ETL Update Strategy
1. Overview
A suitable scheduling strategy can improve work efficiency and ensure data quality, providing strong support for the work of data teams.
By scheduling ETL tasks, you can control when ETL tasks start and run (start time, run cycle, and trigger conditions), helping enterprises achieve automated processing of massive data and providing strong support for data teams.
Enterprises can develop different task scheduling strategies as needed, including configuring ETL update methods, task priorities, timeout limits, etc., to meet different data processing needs.
2. Usage Instructions
2.1. Entry Description
Entry 1: ETL Task Details Page > ETL Update Module
Entry 2: ETL Task Editing Page > Update Settings
2.2. Configuration Instructions
Below is an example of configuring a scheduled update.
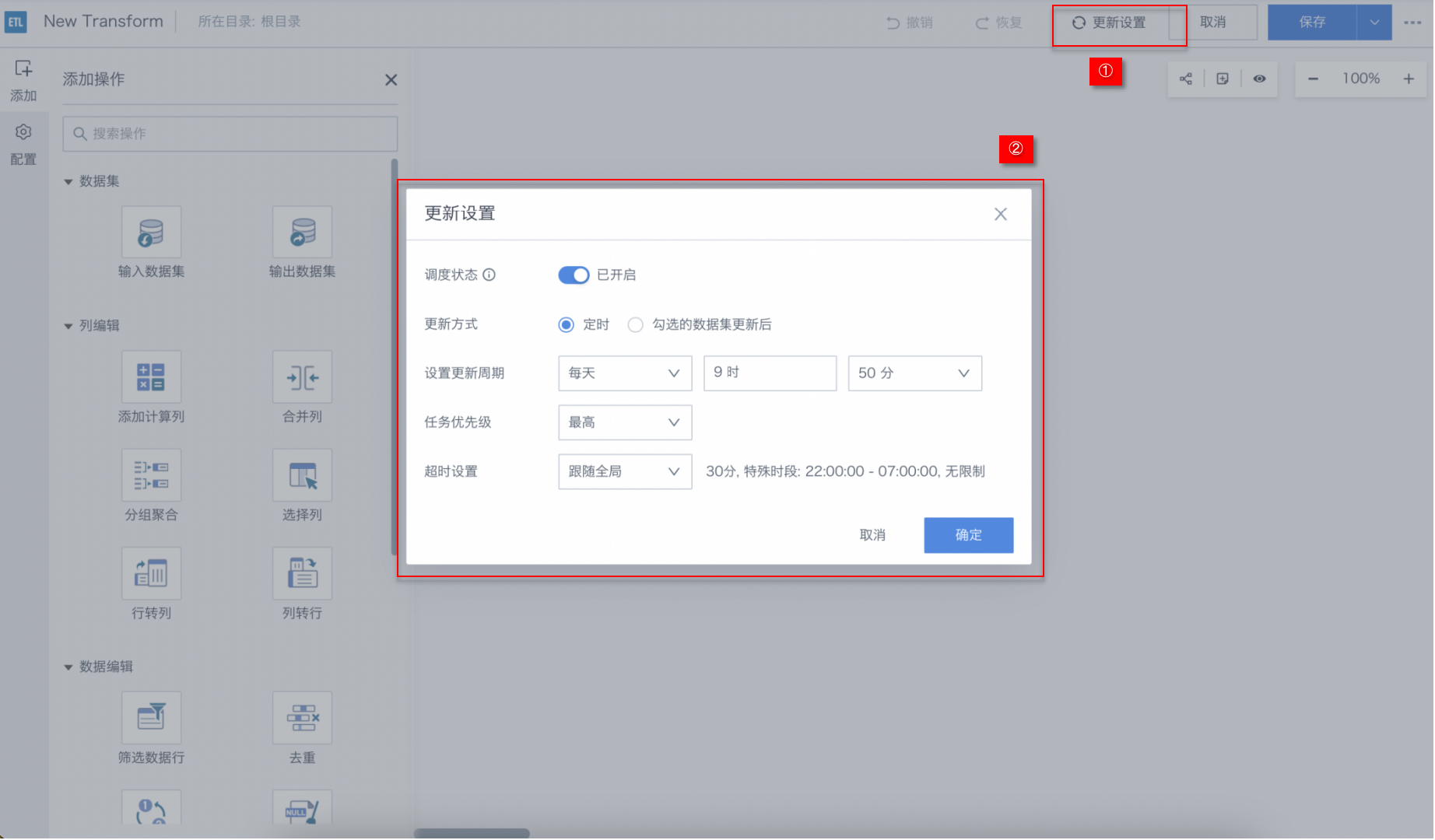
- Enter the Smart ETL page, and click Update Settings in the upper right corner of the page.
- In the Update Settings dialog, turn on the scheduling status switch.
- As needed, select the update method as "Scheduled" and set the update cycle (for example, if the latest sales indicators need to be demonstrated at the 10 a.m. morning meeting every day, set the ETL update cycle to 9:50 a.m. daily), high task priority, and timeout settings.
- After configuration, click OK.
- In the future, you can view or modify it in ETL Task Details Page > ETL Update Module.
[Why does the ETL update when the update method is set to "all checked datasets are updated" but not all datasets have been updated?](../../../11-FAQ/1-Data Processing/2-ETL FAQ.md)
The ETL update strategy scheduling configuration items are as follows:
| Configuration Item | Description |
| Scheduling Status Switch | The scheduling status of ETL supports on or off. When on, ETL can be actively scheduled, can run on a schedule or be triggered after dataset updates. When off, only API or manual ETL runs are supported. (More flexible, suitable for scenarios with small data volume or simple tasks, and can adjust the execution time and frequency as needed) |
| Update Method | Provides two modes: scheduled and triggered after dataset update. Scheduled: Automatically executes ETL tasks at preset times or intervals according to business needs and data update frequency. Supports periodic execution, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. Supports multiple intervals within a cycle, such as 0:00, 6:00, 8:00, 12:00, and 24:00 every day. Triggered after dataset update: Triggers ETL tasks when datasets in the ETL process change to ensure real-time data processing. Supports "any checked dataset update triggers ETL" or "all checked datasets update triggers ETL". All datasets must be updated within the same day (00:00:00-23:59:59). Can be checked. |
| Task Priority | Set different run priorities for the current ETL task according to business needs and urgency. Current priorities include "Highest", "High", "Medium", "Low", or "Lowest". "Highest" means it will be executed first among all ETL tasks. Note: If all tasks are set to "Highest", they will be executed in the order of submission. |
| Timeout Setting | Set the threshold for ETL task run duration. If the task cannot be completed within the specified time, the system will terminate the task to avoid long-term occupation of the task queue or computing resources, blocking other tasks. Custom timeout: can be set from 1 to 300 minutes. Follow global timeout: follow the global timeout set by the administrator in Operations Management - Parameter Configuration - ETL Parameter Configuration module. |
Differences between scheduling modes
Scheduled is suitable for data processing tasks executed at fixed intervals, while triggered after dataset update is more suitable for real-time or near-real-time processing scenarios, such as updating sales data before performance analysis.
Compared with scheduled, triggered after dataset update can avoid running tasks when there is no actual data update, reducing resource waste. (If the data is not ready and ETL runs, the output ETL result is not useful.)