Smart ETL Advanced Calculation
1. Data Exploration
Function Description: During the development process of Smart ETL (hereinafter referred to as ETL), it is often necessary to view statistical information of datasets, such as: number of data rows, number of unique values for a field, number of Null values, etc. These often require manual configuration using multiple operations such as "Filter Data Rows" and "Group Aggregation". To simplify the process, Guandata has recently added a "Data Exploration" operator in ETL, which can output dataset statistics at once, improving data processing efficiency.
Specific operation: Enter the ETL editing interface, find Data Exploration under the "Advanced Calculation" category in the left operation bar, drag it into the editing area, connect the relevant data processing operators to Data Exploration, and click to set it.
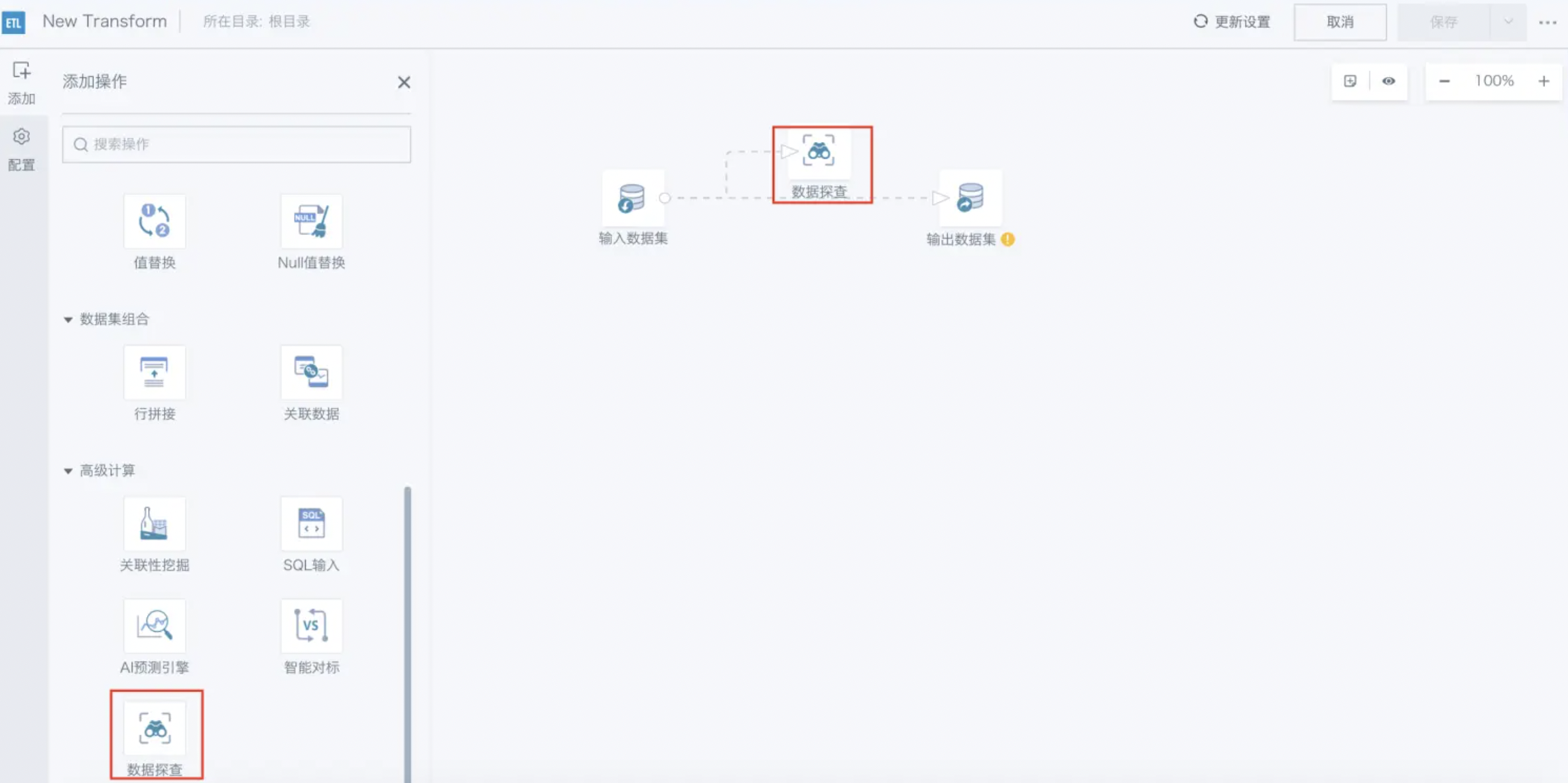
Select the dataset information to be counted. At the table level, you can count the number of rows and columns in the dataset; at the field level, first select the fields to be counted, and you can count the number of Null values, unique values, and enumerated values (up to 200 enumerated values) for a field. Click Query at the bottom of the editing area to view the dataset statistics.
2. SQL Input
SQL Input operator helps data analysts who are accustomed to using SQL statements to output datasets through SQL, shortening the configuration process.
To help ETL visitors view details more clearly, the field expression content of the SQL Input and Add Calculated Field operators in ETL supports external display.
[Why do some field types change when previewing SQL nodes in ETL?](../../../../11-FAQ/1-Data Processing/2-ETL FAQ.md)
[Can custom time macros be used in SQL operators?](../../../../11-FAQ/1-Data Processing/2-ETL FAQ.md)
Function Description: Use SQL to query, extract, and merge data.
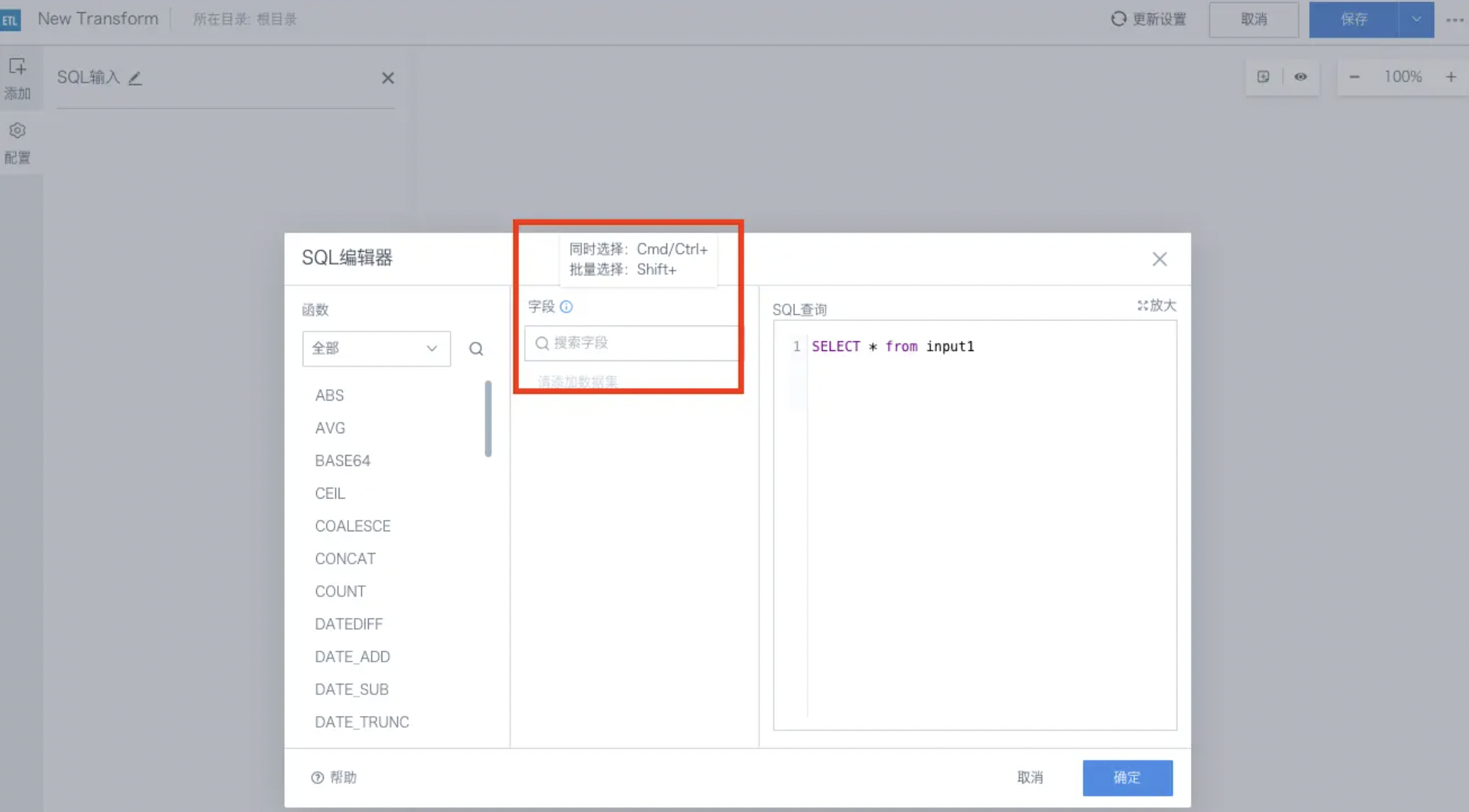
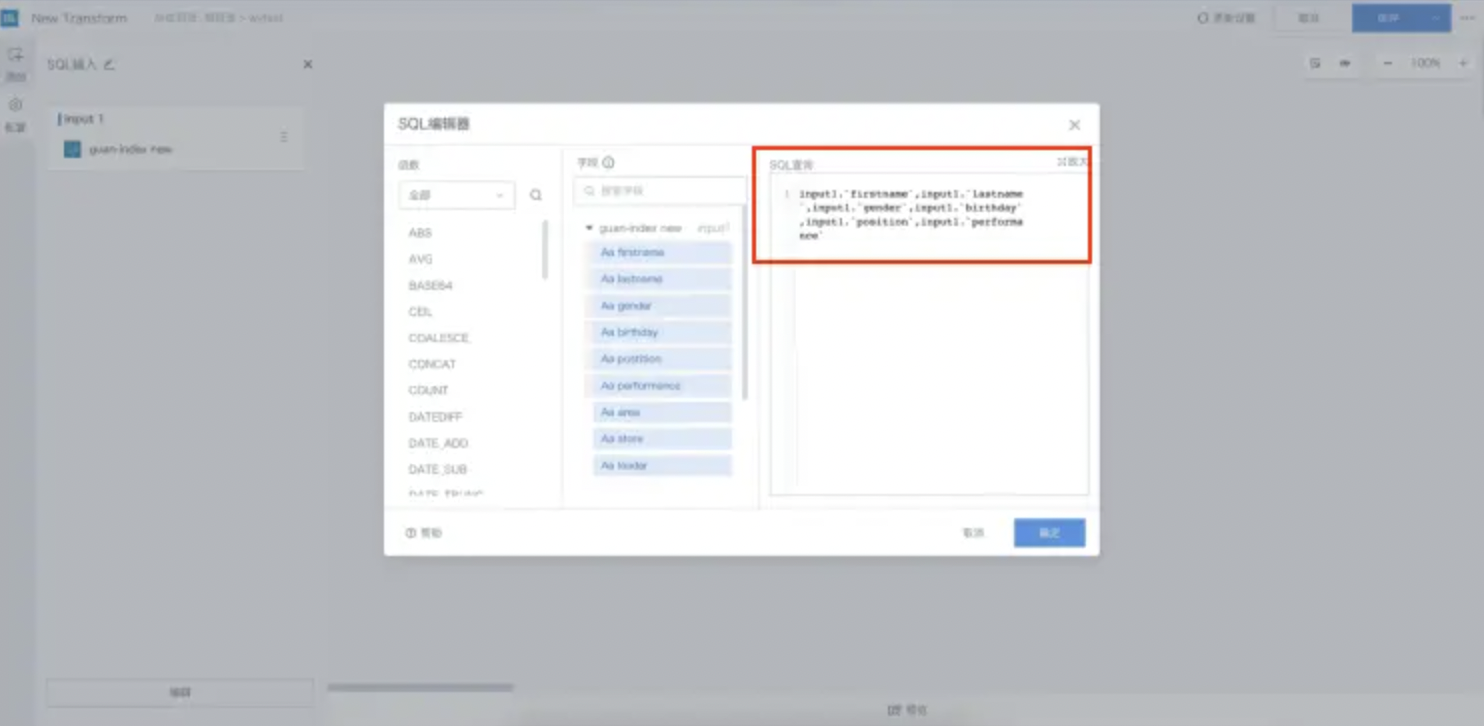
Configuration Description: Drag the SQL Input operator into the canvas, select the node, and then click the Edit button. You can refer to relevant examples to introduce functions, fill in field names, and click the OK button.
At the same time, when selecting fields to add to the SQL editor, you can select multiple fields at once ("shift" for continuous selection, "cmd" for jump selection).
Specific operation: In the Field Bar, click the first input field, then hold down the shift key and select another, which will fill multiple fields into the query box and automatically complete the separator between fields, cmd works similarly.
3. Association Mining
Association Mining operator helps data analysts quickly implement association mining algorithms to find items with high correlation within the data. (This function is a paid module and is not open by default. Please contact Guandata sales for trial or purchase if needed)
4. Smart Benchmarking
Smart Benchmarking operator allows users to specify the main category, related category features, and the number of adjacent subjects, and can automatically obtain the comparison items (comparison stores) for each subject (store), displaying them in a list. (This function is a paid module and is not open by default. Please contact Guandata sales for trial or purchase if needed)
For subsequent use of other data processing operators, see Getting Started.
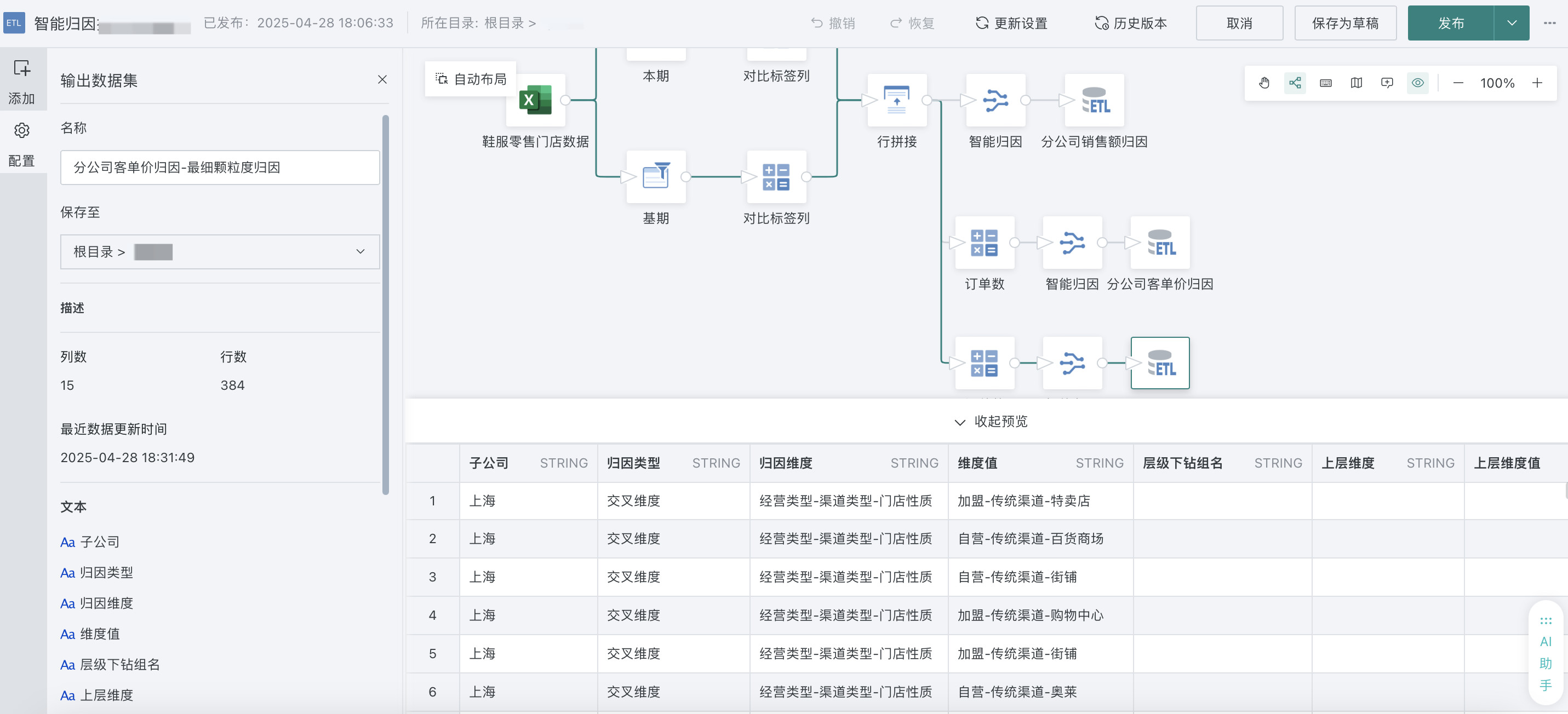
5. Smart Attribution
Function Description
Key indicator attribution is often a comprehensive attribution involving multiple dimensions, cross-analysis, drill-down, indicator decomposition, target achievement gap analysis, and correlation indicator significance analysis. To achieve such complex scenario attribution analysis, Guandata provides the Smart ETL Attribution operator for attribution calculation, and then uses Smart ETL for further data processing and integration, providing ADS layer data for front-end data products.
Attribution principles follow:
- Atomicity: Focus on the basic atomic attribution capability of comparing two sets of data, without considering original data filtering, year-on-year, month-on-month, target comparison, horizontal comparison, etc. (these are provided by other operator capabilities in Smart ETL).
- Standardization: Provide standard dimension decomposition attribution and indicator decomposition attribution capabilities. The calculation process is black-boxed. Users only need to understand the attribution chain and get standard attribution results without caring about the calculation process.
- Batch Processing: Compared to front-end ad-hoc attribution, the Smart ETL Attribution operator needs to provide batch attribution capability, completing attribution analysis for different periods and granularities at once, materializing the attribution result data.
Configuration Description
Drag the "Smart Attribution" operator into the canvas, click the node, and configure smart attribution on the left side of the interface.
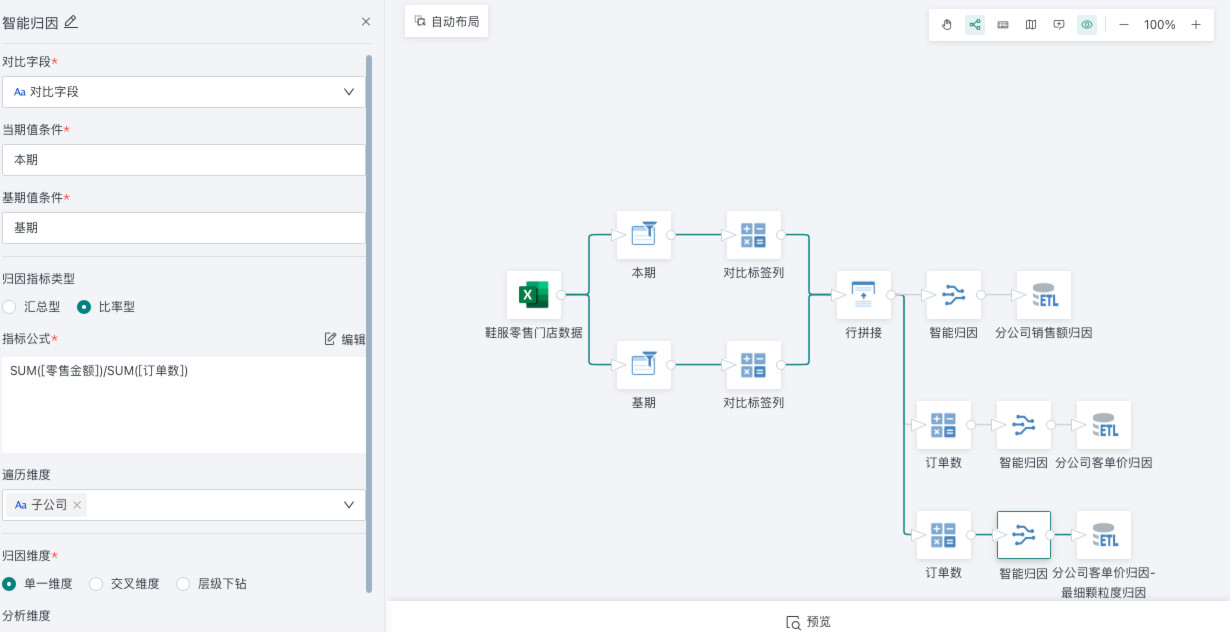
| Configuration Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Comparison field, current value condition, base value condition | Select the comparison field, and enter the conditions for the current and previous values according to the selected field |
| Attribution indicator type | The key indicators to be analyzed and monitored in this attribution. |
| Indicator formula | Click "Edit", select functions and fields, and configure a calculation formula for the main indicator |
| Traversal dimension | Select traversal dimensions, multiple selections supported |
| Attribution dimension | Supports three types of dimension attribution, cannot include traversal dimensions |
Effect Preview
Select the attribution result dataset you want to view, and click "Preview" below to view the attribution results.