How to Correctly Replace Historical Data for Incremental Update Datasets
Scenario
The dataset is set for incremental updates, running on schedule daily.
After a few days or a period of time, it is discovered that historical data for a certain time range is incorrect or incomplete.
Possible reasons: Database data update delay, data was extracted to BI before the update was complete, requiring re-extraction.
For example: MySQL extraction dataset data for 2021-02-21 is incomplete and needs to be updated again for that day.
Recommended Method
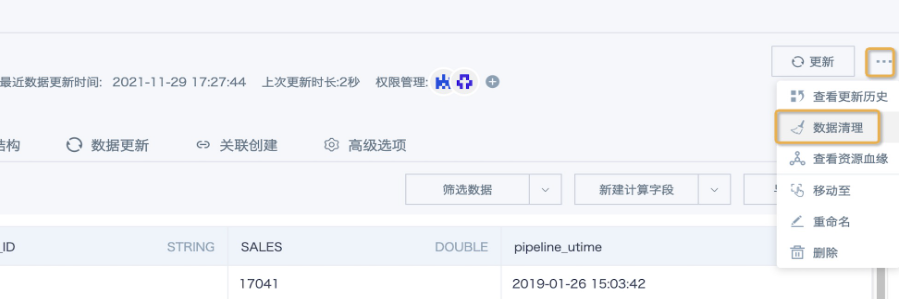
- Enter the dataset overview page, click the menu (…) after the "Update" button, and find "Data Cleanup".
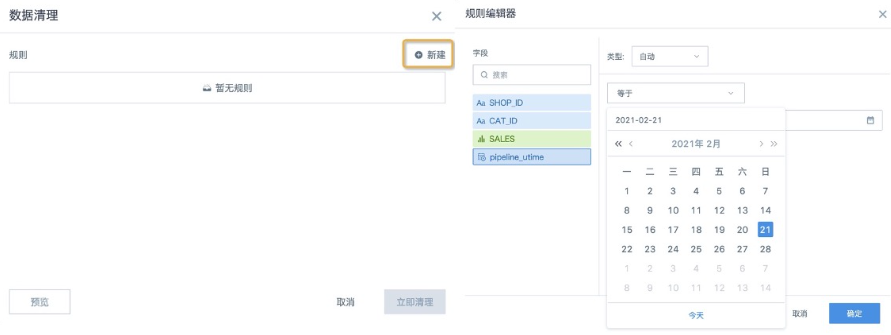
- Click "New Rule", then select the time field, choose the time range for data cleanup, and click "OK" to save.
Note: Date-time type fields can be cleaned by date (day), and the cleanup range cannot be precise to hours, minutes, and seconds.
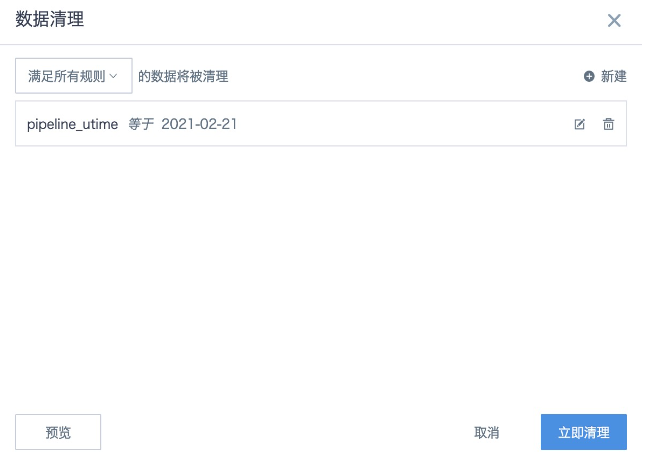
- Click "Preview" in the bottom left to confirm the data, then click "Clean Immediately", and the data for 2021-02-21 will be deleted.
- Click the update button again, and directly modify the original SQL where query condition in the SQL input box.
If the original date field format is date-time (timestamp/datetime), you need to first convert it to date format using the corresponding database function, then compare with the date; of course, you can also compare date-time with date-time, as long as the field types are consistent.
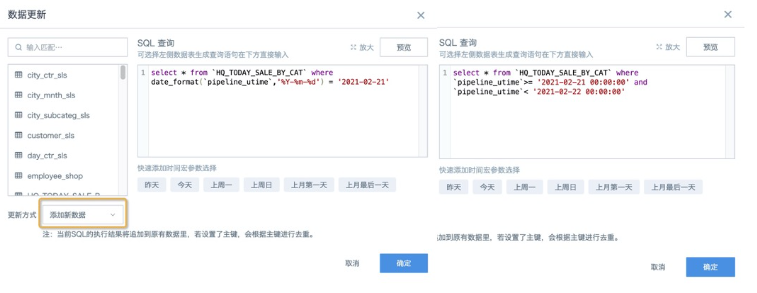
- After previewing the data and confirming it's correct, ensure the update method is "Add New Data", then click "OK" to trigger the dataset update.
At this point, the historical data has been replaced and updated. If there are associated ETLs, you need to re-run the ETL so that the final card data will be updated.
❌ Not Recommended Methods
- Skip "Data Cleanup", directly click the update button, modify SQL, hoping to overwrite historical data through deduplication primary key.
Reason: Deduplication primary key can freely select fields, which may not ensure complete identification of duplicate data and deletion of original historical data. The data retained in the dataset after update may not necessarily be the latest data.
- Directly modify the SQL in the model structure.
Reason: Modifying the SQL in the model structure will cause the original data to be cleared and then re-extracted. For large data volumes, the update time will be very long.
- Directly modify the SQL in incremental updates.
Reason: Once the date condition is modified and updated, you must manually modify the incremental update SQL statement again, which is equivalent to operating twice. If forgotten, subsequent updates will only incrementally update historical data instead of the latest data.