Service Start-Stop Recommendation Manual
Background
During service usage, you may encounter situations such as server migration, computer room inspections, etc., which may require shutting down or restarting the server. In such cases, it is necessary to stop the service in advance. Although our program allows shutting down the server without stopping the service and supports automatic service activation after server startup, for standardized operations and to avoid data loss, it is still necessary to use standardized operations to shut down, start, and check services.
Shutting Down Services
-
Log into the server (all operations below are based on root privileges)
-
Shut down MySQL database (necessary operation, multi-node operations on corresponding nodes)
sudo docker stop guandata_db
- Shut down Cassandra database (necessary operation, multi-node operations on corresponding nodes)
sudo docker stop cassandra
- Shut down k8s service (non-necessary operation, each node needs to be operated)
sudo systemctl stop kubelet
- Shut down docker service (non-necessary operation, each node needs to be operated)
sudo systemctl disable docker
sudo systemctl stop docker
Note: For multi-node operations, it is recommended to start from the master node.
Starting Services
Normally services start automatically on boot. If service abnormalities are found after server restart, you can try the following commands:
- Restart docker service (each node can be operated):
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl restart docker
- Restart k8s service (each node can be operated):
sudo systemctl restart kubelet
- Restart cassandra database (multi-node operations on corresponding nodes)
sudo docker restart cassandra
- Restart mysql database (multi-node operations on corresponding nodes)
sudo docker restart guandata_db
Note: For multi-node operations, it is recommended to start from the master node.
Service Status Check
-
Directly open the Guandata login page to try if it can be opened normally for login.
-
After logging into the server (root privileges), run the kubectl get pods command to get the pods list as shown below
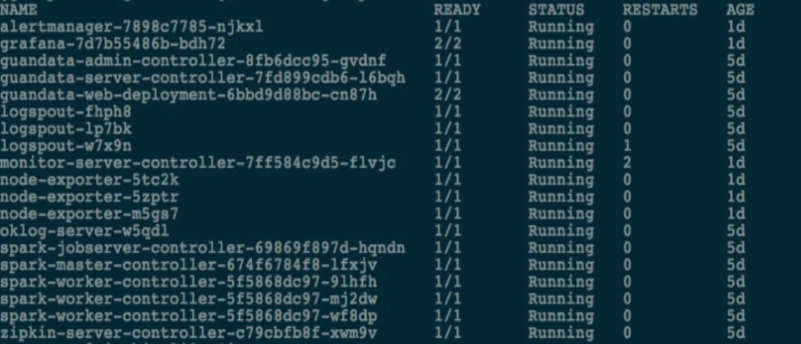
You can view the corresponding status of pods, Running is the normal running status.
If a pod is in abnormal status, you can execute the command: kubectl delete pod guandata-server-pod-name, delete the corresponding pod, the corresponding pod will be automatically recreated to restart after deletion.
When restarting a single pod still cannot restore the service, you can try restarting docker according to the operations in "Starting Services".
Note: If the above operations still cannot normally enable the service, please contact the corresponding Guandata personnel, and we will provide professional support.