Perform Simple Data Processing
1. Overview
In this case, we will guide you to use Smart ETL to efficiently perform data processing tasks. You will learn how to use the powerful operators in Smart ETL to effectively organize and integrate product information tables, store information tables, and retail transaction tables, thereby forming a sales data table with deep data analysis potential.
The datasets used in this case (3 file datasets): New ETL Case - Data.zip
2. Implementation Approach
2.1. Prerequisites
-
In Data Preparation > Datasets and Smart ETL, create folders as needed, respectively for storing input datasets for data connection and output datasets after ETL processing. For this specific case, you can name the folder Case_Store Sales Statistics.
-
In Data Preparation > Datasets under the corresponding folder, connect 3 file datasets as the original data for data processing.
2.2. Formal Steps
-
Enter the Smart ETL page, create a new ETL task under the folder, jump to the ETL editing page, and name the current task;
-
Drag the Input Dataset operator from the ETL operator area to the right canvas editing area, drag 3 times continuously, and upload the product table, store table, and retail table respectively;
-
Merge 3 tables into one data table through multiple ETL operators, remove dirty data, add calculated columns, and form a sales detail data table that can be used for visualization analysis;
-
Drag the Output Dataset operator to the right canvas editing area, preview and check the data flow and output dataset result data, confirm the correctness of the data processing flow, save and run the ETL task;
-
After the ETL task runs successfully, you can view or configure modifications for the current task.
3. Example Steps
3.1. Create New ETL Task
-
Under the corresponding folder in Smart ETL, click New ETL to create a new ETL task;
- After creating a new ETL task, directly enter the ETL editing interface, as shown in the figure below:
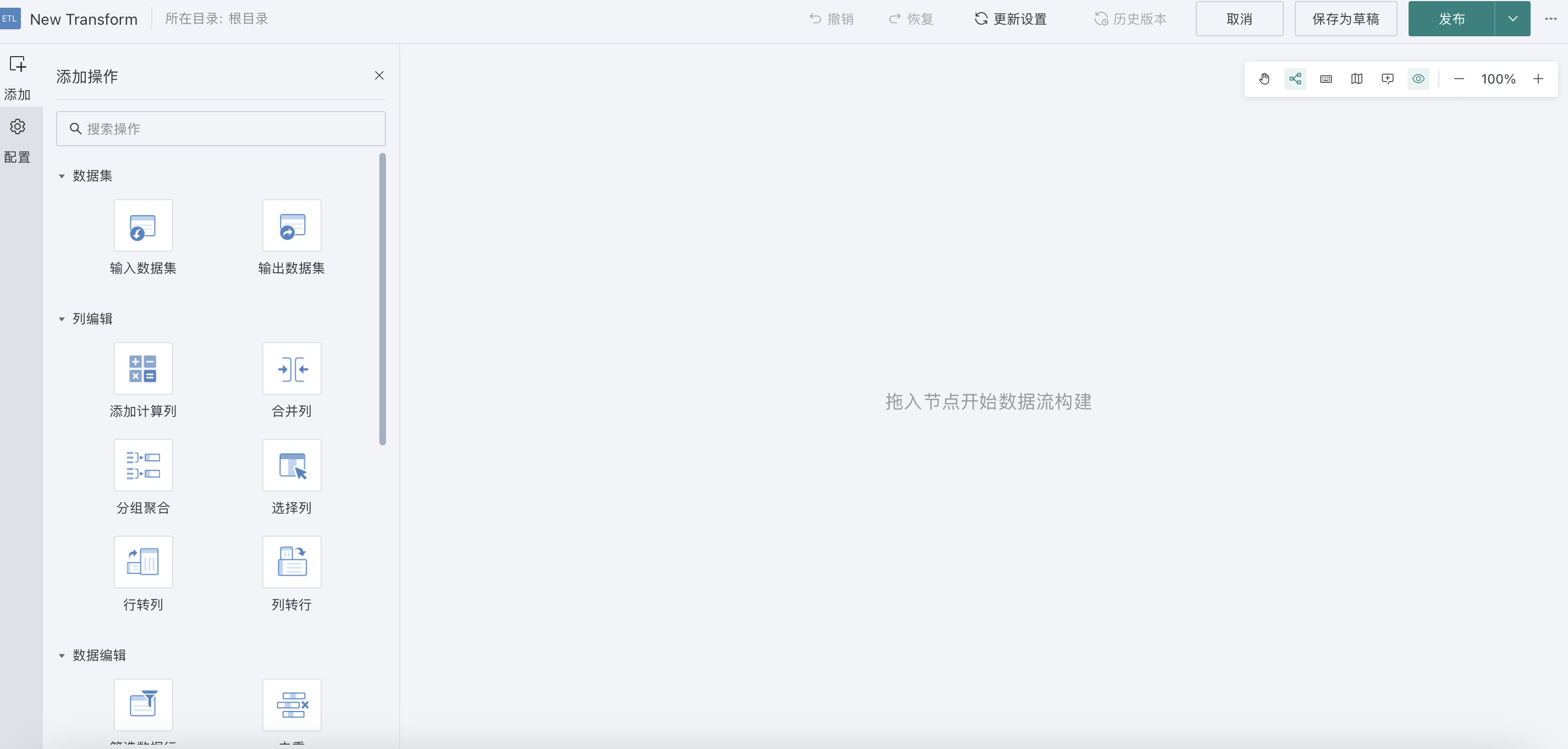
- First name the ETL task as ETL_Store Sales Statistics, then select the storage path. The storage path for this case is Root Directory > Case_Store Sales Statistics;
After entering the ETL editing interface, we will proceed to learn how to use ETL operators.
3.2. Build ETL Data Flow
Drag in Input Datasets
Drag the Input Dataset operator from the ETL operator area to the right canvas editing area, then click the Input Dataset operator and upload the following 3 datasets respectively: 1.0 Product Information, 2.0 Store Information, 3.0 Retail Details. As shown in the figure below:
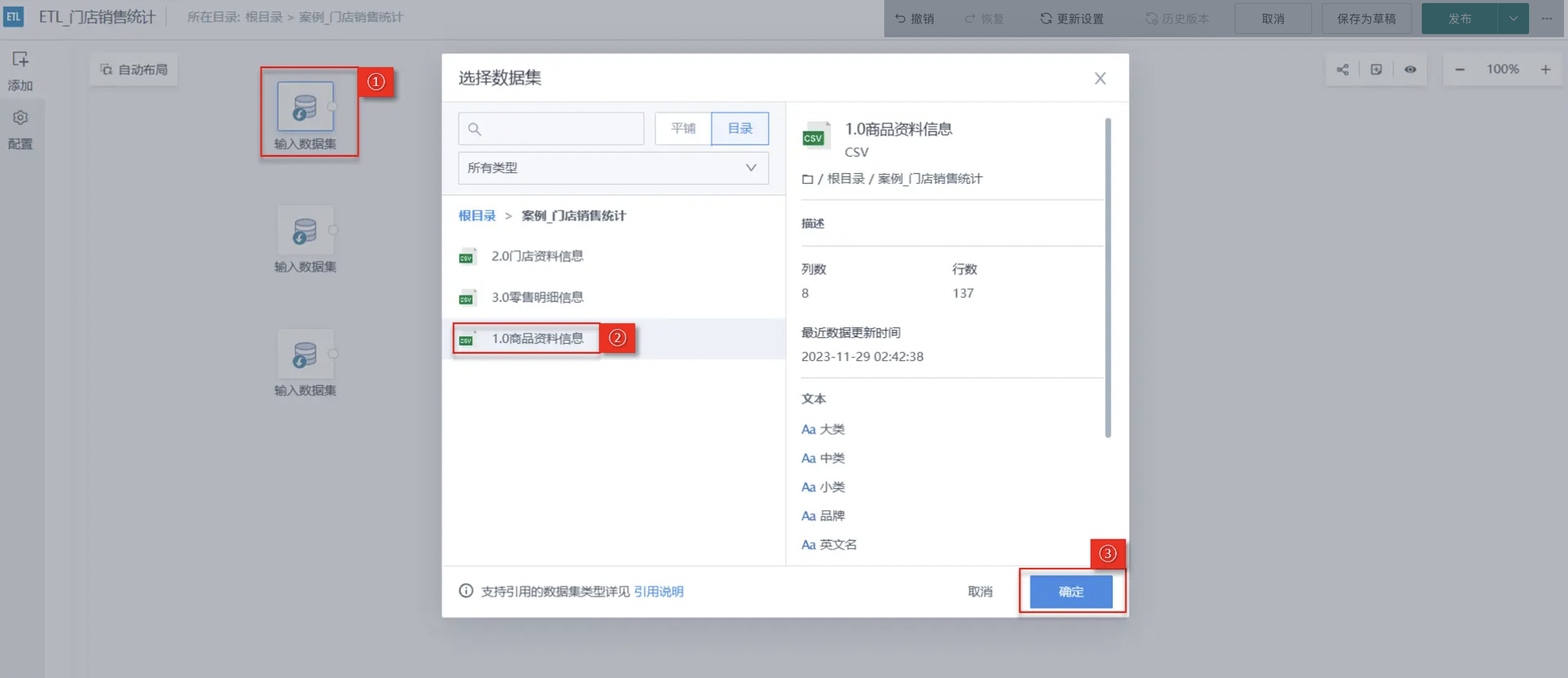
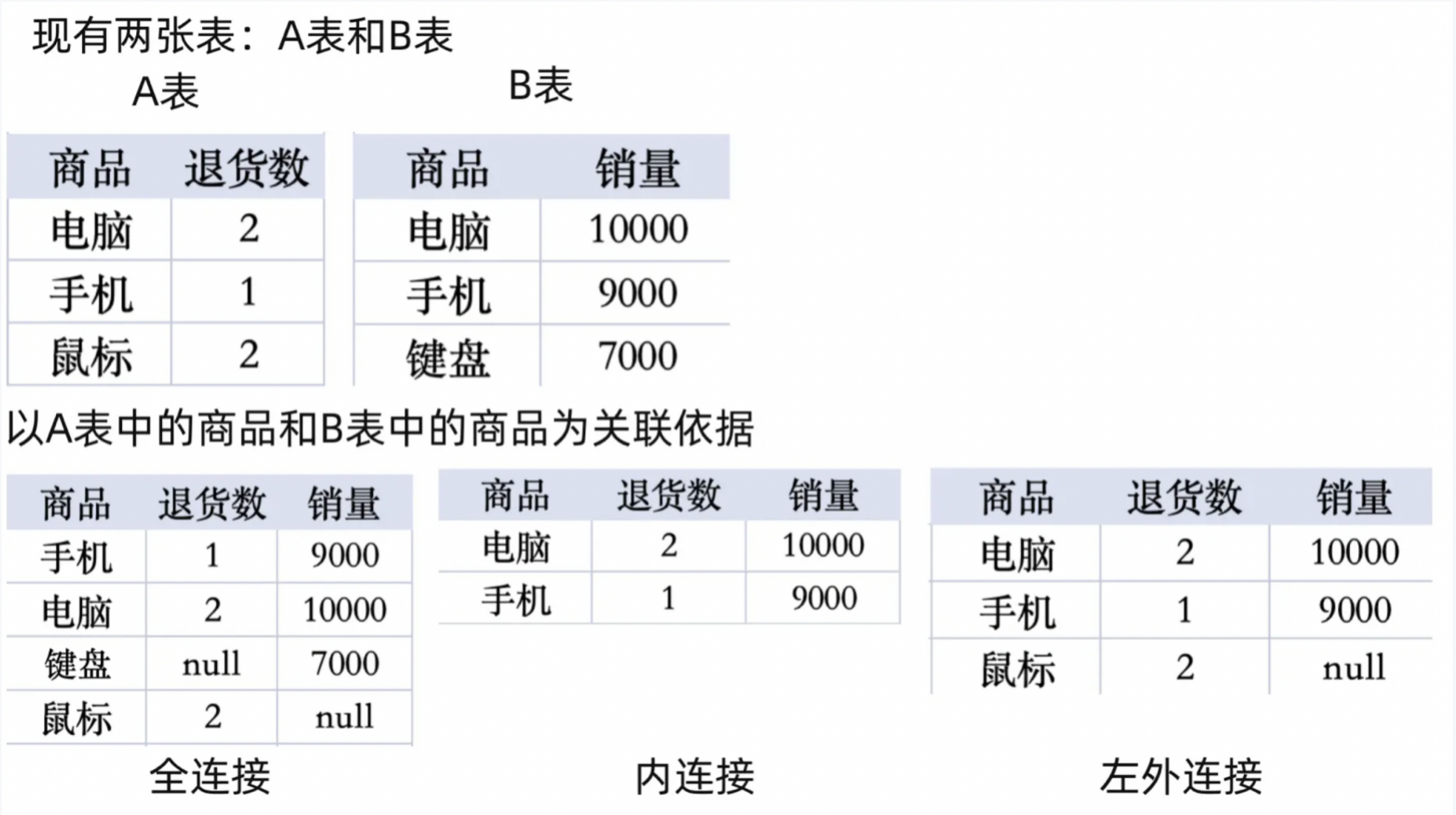
Data Association Settings Between Tables
Next, associate the 3 datasets according to the primary key to merge the scattered datasets into 1, in order to obtain the product sales detail data for each store.
"Associate data" can be popularly understood as "column concatenation". The difference is that data association needs to find the same association columns in both datasets for concatenation; and the concatenation form is also diverse, and the final dataset can also customize columns.
-
First drag in the Associate Data operator, then connect each Input Dataset and Associate Data operator with connection lines;
-
Associate the 3 datasets according to the following rules for left outer join:
· 3.0 Retail Details/Product Code = 1.0 Product Information/Product Code.
· 3.0 Retail Details/Store Code = 2.0 Store Information/Store Code.
Note: The difference between inner join, left join and full join:
Full join: Join the intersection rows in the association column and output together with unmatched rows;
Inner join: Only join the intersection in the association column (the intersecting part of data rows in two tables;
Left outer join: By default output all rows of the left table, and join the columns that match the association in the right table (use the left table as the base, and the right table merges toward the left table).
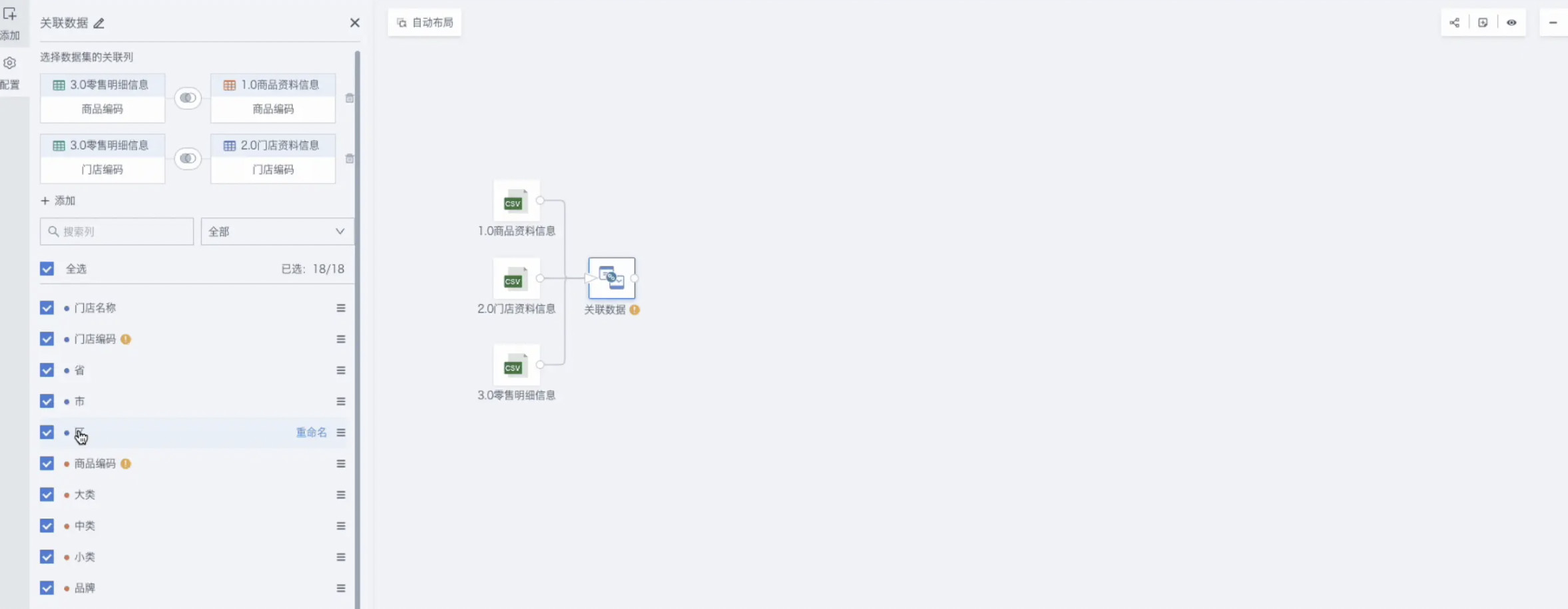
Remove Invalid Dirty Data
When source data contains a large amount of dirty data, or only part of the analysis data is needed, it can be achieved through the "Filter Data Rows" operator.
In actual business, data related to "Materials" and "Coffee" are not counted in store consumption and need to be removed.
-
In the ETL editing area, find and drag in the "Filter Data Rows" operator;
-
Click the current operator Add filter condition: Category not equal to "Materials", Category not equal to "Coffee".
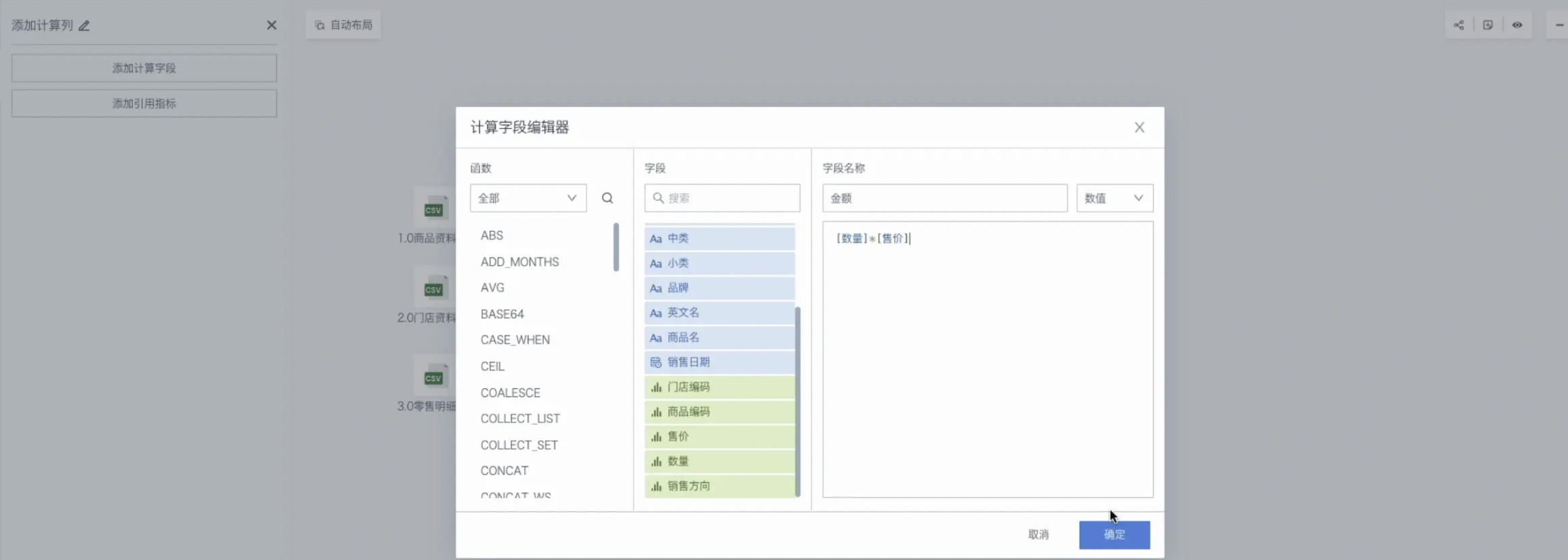
Extend Calculated Columns
Extend or merge calculate existing column dimensions in the dataset, which can add new indicators needed for analysis, etc.
Next, we will calculate "Amount" based on existing fields and include it in the data table as a new indicator for our subsequent visualization analysis.
Drag in the Add Calculated Column operator, then Add Calculated Field, then add the "Amount" field (Amount = Quantity × Unit Price), select the field type as Numeric.
Output Dataset and ETL Execution
Output the processed data as a dataset.
Finally, we will output the sales detail data table, which can be used for subsequent data analysis and visualization.
-
First drag in the Output Dataset operator, then name it Sales Detail Data Table, then select the storage location for the output dataset. The output path for this case is Root Directory > Case_Store Sales Statistics;
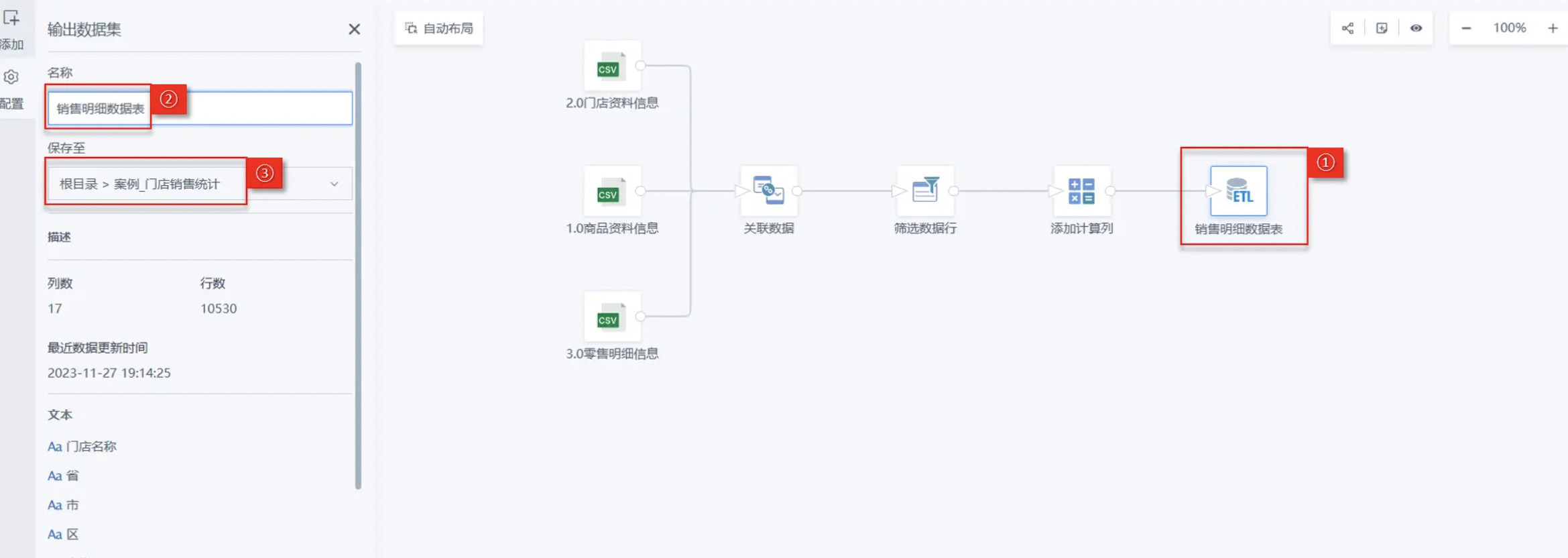
-
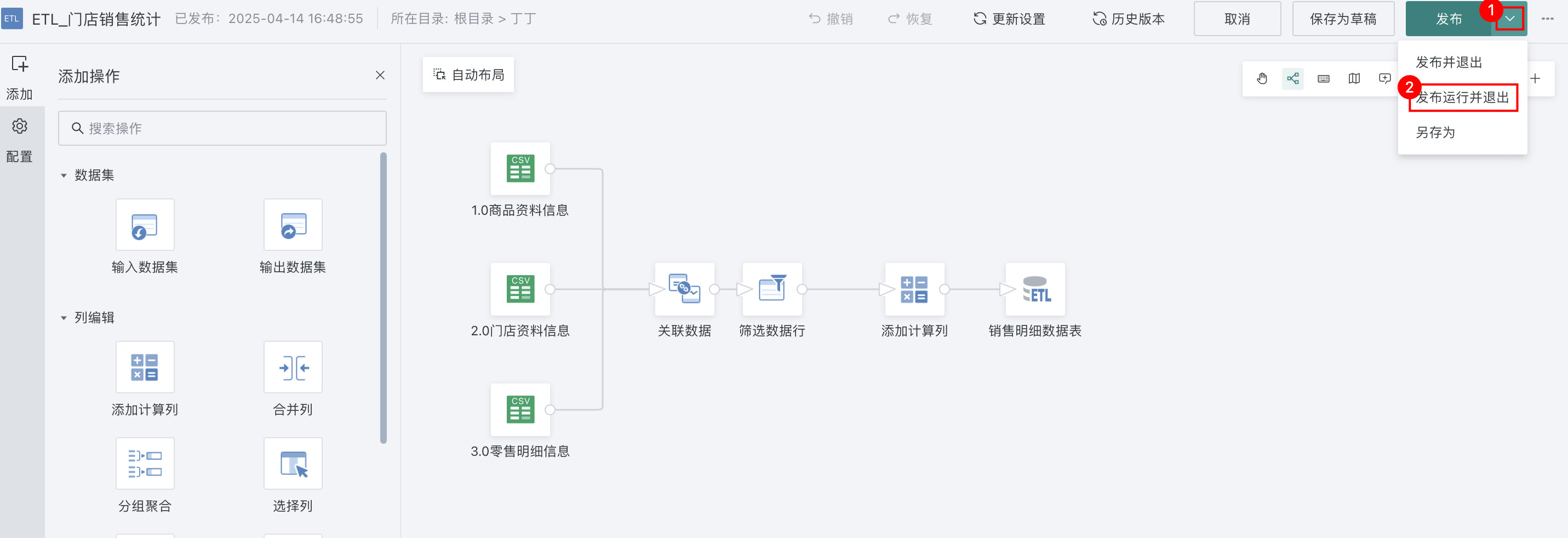
Click the "Publish" dropdown button in the upper right corner of the page, select "Publish Run and Exit", and automatically jump to your ETL task storage path after running is completed.
ETL supports version management. For detailed operations, please refer to ETL Version Management.
-
After running is completed, you can enter the ETL details page to view the ETL output dataset and complete data processing.
3.3. View ETL Task
On the ETL list page, you can see the ETL task completion time and running time, and you can also enter the details page to view the ETL output dataset, as shown in the figure below:
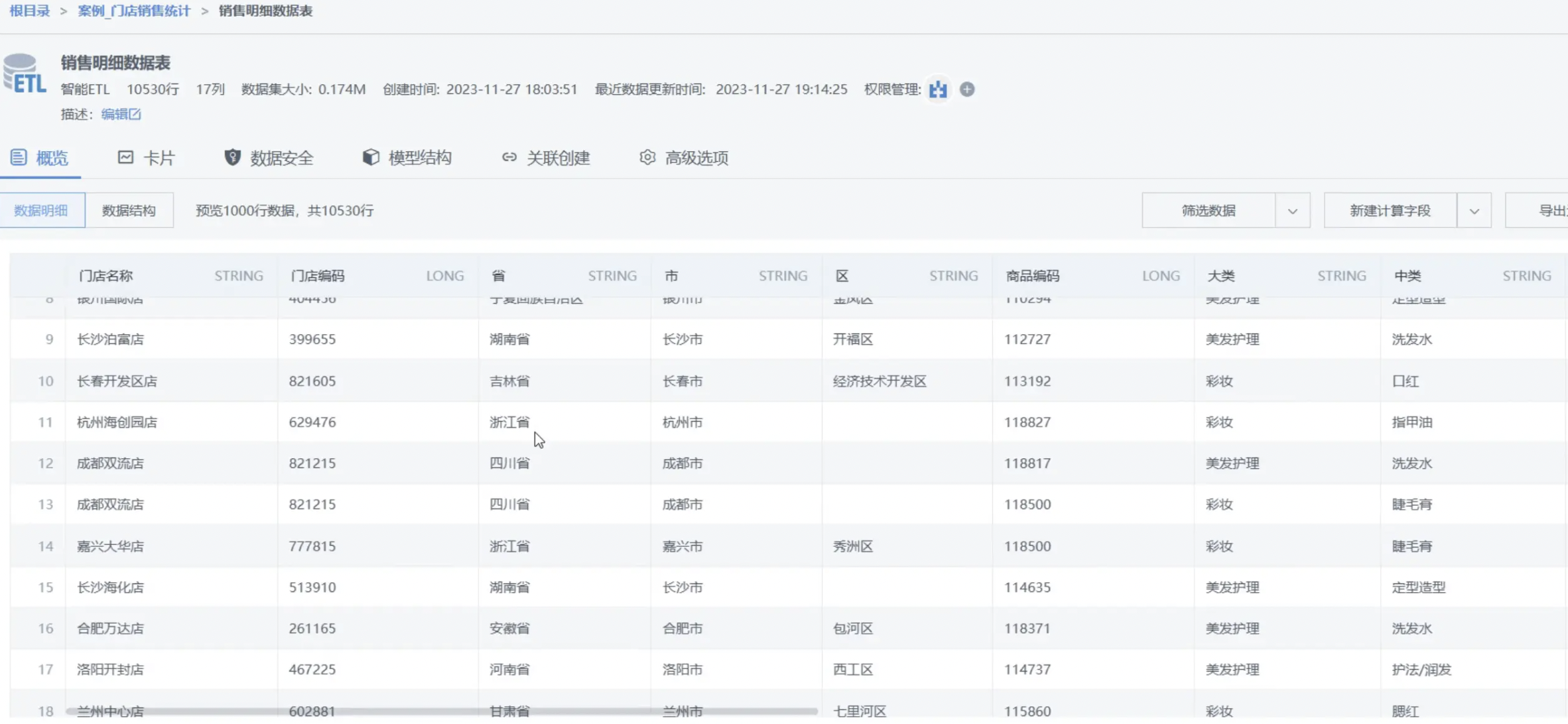
After completing the ETL task setup, we will introduce how to manage ETL tasks.
3.4. Manage ETL Tasks
ETL Scheduling Settings
When you are processing real-time streaming data, you can set ETL tasks to run on a schedule or run after specified datasets are updated to ensure that the output data can reflect the latest information status. When you need to run multiple ETL tasks, you can also specify priorities for them to ensure data operations are executed according to business importance and logical order. This case takes running after dataset update as an example:
-
Click the edit icon on the ETL list page to enter the ETL details interface, select Update Settings, at this time the Scheduling Status is closed by default, and you can see the scheduling status, update method, update cycle and other related configuration item information;
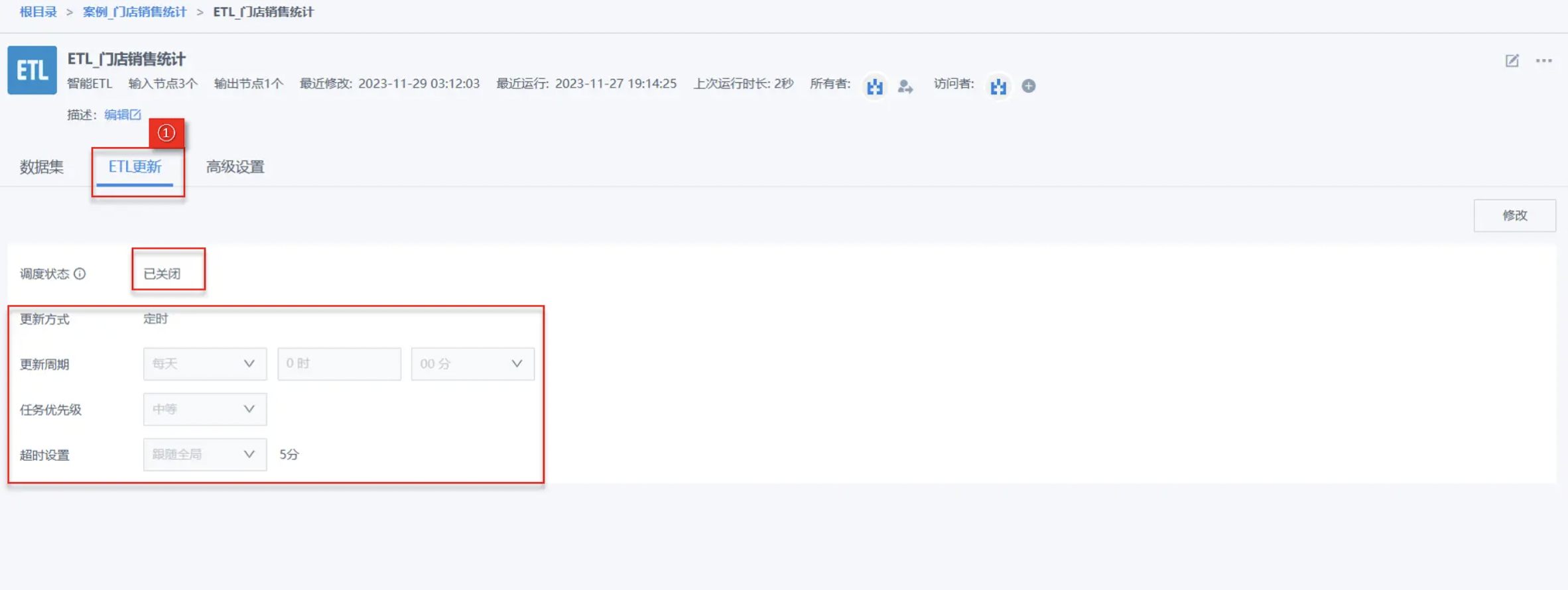
- Click the edit icon to enter the ETL editing interface, select Update Settings, and turn on the Scheduling Status switch;
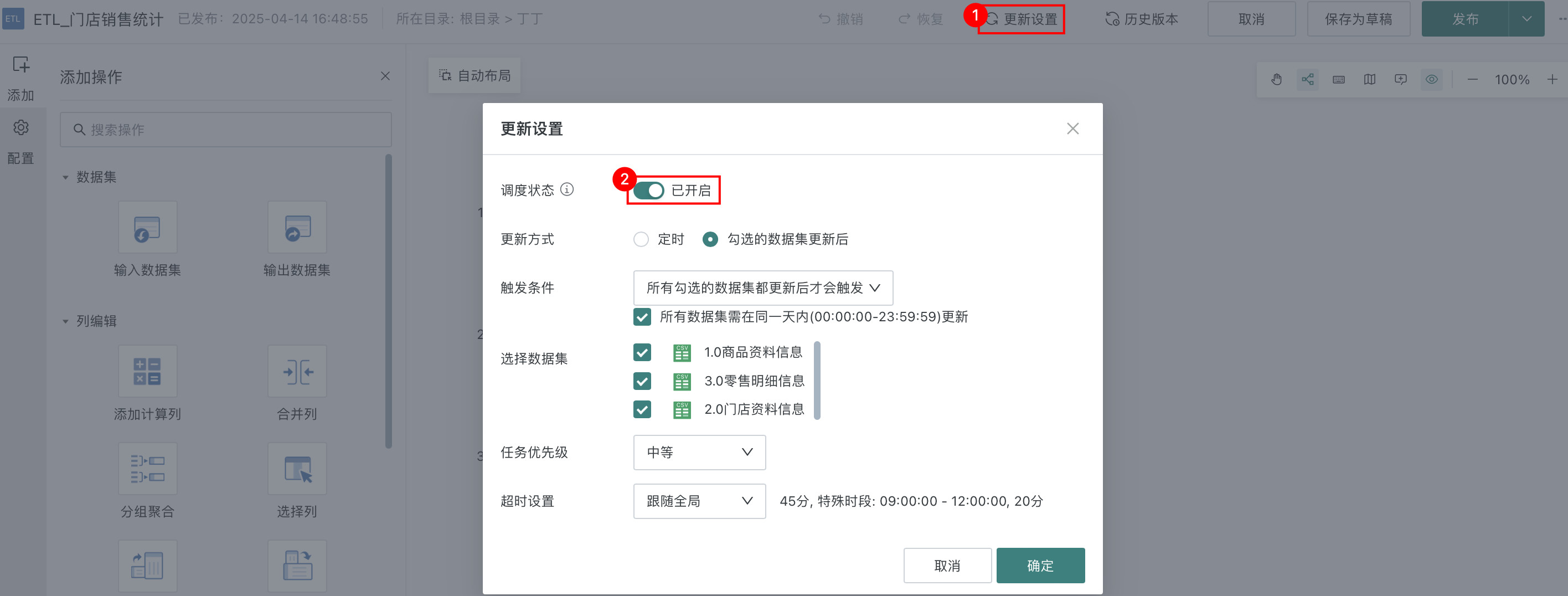
- After turning on Scheduling Status, you can set the following as needed:
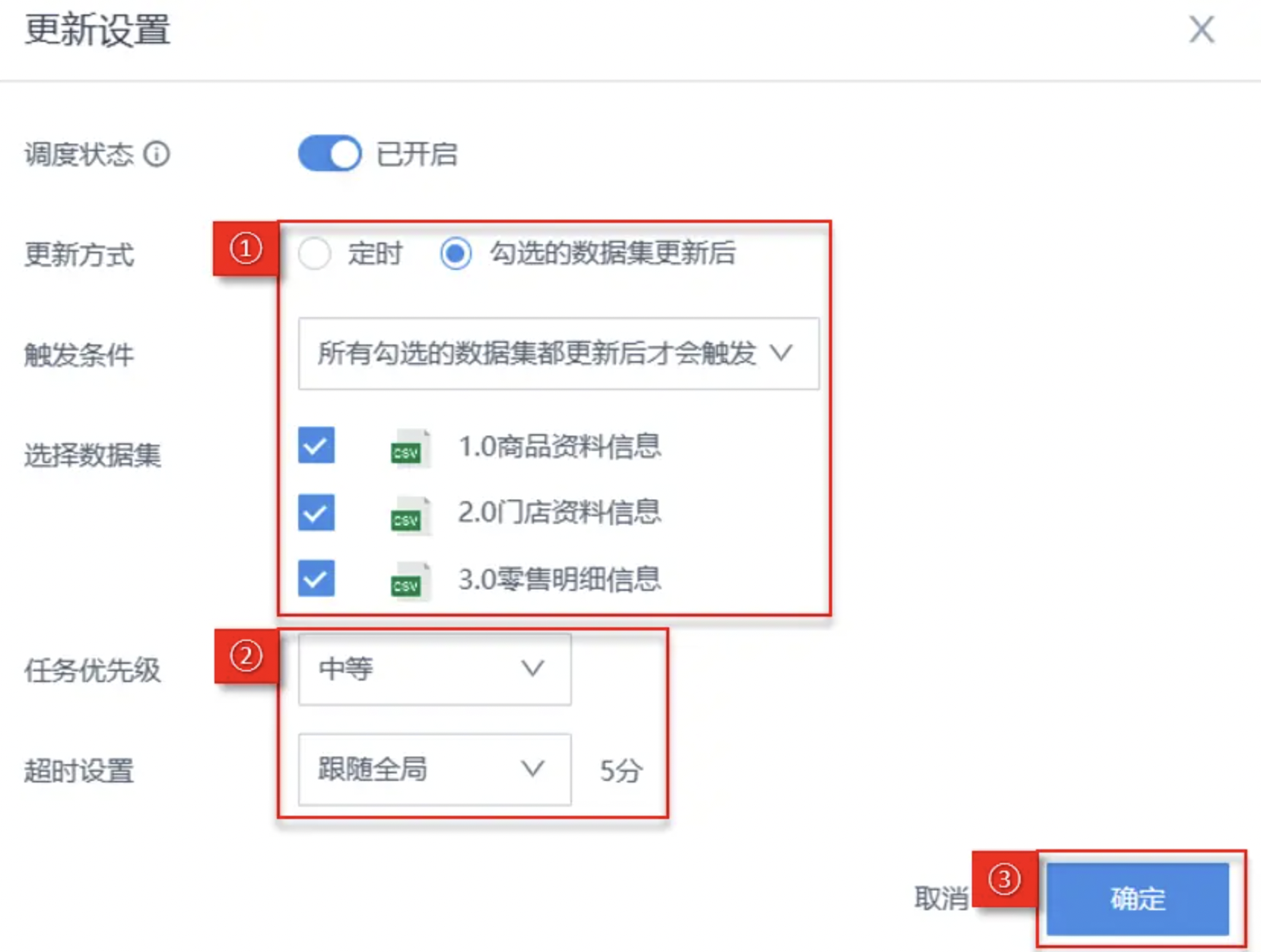
(1) Select After all checked datasets are updated, set Trigger Condition to trigger only after all checked datasets are updated, check 3 data tables;
(2) Select Task Priority as Medium, Timeout Setting follows global;
(3) Click OK to complete Update Settings, as shown in the figure below:
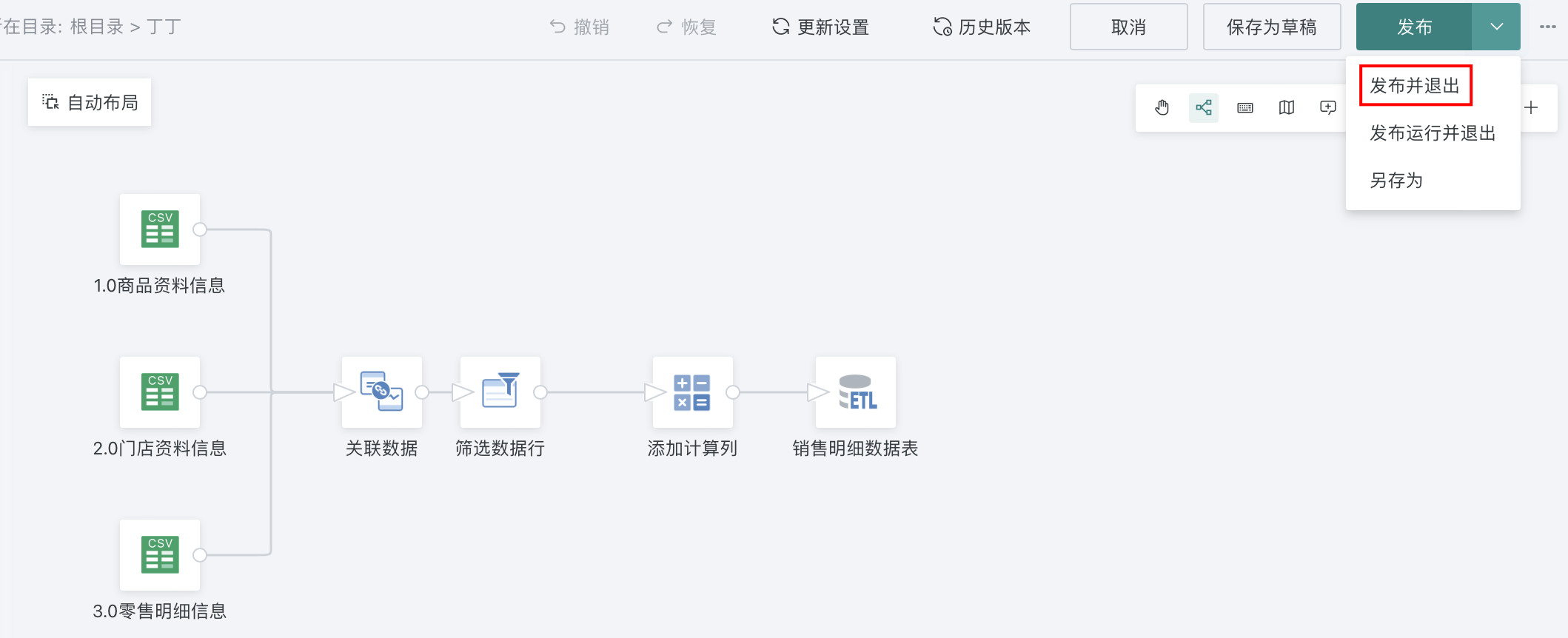
(4) Select Publish and Exit, automatically jump to the ETL details page;
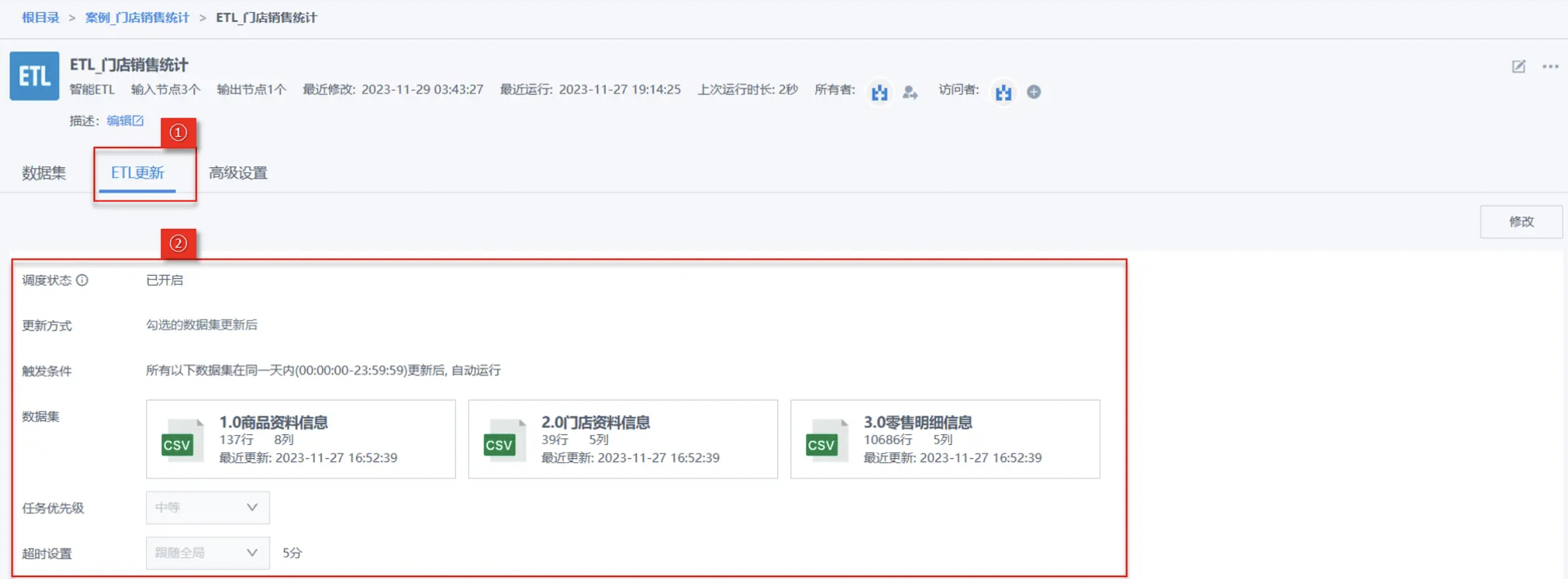
(5) Click Update Settings to view the configuration items we just set.
For more details, see ETL Update Strategy.
Permission Changes
In actual business scenarios, for the convenience of collaborative sharing, we can transfer the ETL task owner permissions to other users, or add access permissions for other users.
This case takes adding access permissions for other users as an example:
- On the ETL details page, click the plus button (as shown in the figure), and select users as needed in the Accessor Management popup.
For more details, see Permission Management.
4. More
You have learned the most core analysis steps of Smart ETL. Next, you can enter Beginner's Guide to learn about the specific analysis methods of each operator in detail.