Common Function FAQ
1. How to properly handle cross-year week display errors
Scenario: Using the function concat(year([date]),'年第',weekofyear([date]),'周') in datasets or ETL to get the week of the date. For cross-year weeks, such as 2021-01-01 which is actually week 53 of 2020, but the returned result becomes week 53 of 2021.
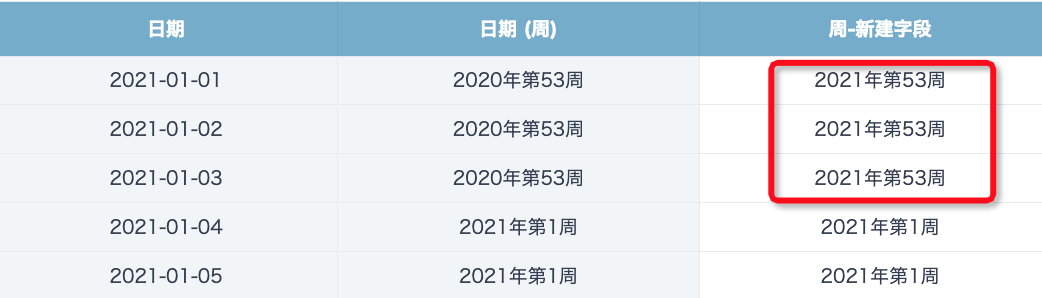
【Solution】: Use the Thursday date of that week to get the year data for cross-year weeks. Principle: Spark uses ISO-8601 standard for week numbering: if a week containing January 1st (starting from Monday) has more than 3 days in the new year, it is week 1 of the new year; otherwise, it is the last week of the previous year. So the year of Thursday in the cross-year week is the year to which this week belongs. The function syntax is as follows:
concat(year(date_add(trunc([date],'week'),3)),'年第',weekofyear([date]),'周')
Note: If in card editing scenarios, it's recommended to directly use the system's built-in date-week.
2. How to convert string format timestamps to timestamp format
For example: The time format stored in the database is string format 20200905174444, and you want to convert it to timestamp format like 2020-09-05 17:44:44.
【Solution】: First change the field to timestamp format, then use DATE_FORMAT to change it to the desired format.
DATE_FORMAT(CAST(UNIX_TIMESTAMP([date], 'yyyyMMddHHmmss') AS TIMESTAMP), 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')
Explanation:
-
The above function is Spark syntax, applicable to non-direct connection datasets. Direct connection datasets need to use the corresponding database syntax, such as Oracle syntax: to_date([date],'yyyyMMddhh24:mi:ss');
-
Choose "Date and Time" format. If you choose "Date", hours, minutes, and seconds will not be displayed;
-
If the format is numeric, you need to convert the field to string format first.
3. Why doesn't unbase64 decoding work after use?
【Reason】: After unbase64, it returns binary data, which needs to be converted to string type using cast.
【Solution】: Change to cast(unbase64([encrypted string]) as string)
4. Why does the power() function return 0 for all results?
【Reason】: POW(x,y), this is a limitation of the POW function itself. When x<0, y<1 (i.e., y is a fraction or decimal), the result will be 0; additionally: if the base x is negative and the exponent y is not an integer, it will cause a domain error. You can indirectly solve this problem using the case when function: case when x<0 then -POW(ABS(x),y) else POW(x,y) end
5. Why does using the sequence function cause errors?
For example, the error is as follows:
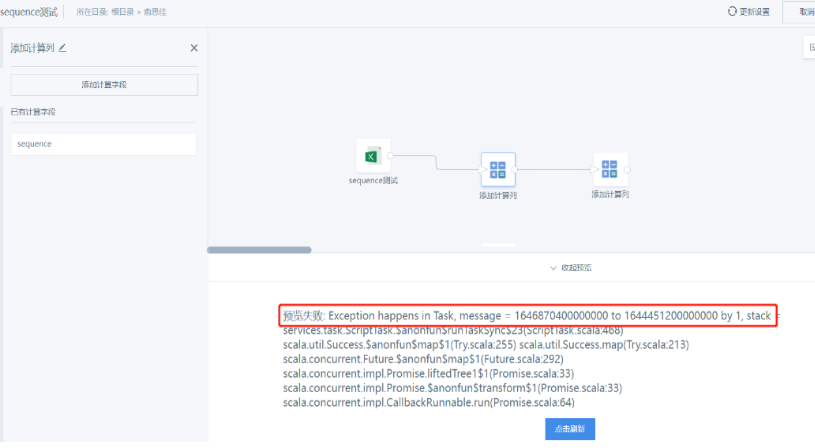
【Possible reasons】
-
The start date and end date positions might be reversed. The correct format should be: sequence([start date],[end date],interval 1 month)
-
The third parameter step size might be negative, it should be positive.
-
There might be dirty data in the original data, such as the start date being greater than the end date. (You can filter out such data first)
6. How to get yesterday's data with hours, minutes, and seconds using the now function?
from_unixtime(to_unix_timestamp(now()) - 86400, 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')
7. Why can't the SUBSTRING function extract from the end when the starting position is negative?
For example: substring([store name],-1,4) cannot get the last four characters from the end
If it's a SQL Server data source, you can refer to: substring([store name],Len([store name])-1,4). (Built-in functions for direct connection databases may not be universal, you can use the data source's own syntax.)
8. How to get the latest time from column time data?
max([time field])over(partition by [field])
If you want to get the maximum for all data, you can write: max([time field])over(partition by null)
9. How to remove the decimal point after using the round() function for rounding?
You can nest an int function outside for rounding: int(round())
10. What might be the reason for calculation errors in newly created fields?
When there are null values, the calculation result will be null. It's recommended to add a "null value replacement" step before ETL output.
11. How to convert string format dates to date? Using to_date() directly results in null values?
If the original format is 12/25/19 (month/day/year), then you need to write to_date([date],"MM/dd/yy"), that is, you need to specify the original format after to_date for normal conversion.
12. Why do data row counts have issues when using dense_rank function to get top rankings?
For example: if(dense_rank() over (partition by null order by [amount] desc)>8,'Others',[country]) will get more than 8 countries?
【Reason】: dense_rank ranking returns results like 12234455667788, so there might be more than 8 results >8.
【Solution】: You can use row_number() over(partition by [field] order by [field])
13. How to implement week number calculation with January 1st of each year as the first day of the first week (Oracle standard week)?
【Solution】: In addition to the internationally common ISO week calculation method, Oracle also supports another standard week counting method: January 01/01 of each year is the start of the first week, date+6 days is the end of a week. The function usage is:
to_char(date,'ww')
For other databases, you can use existing date functions to calculate which day of the year the specified date is, divide by 7 and round up. Functions to get the position of a specified date in a year generally include the following (all these functions can be used in Spark), and usage may vary slightly for different databases.
dayofyear(date)
date_format(date,'D')
date_part('doy', date)
extract(doy FROM date)
Functions for rounding up in numerical calculations generally include ceiling/ceil. Nested usage is as follows, or you can also use remainder to determine week numbers.
Method 1: ceil(dayofyear(date)/7)
Method 2:
Writing 1: if(date_format(date,'D')%7=0,cast((date_format(date,'D')/7) as int),cast((date_format(date,'D')/7) as int)+1);
Writing 2: case when cast(EXTRACT(DOY FROM date) as int)%7 = 0
then cast((cast(EXTRACT(DOY FROM date) as int)/7) as int)
else cast((cast(EXTRACT(DOY FROM date) as int)/7) as int)+1
end