Overview
1. Overview
1.1. Function Description
The maintenance and management of Smart ETL tasks are key to ensuring the normal operation of data processing flows, adapting to business changes, and improving data quality and operational efficiency.
You can also solve system stability issues by monitoring task execution and regularly adjusting scheduling strategies.
2. Usage Instructions
2.1. Entry Description
For ETL management and maintenance, Guandata BI provides two entry points.
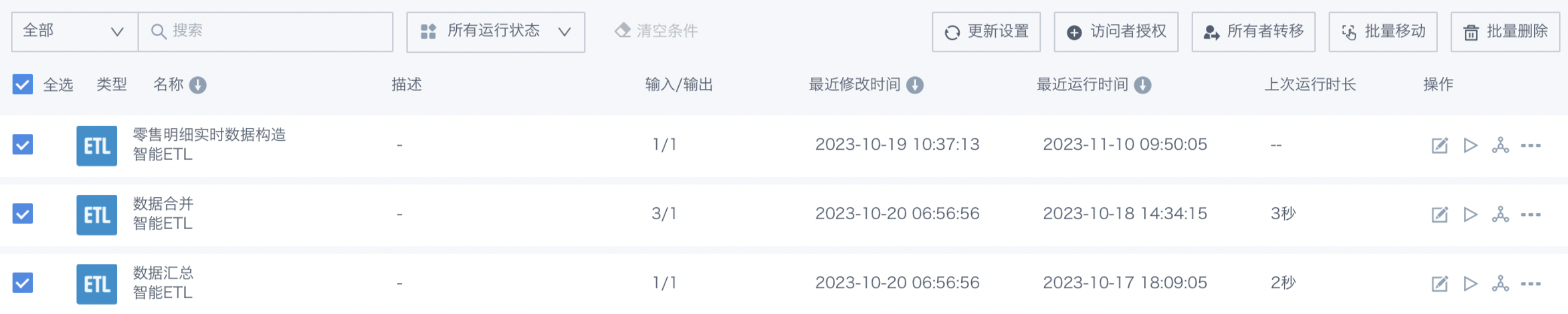
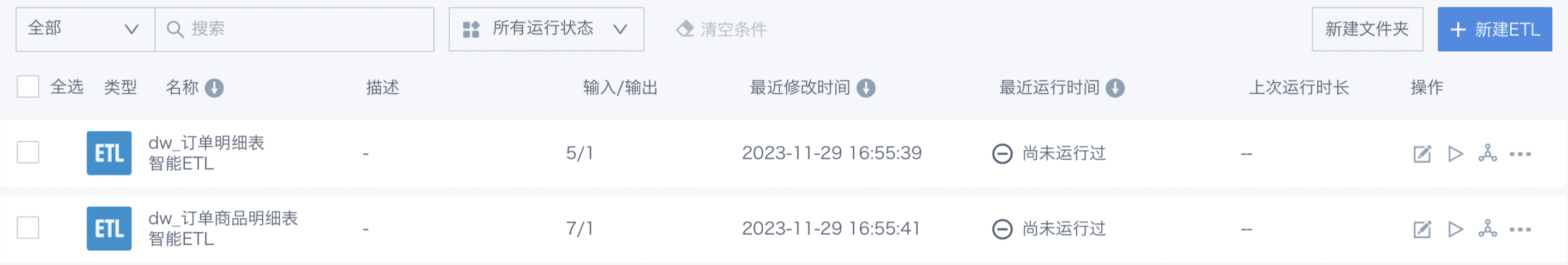
List Management Entry: The ETL list page supports unified management of ETL tasks, listing the basic information of current ETL tasks in a concise way and providing basic operations.
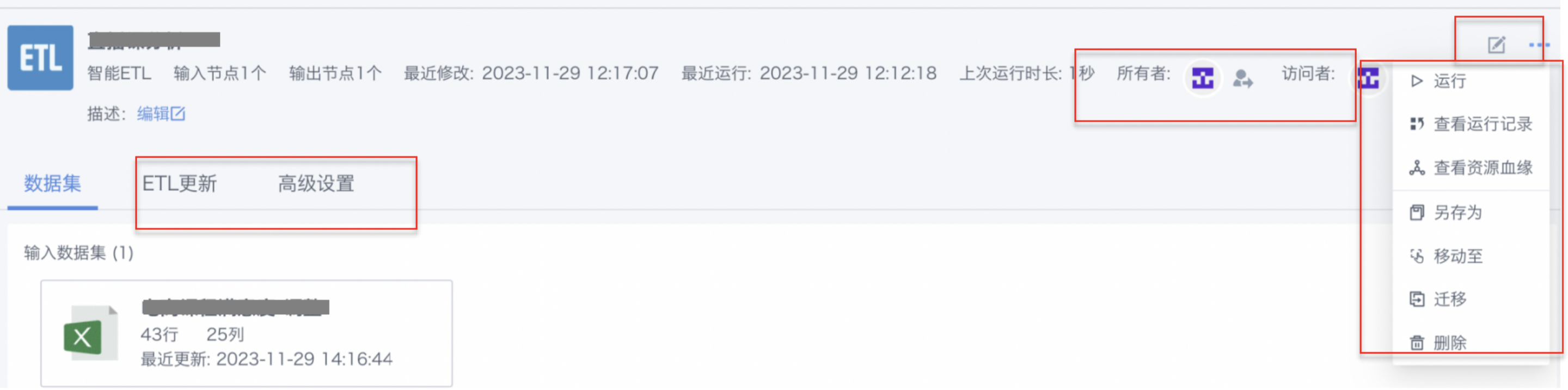
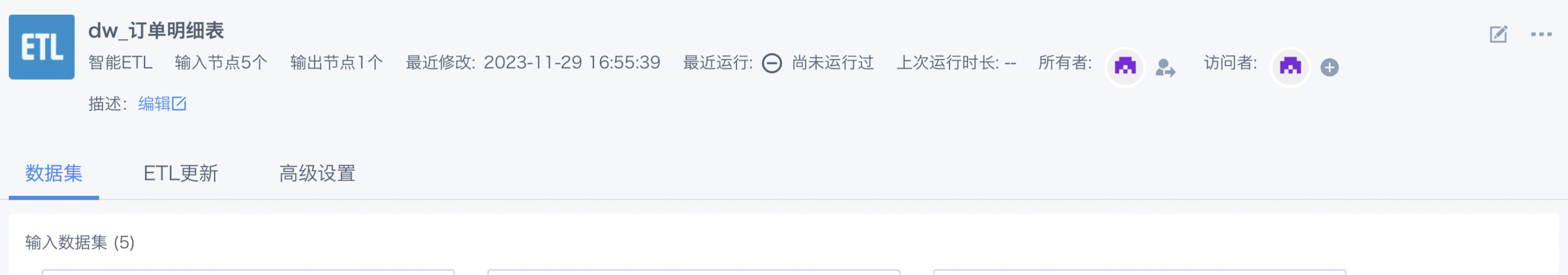
Task Details Entry: The ETL details page provides a more detailed and comprehensive view of the task and allows users to deeply manage all configurations and advanced features of a single task.
[Why can't I view ETL details?](../../../11-FAQ/1-Data Processing/2-ETL FAQ.md)
2.2. Management Operations
| Operation | Description |
| Edit | Modify and adjust the configuration and parameters of created ETL tasks to adapt to business needs or optimize ETL flows. |
| Run | Manually start or trigger created ETL tasks to execute the data processing flow, usually used to verify task configuration and obtain real-time processing results. |
| View Resource Lineage | View the relationships between data resources involved in ETL task execution. Through resource lineage, you can easily see the associations between each data application, analysis dashboard, ETL, dataset, etc. |
| View Run Records | View the execution records of ETL tasks, including start time, completion time, run duration, and status, to monitor execution and troubleshoot problems. |
| Save As | Copy and create a new ETL task, modify it based on the existing configuration to meet new business needs while retaining the original task. |
| Rename | Change the name of the ETL task to better reflect its purpose, content, or business scenario. |
| Move To | Move the ETL task from its current location to a specified folder or directory to organize and manage the task hierarchy. |
| Migrate | Migrate ETL task resources from the current environment to another environment. |
| Delete | Delete created ETL tasks from the management system. Use with caution, as deletion will clear the task and its related configuration and execution records. |
| Permission Settings | Configure permissions for ETL tasks, including owner transfer and visitor assignment, to ensure data security and compliance. Owner transfer: transfer task ownership to another user, who will have all permissions for the current task. Visitor authorization: assign access permissions to other users or team members. These permissions may include viewing, editing, running, and viewing run records. |
| ETL Update | Set different scheduling strategies for ETL tasks to control when they start and run (start time, run cycle, and trigger conditions) to meet different data processing needs. For details, see [ETL Update Strategy](1-ETL Update Strategy.md) |
Note: The ETL list supports batch operations on multiple Smart ETL tasks, including update settings, permission configuration (owner transfer, visitor authorization), move, or delete. This saves time on repetitive operations and improves work efficiency.
2.3. Operation Instructions
ETL Editing
Click the edit button in the upper right corner to enter the ETL editing page for operations.
ETL Running
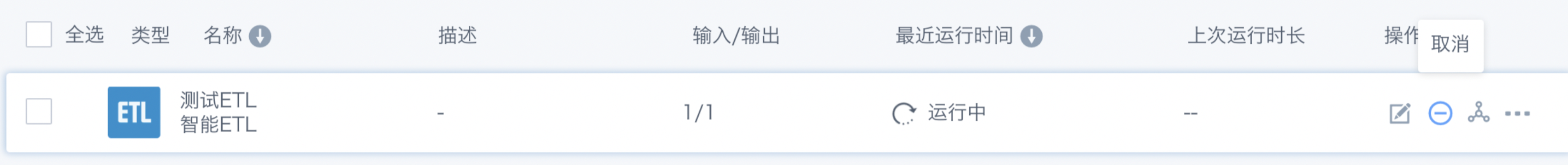
Manually start or trigger created ETL tasks to execute the data processing flow, usually used to verify task configuration and obtain real-time processing results.
After saving Smart ETL, you need to run it to output the dataset. The first run will generate the "output dataset"; subsequent runs will update the output dataset according to the current logic.
Users can directly find the corresponding ETL processing flow in ETL to run, or enter the details page to run. After clicking Run, the ETL task status changes to "Running".
Error details: [Found duplicate column(s) ...](../../../12-Error Description.md)
Note:
- Only by running can you output the dataset;
- If necessary, you can manually update the output dataset;
- If the run fails, it means there is a problem with the ETL processing flow and further troubleshooting and improvement are needed;
- Automatic running enables automatic execution from input dataset to output dataset;
- For ETLs with multiple input data sources, if you choose to trigger updates by "checked datasets", it is recommended to select the input data source with the latest update time to trigger.
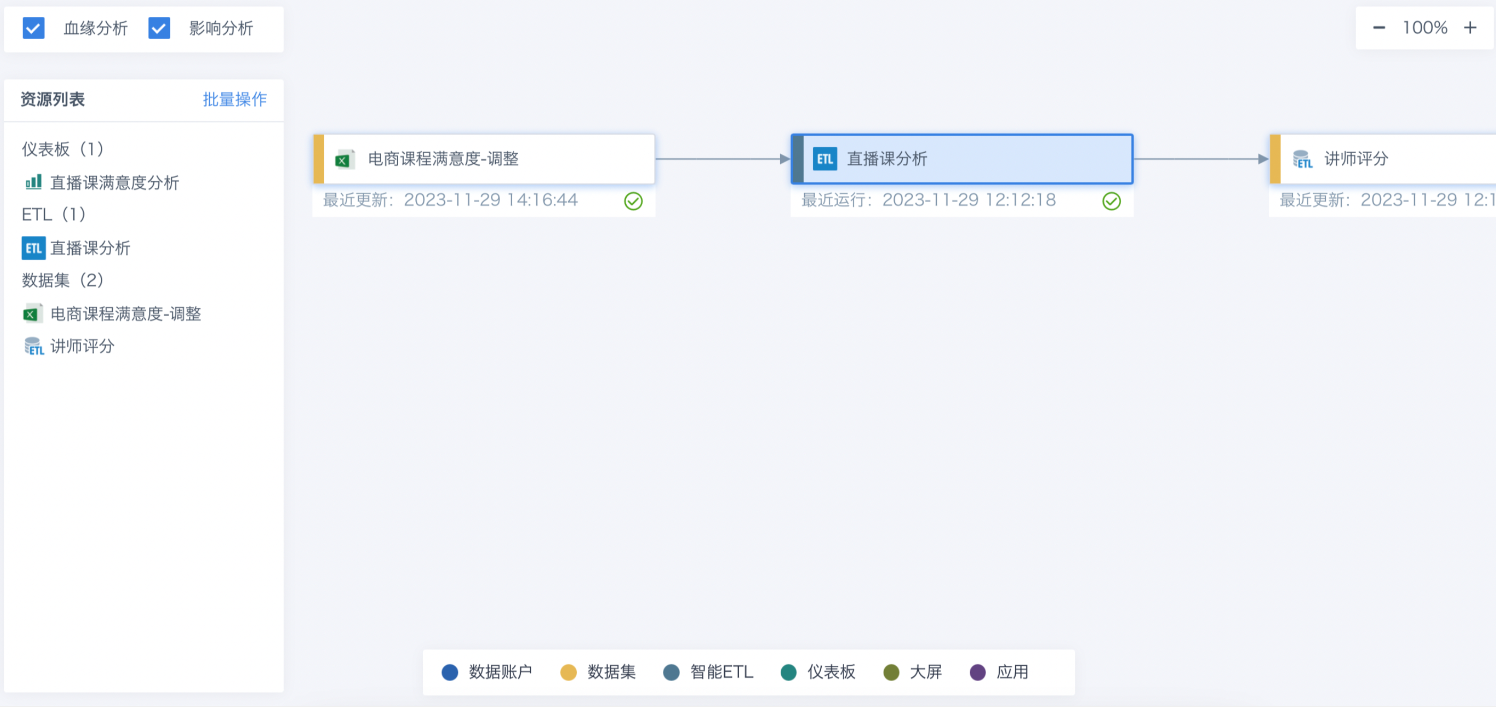
View Resource Lineage
View the relationships between data resources involved in ETL task execution. Through resource lineage, you can easily see the associations between each data application, analysis dashboard, ETL, dataset, etc., and the direction of data analysis flows, enabling quick data governance, understanding upstream and downstream dependencies, and risk assessment. When troubleshooting, you can also quickly locate the problem. For details, see [Resource Lineage](../../../4-Multi-source Data Access/5-Dataset Management/6-Resource Lineage.md)
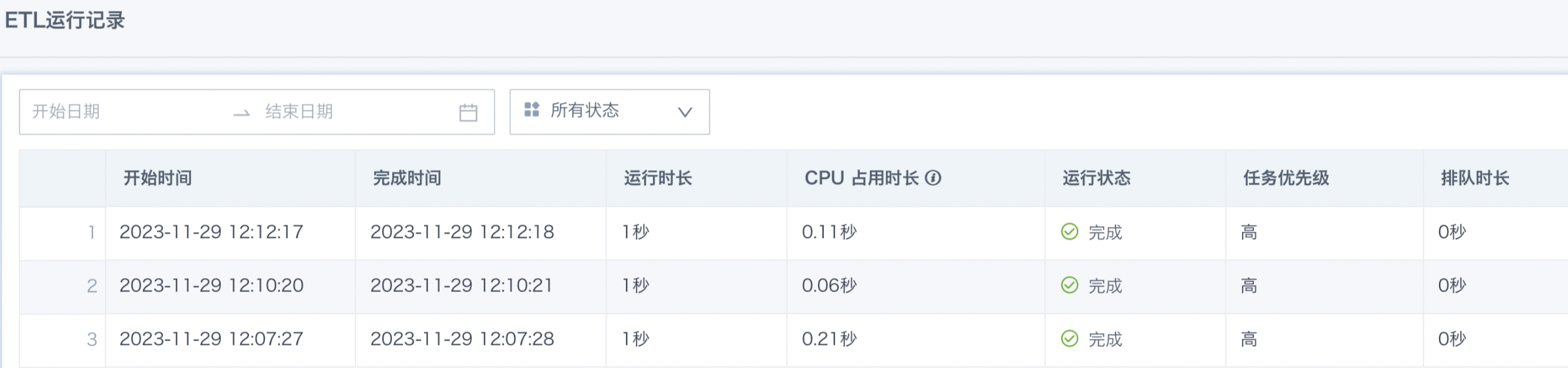
View Run Records
Provides the current ETL task's running status and historical execution. Each run can be traced, including start time, completion time, run duration, and status, which helps monitor execution and troubleshoot problems.
If the run fails, it means there is a problem with the ETL processing flow and further troubleshooting and improvement are needed.
Save As
Copy and create a new ETL task, suitable for frequently creating similar tasks or quickly adapting to new data sources, avoiding starting from scratch and saving configuration time.
After saving as, users can directly modify or replace the dataset based on the existing configuration.
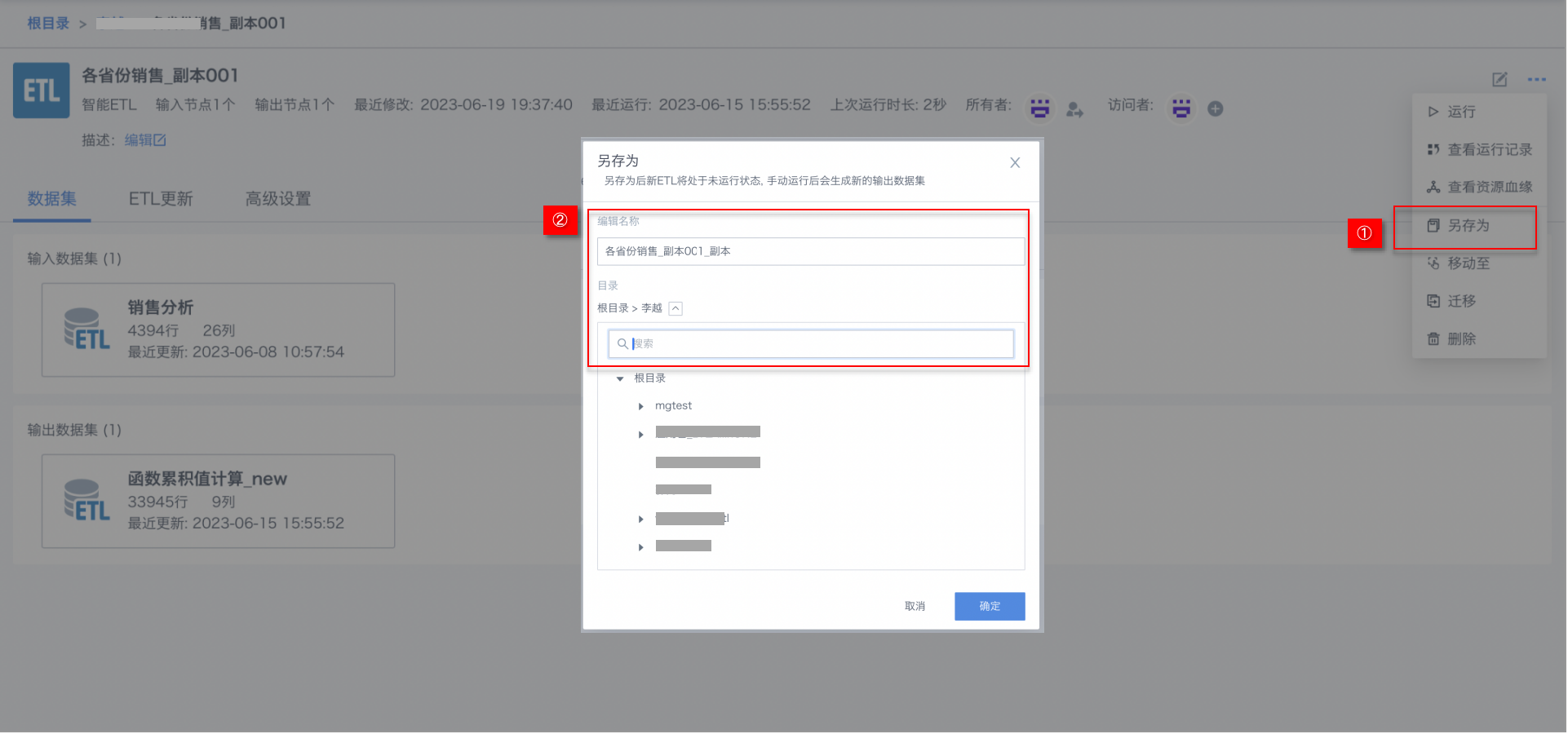
Rename
Change the name of the ETL task to better reflect its purpose, content, or business scenario.
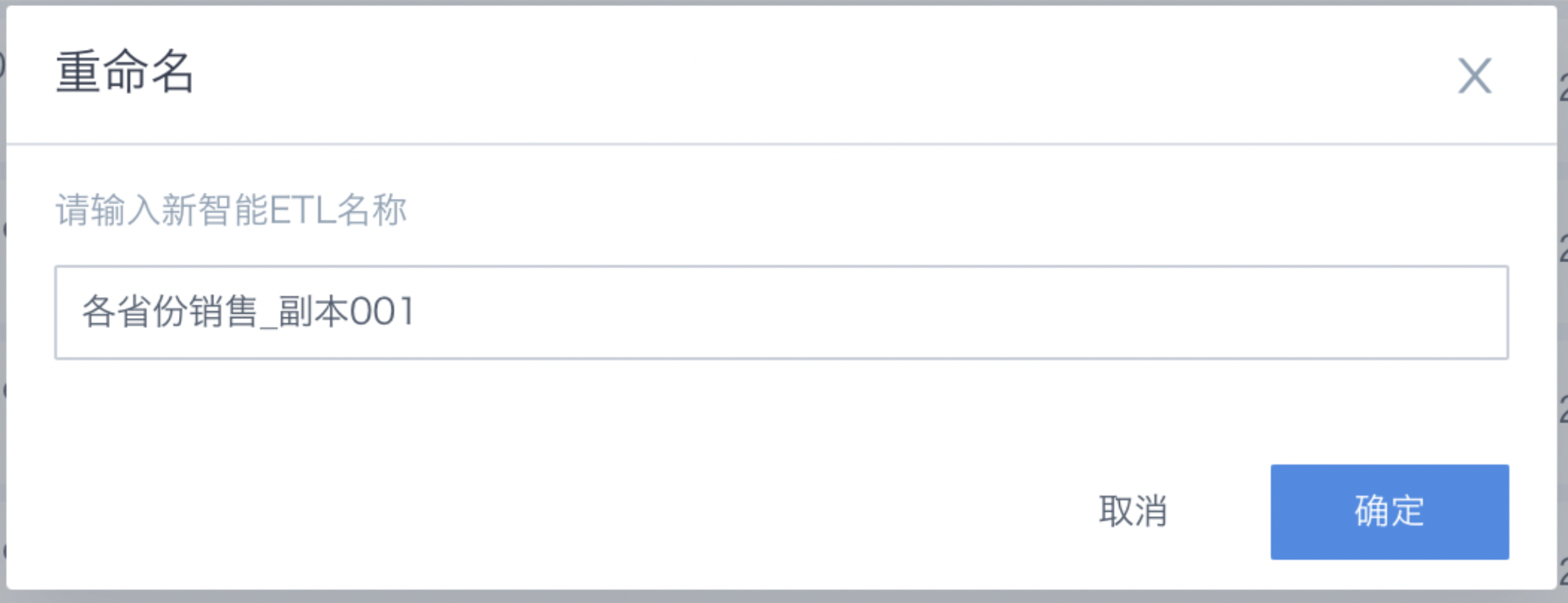
Move To
Move the ETL task from its current location to a specified folder or directory to organize and manage the task hierarchy.
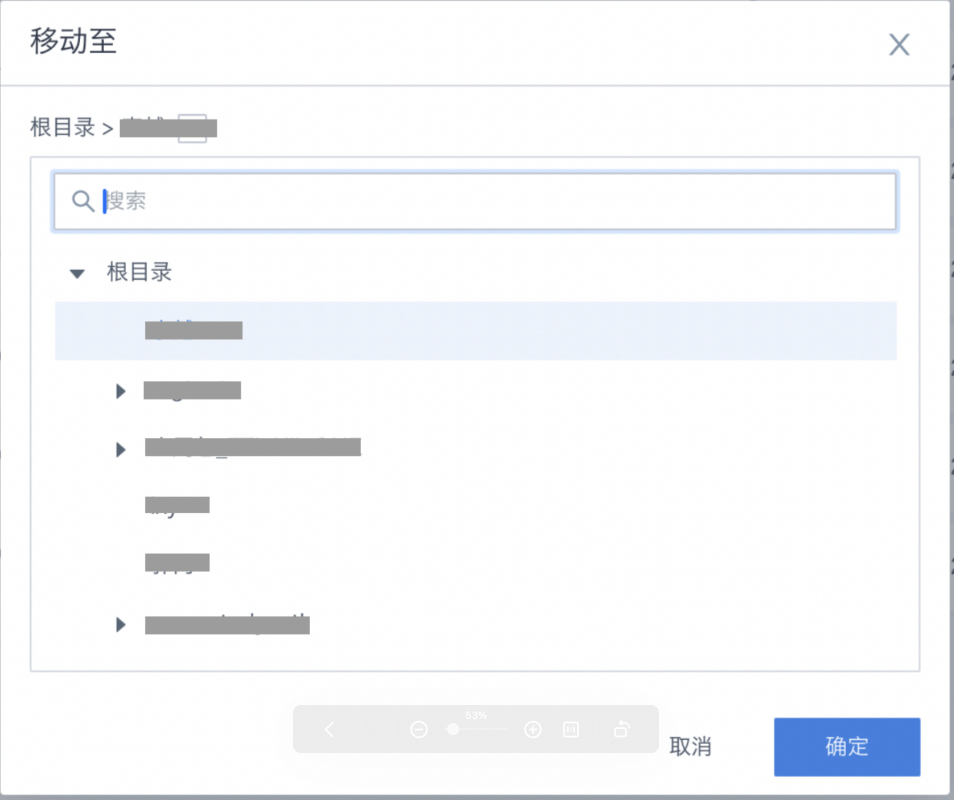
Migrate
Migrate ETL task resources from the current environment to another environment. For details, see Resource Migration
Delete
Users can clean up ETL tasks that are no longer needed, suitable for idle ETL tasks that have never been run or used, or zombie ETLs that occupy CPU resources.
Before deleting an ETL task, please understand its purpose, impact, and related dependencies to avoid unnecessary impact on the system.
Be cautious, as deletion will clear the task and its related configuration and execution records, and the operation is irreversible (cannot be recovered from the recycle bin).
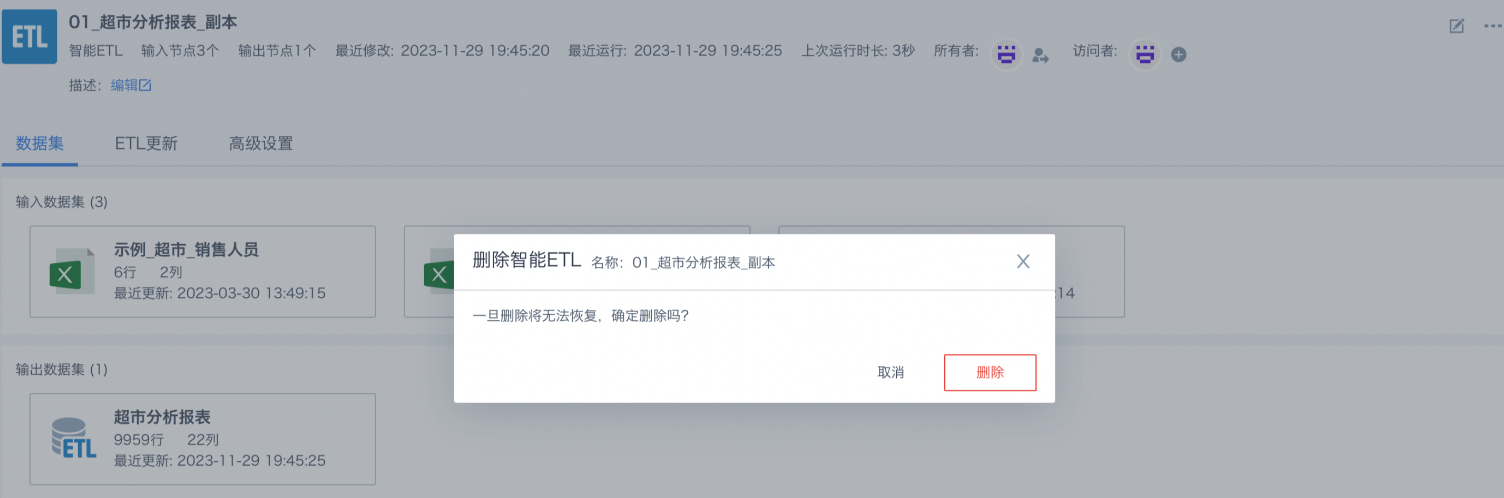
Note:
When an ETL is referenced by advanced scheduling, deletion may fail. — Solution: Go to the advanced scheduling module and delete the ETL task referenced in the corresponding workflow.
When the ETL output dataset already exists, deletion may fail. — Solution: If it does not affect business analysis, consider deleting the ETL output dataset.
Permission Settings
Owner Transfer: Transfer task ownership to another user, who will have all permissions for the current task.
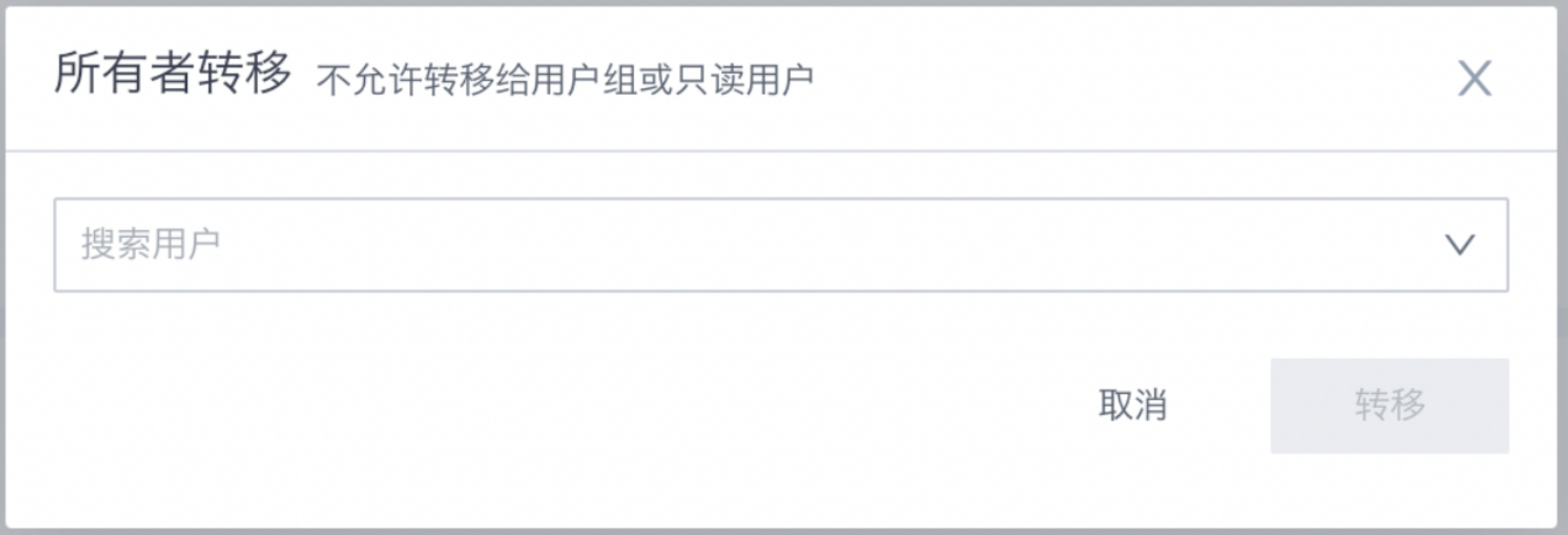
Visitor Authorization: Assign access permissions for the current ETL task to other users or team members. These permissions may include viewing, editing, running, and viewing run records.
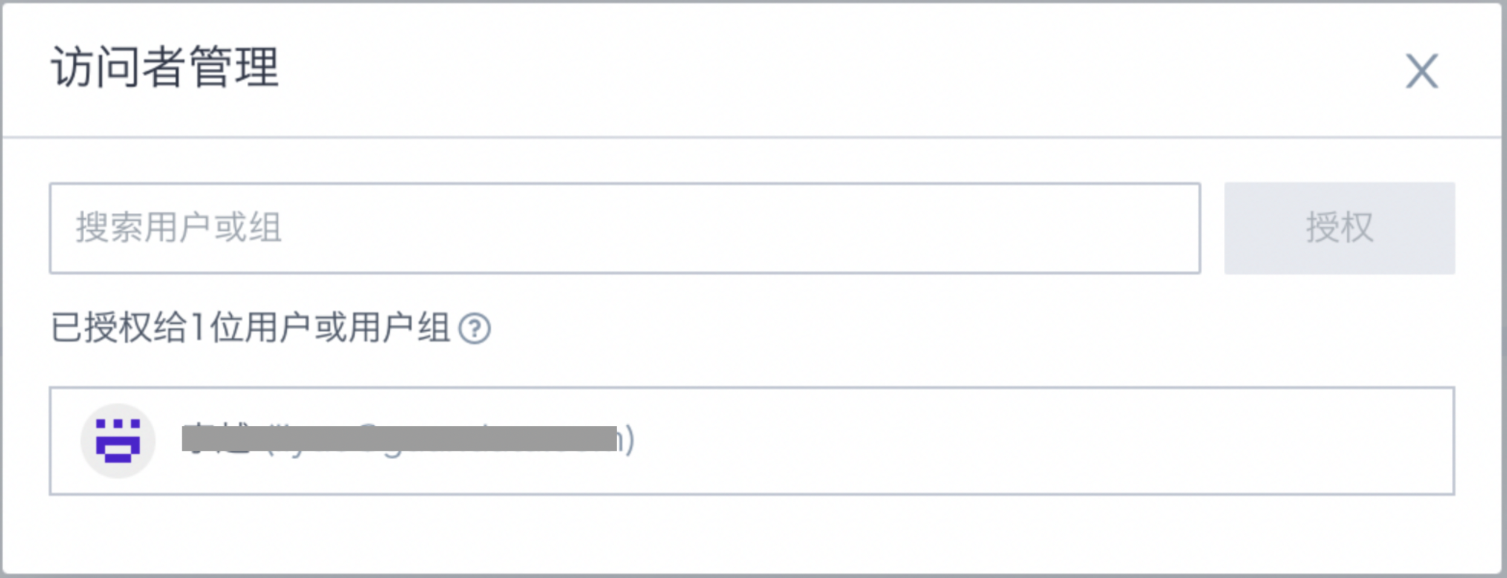
See more [ETL Permission Management](2-ETL Permission Management.md) .
Note:
Owner transfer does not allow selecting user groups or read-only users.
Owner transfer and visitor authorization support batch operations. Entry: After selecting ETL tasks in the Smart ETL list, a batch operation item will appear in the top shortcut bar.
ETL Update
Set different scheduling strategies for ETL tasks to control when they start and run (start time, run cycle, and trigger conditions) to meet different data processing needs.
For details, see [ETL Update Strategy](1-ETL Update Strategy.md)