Migration Chart Usage Instructions
Background Description
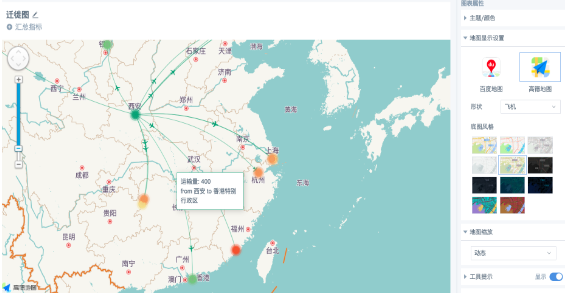
Migration charts dynamically and real-time display data migration trajectories and migration volumes in maps, allowing intuitive viewing of data sources and destinations. Commonly used in scenarios such as population migration, logistics migration, traffic monitoring, and security attack source monitoring. Guandata now supports Chinese map migration charts.
Dataset Preparation
The dataset needs to contain at least 3 fields: the starting point of the migration path, the ending point, and the measurement indicator. The starting point and ending point fields are in string text format, with values being Chinese administrative divisions, supporting provinces, cities, and districts/counties. It is necessary to maintain standardized and unified names as much as possible to avoid unrecognized or incorrectly identified situations.
Precautions
1. For example, "Hangzhou City" and "Hangzhou" can both be recognized by the system, but if used mixed together, the data will be counted and displayed separately. It's best to use one writing method uniformly. However, not all administrative divisions can be recognized after removing suffixes. For example, "Pudong New District" can be recognized, but abbreviated as "Pudong" cannot be recognized; "Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture" can be recognized, but abbreviated as "Yanbian" cannot be recognized.
2. When there are cities and counties with the same name or other duplicate names (for example, Hotan City/Hotan County), try to keep the administrative division complete, don't use the writing method of "Hotan".
3. To ensure visualization effects, it is recommended to use administrative divisions of the same level for starting points and ending points, for example, use city—city nationwide, district—district within cities.
Usage Steps
1. Create a "Visualization Chart" card, select "Migration Chart" under the "Map" type. According to the visualization drawing prompts, drag the corresponding fields to the drawing area (starting point first, ending point second). When the graph is cluttered, it is recommended to set filter conditions.
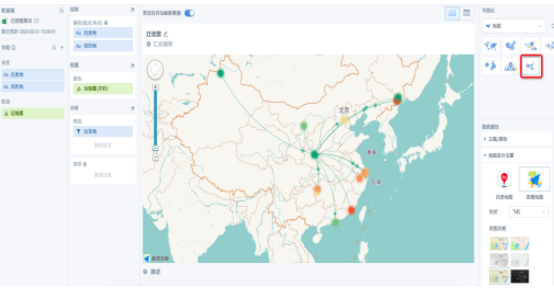
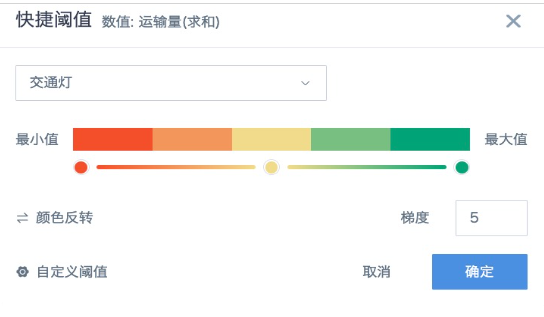
2. The color field is recommended to use numerical fields (such as "Transport Volume"), set aggregation methods, advanced calculations, and data formats according to requirements. Color settings can choose color styles according to the desired gradient, or set "Custom Thresholds". If using text fields, color settings temporarily don't take effect (to be optimized), default to using the first color of the selected theme in "Theme/Color" on the right.
Other Style Settings
-
The edit page on the right provides multiple style settings, for example, the map has "Baidu Map" and "Gaode Map" options, with multiple base map styles, and migration path icons can choose from airplane, truck, arrow, and circle.
-
Numerical labels and values, format is not supported for setting, only displayed in floating windows when the mouse moves over the migration path.
-
Click the plus and minus signs on the left zoom bar, or use the mouse wheel and touchpad to zoom the map scale.