Audit Log
1. Overview of Audit Log
The audit log is a functional module that helps enterprise IT and information security personnel understand the secure operation status of the BI system.
By providing an interface-based system audit log, users can efficiently search and query audit log data, and administrators can download audit logs for further analysis. This helps users identify attacks and intrusions against BI, as well as internal violations and information leaks, and provides necessary information for post-incident analysis and investigation.
2. Audit Log Usage Scenarios
-
Daily security audit, perceiving system security status
As IT/information security personnel maintaining the BI system, you need to regularly know which IP each user uses to access the system, whether there are multiple login attempts from the same IP in a short period, etc.
-
Incident investigation and accountability
As IT/information security personnel maintaining the BI system, if a user reports that a previously accessible dashboard no longer exists, you can use the audit log to find out who deleted the dashboard or removed the user from the dashboard visitors.
-
Enterprise-level security audit, administrator insight
As an enterprise manager, security auditing is crucial for the company's fate. You need clear management and insight, and hope to view audit logs in the "Management Center" for easy O&M management.
3. Instructions for Audit Log
-
Supports fuzzy queries by operation object, operator, and time.
-
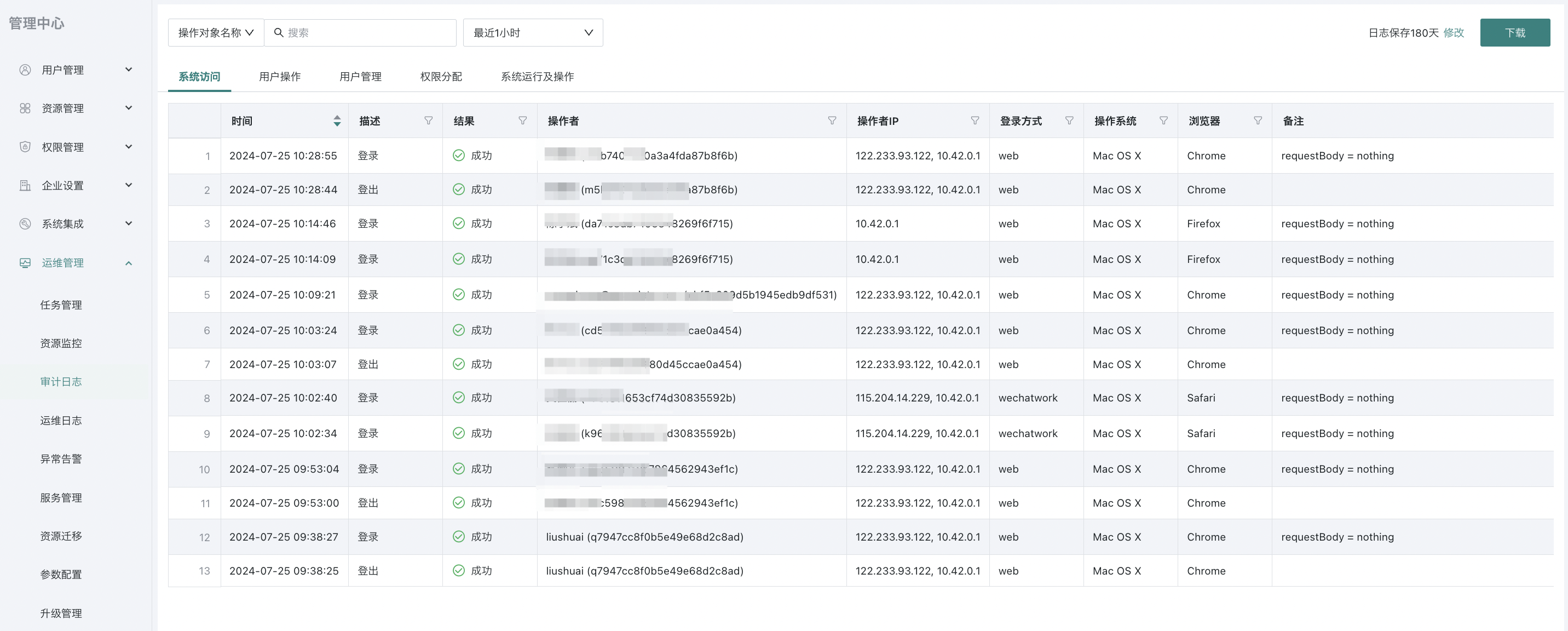
Currently includes system access records, user operations, user management, permission assignment, and system operation records:
-
System access records: Record user access to the system, including successful login, logout, and failed login logs;
-
User operation records: Record user operations on resources, including creation, modification/editing, moving/deleting, export, and export file size and row/column count, etc. Resources include cards, pages, datasets, ETL;
-
User management records: Record logs related to user management, including user and user group operations such as creation, editing, deletion, etc.;
-
Permission assignment records: Record logs related to user and resource permission assignment, including user, user group, page, folder, dataset, and ETL permission assignment logs;
-
System operation records: Record system-level operation logs, including data export switches, domain update export data whitelist logs;
-
System integration records: For enterprise-level management, administrator operations in the "Management Center - System Integration" menu are also tracked and monitored and recorded in the audit log.
Log download and retention period settings:
-
Administrators can export all types of log details after retrieval and query, exported as Excel files;
-
Administrators can set the log retention period: unit is days, minimum is 30 days, maximum is 360 days;
-
It is recommended to set the log retention period within a reasonable range. If the retention period is too long, it will occupy server storage space.
-
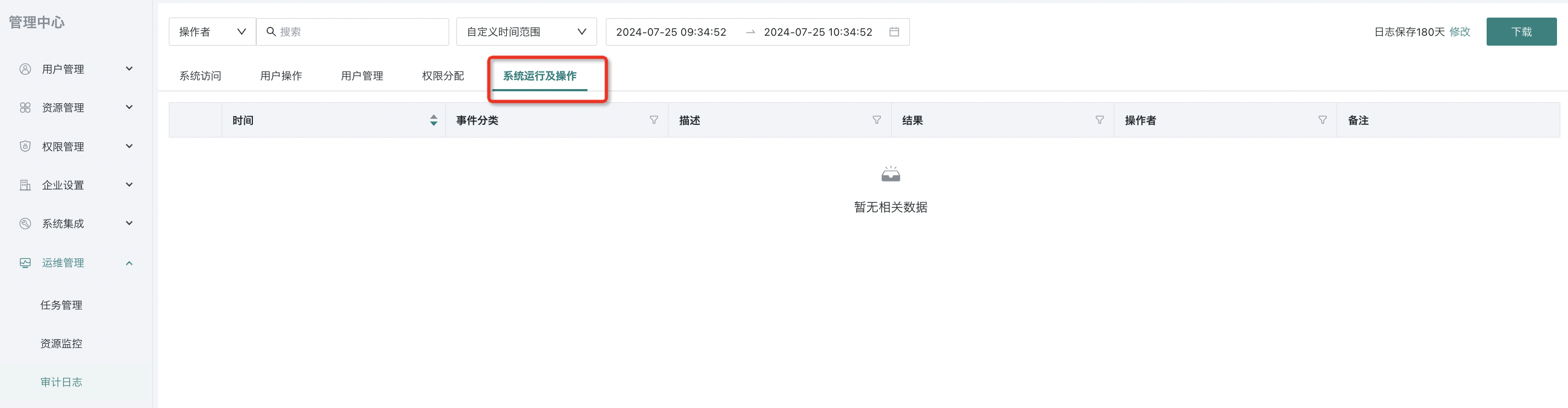
- Administrator operation viewing:
Administrator operations in the "Management Center > System Integration" menu are recorded as audit logs and displayed in "Management Center > Operation & Maintenance Management > Audit Log" under "System Operation Records". Administrators can view them in time to grasp the audit situation.
4. Notes on Audit Log
-
The rule for writing audit log data to the database is: every 5 minutes (based on the server's last startup time) or when 500 rows of data are accumulated.
-
Since the server will mask the real IP address by default, the operator's IP may not be the real IP address. If you need to obtain the real IP address of the operator, please contact Guanyuan business/Guanyuan assistant.
-
If the log retention period is changed from large to small, such as from 60 days to 30 days, the system will automatically clean up expired logs at midnight, and this operation is irreversible. Please operate with caution.