How to Use View Datasets and Case Sharing
A view dataset is a dynamic dataset based on Spark SQL that supports parameterized execution. It allows dynamic association and calculation of non-direct connection datasets, providing more flexible data analysis and solving complex ad-hoc analysis scenarios. A typical application is retail PSD calculation.
Function
A view dataset adds a calculation layer between cards and datasets, similar to a subquery. The view dataset first calculates an intermediate result from the source dataset(s) according to its definition, then provides it for card display. Specific functions include:
- Add global parameters in the view dataset to perform dynamic calculations under different filter conditions based on parameter values.
- Through a view dataset, the same source dataset can be aggregated at different granularities, allowing one source dataset to be used as multiple source tables.
- Multiple source datasets can be joined in a view dataset, enabling multi-table fusion without occupying storage space.
Applicable Scenarios
Dynamic filtering: member tags, sales ranking
Multi-table fusion: store coverage rate, out-of-stock rate
Date completion (zipper table): sell-through rate, activation rate, digestion rate
Prerequisites
- This is a free built-in feature, disabled by default. Contact Guandata support to enable it.
- Use Spark SQL syntax to query non-direct connection datasets. Users need to be familiar with basic Spark SQL usage.
Usage Steps
- Go to the dataset page in the Data Center, click "New Dataset" in the upper right, and select "View Dataset".
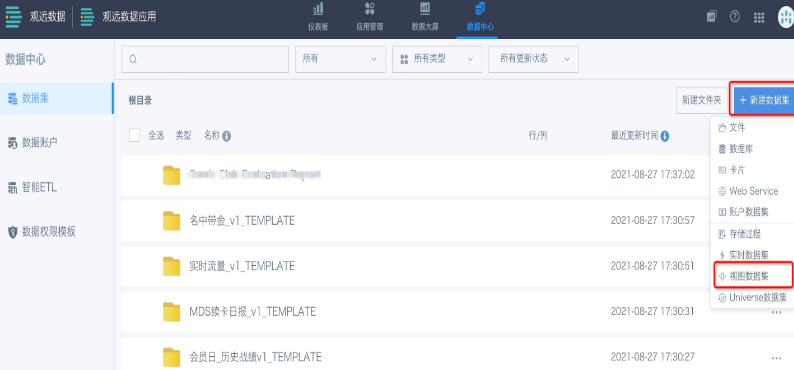
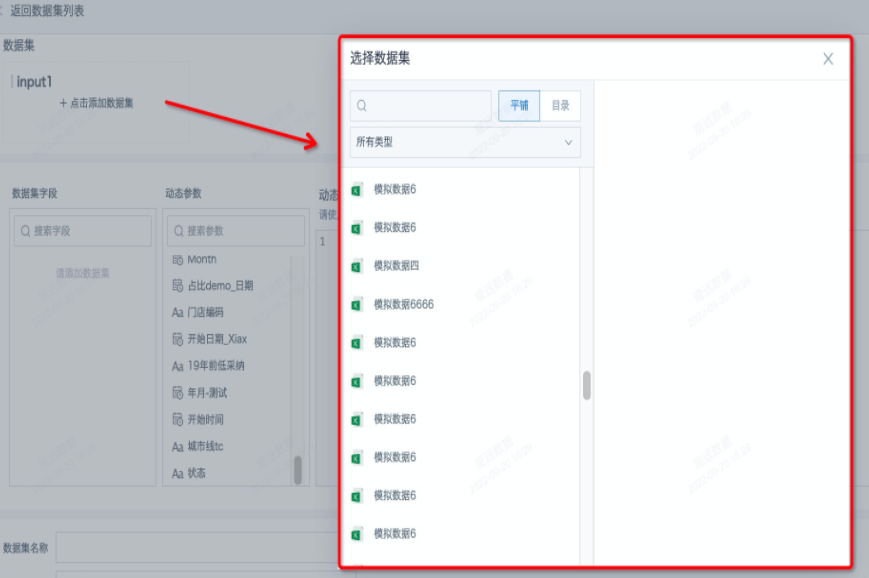
- In the dataset details page, click to add one or more non-direct connection datasets (no more than 2 is recommended).
- Enter dynamic query SQL. You can select "dataset fields" and "dynamic parameters" from the left to complete the SQL and preview. Dynamic parameters are global parameters, which must be added in admin settings in advance.
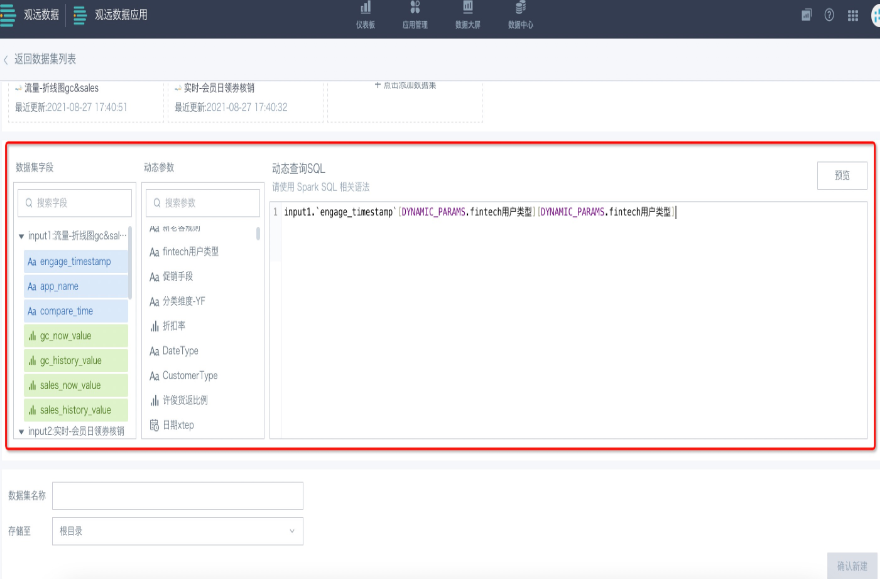
- Specify the dataset name and save location. Click "Confirm New" to create the dataset. You can find it in the corresponding folder.
Notes
View datasets and frontend cards are both based on Guandata's built-in calculation engine. The time required for the same calculation is the same. The following tips help ensure view dataset performance:
- Smart ETL provides convenient backend calculation, so view datasets should only be used for necessary calculations.
- Frontend filters are applied after the view dataset calculation. If this is not required, try to push filtering into the view dataset using parameters.
Case
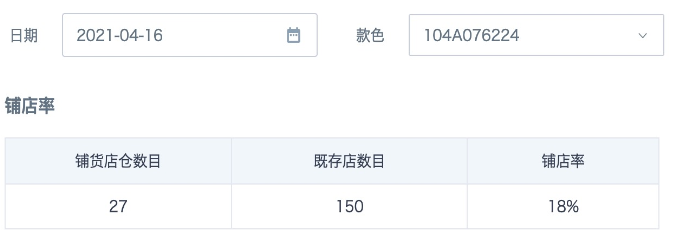
Case 1: Calculate Store Coverage Rate for a Style in the Selected Month by Filtering Date and Style
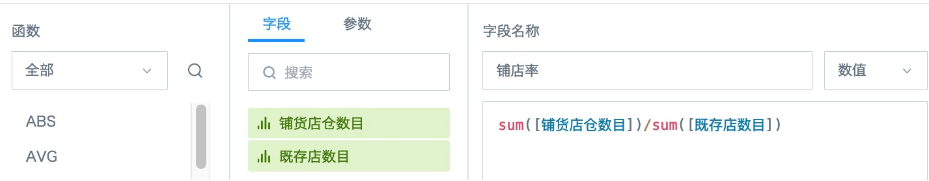
Store Coverage Rate = Number of Stores Stocked / Number of Existing Stores
Scenario Analysis
The number of stores stocked comes from the purchase and retail tables, while the number of existing stores is calculated from the store-warehouse dimension table.
Without a view dataset, you would left join the store-warehouse dimension table with the purchase and retail tables, causing data explosion. Using a view dataset to merge multiple sources is a better data organization.
Implementation:
- Create a view dataset with the following model structure.
This scenario uses a Common Table Expression (CTE) to define a temporary result set t, which stores the number of existing stores for the selected month. The SQL then references this result set. The number of existing stores is only affected by the date filter, while the number of stores stocked is affected by both date and style filters.
with t as (SELECT count(DISTINCT input2.`Storehouse ID`) AS `Number of Existing Stores`
FROM input2
where (input2.`Opening Date` LAST_DAY([DYNAMIC_PARAMS.Date]))))
SELECT a.`Number of Stores Stocked`,t.`Number of Existing Stores`
from
(SELECT
COUNT( DISTINCT case when ifnull(input1.`Cumulative Purchase Qty`,0)+ifnull(input1.`Cumulative Retail Qty`,0) > 5 then input1.`Storehouse ID` else null end) as `Number of Stores Stocked`
from
input1
where input1.`Style` = [DYNAMIC_PARAMS.SKC&SKU] AND input1.`Month End Date` = LAST_DAY([DYNAMIC_PARAMS.Date])) as a,
t
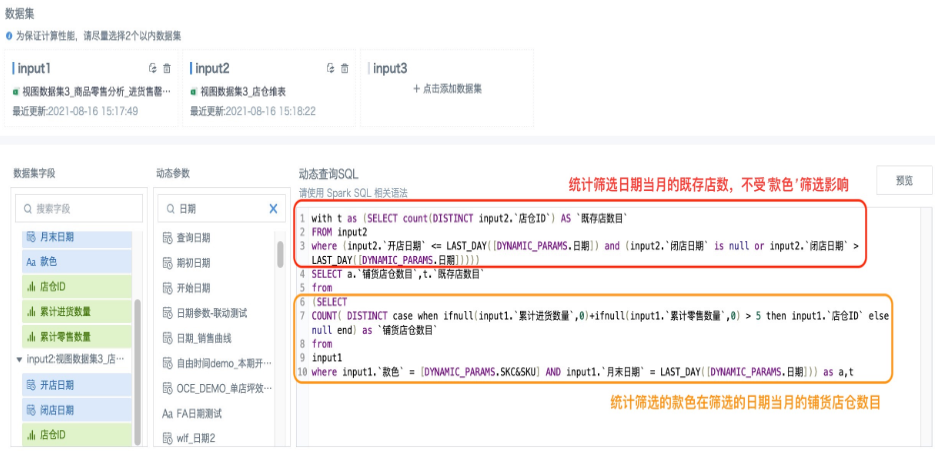
- Create a card, add a calculated field "Store Coverage Rate", drag it into the value bar, and save the card. If there is no data in the preview, temporarily enter valid parameter values on the right to ensure data is available for preview.
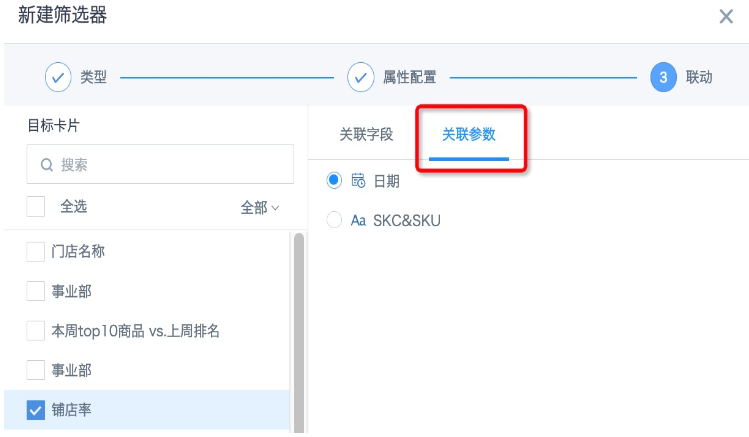
- On the page, create a parameter filter, select the date parameter used in the view dataset, and save to automatically link the card. Or create a date filter, link the dataset's date parameter. Similarly, create a parameter filter or selection filter for "Style" and link it.
- The final effect is as follows: