ETL FAQ
1. Overview
This article introduces common issues with the Smart ETL module in Guandata BI's data preparation.
2. Smart ETL
Why is the ETL output dataset model structure empty?
Problem description:
Other possible manifestations:
The dataset overview page "Model Structure" and "Association Creation" are both empty;
Cannot find the ETL that the dataset belongs to, nor can the dataset be updated.
Problem cause:
After the ETL was successfully created and run, the owner deleted the output dataset node when modifying the ETL; then added a new output dataset node and saved and ran it. Even if the new output dataset has the same name as the original dataset (same name can only be saved in different folders), it's not the same dataset.
Solution:
(1) Try to avoid deleting output nodes in ETL. If you need to add new nodes before the output node, click the connection line before the last node and delete the connection line, don't delete the output node.
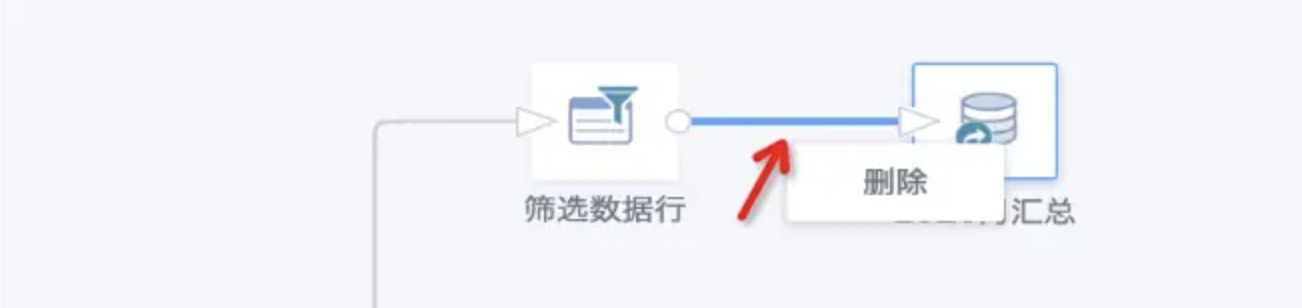
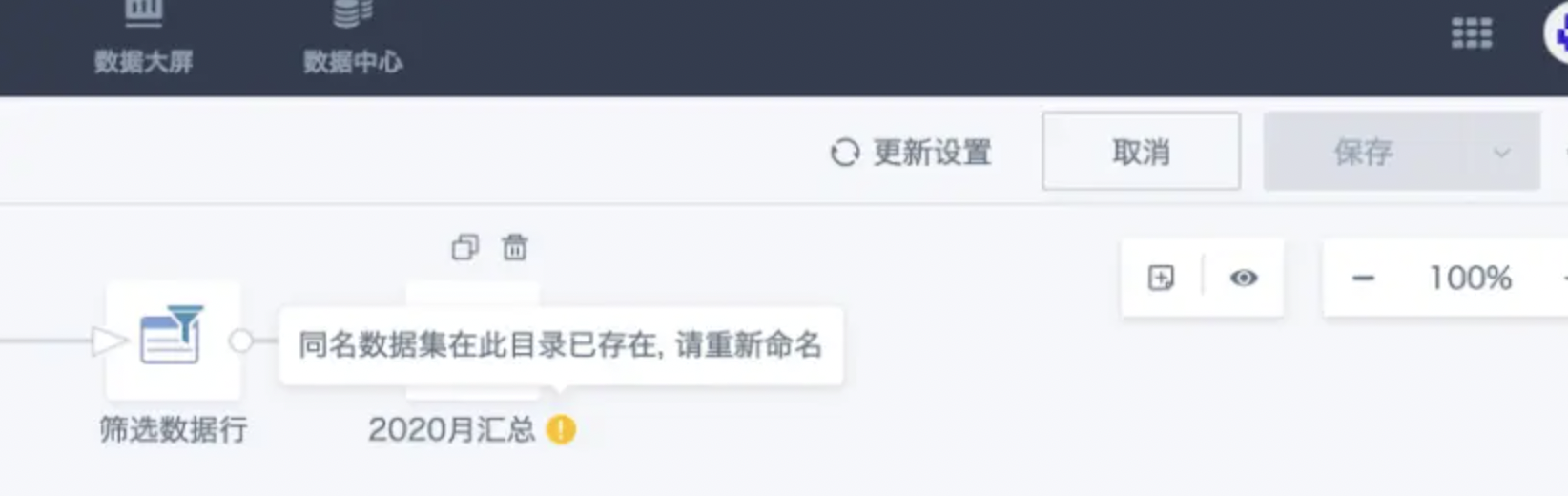
(2) If the output node has already been deleted, if you set the new output node to save in the same folder and use exactly the same name, the system will prompt: Dataset with the same name already exists in this directory, please rename. At this time, it's best not to force save the ETL, cancel save and exit. Then re-enter the editing interface and follow suggestion 1.
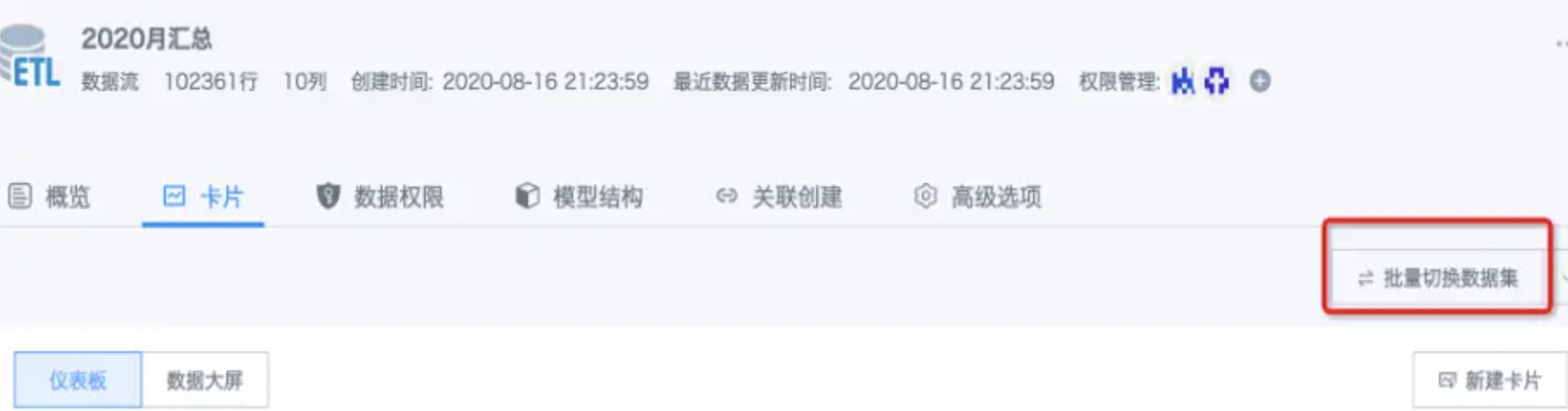
(3) If the node has been deleted and you've made many modifications and don't want to give up, you can only save with a different name or different path. Then the original output dataset will lose connection with the ETL, and the model structure will show as empty. At this time, you need to batch switch cards that depend on the old dataset to the new dataset, then delete the old dataset.
ETL SQL node double quotes usage issue
Problem cause:
Fields in SQL node query statements use double quotes, which are treated as strings. Remove the double quotes or change to backticks.
Solution:
Spark syntax is consistent with MySQL. Backticks `` are used to avoid conflicts between user-defined identifiers (field names, table names, etc.) and database SQL keywords (such as FROM, CREATE, etc.). Generally, table names and field names use backticks, but they can also be omitted.
Under what circumstances will ETL input dataset preview have no data?
Problem cause:
In ETL, row and column permissions for input datasets are judged according to the ETL owner. Even if an administrator runs this ETL, permissions are judged according to the ETL owner. In most cases, the owner has permissions for the input dataset, but it's not excluded that there have been changes to row and column permissions after the input dataset, or that the ETL has had ownership transfer operations.
When using null value replacement in ETL, why are some null values not successfully replaced?
Problem cause 1:
The field value is an empty string, but null value replacement was mistakenly used.
Solution:
Use the "Value Replacement" node to replace empty strings with null.
Problem cause 2:
The replacement target value is inconsistent with the field type. For example, replacing null values in date type with 0 is not effective.
Solution:
Ensure the null value replacement target value is consistent with the field type.
Explanation of ETL filter data row trigger conditions
- When all filtering rules select "equals":
a. Satisfy all rules: That is, filter out data that satisfies two or more conditions. For example, selecting province=Zhejiang Province, date=2017-10-05, filter out only one piece of data that satisfies both conditions.
b. Satisfy any rule: That is, filter out data that satisfies one of two or more conditions. For example, selecting province=Zhejiang Province, date=2017-10-05, filter out data from Zhejiang Province or with date 2017-10-05.
- When all filtering rules select "not equals":
a. Satisfy all rules: That is, filter out data that satisfies two or more not-equals conditions. For example, selecting province not equals Zhejiang Province, date not equals 2017-10-05, filter out data that satisfies both conditions. The result is that Zhejiang Province doesn't exist in provinces, and 2017-10-05 doesn't exist in dates.
Selecting province=Zhejiang Province alone, no data;
Selecting date=2017-10-05 alone, no data;
b. Satisfy any rule: That is, filter out data that satisfies one of two or more conditions. For example, selecting province not equals Zhejiang Province, date not equals 2017-10-05, will filter out data that doesn't equal Zhejiang Province and date doesn't equal 2017-10-05. Selecting province=Zhejiang Province alone, has data;
Selecting date=2017-10-05 alone, has data;
Selecting province=Zhejiang Province and date=2017-10-05, no data;
- Summary
a. When filtering rules are "equals", the logic is easier to understand. Satisfy all rules means satisfying two or more conditions, satisfy any rule means satisfying one of the conditions.
b. When filtering rules are "not equals", if the desired effect is to filter out all data that satisfies the conditions, such as in this case wanting to filter out data from Zhejiang Province on October 5, 2018, then the trigger rule needs to select satisfy any rule.
Do ETL and datasets have backup mechanisms?
There's no separate backup mechanism, but BI overall data has backup mechanisms. Data is automatically backed up at 2:30 AM every day.
When BI does data backup, it includes ETL and dataset content.
Can SQL operators use custom time macros?
ETL doesn't support using global parameters or dynamic time macros, but you can use related dynamic date functions such as now(), current_date().
In ETL, using sum to sum up in new fields will report an error, why?
Problem cause:
Just writing sum, ETL doesn't know what dimension to aggregate by. In cards, when you drag in dimension fields, then drag in the corresponding numeric field, it will automatically aggregate according to the dimension fields.
Solution:
Use grouping aggregation nodes to sum, or use window functions like sum() over(partition by) in new fields.
Can ETL processing result datasets be written back to our database?
BI platform 5.7 and newer versions support data writeback. Previous versions could only be achieved through API integration. For those using data development platform products, you can achieve direct writeback to specified databases in the universe platform.
Why can't ETL details be viewed?
Problem cause:
Regular users who are not ETL owners cannot view ETL details. Only ETL owners or users with administrator permissions can view ETL details.
What's the impact of restarting jobserver and server restart on BI task status?
In service management, restarting ETL's jobserver can kill all running tasks.
Restarting BI on the server can kill all running tasks and queued tasks.
What input datasets does ETL support?
Including file datasets, database datasets (excluding direct connection databases, view datasets), and output datasets from other Smart ETL.
In ETL page operators, after using the merge columns operator, how to split the merged fields again?
In the merge columns operator, you can choose whether to delete original fields. It's recommended to retain original fields, so you have both original fields and merged fields available; if original fields are not retained, you can use the add calculated field operator, using substr and instr to split the merged fields.
Can random numbers be fixed in ETL?
When the output dataset doesn't update in ETL, random numbers can remain unchanged. If you want to retain a certain result, you can export the output dataset.
Want to replace a certain ETL's input dataset, through this ETL to this dataset, to replace data, why are other ETLs' input datasets also replaced?
Problem cause:
The replace data in dataset overview here replaces the dataset itself, not just replacing a certain ETL's input dataset.
Solution:
If you only want to replace a certain ETL's input dataset, you need to click edit to replace.
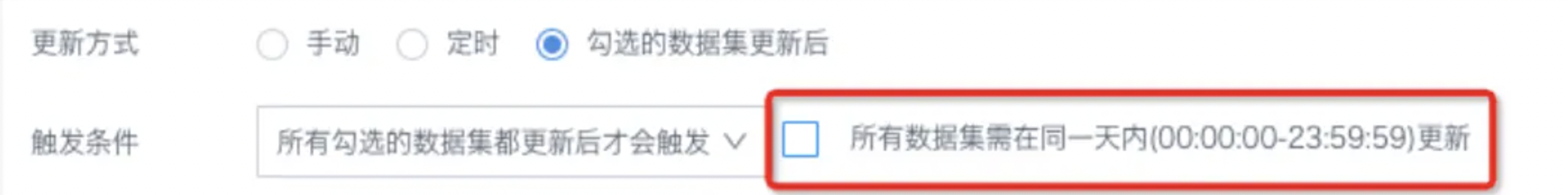
ETL update method is set to "Only trigger after all checked datasets are updated", but why does ETL automatically trigger updates without waiting for all datasets to update?
Problem cause:
The "All datasets need to be updated within the same day (00:00:00-23:59:59)" option is not checked. In this case, if the checked datasets complete a round of updates across days, it also meets the trigger conditions.
Solution: If you want to run after all datasets are updated on the same day, please check the same day option.
SQL node preview, why do some field types change?
SQL nodes will re-judge field types from the backend, not directly inherit the previously displayed types. If type changes are found, you need to check whether previous node operations are standardized.
Problem cause 1:
There's a "Row Concatenation" node in front, concatenating two fields with the same name but different types, causing the backend to be unable to accurately judge the type, and it will default to string type.
Solution:
Check problem field types before "Row Concatenation", use functions to convert types consistently before concatenating datasets.
Problem cause 2:
The problem field is generated by previous nodes or upper-level ETL "Add Calculated Column", not using functions standardized, causing the field's own type to be inconsistent with the manually selected type in the upper right corner. In this case, the field type corrected by the SQL node may be correct.
Solution:
Check previous field generation nodes, use functions to convert field types; or don't modify, use the field type output by SQL.
ETL output type doesn't match expectations
Problem description:
SQL node preview, some field types are inconsistent with previous nodes; or after ETL runs, some field types are different from original types.
Problem cause:
(1) There's a "Row Concatenation" node in ETL, concatenating fields with the same name but different types from different data sources. If fields with the same name contain string type and other types, they will be displayed as string;
(2) New fields generated by "Add Calculated Column" don't use functions standardized, causing the field's own type to be inconsistent with the manually selected type in the upper right corner; SQL nodes will re-judge field types, not directly inherit previously displayed types, causing some type inconsistencies.
Solution:
(1) Try to check problem field types before "Row Concatenation", use functions to convert types consistently before concatenating datasets.
(2) When "Add Calculated Column", use functions to convert field types, ensuring numeric types are consistent with manually selected types.
After updating License, all scheduled tasks don't run automatically
Problem description:
After the old License expires, update the License, then all scheduled tasks (such as datasets, ETL, subscriptions) don't trigger automatically; after environment migration, activating the new environment License, all scheduled tasks become invalid.
Problem cause:
After the License expires and becomes invalid, the BI service will terminate, and all scheduled tasks will terminate. Even after reactivating the License, scheduled tasks won't trigger automatically. For BI 5.3.0 and all subsequent versions, after activating the new BI environment, guandata-server must be restarted, otherwise scheduled tasks become invalid.
Solution:
After reactivating the License, contact Guandata service personnel to restart the entire BI service.
ETL updates twice consecutively, duplicate updates
Problem description:
The same ETL, checked "Update ETL only after all datasets are updated", two input datasets only updated once each, but the ETL was triggered twice, and both runs were successful.
Problem cause:
The two input datasets basically completed updates at the same time, with very small time difference, causing the system to judge twice that the conditions for triggering ETL run were met, thus running twice.
Solution:
Basically doesn't affect usage, can wait for Guandata product optimization; slightly stagger the update times of input datasets.
After dataset update, ETL doesn't update
Problem description:
ETL update method is configured as "After checked datasets update", but found that datasets updated but ETL didn't update. For example, set "Any checked dataset update will trigger", checked 5 datasets, all 5 datasets updated within a day, but ETL only ran twice.
Problem cause:
Observe the update times of input datasets and ETL update queuing times. The update times of 5 input datasets are too close, causing task queuing, so the first run hasn't finished, new tasks have been triggered and started queuing. Once multiple queuing tasks appear for the same ETL simultaneously, later duplicate queuing tasks will be automatically deduplicated and discarded by the system.
Solution:
It's recommended to use "Update ETL only after all checked datasets are updated"; if data timeliness is required and you need to set "Any checked dataset update will trigger", then ensure multiple input dataset update times are staggered, don't cluster together (time interval should be greater than ETL run duration, and leave room for queuing).