Pareto Chart Usage Methods and Scenarios
Background Introduction
Pareto Chart (also known as Pareto Analysis) is a type of bar chart. The length of the bars represents frequency or cost (time or money), arranged with the longest bars on the left and shortest bars on the right. In this way, the chart can intuitively depict which situations are more important. Cause analysis tools are considered one of the seven quality tools.
Pareto Analysis is a statistical technique in decision-making used to select a limited number of tasks that produce significant overall effects. It uses the Pareto Principle (also known as the 80/20 rule), where by completing only 20% of the work, you can achieve 80% of the benefits of the entire work.
Taking quality improvement as an example, the vast majority of problems (80%) are caused by some key reasons (20%). This technique is also called "Critical Few" and "Trivial Many" (also an important concept in Six Sigma and DMAIC).
Knowledge Extension
(1) Six Sigma (6 Sigma) is a management strategy that primarily emphasizes setting extremely high goals, collecting data, and analyzing results to reduce defects in products and services. The principle behind Six Sigma is that if you detect how many defects there are in your project, you can find ways to systematically reduce defects and make your project as perfect as possible. For an enterprise to achieve Six Sigma standards, its error rate cannot exceed 3.4 per million.
(2) DMAIC is an important tool for process improvement in Six Sigma Management, referring to the five-stage process improvement method consisting of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is generally used for improving existing processes, including manufacturing processes, service processes, and work processes.
Pareto Chart Application Scenarios
(1) When analyzing data on the frequency of problems or causes in a process;
(2) When there are many problems or causes, and you want to focus on the most important ones;
(3) When analyzing broad causes by looking at specific causes;
Application Examples
Here we use a simple usage scenario as an example:
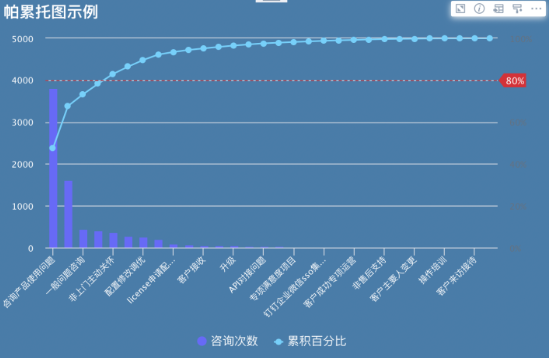
Providing after-sales service for customer products, using Pareto charts to analyze which types of problems staff solve daily in customer service work account for the most proportion, thereby identifying which aspects customer problems mainly converge on, to focus on determining the capabilities that staff must have as recruitment requirements or training focus goals, facilitating decision-making and improving efficiency.
-
Data preparation: Prepare the corresponding dataset, it is recommended to do data cleaning work in advance;
-
Create new card: New card - Visualization chart - Select data table - Search for Pareto chart;
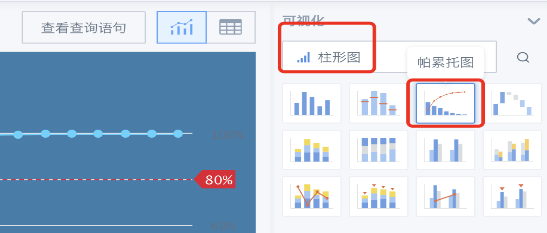
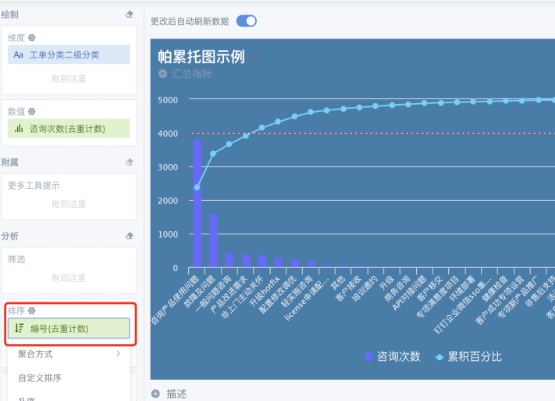
- You can drag dimension fields and a numerical field as needed, sort the numerical field, it is recommended to sort in descending order to increase the readability of the chart;
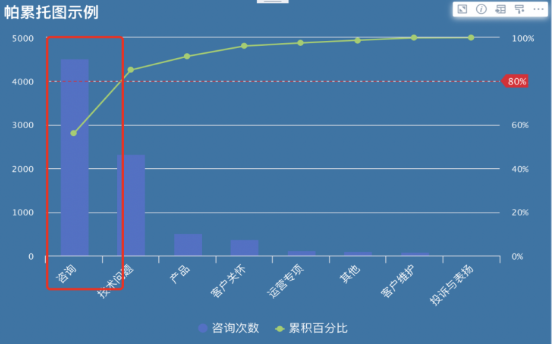
(1) It is recommended to make good use of chart properties, adjust theme colors, legend settings, card property settings, etc. to beautify the chart and enhance visualization.
(2) It is recommended to add an 80% auxiliary line in the Pareto chart to make the important 20% clear at a glance.

Effect Image Display