Data Writeback to Database
Note: This product module is a value-added feature. If you wish to try it, please contact Guanyuan Data's business personnel or your Customer Success Manager (usually your company's current service contact).
1. Overview
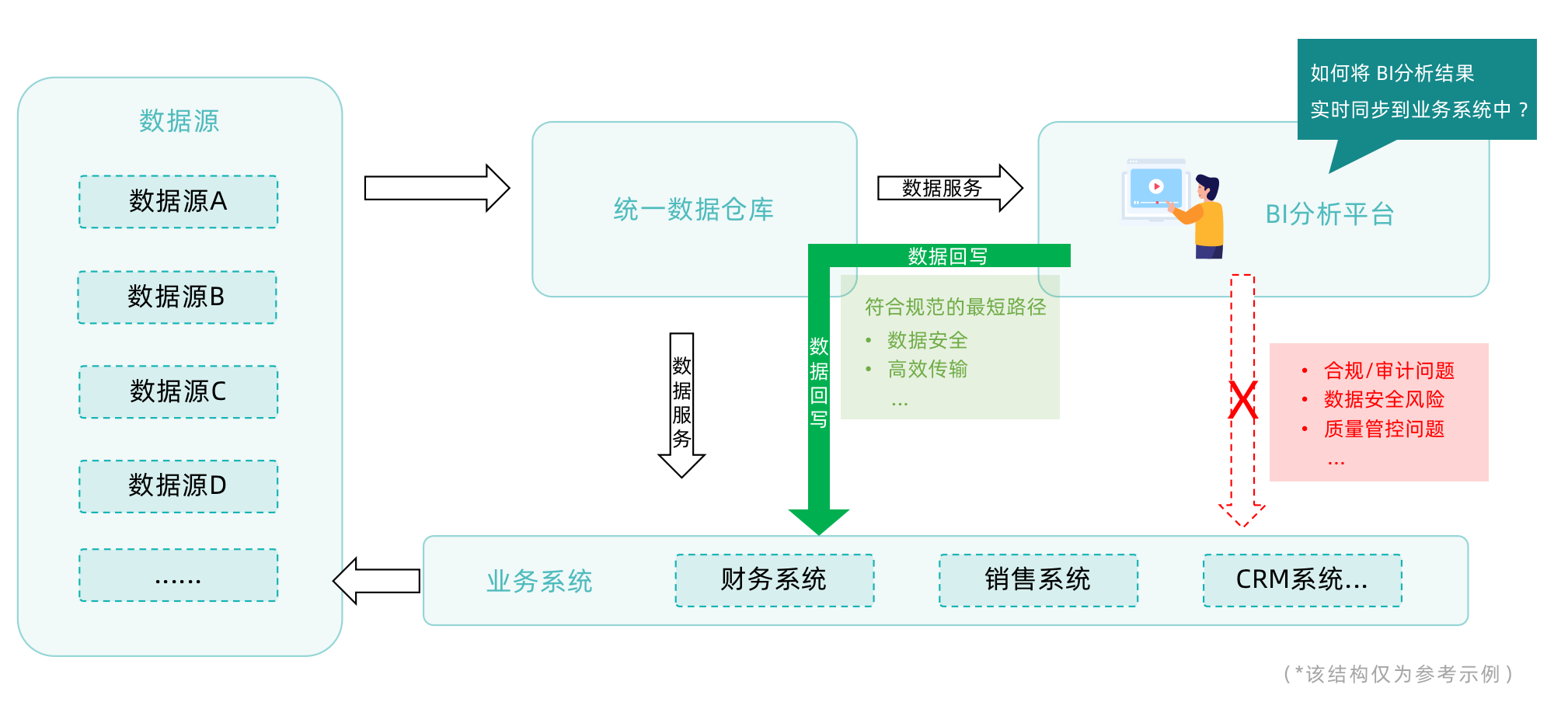
This feature allows users to write datasets that have been processed and analyzed in the BI platform into their business systems or underlying data warehouses through online configuration. It helps users close the loop for subsequent business marketing and data sharing scenarios, and provides online operation and maintenance management capabilities. Compared with the Public API data integration method, data writeback lowers the development and management threshold for writeback scenarios and offers significant performance advantages for large-scale data writeback.
2. Application Scenarios
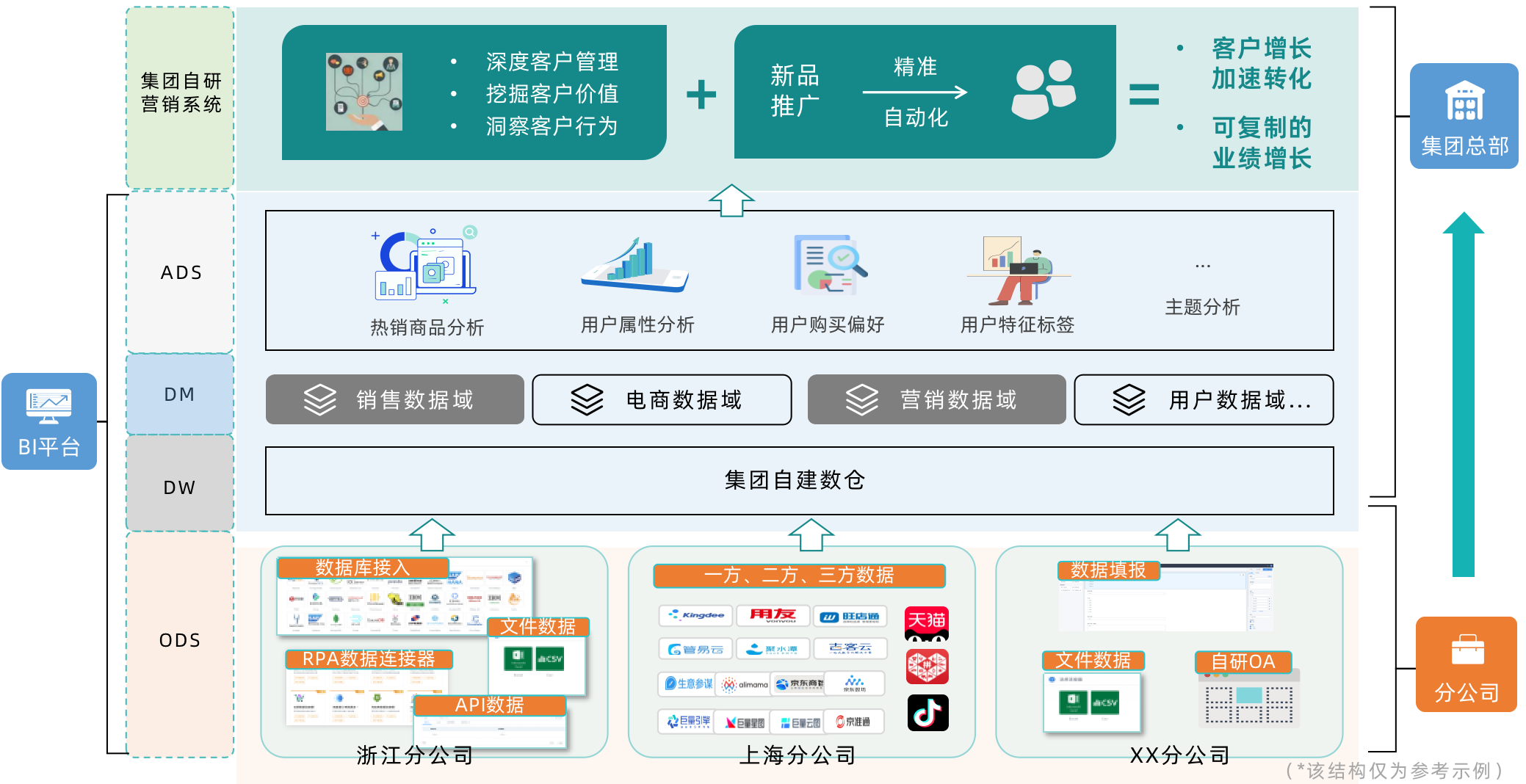
2.1 Precision Marketing
After conducting user profiling analysis in BI, the marketing team may want to send relevant information to target customer groups during new product promotions. With data writeback, user attribute analysis data, purchase preference results, user feature tags, and other data can be automatically sent back to the marketing system database. Marketing plans can then be configured in the marketing system to target these groups, completing the process from marketing to conversion and accelerating business growth.
2.2 ERP/Supply Chain Demand Planning
After completing sales analysis of hot-selling products in BI, the corresponding analysis results can be sent back to the ERP or supply chain system to support subsequent procurement planning, reduce inventory backlog, and improve capital utilization.
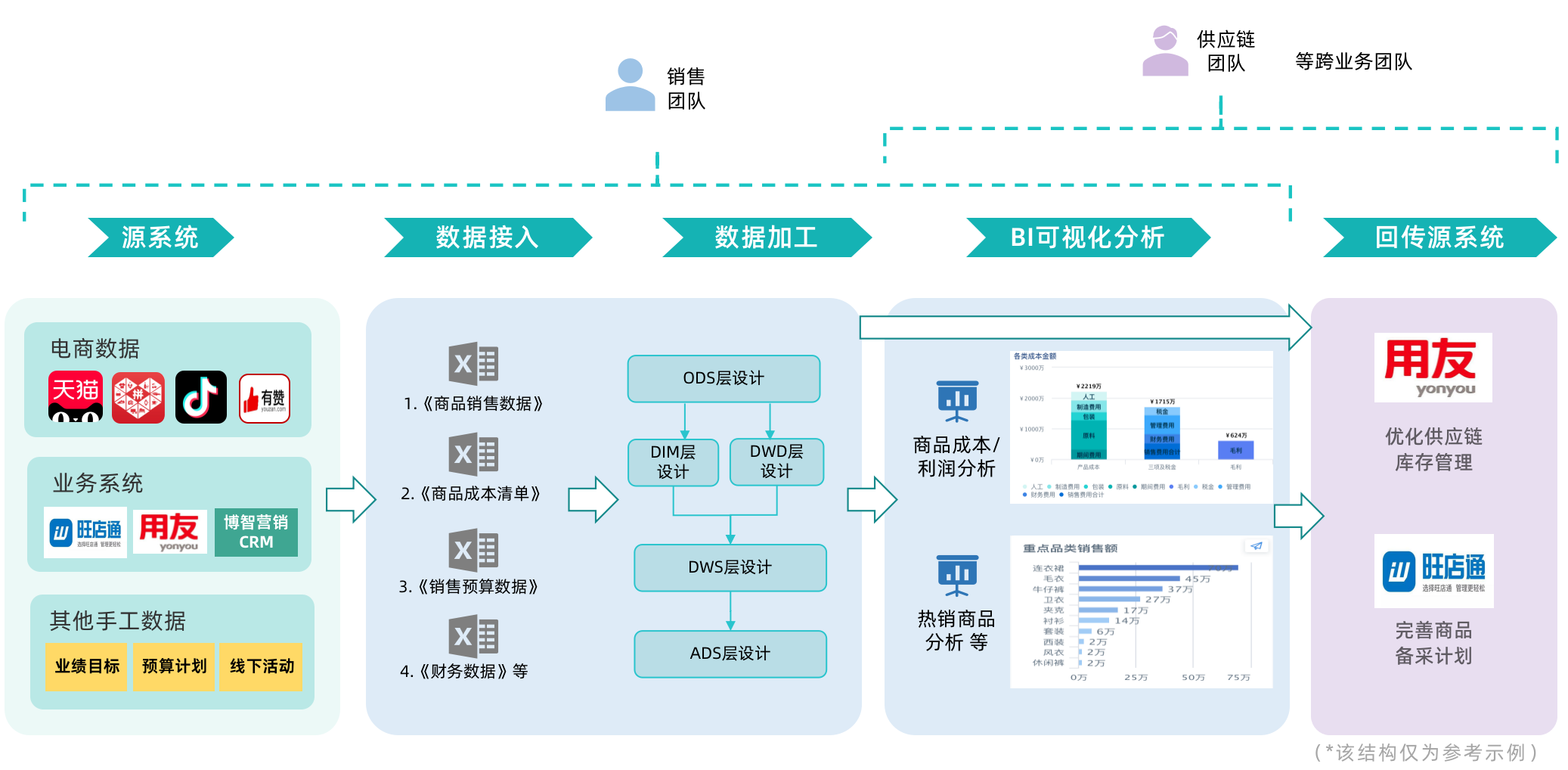
2.3 Enterprise Data Warehouse - Data Service Scenarios
In enterprise-level data warehouse architectures, there are strict data usage regulations, and BI data cannot be directly accessed by other business systems. Data writeback allows BI analysis results to be sent back to the unified data warehouse, which can then feed other business applications.
3. Product Value
Lower Ownership Cost:
In the past, many enterprises used standalone product applications to complete data synchronization tasks. While these applications could meet data sync needs, they required the purchase of expensive software services and high-performance servers, increasing procurement costs and deployment burdens. Now, with data writeback integrated into the Guanyuan BI platform, users only need to purchase the corresponding module and upgrade to 2GB of memory to achieve low-cost data synchronization.
Lower Development and O&M Threshold:
Besides standalone applications, some enterprises use API integration for data sync, but this approach has high development and maintenance barriers. API integration requires developers to write custom interface code and maintain complex documentation, increasing the difficulty and cost of data sync and adding to labor expenses. The data writeback feature provided by Guanyuan BI allows users to easily complete data sync configuration online, and later centrally manage writeback tasks in the data center. Even business users without coding skills can develop and maintain data sync tasks, greatly reducing the development and O&M threshold, improving efficiency, and saving labor costs for enterprises.
Larger Data Transfer Scale:
Traditional API solutions often limit the number of records per transfer for security reasons, posing challenges for users with large data transfer needs. The Guanyuan BI writeback module supports data transfer scales starting from 200 million records, meeting urgent needs for large-scale data sync and significantly improving overall efficiency and security.
4. Instructions
4.1 Task Creation
Entry Point
Data Preparation > Data Writeback > New Data Writeback
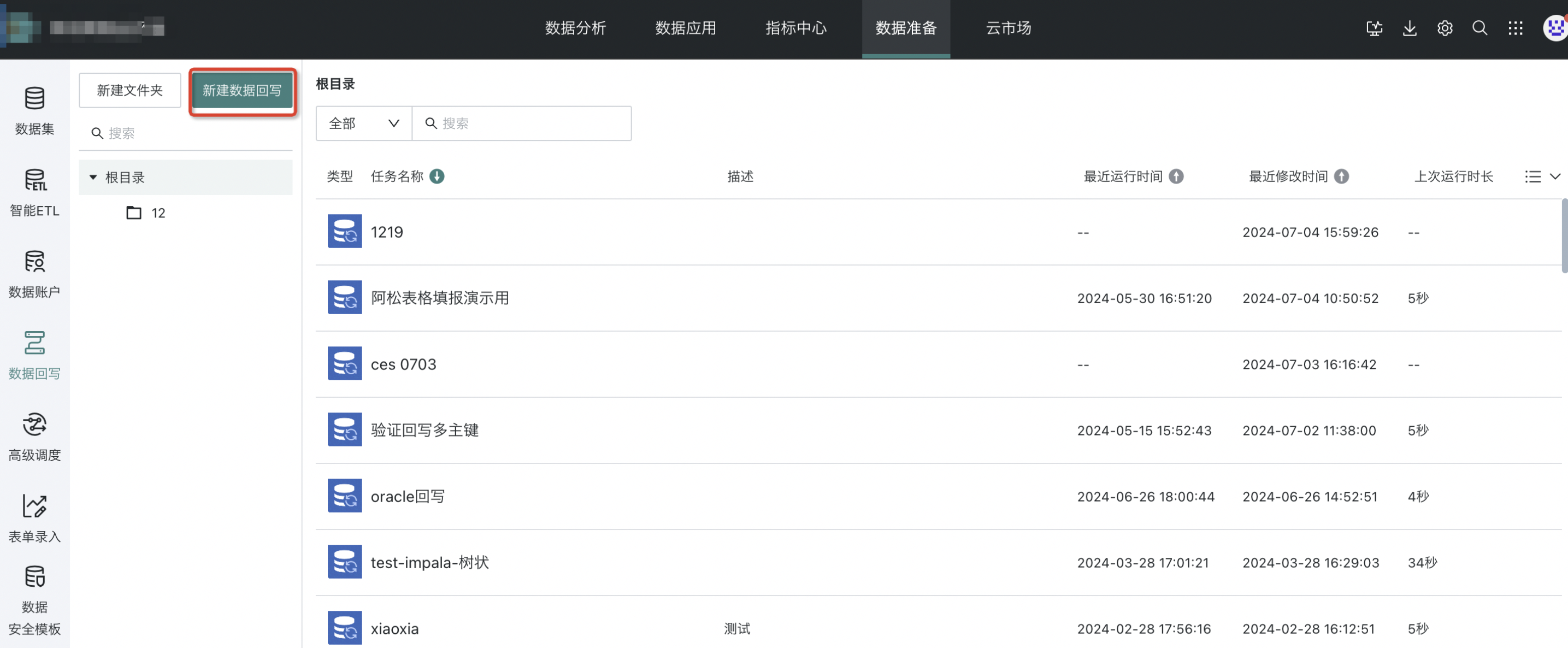
Task Editing
- Fill in basic information: customize the writeback task name (required) and description (optional).
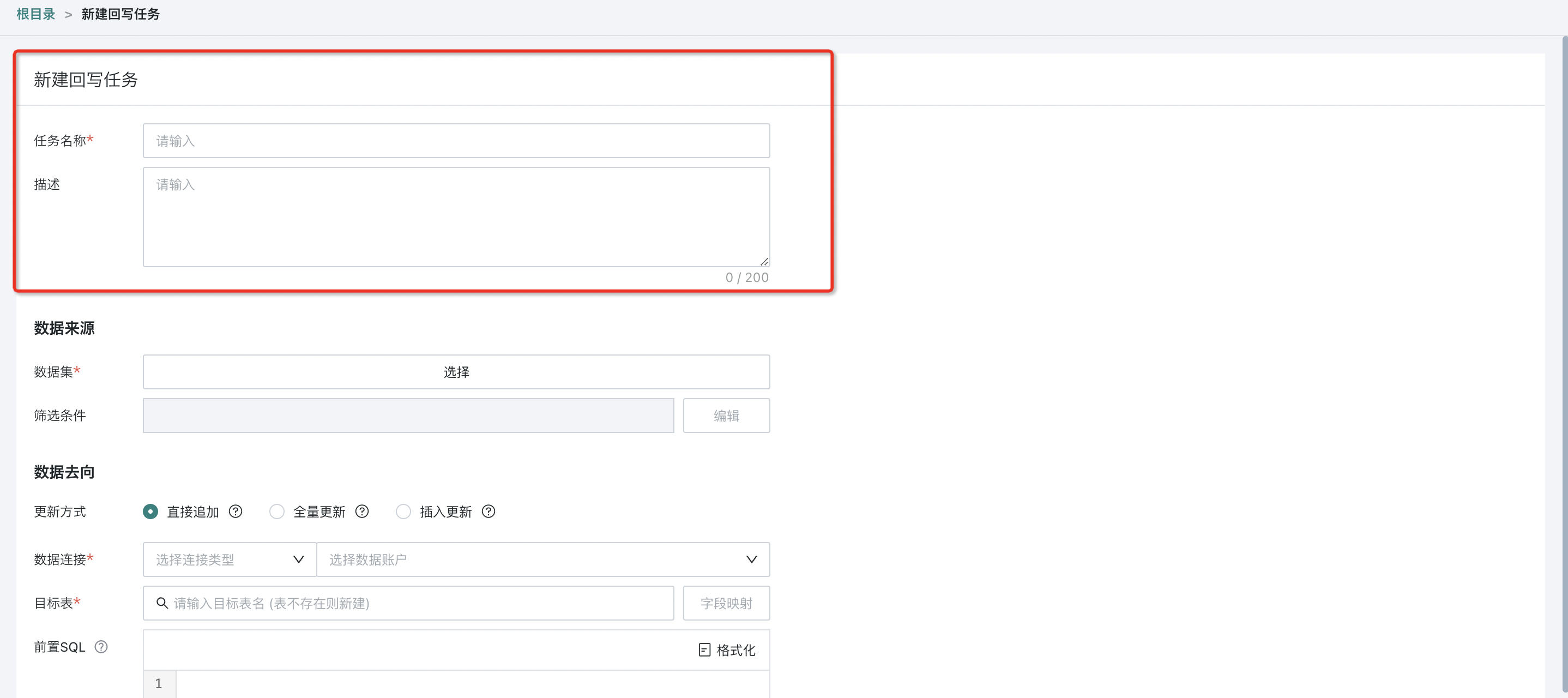
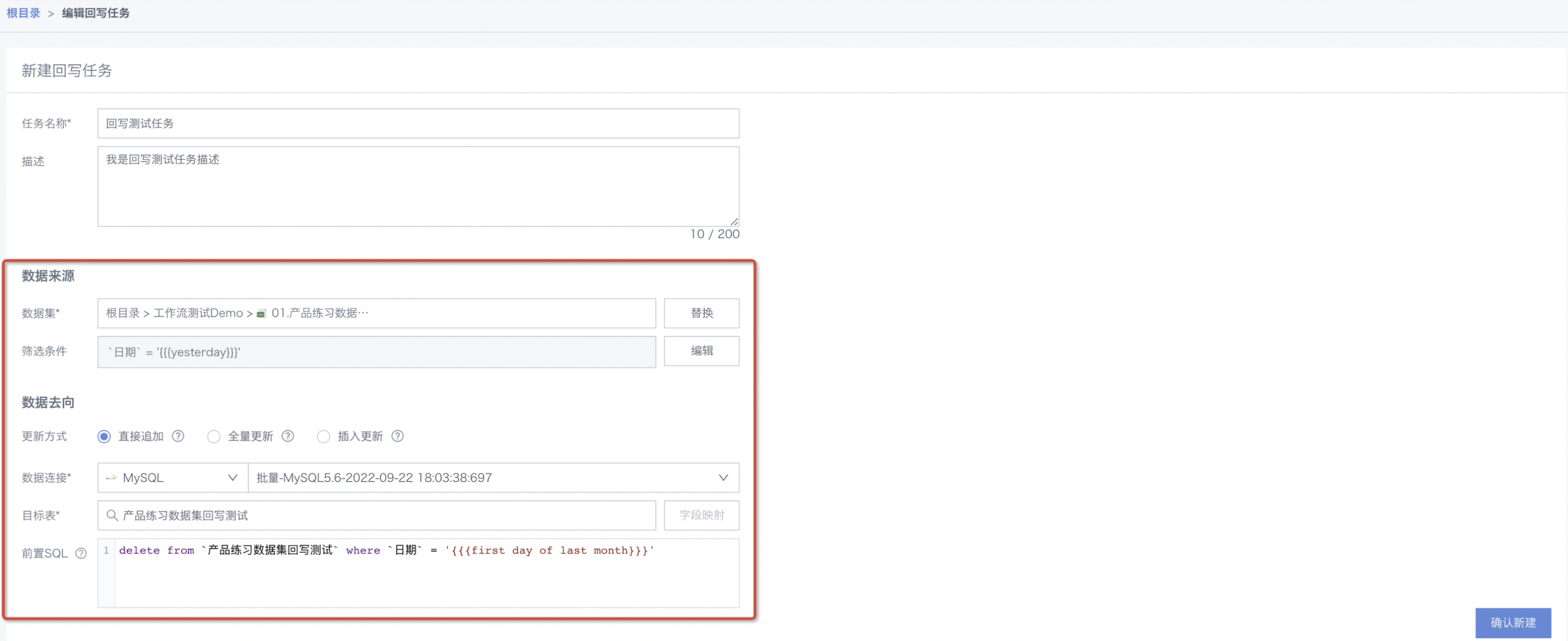
- Configure data source: select the data source to be written to the business system or data warehouse, and set filter conditions.
-
Dataset: includes ETL result sets, card datasets, reporting datasets, etc., within the current user's permission scope for writeback scenarios.
-
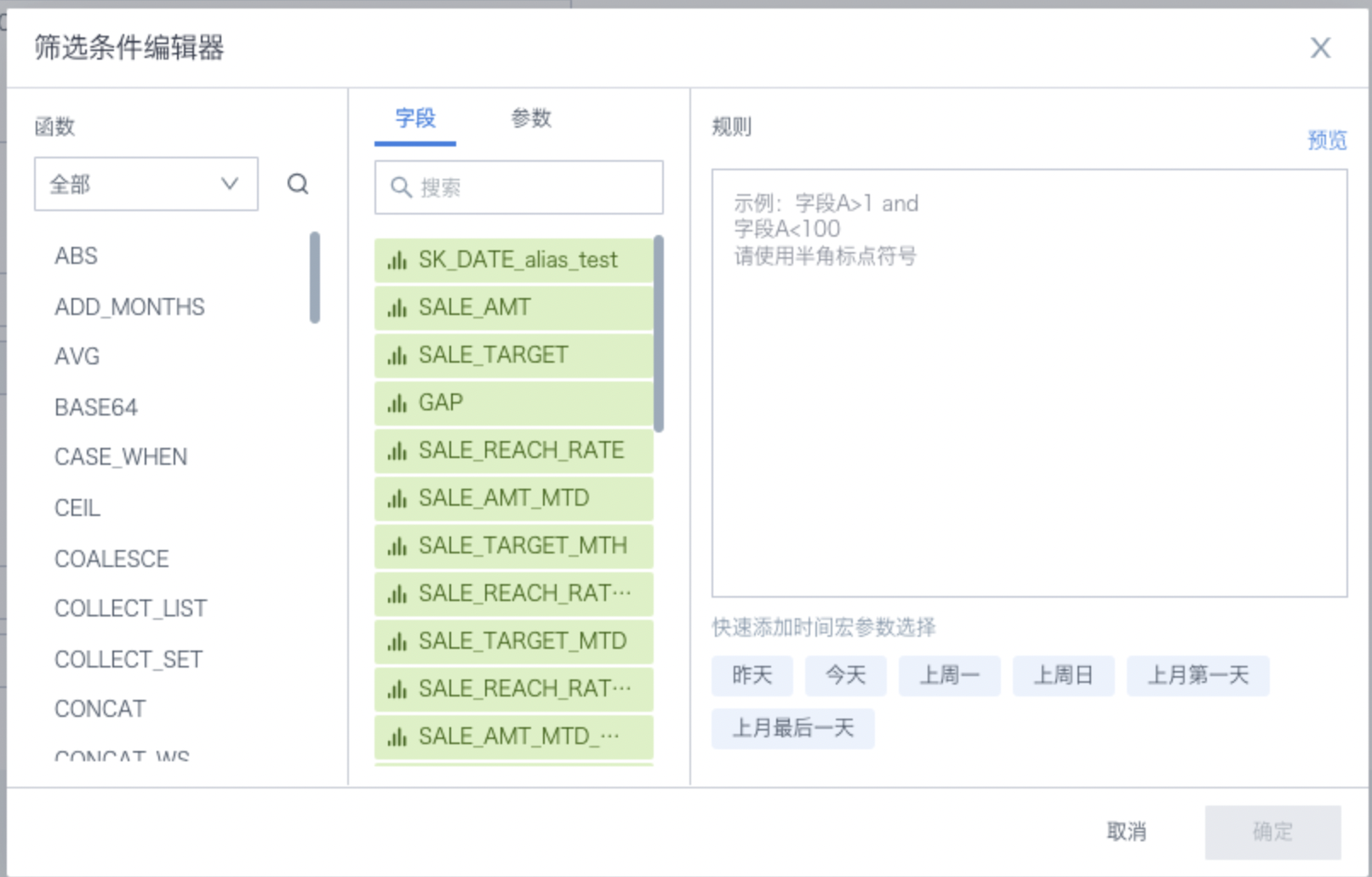
Filter conditions: support using time macros and global parameters to define filter conditions for the source dataset. For example, a periodic writeback task can use a time macro to filter the previous day's incremental data for writeback. The logic for configuring filter conditions is basically the same as for chart drawing. See the [Chart Drawing](../../6-Data%20Analysis%20and%20Visualization%2F1-Build%20Dashboard%2F0-Basic%20Card%20Creation%2F0-Visualization%20Chart%2F3-Chart%20Configuration%2F1-Fields%20and%20Drawing%2F0-Chart%20Drawing.md#41-Data Filtering) section for details.
- Configure data destination: specify the target object to write to, usually a business system or data warehouse (must specify the database and table).
-
Update methods
- Append: keep existing data in the target table and write new data.
- Full update: clear historical data in the target table before writing new data.
- Upsert: according to the comparison field, if a match is found in the target table, update the data; otherwise, append new data.
-
Data connection + target table
- Currently supported target databases: MySQL, Oracle, SQLServer, Hive, Maxcompute, ClickHouse, PostgreSQL, Greenplum, Gbase, GaussDB, Impala, TiDB, StarRocks.
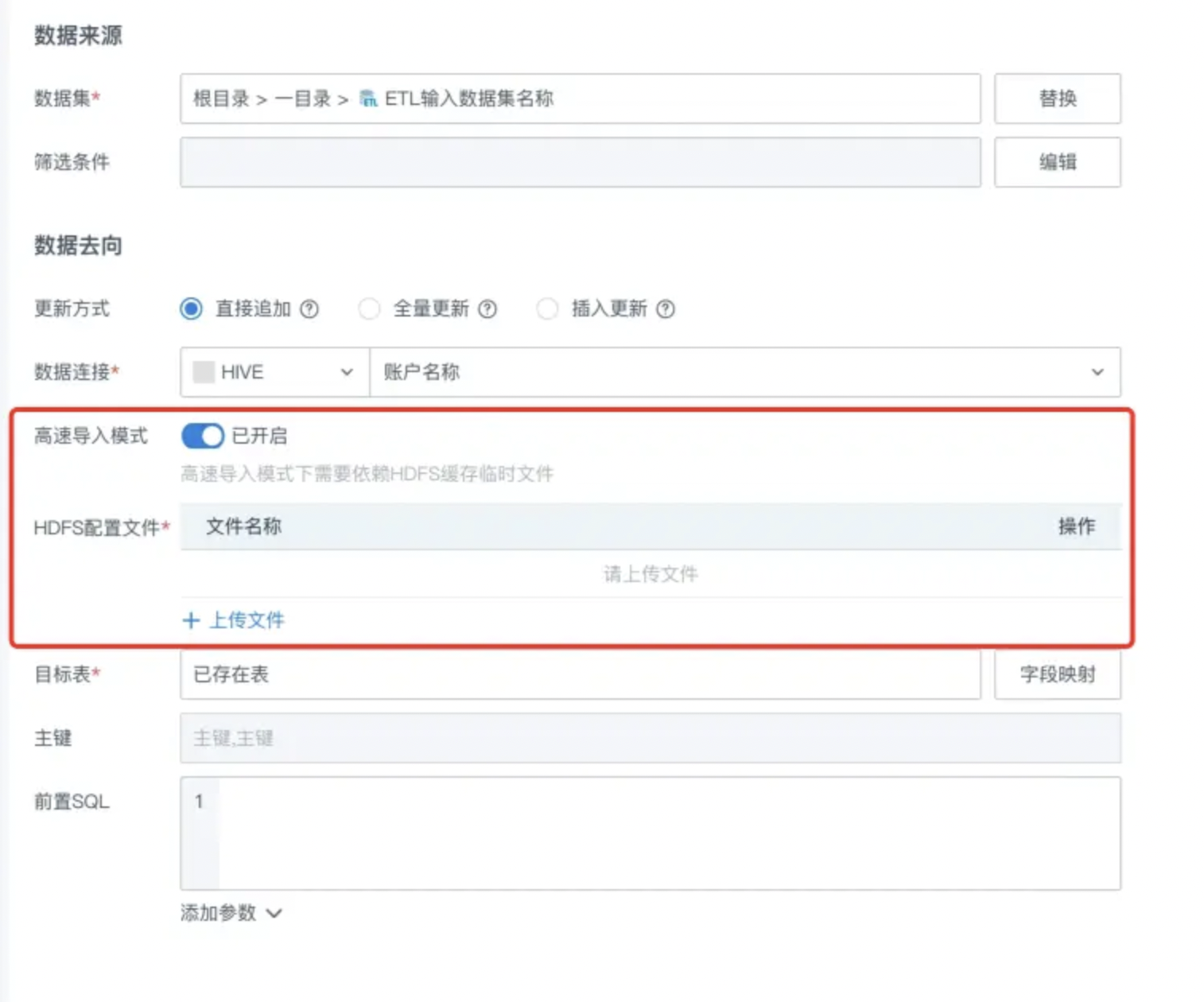
For Hive as the target, file-based high-speed import mode is supported. When creating or editing a writeback task and selecting a HIVE connection, you can enable "High-Speed Import Mode". After enabling, you need to upload the core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml configuration files required for HDFS connection for temporary file caching to HDFS.
-
The target table supports selecting an existing table or creating a new one. The new table structure will match the structure of the dataset to be written back.
-
Field mapping: for existing target tables, you need to set the field mapping between the dataset and the target table. Fields in the target table without a mapping will be written as null.
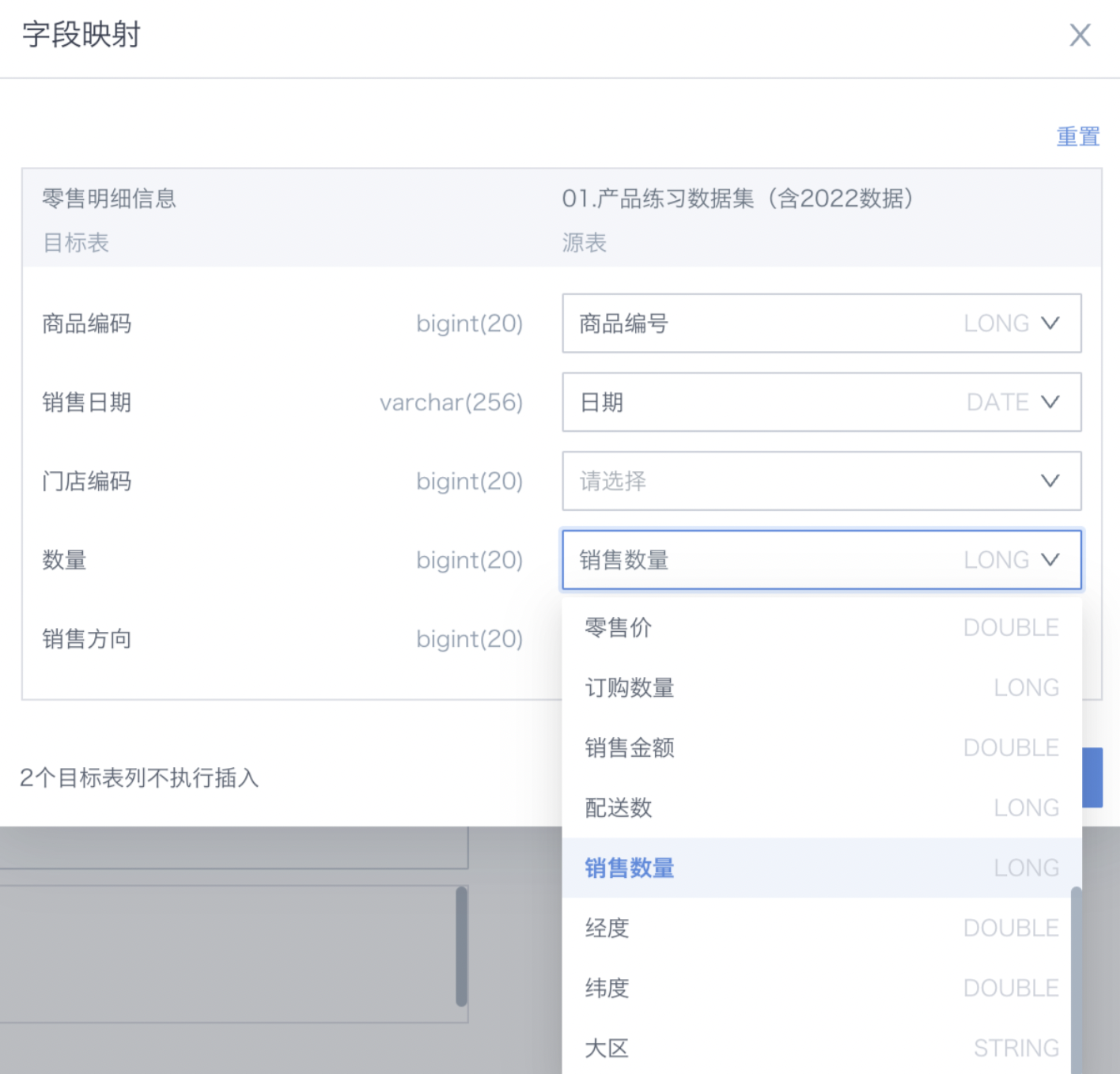
-
Pre-SQL: execute pre-SQL before writing data to the target table, such as deleting historical data.
-
Supports quick addition and use of global parameters & time macros for dynamic data deletion.
-
Typical scenario: only keep the last 30 days of data in the target table. Before each write, delete data older than 30 days: DELETE FROM table_name WHERE "date" <= "{{{today-30days}}}";
-
Usage restriction: only DELETE and TRUNCATE statements are supported for the target table.
-
4.2 Scheduling Strategy Configuration
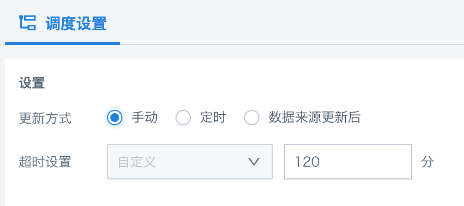
After creating the writeback task, go to the task details page and configure the execution strategy via "Scheduling Configuration", including manual, scheduled, and data source update triggers.
-
Manual: non-automatic scheduling, triggered by user action.
-
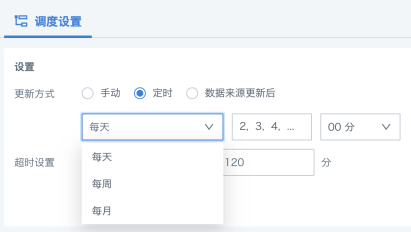
Scheduled: configure daily/weekly/monthly schedules, and the system will automatically run the writeback task at the specified time.
After the data source is updated, the writeback task will automatically run when the upstream dataset is updated.
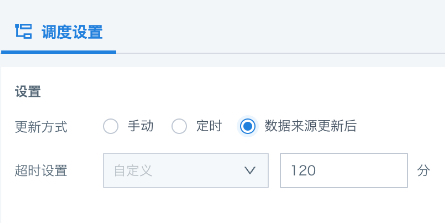
Timeout settings are also supported to prevent abnormal resource occupation. The default is 120 minutes (configurable range: 1~300 minutes).
4.3 Task Management and O&M
Supports management of data writeback tasks, including viewing run records, modifying task configuration, transferring ownership, granting access, and more.
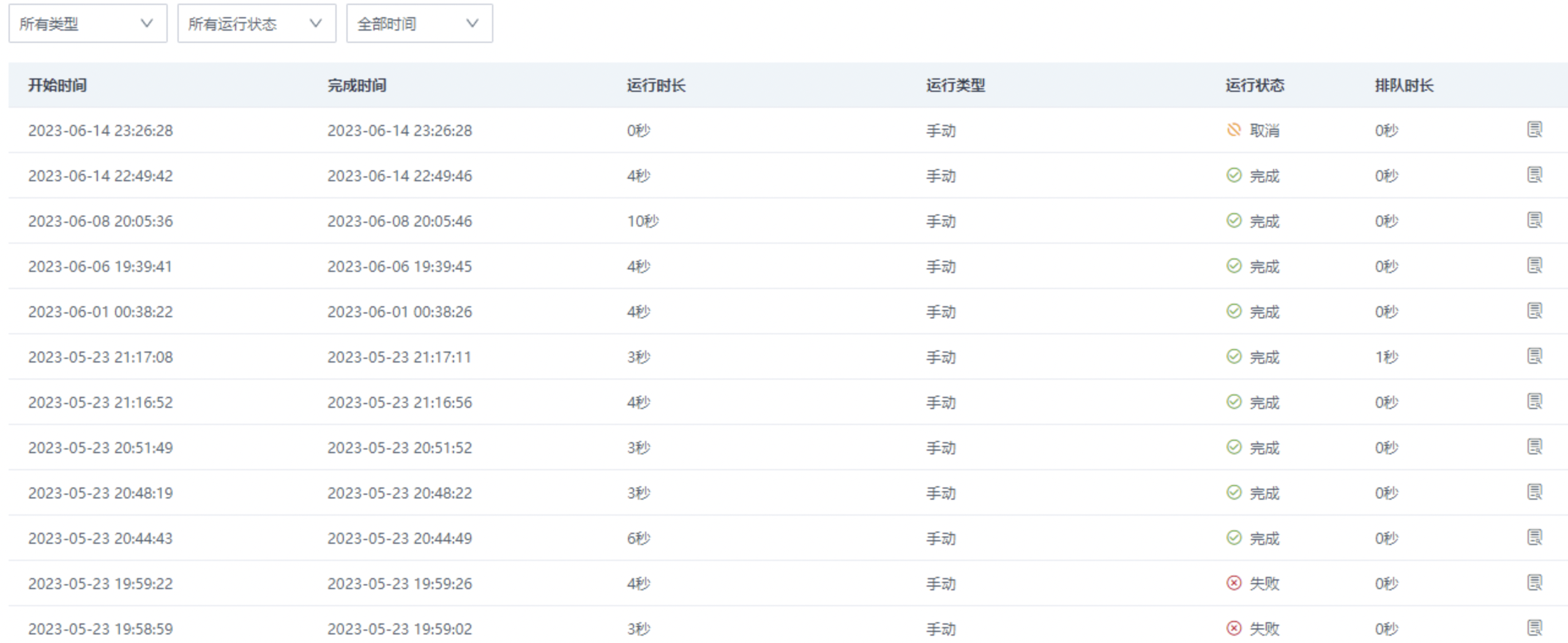
- View run records: provides the current status and historical execution of the data writeback task.
-
Task statuses include: completed, failed, canceled (canceled means the task was manually stopped by the user during execution).
-
Each run is traceable, including run duration, scheduling type, queue time, and run logs (OKLlog). Run logs can be viewed online or downloaded for analysis.
-
Transfer ownership: transfer the writeback task as a resource entity to another user. Note: transfer to user groups or read-only users is not allowed.
-
Grant access: assign control of the writeback task to users or user groups. Note: if assigned to a read-only user, they can only view the task (read-only permission).
-
Delete writeback task: deletion is irreversible and cannot be undone.
-
Modify task configuration: supports re-editing the configuration window for "Create Writeback Task". Note: if you change any configuration in "Data Source" or "Data Destination", please recheck the field mapping in the target table to avoid potential data write errors.