System Performance Boundary Parameter Configuration
I. Origin of System Performance Boundaries
The product system boundaries are mainly designed to find the limits that can identify Guandata system's processing capabilities under certain computing resource conditions. These boundary parameters are exposed in the product to facilitate administrator control, and we will also recommend reasonable default configurations based on users' computing resources.
Common abnormal scenarios that can be resolved:
-
During BI usage, the system suddenly becomes unavailable, reporting errors 502 or 504, and users cannot log in;
-
Card pages load slowly with many socket hang up errors, and checking the task management interface reveals a large number of queued tasks;
-
Dataset updates run for several hours, cannot extract data but also don't fail, preventing other datasets from updating;
-
Large data volume card editing loads very slowly.
II. Operation Entry
Administrator Settings - System Settings - General Settings - Runtime Parameters (Different BI versions may have different parameter configurations. If you find that the above parameters are not available but needed, please contact Guandata for version upgrade~)
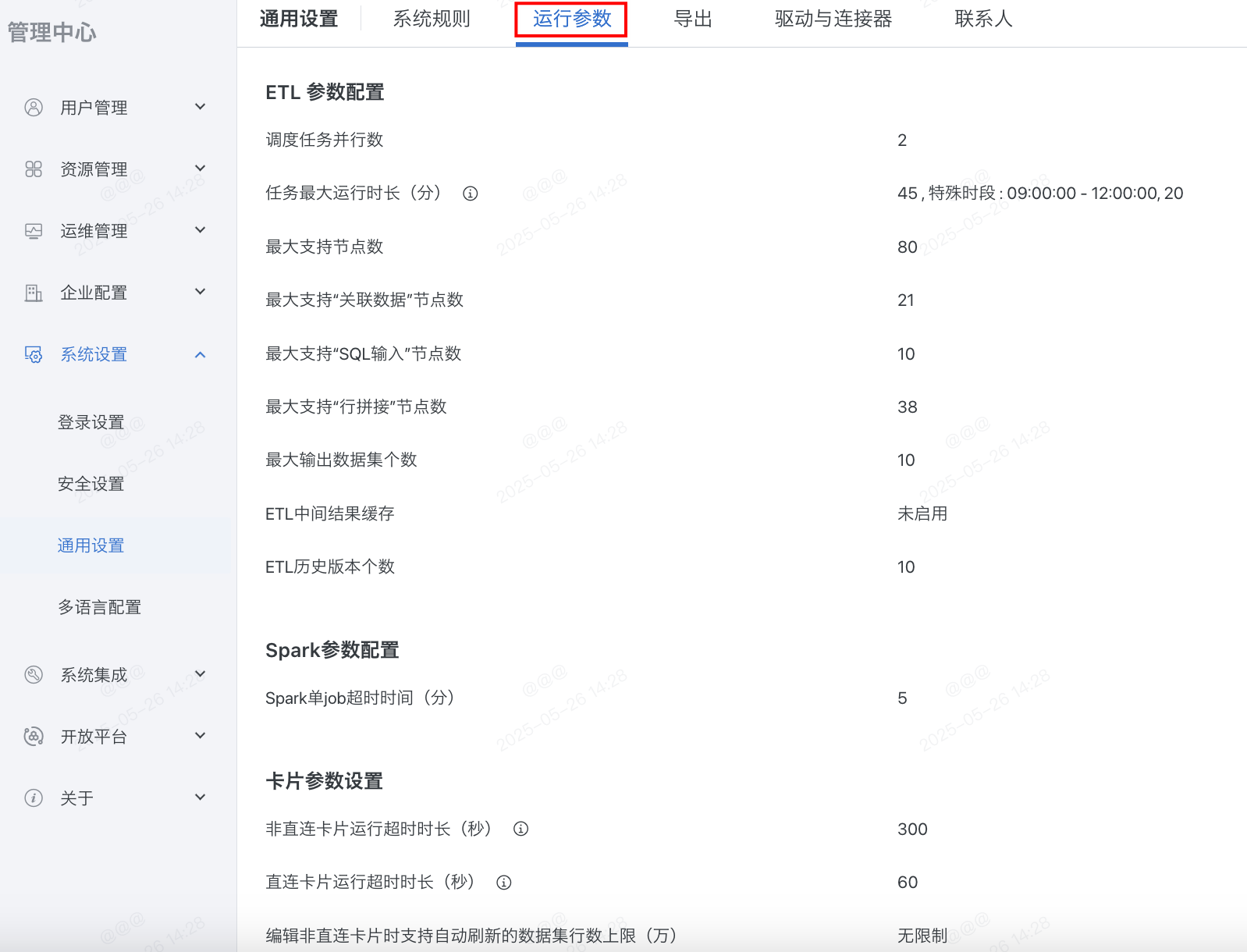
III. Specific Parameter Configuration and Explanation
1. ETL Parameter Configuration
① ETL scheduled task parallelism: Parallelism of ETL tasks triggered by scheduled and cascading (after selected dataset updates) updates, range 1~20. Note: Only configurable in single-domain environment, multi-domain environment has no such configuration;
② Maximum task runtime (minutes): Maximum runtime of individual ETL tasks, tasks will be interrupted after exceeding, range 5~120 minutes. Version 4.7.0 and later support special time period settings;

③ Maximum supported nodes: Cannot drag in new operator nodes after reaching threshold, range 10~200;
④ Maximum supported "Associate Data" nodes: Cannot drag in new "Associate Data" nodes after reaching threshold, range 1~50;
⑤ Maximum supported "SQL Input" nodes: Cannot drag in new "SQL Input" nodes after reaching threshold, range 1~50;
⑥ Maximum supported "Row Concatenation" nodes: Cannot drag in new "Associate Data" nodes after reaching threshold, range 1~50;
⑦ Maximum output dataset count: Cannot drag in new "Output Dataset" nodes after reaching threshold, range 1~20;
⑧ ETL intermediate result cache: When an ETL has multiple outputs, the system will cache the running result of one intermediate node to improve running efficiency. Default ETL complexity is 100, generally not recommended to modify the default value.
The above ③~⑦ do not apply to imported ETLs. The main factors determining ETL runtime resource consumption are: number of nodes, "Associate Data" nodes, "SQL Input" nodes, and output dataset count. In cases of large data volumes, adding one "Associate Data", "SQL Input", or output dataset will significantly increase or even double resource consumption. This way, if any of the server CPU, memory, or disk resource usage is too high (threshold generally 90%), it will cause system downtime or restart, causing all other queued or running tasks to fail or be cancelled, with great impact. Therefore, these parameters need to be adjusted according to your system usage conditions.
⑧ ETL intermediate result cache is a global setting, and Guandata BI also allows individual ETL settings for whether to enable this setting, path: ETL interface - Advanced Settings. Custom settings take precedence over global settings.
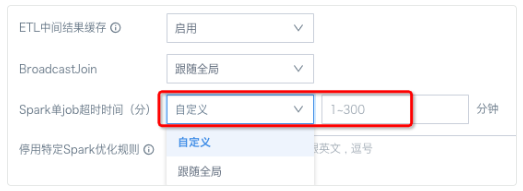
2. Spark Parameter Configuration
① Spark single job timeout (minutes): Maximum runtime of individual Spark jobs, tasks will be interrupted after exceeding, range 5~120 minutes.
Note: Spark jobs can be ETL or cards. An ETL run or card query may consist of multiple Spark jobs depending on different situations. Guandata BI allows custom settings for individual ETLs, with a definable range of 1-300 minutes, path: ETL interface - Advanced Settings.
3. Card Parameter Settings
① Non-direct connection card runtime timeout (seconds): Only applies to Guan-Index type cards, runtime does not include queuing time, will automatically fail after actual runtime timeout, range 1~600 seconds;
② Direct connection card runtime timeout (seconds): Same as above, applies to direct connection cards;
③ Maximum dataset row count limit for automatic refresh when editing non-direct connection cards (10K): After reaching threshold, card editing page cannot open automatic refresh, prompt as follows;
④ Maximum dataset row count limit for automatic refresh when editing direct connection cards (10K): After reaching threshold, card editing page cannot open automatic refresh, prompt as ③;
⑤ Card queuing timeout cancellation duration (seconds): After reaching threshold, card queuing tasks will be cancelled, range 1~600.
⑥ Maximum dimension values supported by mini charts: Cannot generate mini charts after reaching threshold (version 5.1), range 12~200;
4. Dataset Parameter Settings

① Do not actively update row count when updating direct connection datasets: In direct database connection cases, dataset row count can support not automatically updating after dataset updates, reducing unnecessary database queries, enable/disable.
② Database dataset updates support failure retry: Only supports automatic updates (including: scheduled updates, URL triggers) retry once after failure, does not support manual updates; retry time range is 5~15 minutes; default is off.
③ 1-hour dataset scheduled update count limit: Used to adjust the number of scheduled update dataset tasks and congestion level within time periods, making reasonable planning. Please refer to [Dataset: Support for Scheduled Update Task Density Chart](../../2-Product Release Notes/2-2023 Year/11-2023 January: 5.3.0 Important Feature Updates.md#12-数据集支持定时更新任务密度图) (version 5.3 feature)
④ View dataset preview timeout limit (seconds): Default value 60 seconds, will stop preview tasks after reaching threshold.
5. Database Parameter Settings

① Default maximum value for individual direct connection database connection pool: Maximum connection pool for individual databases, cannot connect after exceeding, range: 1~999; Setting this parameter can partially alleviate dataset update failures caused by full connection pools,
② Database connection timeout (Socket timeout) (minutes): Socket-timeout when connecting to database during data extraction. After setting this parameter, when extracting dataset updates, if still not connected to database after this time, dataset update tasks will be automatically cancelled. Can help alleviate long dataset update times and failure to extract data, preventing task accumulation.
6. Recycle Bin Parameter Settings
① Automatic cleanup cycle (days): Execute cleanup tasks daily at 23:59, page and card resource retention time in recycle bin ranges from 1~90 days.
7. Subscription Alert Parameter Settings
① Maximum number of distribution conditions supported by single subscription: Version 5.8 subscriptions support distribution, default each subscription supports up to 10 rules (maximum 100). By configuring distribution condition limits on subscription recipient visibility scope, data isolation can be achieved. Distribution conditions will be used as filter conditions, filtering data involving subscription sent URLs, images, attachments. For example, subscribing to sales data, South China sales only see South China sales data, North China only sees North China data.

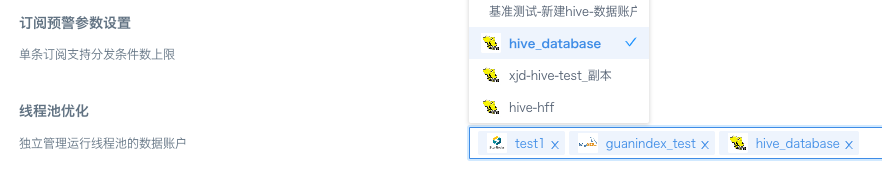
8. Thread Pool Optimization
① Data accounts with independently managed runtime thread pools: Enter search keywords to select target data accounts, supports up to 3 accounts with independently managed thread pools.
In scenarios with heavy use of direct connection datasets, problems often occur where excessive concurrent query requests cause user databases to be inaccessible, leading to unstable BI services. Since all data connections in BI currently use a unified thread pool, problems with one direct connection account can spread and affect query requests from other data accounts, causing overall BI service unavailability. Isolating key data accounts helps improve platform stability for customer groups with large direct connection concurrency.