Spark SQL Array Processing Functions and Applications
Definition
Array (Array) is an ordered sequence of elements, and the individual variables that make up the array are called array elements. Arrays are a form used in programming to organize several elements of the same type in an ordered form for processing convenience. According to the different types of array elements, arrays can be divided into numeric arrays, character arrays, and various other categories. Array processing methods differ in various programming languages, and this article only lists the functions and application cases of arrays in Spark SQL.
Characteristics
-
Arrays are collections of elements of the same data type.
-
The storage of elements in arrays has a sequential order, and they are stored continuously in memory according to this sequential order.
-
Array elements are queried using the entire array name and their own sequential position (index) in the array.
-
Arrays are displayed as string-like objects enclosed in square brackets in the database, with each element separated by commas. For example [1, 2, 3].
Main Functions
Array Generation and Conversion
Common Functions
Purpose | Function | Example | Result |
Merge multiple rows into one row, return array withno deduplication | collect_list(expr) | collect_list([field]) [field] values are A,A,B,B,C,D respectively | [A,A,B,B,C,D] |
Merge multiple rows into one row, return array afterdeduplication | collect_set(expr) | collect_set([field]) [field] values are A,A,B,B,C,D respectively | [A,B,C,D] |
Merge multiple columns into one column | array(expr, ...) | array(1, 2, 3) | [1,2,3] |
Split string with delimiter, return array. | split(str, regex[, limit]) [, limit] limits the number of split elements, can be omitted | split('A-B-C', '-'); split('A-B-C', '-',2) | [A,B,C]; [A,B-C] |
Split one row into multiple rows | explode(expr) | explode(array('A','B')) | A B |
Join array elements with delimiter into string | array_join(array, sep[, nullRep]) [, nullRep] used to specify replacement value for null values, removes null when omitted | array_join(array('hello', null ,'world'), ' ', ',') | hello, world |
concat_ws(sep[, str | array(str)]+) removes null, can concatenate multiple arrays and strings | concat_ws(',',array('hello', null ,'world')) | hello,world | |
Split text into nested arrays according to punctuation and spaces | sentences(str[, lang, country]) | sentences('Hi there! Good morning.') | [["Hi","there"],["Good","morning"]] |
Generate sequence array with fixed step increment, used for numeric and datetime types | sequence(start, stop, step) | sequence(1, 5); sequence(to_date('2021-01-01'), to_date('2021-03-01'), interval 1 month) | [1,2,3,4,5]; [2021-01-01,2021-02-01,2021-03-01] |
Common Scenarios
-
Merge multiple rows of data in dataset into one row, split one row into multiple rows. Mainly uses combination of functions like
concat_ws(collect_set( )), explode(split( ))etc. For specific usage cases, please refer to: 《Processing Data Row Merging and Splitting through ETL》 -
Because of missing data (e.g., no sales records) causing year-over-year and month-over-month data to not match, need to supplement data, or other scenarios requiring Cartesian product. For example, use combination function
explode(sequence([start date],[end date],interval 1 month))to supplement calendar. For specific usage cases, please refer to: ETL Data Supplementation Methods. -
Distinct count. *count(distinct( )) function does not support window function usage, when data volume is not large, can use
size(collect_set([field])over(partition by [group column name]))to perform distinct count. For specific usage cases, please refer to: Distinct Count Function Implementation with Window Functions.
Array Basic Operations
Common Functions
Purpose | Function | Example | Result |
Deduplicate array elements | array_distinct(array) | array_distinct(array(1, 2, 3, null, 3)) | [1,2,3,null] |
Return number of array elements | size(expr) | size(array('b', 'd', 'c', 'a')) | 4 |
Remove all specified elements from array | array_remove(array, element) (null cannot be removed) | array_remove(array(1, 2, 3, null, 3), 3) | [1,2,null] |
Return array composed of element repeated specified number of times | array_repeat(element, count) | array_repeat('123', 2) | ["123","123"] |
Extract subarray of fixed length from fixed position | slice(x, start, length) | slice(array(1, 2, 3, 4), 2, 2) | [2,3] |
Process all elements in array according to specified method, return new array | transform(expr, func) | transform(array(1, 2, 3), x -> x + 1); transform(array('A','B','C'),(x,i)->i||x) | [2,3,4]; [0A,1B,2C] |
Reverse sort array | reverse(array) | reverse(array(2, 1, 4, 3)) | [3,4,1,2] |
Randomly sort array | shuffle(array) | shuffle(array(1, 20, 3, 5)) | [3,1,5,20] |
Sort array | array_sort(expr, func) func specifies sorting method, ascending order when omitted, null at end | array_sort(array('b', 'd', null, 'c', 'a')) | ["a","b","c","d",null] |
sort_array(array[, true/false]) When ascending (true), null at front, when descending (false), null at end | sort_array(array('b', 'd', null, 'c', 'a'), true) | [null,"a","b","c","d"] |
Array Query and Calculation
Common Functions
Purpose | Function | Example | Result |
Return maximum value in array | array_max(array) | array_max(array(1, 20, null, 3)) | 20 |
Return minimum value in array | array_min(array) | array_max(array(1, 20, null, 4)) | 1 |
Query if element exists in array, return true/false | array_contains(array, value) | array_contains(array(1, 2, 3), 2) | true |
Query position/index of element in array | array_position(array, element) | array_position(array('A','B','C'), B) | 2 |
Query nth element in array | element_at(array, n) n starts from 1, when negative, query from back to front | element_at(array('A','B','C'), -1) | C |
array[n] n starts from 0, cannot be negative | array('A','B','C')[0] | A | |
Filter array with specified condition/method, return array containing elements that meet conditions | filter(expr, func) | filter(array(1, 2, 3), x -> x % 2 == 1) | [1,3] |
Query if any element in array meets judgment condition, return true/false | exists(expr, pred) Need to filter null values in advance, otherwise may cause result to return null. | exists(array(1, 2, 3), x -> x % 2 == 0) | true |
Query if all elements in array meet judgment condition, return true/false | forall(expr, pred) Need to filter null values in advance, otherwise may cause result to return null. | forall(array(1, 2, 3), x -> x % 2 == 0) | false |
Aggregate array elements into one result value according to binary operation | aggregate(expr, start, merge, finish) | aggregate(array(1, 2, 3), 0, (acc, x) -> acc + x) Sum elements in array | 6 |
Common Scenarios
- User attributes are multi-valued, set dataset row and column permissions.
Multi-valued user attributes in database are in string format connected by delimiters, need to be split into arrays for processing when applied. For example, commonly used row permission formula array_contains(split([CURRENT_USER.city],','),[city]) uses function split() to split user attribute values with commas into arrays, then array_contains() is used to judge whether the array includes the value in dataset field [city]. In this way, "Anshan" will exactly match "Anshan", and won't mistakenly match "Maanshan". Related cases please refer to: Row Permission Usage Case Sharing.
- Multiple keywords, mutually "OR" relationship, fuzzy match long strings.
For example, to filter products whose titles contain flavor keywords like "original flavor" or "spicy", can use exists(split([flavor],','), x -> instr([product title],x)>0). Related cases please refer to: Filter Fuzzy Matching Implementation Methods
Multi-array Processing
Common Functions
Purpose | Function | Example | Result |
Concatenate arrays, elements not deduplicated | expr1 || expr2 | array(1, 2, 3) || array(4, 5) || array(6) | [1,2,3,4,5,6] |
concat(col1, col2, ..., colN) | concat(array(1, 2, 3), array(4, 5), array(6)) | ||
Return list of elements that exist in array1 but not in array2, elements deduplicated | array_except(array1, array2) | array_except(array(1, 2, 3), array(1, 3, 5)) | [2] |
Return intersection of array1 and array2, result deduplicated | array_intersect(array1, array2) | array_intersect(array(1, 2, 3), array(1, 3, 5)) | [1,3] |
Return union of array1 and array3, result deduplicated | array_union(array1, array2) | array_union(array(1, 2, 3), array(1, 3, 5)) | [1,2,3,5] |
Query if array1 and array2 have non-null value intersection, return true/false | arrays_overlap(array1, array2) | arrays_overlap(array(1, 2, 3), array(3, 4, 5)) | true |
Merge two-dimensional array into one-dimensional array | flatten(arrayOfArrays) | flatten(array(array(1, 2), array(3, 4))) | [1,2,3,4] |
Common Scenarios
- Extract content from long strings.
For example, string 'GUANDATA 202109R2(3.10.3)', extract the middle 202109R2 and 3.10.3 in parentheses, there are many extraction methods, among which element_at(flatten(sentences([Sprint])),3) first uses sentences() to split the string into nested arrays, then uses flatten() to merge nested arrays into a single array, finally uses element_at() to extract element content according to element position. For details please refer to: Spark SQL Text String Processing Functions and Applications.
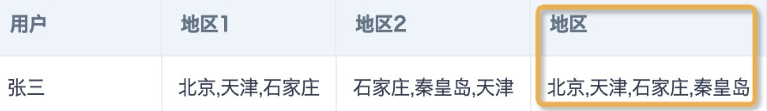
- Merge multiple long strings, and remove duplicate content in strings. For example, to achieve the following effect, can refer to the following combination function.
array_join(array_union(split([region1],','),split([region2],',')),',')
--or--
concat_ws(',',array_distinct(split(concat_ws(',',[region1],[region2]),',')))
- Dataset field format is single-layer or multi-layer nested json array, need to extract json content. Related cases: How to Use ETL to Parse JSON.
Note: In cases with large data volume, try to avoid multi-layer nested functions, recommend splitting into multiple calculated fields for step-by-step operations.