Ordinary Table Column Total Calculation Logic
Function Introduction
In ordinary tables, subtotals/totals have 3 calculation methods:
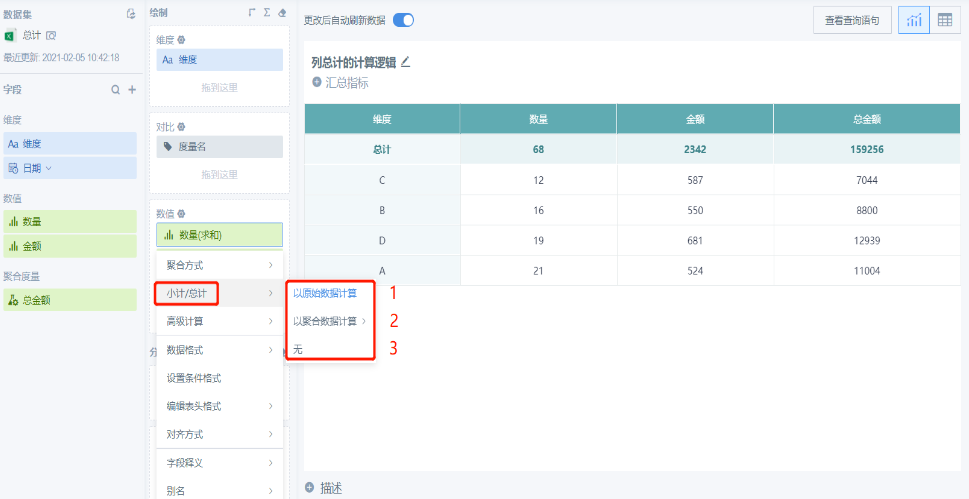
Method 1: Calculate based on original data. The total result of this method is generally the sum of each row's corresponding data (specific logic will be described below).
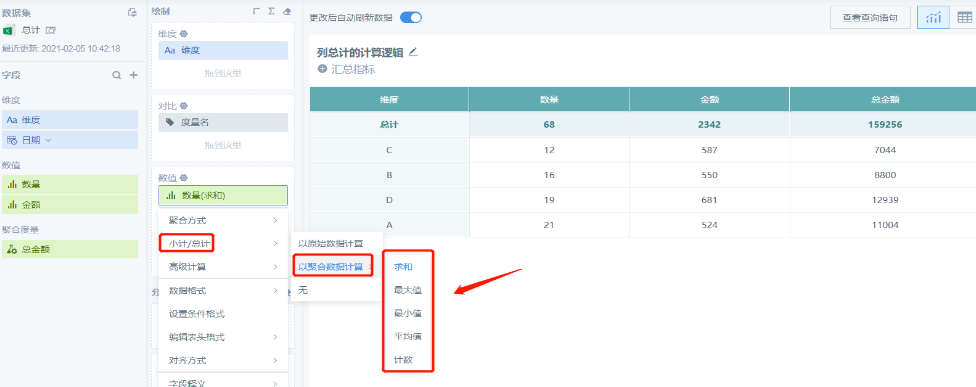
Method 2: Calculate based on aggregated data. This method can choose aggregation method later:
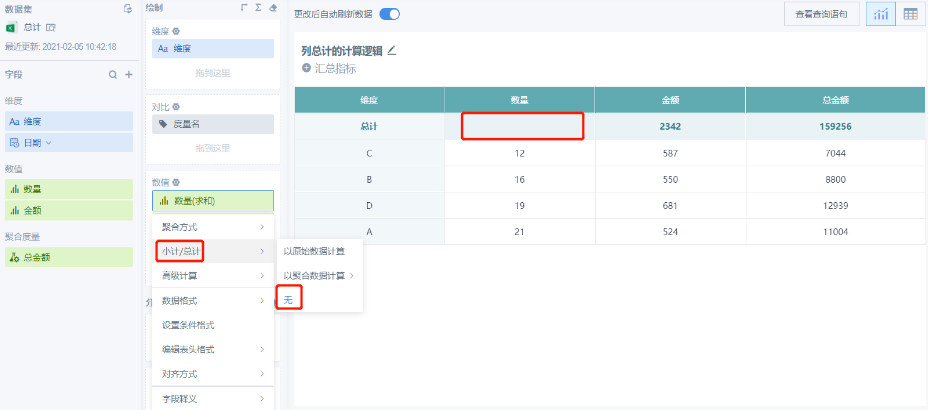
Method 3: None. That is, no subtotals or totals, the total here will display as empty:
Function Details
1. Calculation Logic When Field Structure is Different
When the field is original field or aggregated metric, the calculation logic difference:
Original field: When the field is an original field and the aggregation method is sum, the result of choosing to calculate based on original field or aggregated field (sum) is the same,
Aggregated metric: But if the field is an aggregated metric, these two settings have differences:
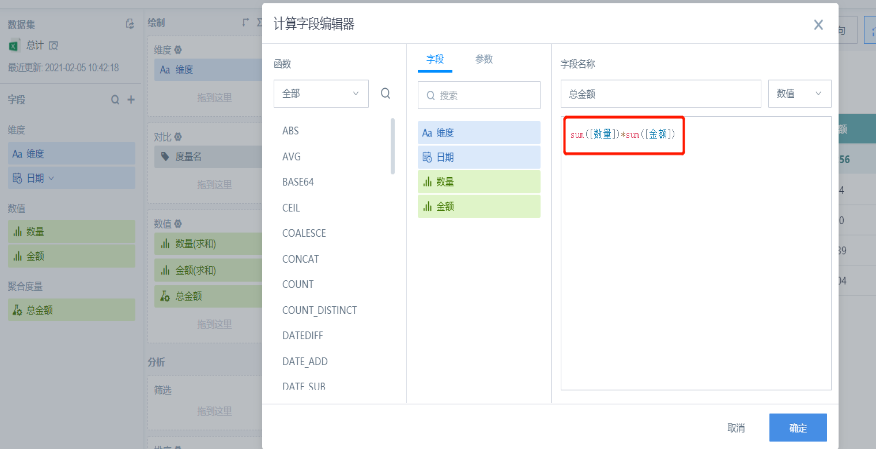
For example: When the field is sum([Quantity])*sum([Amount]),
Choose to calculate based on original field, the total result is the sum of field [Quantity] multiplied by the sum of field [Amount]:
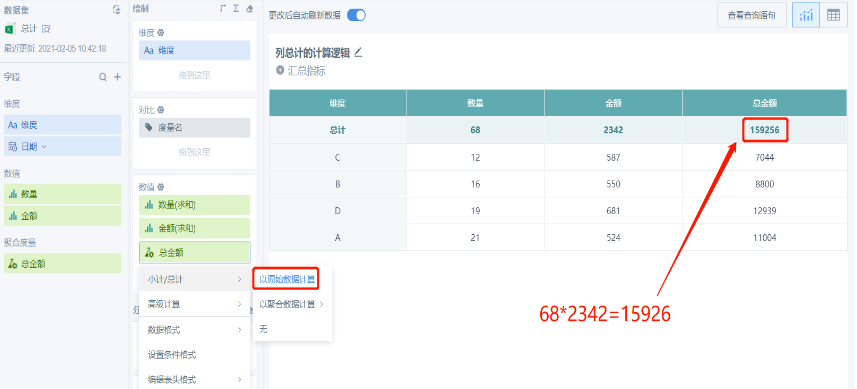
Choose to calculate based on aggregated field (such as sum), the total result is the sum of each row's [Quantity] multiplied by [Amount]:
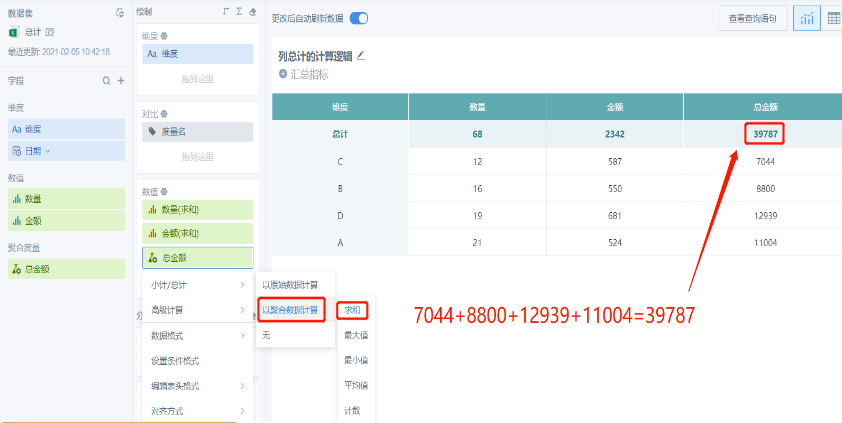
2. General Calculation Logic, When Choosing to Calculate Based on Aggregated Field (Maximum, Minimum, Average, Count), Original Field and Aggregated Field Have the Same Calculation Logic
Choose to calculate based on aggregated field (such as maximum, minimum), the total result is the largest number, smallest number in the corresponding column:
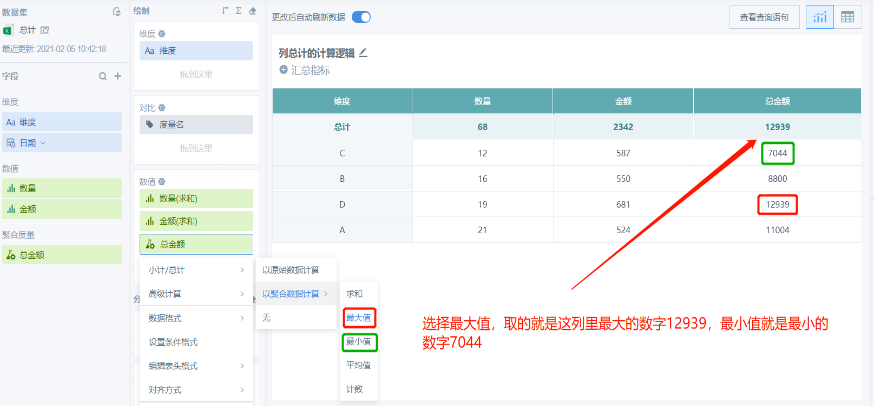
Choose to calculate based on aggregated field (such as average), the total result is the average of the data in the corresponding column:
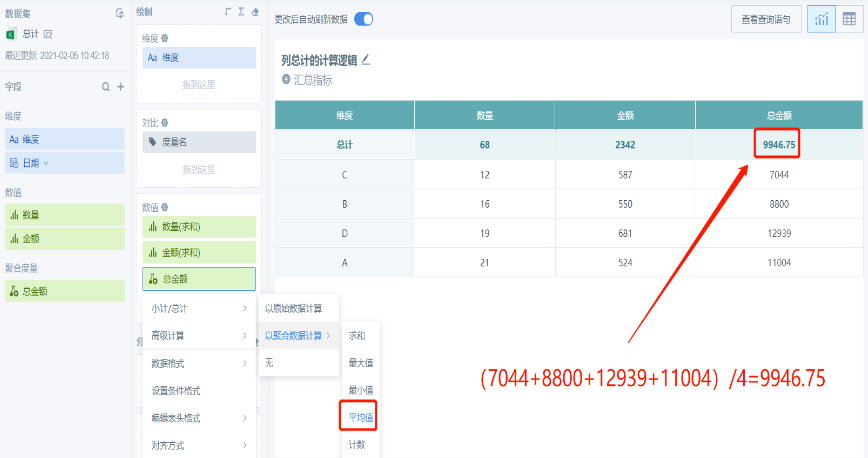
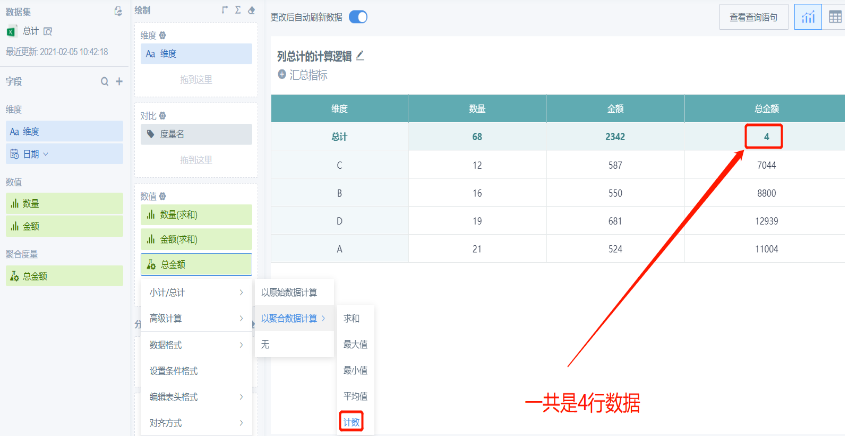
Choose to calculate based on aggregated field (such as count), the total result is the quantity of data in the corresponding column:
Notes
-
The above examples use sum as an example. If it's avg(), max(), etc. themselves, then the logic is related to the function's own meaning. For example, avg(), then calculating based on original field and calculating based on aggregated field (average) have the same calculation result. Other specific cases can be verified by trying them yourself;
-
Window functions refer to the calculation logic of original fields.
Common Questions
- Why do some columns have no data in the total row?
Possible reason 1: The numerical bar field doesn't have an aggregation method set, that is, "None". In the case of no aggregation, totals are not calculated by default.
Solution: Set an aggregation method for the numerical bar field.
Possible reason 2: The corresponding numerical bar field is an aggregated metric, may have used functions or complex calculation formulas, or added advanced calculations, and the system cannot accurately judge the logic and calculate totals.
Solution: Due to technical barriers, it's temporarily impossible to achieve in the same card. It's recommended to create a new card to calculate totals separately.
- Why doesn't setting column totals to display at the top take effect, only showing after filtering data?
Reason: Table cards can only display 20,000 rows of data. Only when the aggregated data doesn't exceed 20,000 rows can column totals take effect.
Solution: Set filter conditions to aggregate data to within 20,000 rows.