Dataset FAQ
1. Overview
This article introduces common issues with the multi-source data integration module datasets in Guandata BI.
2. Dataset
Why don't the set row and column permissions take effect for dataset owners?
Problem cause: The user is the owner of the dataset and has not checked "Whether the above row and column permission settings take effect for dataset owners and managers" below.
Solution: Row and column permissions are a very practical function for controlling data security. After setting row and column permissions, all resources involved with the dataset will be affected, including but not limited to cards, datasets, ETL operations, etc.
What's the difference between direct connection and guan_index extraction?
(1) Direct connection queries the database directly, suitable for scenarios requiring high real-time query performance; guan_index is extraction, which first extracts data from the database to the BI platform, then processes and calculates directly on the BI platform, suitable for scenarios with low real-time requirements.
(2) When writing functions for calculation in cards of direct connection datasets, use the syntax of the corresponding database; extraction datasets should use Spark syntax.
(3) Direct connection cannot use ETL.
What syntax should be used when using BI?
-
Creating database datasets: Use the syntax of the corresponding database when creating database datasets.
-
Creating new calculated fields or setting row and column permissions: Direct connection datasets/cards: Use the syntax of the corresponding database; Extraction datasets/cards: Regular types use Spark syntax; High-performance datasets use ClickHouse syntax;
-
Creating new calculated fields/SQL input nodes in ETL use Spark syntax.
How to exclude unwanted columns in SQL queries
Background: Don't need to query all fields (select *), and when there are join operations, creating a dataset cannot use select *, which will cause an error "some field is not unique in Record" because the platform doesn't allow duplicate field names, so duplicate fields must be excluded. However, sometimes there are many fields, and listing them all in SQL is tedious work.
Solution: Query all fields in the database connection tool; then copy only the field names that need to be retained.
Taking MySQL as an example, use Navicat tool for querying. The query statement is as follows, and the results will be automatically separated by commas for easy copying.
SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(COLUMN_NAME SEPARATOR ",") FROM information_schema.COLUMNS
WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = 'db_name' AND TABLE_NAME = 'tb_name';
db_name: database name
tb_name: table name
Why doesn't modifying column names with SQL in the dataset model structure take effect?
Field association is enabled by default. Just select "No Association" for the target field.
The dataset ID has been obtained, which table can be associated with the Chinese name of the dataset?
The Chinese name of the dataset is in the built-in dataset builtin_data_source.
Why does the same row permission condition setting report an error when copied from one dataset to another?
Problem cause 1: Row and column permissions take effect only in the corresponding database, and different databases use different SQL functions.
Solution: For example, GuanIndex datasets correspond to the Spark computing engine, while direct connection datasets correspond to the customer's database. Please edit appropriate SQL filtering conditions according to the corresponding database.
Problem cause 2: The target dataset lacks fields used in the row permission conditions, causing system validation to fail.
Solution: Modify the permission conditions to ensure the fields exist in the target dataset.
Can API uploaded data datasets specify the folder to store the dataset?
Cannot specify during API upload. By default, it's stored in the root directory. After successful upload, you can move it to your desired location.
What's the difference between manual table append data and replace data?
(1) Replace data has two types:
a. When replacing data, if the fields existed before, when you replace data and upload the dataset, it will pop up the replace data dialog according to the position of the field you want to replace, not according to the order of the Excel you uploaded.
b. When replacing data, if the fields don't exist, then the newly added column will be at the end.
(2) Append data: Appended data adds data rows under the existing column fields.
Manual table append data, using exactly the same dataset to append, and selecting deduplication primary key, why does the data volume expand?
Problem cause: The field selected as the deduplication primary key may contain null values. Null values cannot be judged as duplicates, so they are all retained, causing the data volume to expand.
Solution: Fields containing null values must not be used as deduplication primary keys, whether for manual table append data or dataset incremental update primary key deduplication.
When uploading manual tables to create datasets on Guandata BI, can compressed files of Excel and CSV be used?
(1) When selecting Excel file type during upload, Excel compressed files cannot be uploaded.
(2) When selecting CSV file type during upload, Excel compressed files can be selected when choosing files, but it will prompt upload failure. CSV compressed files can be uploaded successfully. CSV supports uploading compressed packages (zip files) and supports automatic parsing.
What's the shortest interval refresh time for guan_index extracted data?
Automatic scheduled updates can be done up to 4 times per day. You can set the dataset update frequency according to business needs.
If higher real-time requirements (such as checking data every 15 minutes), consider using direct connection, which has higher real-time performance, but note that ETL cannot be used.
If datasets are updated too frequently, the following risks may exist:
(1) Data quality: Frequent data updates may lead to decreased data quality. Large amounts of data updates in a short time may cause data errors or missing data. Ensure data accuracy and completeness;
(2) System performance: Frequent data updates may negatively impact system performance. Each update consumes system resources. If the update frequency is too high, the system may run slowly or even crash. Evaluate system performance and resource consumption;
(3) Database pressure: Frequent data updates consume a lot of database computing resources, computing time, and response time. Reduce pressure on the database to reduce the overall impact on the system.
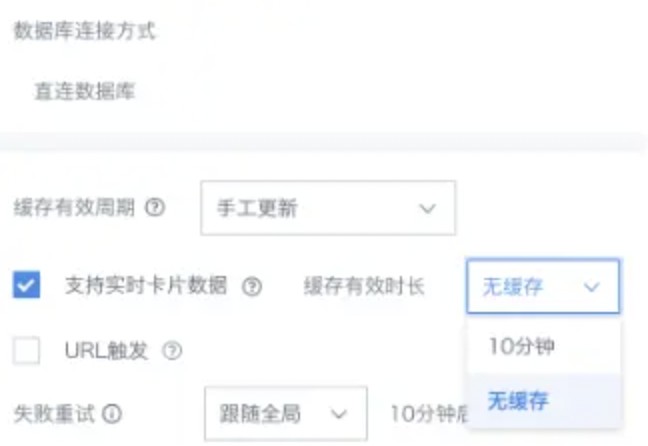
Direct connection databases also follow cache validity periods. Should URL triggering be checked?
(1) Direct connections generally query the database directly, but if every query goes to the database, the database pressure will be very high, so we have a caching mechanism.
(2) The caching mechanism is that only when cards have the same query SQL and the cache version hasn't expired can the cache be hit.
(3) URL triggering is just an external trigger update mechanism. Regardless of which update method triggers the update, if the dataset is updated, the cache version number will be refreshed.
(4) If high real-time requirements are needed, you can check "Support real-time card data". When real-time card support is selected, if you need to reduce some database pressure, you can adjust the default cache validity time.
Can tables from two data accounts be joined?
Tables across databases in the same data account can be associated in the dataset model structure, but cross-data accounts cannot. It's recommended to extract separately and then use ETL for table association.
After manual table (CSV, Excel) replace data operation, why do extra columns still exist?
Problem cause: Originally existing numeric columns won't be directly deleted. After replacing with a new table, if association is set, the original columns will be directly replaced by the new associated fields, but if there's no association, the column will become null values. Direct column deletion is not currently supported.
If the calculated field logic is written into the dataset SQL, can it shorten query time?
Example scenario:
Currently, a dataset with less than 1 million records takes over 10 seconds to query. The dataset SQL queries on the big data platform in less than 1 second. In Guandata, dozens of year-over-year calculated fields are added, using functions like sum.
The data should be using direct connection datasets. Time includes three parts: fetching data from the database, calculation time in BI (such as adding dozens of year-over-year calculated fields, using functions like sum), plus card style rendering time.
If complex calculations are placed in SQL, the time for fetching data from the database will be extended. To fundamentally solve this problem, these complex calculated indicators should be pre-calculated in the underlying data warehouse, and direct data fetching operations should be performed here. (It's a bit of a trade-off)
Want to batch get all table names in a dataset
The dataset's model structure can view the dataset's SQL information, which shows which table the dataset uses.
Batch operations can be done through API. To see the database table corresponding to the dataset, you need to look at the dataset's query information. The method can be referenced:
How to determine if a dataset table is "full update"?
The update method can be seen on the dataset update page. As long as incremental update is not checked and there's no time condition limit in the SQL statement, it's a full update.
If full update: Note ⚠️ If the data structure in the customer's ERP hasn't changed, it will be updated. If field names or quantities change, the changed parts won't be updated;
Full update is only based on the originally extracted fields for full update. Newly added columns won't be automatically updated;
(1) If fields have changed, re-update is needed.
(2) If there are no field updates, only content changes, re-update is not needed.
Do read-only users not have the CSV export function for datasets?
Read-only users only support exporting Excel, not CSV. Additionally, cards of direct connection datasets for regular users and owners can only export Excel.
When setting column permissions for datasets, on the dataset overview page, users without permissions can only see null data under that column. Can columns without permissions be directly hidden?
The dataset details page itself is meant to display the complete data structure. If hidden, there will be information asymmetry issues (it says 10 columns above, but below, due to lack of column permissions, only 5 columns can be seen, which is more likely to cause misunderstanding, thinking the system has bugs). If made into a table card, if there's no column permission for that column, the column field will be hidden, so it doesn't affect actual usage.
Why aren't real-time uncached card alerts for direct connection datasets triggered?
Problem cause: "Support real-time card data" is checked, but the "Real-time data" switch is not turned on on the page. If the page is not accessed, the page data won't be updated, so alerts won't be triggered.
Do datasets support "Save As"?
Yes, you can turn on the switch in "Administrator Settings/System Settings/Advanced Settings/Allow Dataset Save As".
After adding primary key, why doesn't the data retrieval amount match the original data quantity?
Problem cause: Are there many null rows in the primary key? If the deduplication primary key has nulls and the column is numeric type, all null rows will be discarded, causing data reduction.
Solution: It's recommended to handle nulls first before extraction, or do a full update.
When uploading datasets, can duplicate names be uploaded?
Datasets with the same name are not supported in the same folder, but two datasets with the same name are allowed in different folders.
Can the connection method be changed after the dataset is created?
No.
When creating a new database dataset, using nested IF functions, why does preview fail?
Problem cause: Due to the high time complexity of nested IF functions, which grows exponentially, if multiple nested IF SQL statements are used in the preview interface, it's very likely to cause preview timeout.
Solution: It's recommended to use case when instead of nested IF functions.
What are the default concurrency numbers for ETL, cards, and datasets?
ETL automatic tasks default to 1 concurrency; dataset automatic tasks to 4; card concurrency: extraction defaults to 10, direct connection unlimited;
This is the default setting. If you previously applied for concurrency adjustments, the actual modified values will apply. Administrators can enter Administrator Settings--Operation Management--Parameter Configuration page to modify ETL concurrency; if you want to adjust card and dataset concurrency, you can provide feedback to after-sales support, and after evaluation by R&D and operations, the modification will be executed. This parameter doesn't support customer custom modification.
BI system dataset update queue is very large, unable to load pages
This is usually caused by large tasks running and blocking other tasks. You can check the task management page to see what the longest running task is. After canceling the longest running task, the system will generally automatically recover.
Dataset preview has data, update is successful but no data, but the dataset shows n rows and n columns
It's recommended to troubleshoot from the following aspects:
(1) Whether the dataset has set filtering conditions;
(2) In the dataset's data permission module, whether permission control is set, row permissions are enabled;
(3) If row/column permissions are enabled and the switch "Whether to take effect for dataset owners and administrators" is turned on, then even administrators without row and column permissions cannot see data.
For view dataset updates, do they automatically update when the selected datasets update? Does this need additional settings?
View dataset updates mainly refer to updating the model structure SQL. When upstream datasets are updated, data views will also be updated.
Card dataset update method
Prerequisite: Dataset a creates card b, and card dataset c is created based on card b.
(1) Regarding card dataset structure: If card b is modified, card dataset c won't automatically sync and needs manual update to sync.
(2) Regarding card dataset data content: When the original dataset a is updated, it will trigger data update of card dataset c.
What's the difference between real-time card data for direct connection databases and the paid module's real-time data?
(1) Real-time card data for direct connection databases is near real-time: Select "Support real-time card data", dataset cache validity time supports no cache, achieving near real-time page card data effects. However, this processing method puts great pressure on the business database and cannot achieve multi-source data fusion.
(2) The paid module's real-time data is Lambda architecture and can support simple pre-made calculations like year-over-year comparisons: Separating historical data and real-time data processing, it can achieve multi-source data fusion and support incremental updates while occupying fewer computing resources.
From an operational perspective, Guandata's built-in "Direct Connection Data" configuration is more convenient, while the paid "Real-time Data" module has a certain learning curve.
After uploading data via API, it shows success but there's no data in the dataset
Problem cause: "batchFinish": false /* Optional, defaults to false. When uploading in batches, indicates whether this is the last batch. When set to false, row count is not updated, nor is card cache refreshed */
Solution: Add "batchFinish": true to the request parameters. If not added, it defaults to no update.
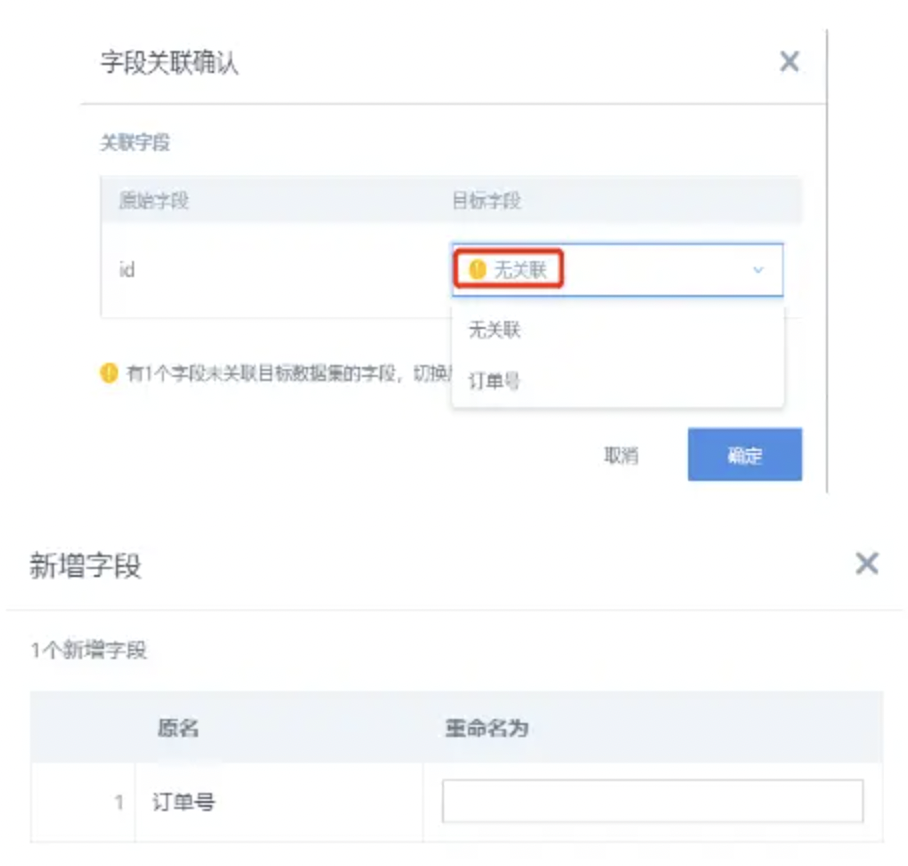
Using SQL to modify column names in model structure, but it doesn't take effect
Problem cause: There's field renaming in the data structure.
Solution:
(1) [Recommended] Rename fields in the data structure/or change to empty (default is the field naming in the model structure statement)
(2) After modifying the model structure, select "No Association" in the association dialog, then rename the field in the next dialog.
Differences between different incremental update methods
Prerequisites for incremental updates:
-
The data source (database) stores the creation time or update time of each record;
-
There's a non-duplicate primary key column.
(1) When deduplication primary key is not set
Add new data: Incremental update extracted data will all be treated as new data.
Overwrite old data: Will clear original data, and the updated data will be the data queried by the incremental update statement.
(2) When deduplication primary key is set
Add new data: If the incremental update extracted data has duplicate primary keys with existing data, the incremental update extracted data will be overwritten. Other extracted data will be treated as new data.
Overwrite old data: Will clear original data, and the updated data will be the data queried by the incremental update statement.
When creating datasets, what's the maximum file size supported for uploading related data via Excel
In version 7.1, when creating new datasets, uploaded Excel (xlsx) files cannot exceed 500M, old version Excel files like xls cannot exceed 5M (and the maximum number of rows cannot exceed 1,048,576 rows of data); CSV files (can be compressed into zip) cannot exceed 500M.
Do ETL datasets support modifying field names and field types in Data Overview-Data Structure?
When field names and types of ETL datasets need to be modified, it's recommended to edit directly in ETL; you can create new calculated fields/grouping fields, and newly created fields can be edited.
How to extract fields from Web Service datasets?
(1) First observe visually (or with JSON tools), check the structure of the returned data, and identify the specific child nodes where the fields to be queried are located. For example, in the figure below, you can see that refund_order is under data, and in BI, the path can be written as $.data.refund_order[*] to get the fields in refund_order.

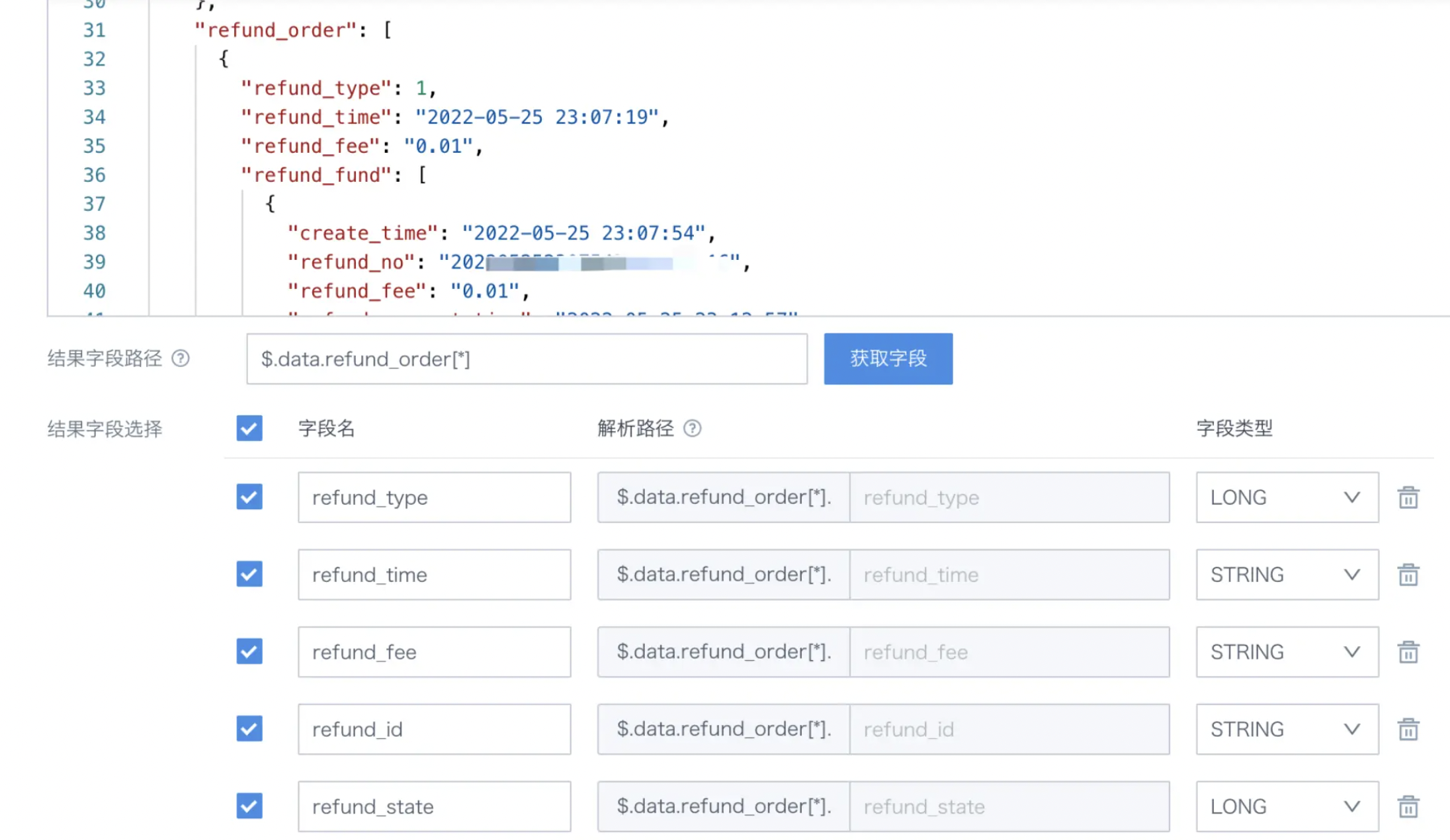
(2) How to get fields from refund_fund
Currently, Guandata BI doesn't support directly splitting nested arrays in JSON, so when getting fields from refund_order through $.data.refund_order[*], refund_fund will be treated as a complete text field for extraction. After the dataset is created, you can use ETL with functions to extract the values of various fields in refund_fund. For details, please refer to Using ETL to Parse JSON
In table cards, the primary key has no null values, but in datasets output through feedback forms/knowledge feedback, there are historical data with null values in the primary key field
Problem cause: The feedback record's submitter lacked data permissions for that primary key at the time. That is, the dataset that the table card depends on has column permissions enabled, and the feedback user was set to have invisible fields.
Solution: Modify the dataset column permissions; or handle null values through ETL.
Why do text fields in datasets display as garbled characters?
[Cause]: The user's database uses character encoding that's not the UTF-8 encoding that BI uses by default. After dataset updates, BI directly reads this incorrectly encoded data. Below are 4 common scenarios where Chinese character garbling occurs:
| Garbling Example | Cause | Characteristics |
| ¹ÛÔ¶Êý¾Ý | Reading GBK encoded text with ISO-8859-1 | Usually English letters with superscripts |
| Զ | Reading GBK encoded text with UTF-8 | Usually question marks with black boxes |
| 瑙傝繙鏁版嵁 | Reading UTF-8 encoded text with GBK | Usually rare traditional characters |
| è§è¿æ°æ® | Reading ISO-8859-1 encoded text with UTF-8 | Contains lowercase Western letters and some symbols |
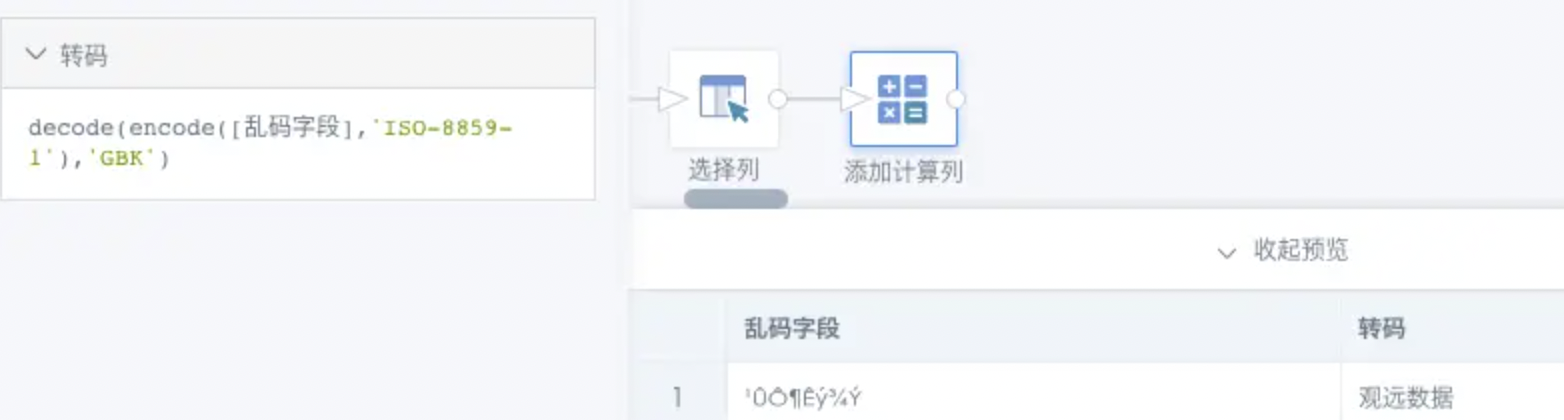
Solution: Modify the source database's character encoding to UTF-8; if locating and modifying the data source is difficult, you can also re-encode this part of the data in BI: First filter out problematic data; locate what type of garbling this part of the data is; then use decode(encode([field_name], 'type1'), 'type2') in new fields to re-encode the data.
Example: Taking "¹ÛÔ¶Êý¾Ý" as an example, it was generated by reading GBK encoding with ISO-8859-1, so the corresponding field needs to be re-encoded to ISO-8859-1 format, then decoded with GBK format. The corresponding new field type would be decode(encode([field_name],'ISO-8859-1'),'GBK'), as shown in the figure:
Do data accounts support SSL certificate access?
For security considerations, Guandata supports mounting SSL certificates for some databases. If needed, please contact your dedicated Guandata after-sales engineer or account manager for further communication and processing.
After updating License, all scheduled tasks don't run automatically
Problem description:
After the old License expires, update the License, then all scheduled tasks (such as datasets, ETL, subscriptions) don't trigger automatically; after environment migration, activating the new environment License, all scheduled tasks become invalid.
Problem cause:
After the License expires and becomes invalid, the BI service will terminate, and all scheduled tasks will terminate. Even after reactivating the License, scheduled tasks won't trigger automatically. For BI 5.3.0 and all subsequent versions, after activating the new BI environment, guandata-server must be restarted, otherwise scheduled tasks become invalid.
Solution:
After reactivating the License, contact Guandata service personnel to restart the entire BI service.