Field Splitting Case Sharing
Background
In some datasets, there are fields that are strings joined by delimiters. Sometimes, you need to split them to extract a fixed position substring or split them into multiple columns.
Case Scenarios
Case 1: Create a calculated field, use string functions to locate the delimiter and split
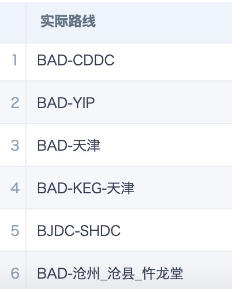
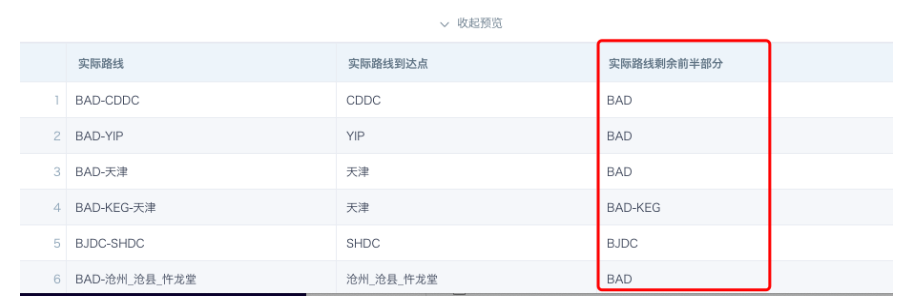
- Actual route start point: extract the substring before the first dash.
Method 1: SUBSTR([Actual Route],0,INSTR([Actual Route],'-')-1)
Method 2: LEFT([Actual Route],INSTR([Actual Route],'-')-1)
Method 3: SUBSTRING_INDEX([Actual Route],'-',1)
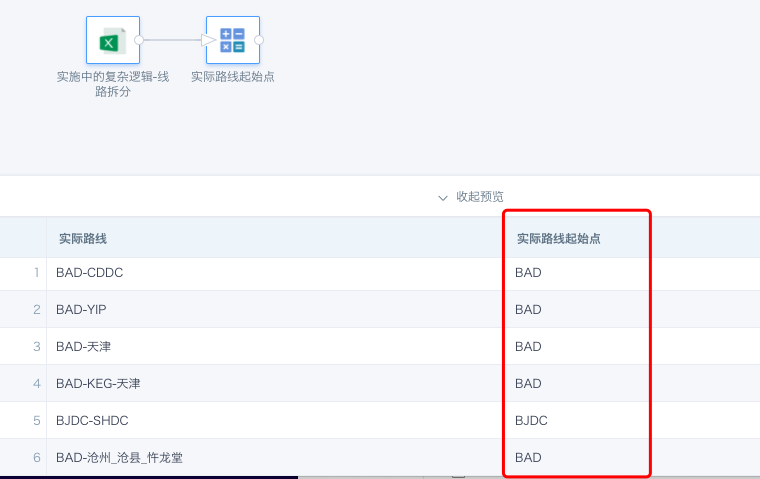
- Remaining part of the actual route: 1 and 2 can be joined to restore the full route.
SUBSTR([Actual Route],INSTR([Actual Route],'-')+1)
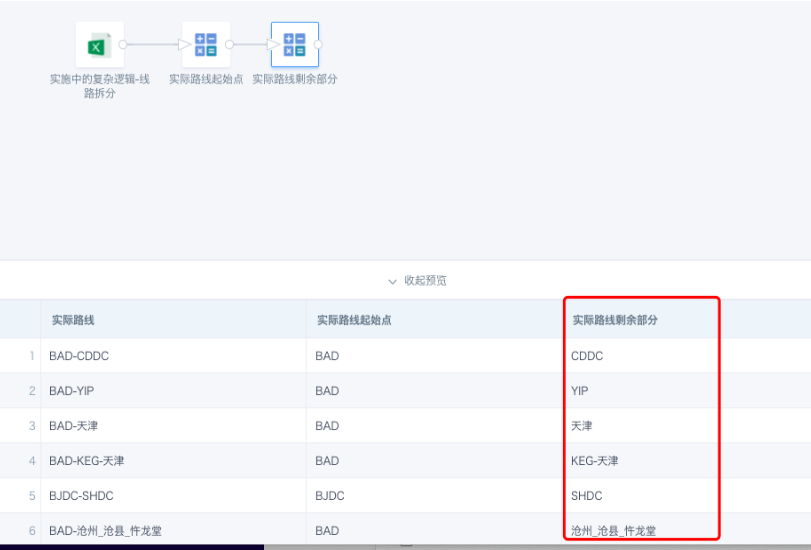
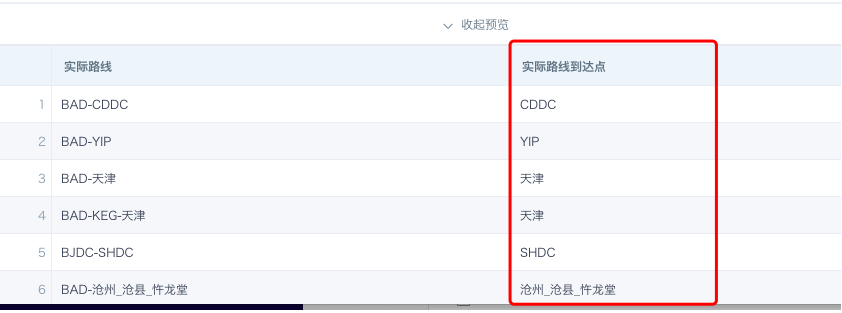
- Actual route endpoint
Method 1: right([Actual Route Endpoint],instr(REVERSE([Actual Route]),'-')-1)
Method 2: SUBSTRING_INDEX([Actual Route],'-',-1)
- First half of the remaining actual route: 3 and 4 can be joined to restore the full route.
REGEXP_EXTRACT([Actual Route],'(.+)(-{1}.+)',1)
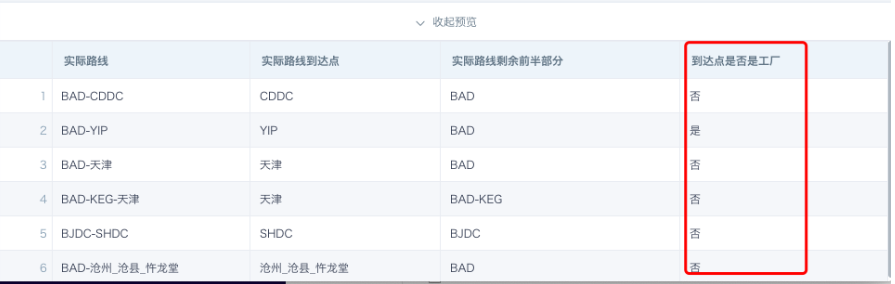
- Is the endpoint a factory: The rule is pure letters and does not end with DC.
when SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],-2)<>'DC' and (SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],0,1) <='Z' AND 'A'<= SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],0,1))
then 'Yes'
when [Actual Route Endpoint] is null or [Actual Route Endpoint] = ''
then 'No'
else 'No'
end
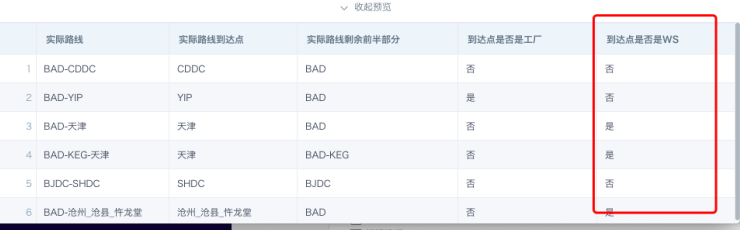
- Is the endpoint WS: The rule is pure Chinese characters, no other letters or numbers.
when SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],-2)='DC' or (SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],0,1) <='Z' AND 'A'<= SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],0,1))
then 'No'
when [Actual Route Endpoint] is null or [Actual Route Endpoint] = ''
then 'No'
else 'Yes'
end
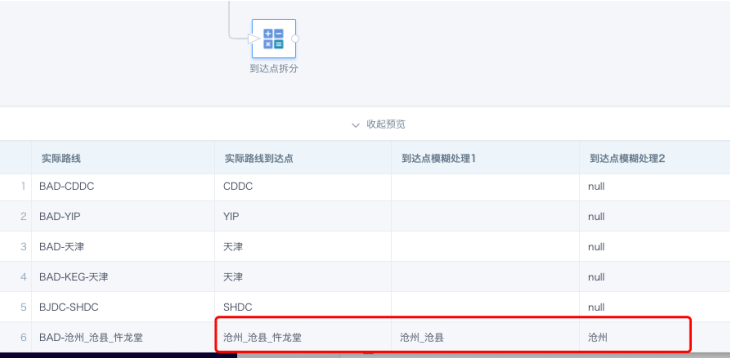
- Endpoint splitting
Example:
Actual Route=BAD-Cangzhou_Cangxian_Wulongtang
Actual Route Endpoint=Cangzhou_Cangxian_Wulongtang
Endpoint Fuzzy 1=Cangzhou_Cangxian
Endpoint Fuzzy 2=Cangzhou
-- Endpoint Fuzzy 1
REGEXP_EXTRACT([Actual Route Endpoint],'(.+)(_{1}.+)',1)
-- Endpoint Fuzzy 2
case when INSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],'_')>0 then SUBSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],0,INSTR([Actual Route Endpoint],'_')-1) end
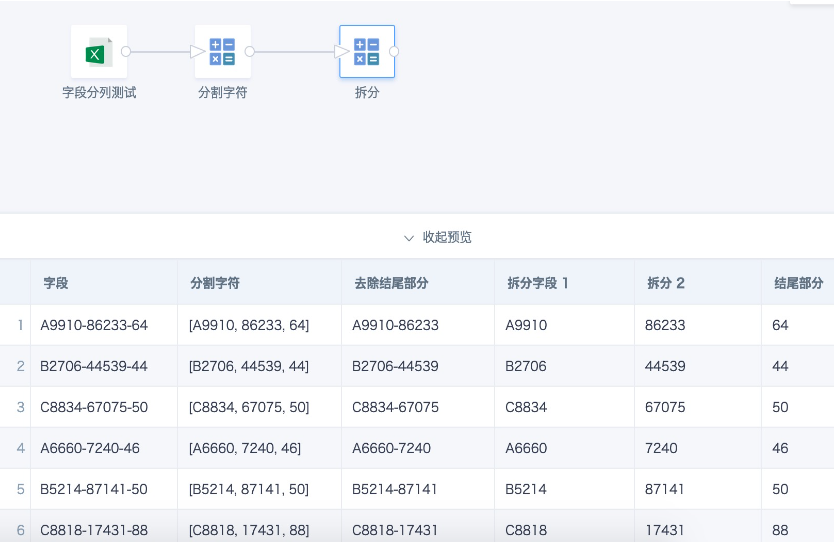
Case 2: Create a calculated field, split the original field into an array by delimiter, and extract array elements
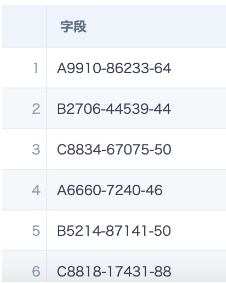
- Split into array: split([Field],'-')
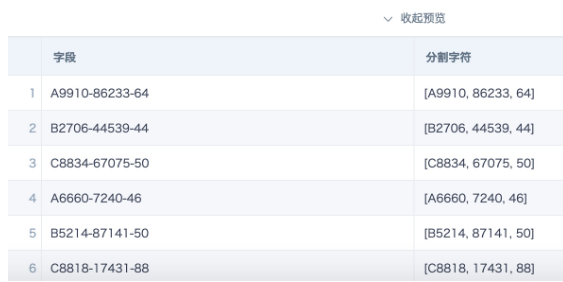
- Remove the ending part: array_join(slice([Split Char],1,size([Split Char])-1),'-')
Split Field 1: [Split Char][0]
Split Field 2: [Split Char][1]
Ending part: array_join(slice([Split Char],size([Split Char]),1),'')
Case 3: Extract Chinese/English part of a string
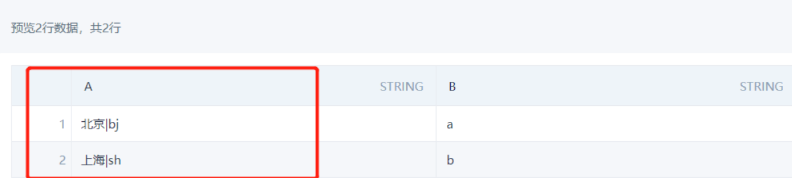
Implementation: You can use regular expressions in a new field.
- Keep Chinese:

- Keep English:

Final result:

Note: The above functions can be used in ETL and non-direct/non-accelerated datasets. For direct datasets, use the corresponding database functions. For high-performance (accelerated) datasets, use Clickhouse functions. For more text processing functions and cases, see Spark SQL Text Functions and Applications.