Recent 7-Day Average Daily Active Users Calculation Implementation
Scenario Introduction: Calculate the average active users (Daily Active User) within 7 days of the selected date.
Solution Approach: Calculating 7-day average DAU involves two layers of aggregation calculations. First, you need to deduplicate and calculate the number of visiting users for each day, then average these seven numbers.
Implementation Methods:
A. ETL: In cases where the logic is fixed, such as aggregating data to "day" granularity without considering other factors, it's recommended to use group aggregation in ETL to get the average daily active users, then calculate the recent 7-day average daily active users in ETL or cards. Disadvantages: Not flexible, once more dimension filters need to be added, ETL needs frequent modifications, and it's easy to affect other cards that depend on the same dataset.
B. Cards/View Datasets: Suitable for scenarios that require flexible and changeable filter dimensions, requiring report creators to be familiar with SQL functions. Disadvantages: When data calculation volume is large, card loading will become slow.
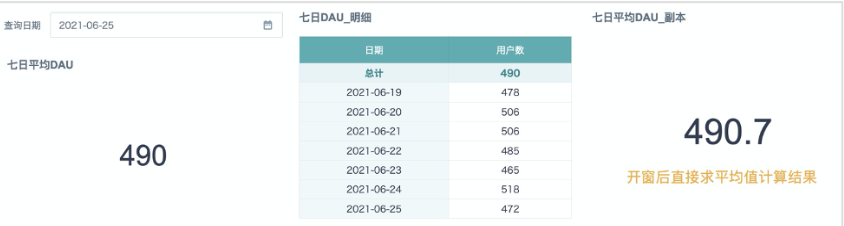
Expected Effect: Select a date, one metric card directly displays the 7-day average DAU, another table displays the daily active users for each of the 7 days and the 7-day average DAU. This article's case study performs calculations directly in cards, the effect is shown in the figure below.
I. Detail Card Implementation Steps
1. Create a new card, put the date field in the dimension column. If the "User ID" field used for deduplication counting is numeric type, directly drag it to the value column, aggregation method select "Distinct Count"; if the "User ID" field is text type, after dragging to the value column, you cannot set subtotals/totals, at this time you need to create a numeric type field "User Count": count(distinct[**User ID]), drag to the value column to get the deduplicated user count for each day.
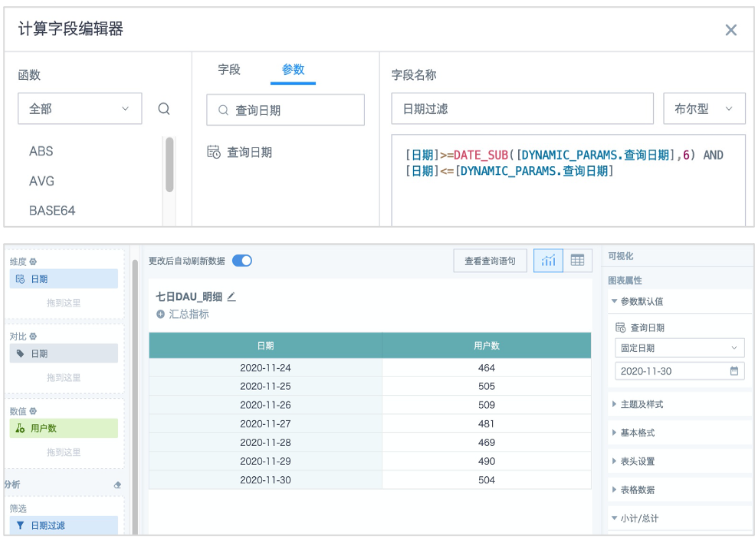
2. Create a second field "Date Filter", type is boolean, reference a date-type global parameter from the parameter list, finally drag this field to the filter column (default select TRUE, no need to modify), extract dates including the parameter date and the previous 6 days, a total of 7 days.
Formula:*[**Date]>=DATE_SUB([DYNAMIC_PARAMS.**Query Date],6) AND [**Date]<=[DYNAMIC_PARAMS.*Query Date]
Note: If the table displays no data, you can temporarily modify the "Parameter Default Values" on the right to ensure there is data display, while verifying data accuracy.
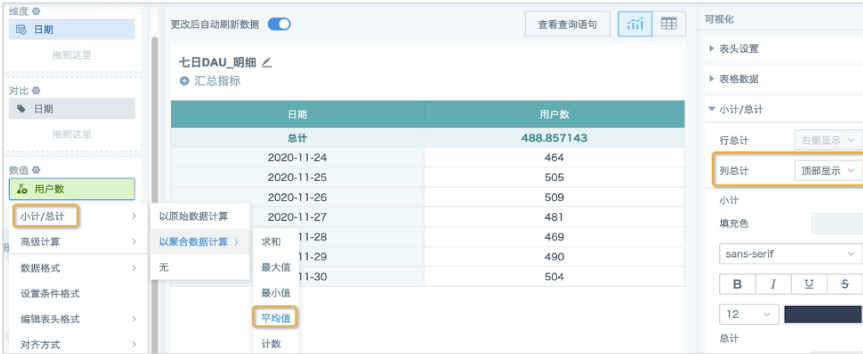
3. Find "Visualization" - "Subtotals/Totals" on the right, set the display position of column totals, then click the "User Count" field in the value column, set the subtotal/total calculation method to: Calculate with aggregated data - Average. At this time, the "Total" row displays the 7-day average active users.
4. Return to the page, create a new date filter, and link it to the global parameter in the card.
II. Metric Card Implementation Steps
1. Reference the boolean field "Date Filter" in the detail table, create a field with the same name in the metric card, drag this field to the filter column (default select TRUE, no need to modify), extract dates including the parameter date and the previous 6 days, a total of 7 days.
Formula:*[****Date]>=DATE_SUB([DYNAMIC_PARAMS.**Query Date],6) AND [**Date]<=[DYNAMIC_PARAMS.*Query Date]
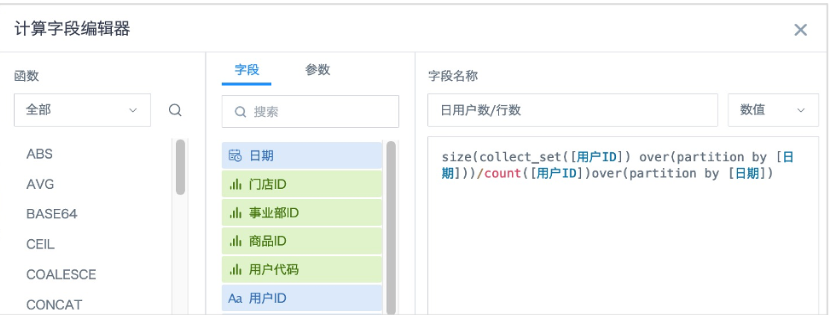
2. Create a new numeric field "Daily User Count/Row Count".
Formula:size(collect_set([User ID]) over(partition by [Date]))/count([User ID])over(partition by [Date])
Logic: First use window function to calculate the deduplicated user count for each day. Since window functions don't reduce the number of rows in the original table, you need to divide by the number of rows for each day's data to distribute the daily deduplicated user count to each row, so that the next step calculation can be performed correctly.
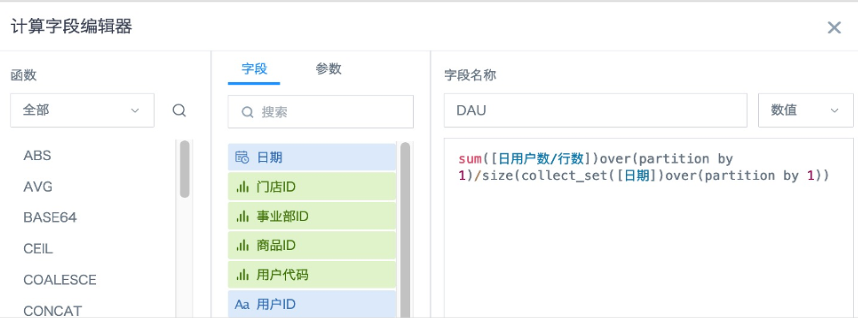
3. Create a new numeric field "DAU" again, drag to the value column, aggregation method select "No Processing", save the card.
Formula:sum([Daily User Count/Row Count])over(partition by 1)/7
Logic: Sum the "Daily User Count/Row Count" obtained in the previous step to get the total of daily active users for each day in the date range, then divide by the number of days to get the average active users within 7 days. If there might be non-consecutive dates, not enough 7 days, and you only need to calculate the average of valid days, the formula can use sum([Daily User Count/Row Count])over(partition by 1)/size(collect_set([Date])over(partition by 1)).
4. Return to the page, create a new date filter, and link it to the global parameter in the card. After filtering the date, the calculation results of the metric card and table card are consistent. You can also add other filters according to requirements.
Q&A:
Q: In the metric card, why not use size(collect_set([User ID]) over(partition by [Date]))* to calculate the daily active users, then use the aggregation method "Average" directly?
A: The built-in aggregation method "Average" in cards has the calculation logic of adding each row of data, then dividing by the number of rows in the original table. Even if 7 days are filtered in the card, it doesn't mean the number of data rows has been aggregated into 7 rows. Using size(collect_set([User ID]) over(partition by [Date]))* to calculate the average directly is equivalent to (Day1a+Day2b+…+Day7g)/(a+b+c+d+e+f+g), the average calculated by this logic is inaccurate. The calculation logic in the article above is (Day1/aa+Day2/bb+…+Day7/gg)/7, first shrink the data then accumulate and expand, equivalent to adding daily active users then dividing by the number of days. The comparison of calculation results using the two methods is shown in the figure below.