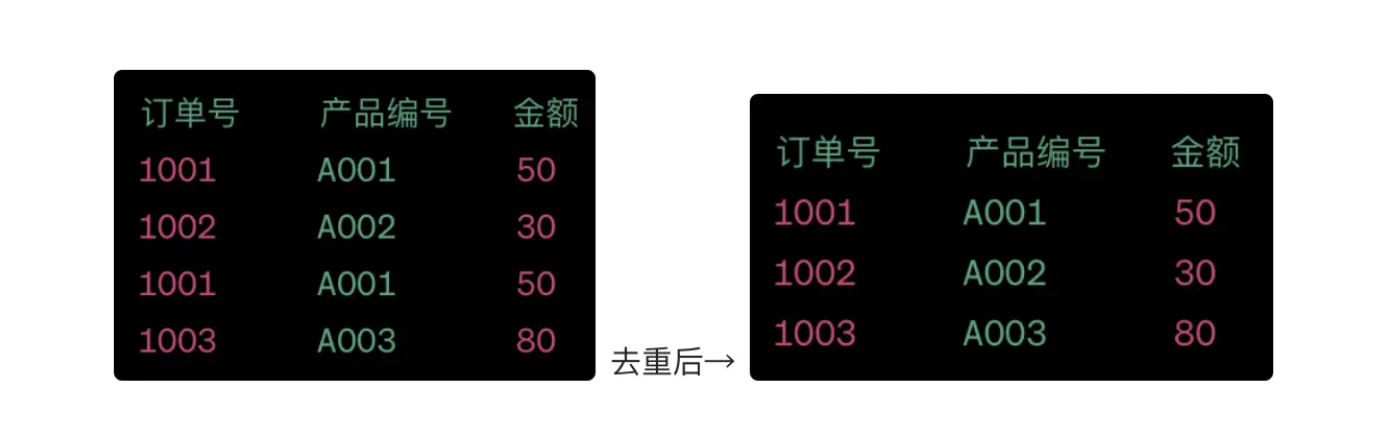
Removing duplicates means detecting and removing duplicate records in the dataset during data processing, ensuring that each record in the result data is unique. By deduplicating on one or more columns, you can avoid analysis errors and inaccurate results caused by duplicate records.
For example, in e-commerce order processing, there may be duplicate order records due to system issues or user misoperation. Deduplication ensures that each order number appears only once, avoiding misleading sales statistics and inventory management.
2. Usage Guide
2.1. Operation Steps
- Drag the Remove Duplicates operator from the ETL operator area to the right canvas editing area;
- Click the Remove Duplicates operator and click Add;
- Select the deduplication key (deduplication column), supports multiple selection;
- Click OK and preview the data result.
2.2. Detailed Description
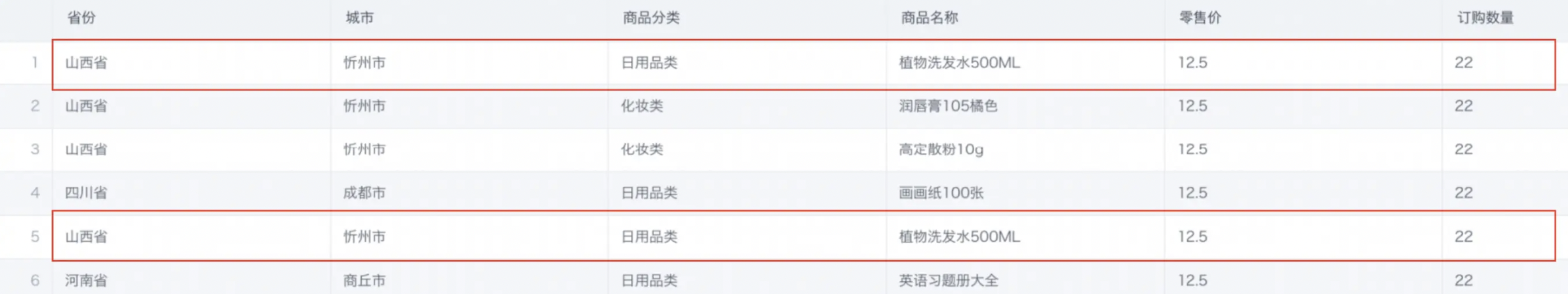
Below is an example of deduplicating by Product Name.
Prerequisite: The upstream node is a product demo dataset containing duplicate data.
- Drag the Remove Duplicates operator from the ETL operator area to the right canvas editing area and connect it to the upstream node;
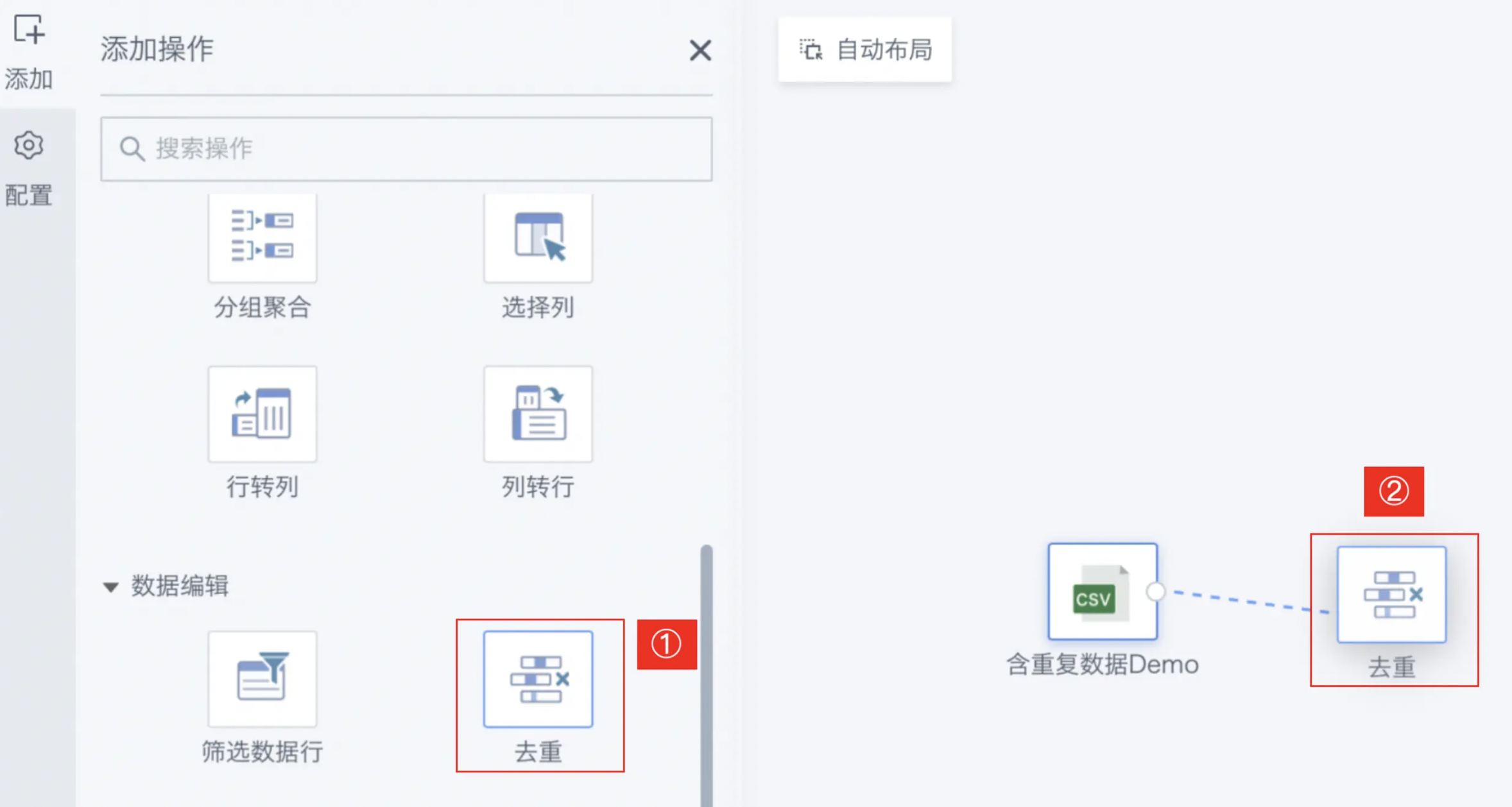
- Click the Remove Duplicates operator, the left area becomes the current operator configuration area. Click Add and select the target field for deduplication;
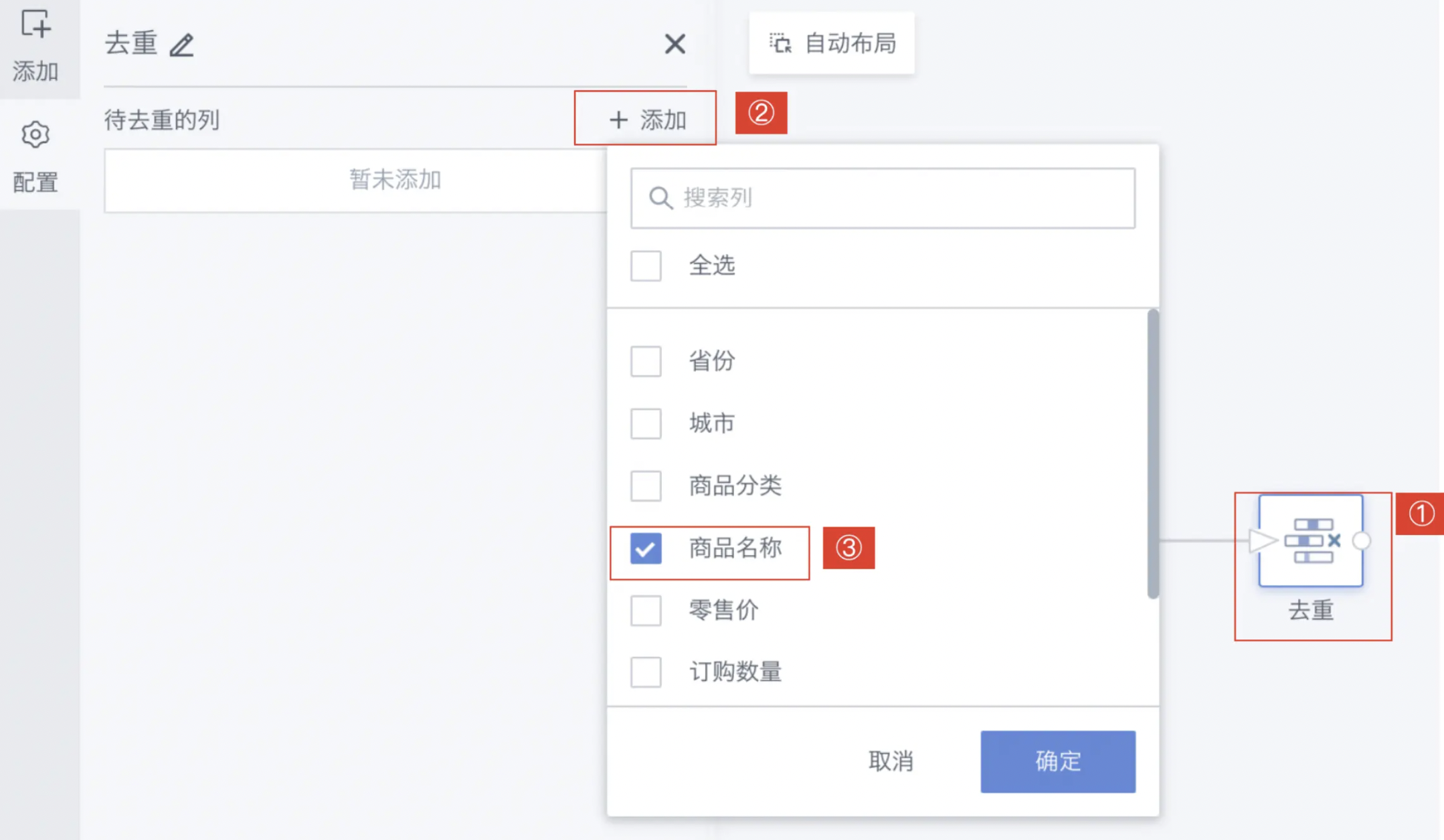
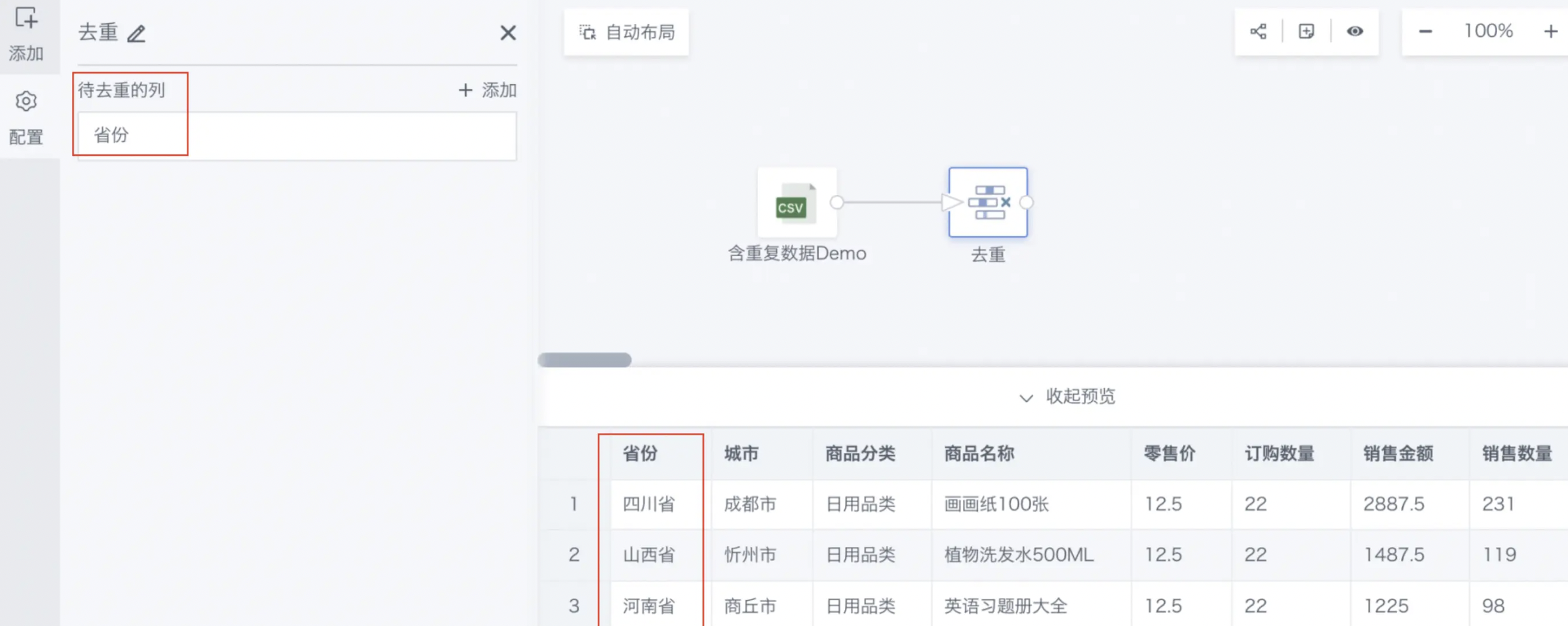
Note: Usually, the primary key of the input dataset is used as the deduplication column. Primary key: one or more fields in the table whose values uniquely identify a record in the table. If you select "Province" as the deduplication column, the effect is as follows:
| Province | City | Product Category | Product Name | Retail Price |
| Shanxi | Xinzhou | Daily Necessities | Plant Shampoo 500ML | 12.5 |
| Sichuan | Chengdu | Daily Necessities | Drawing Paper 100 Sheets | 12.5 |
| Henan | Shangqiu | Daily Necessities | English Exercise Book Collection | 12.5 |
- Click OK and preview the processed data to confirm successful deduplication.
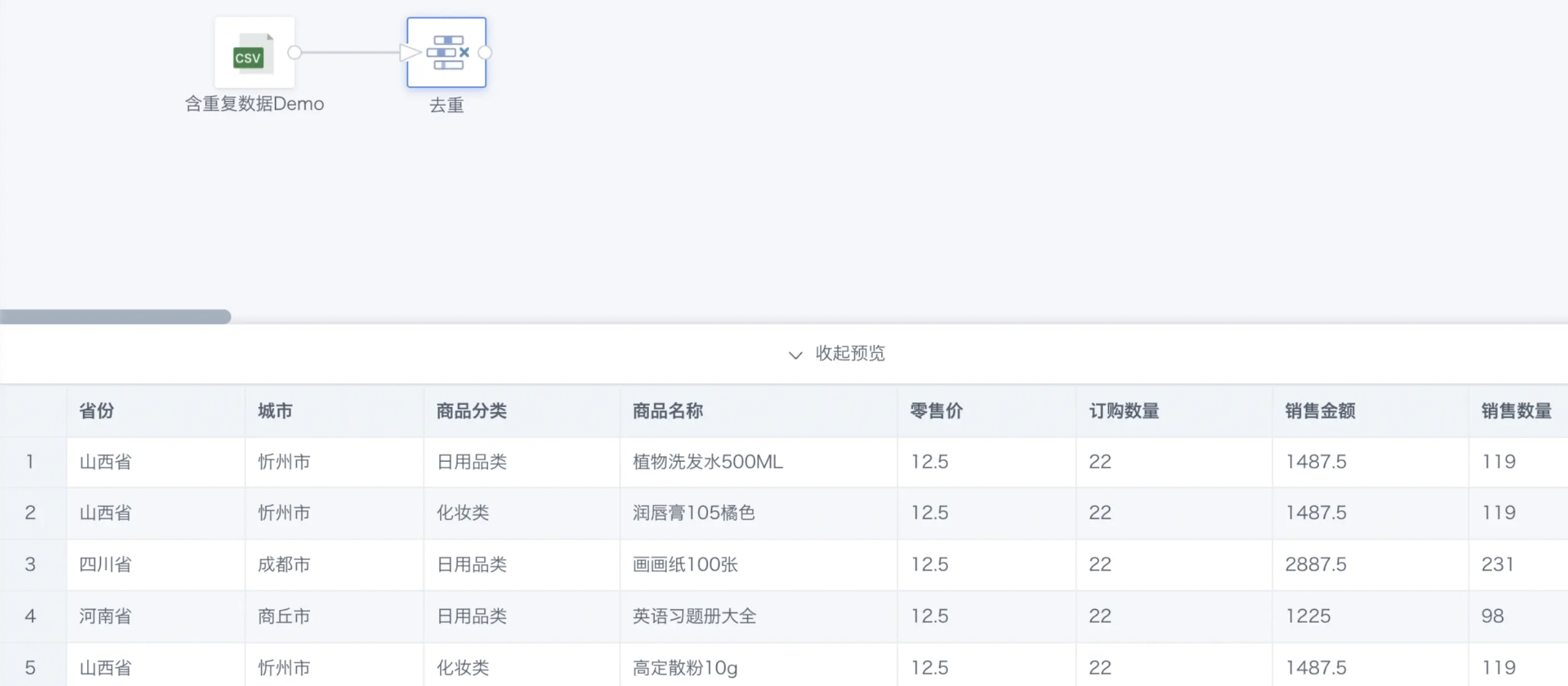
For subsequent use of other data processing operators, see Getting Started.