Smart ETL Dataset Combination
This document introduces the functional description and specific operations of dataset combination in Smart ETL.
1. Row Concatenation
1.1. Functional Description
Business data of the same type may come from different subsidiaries or stores. Even within the same organization, there are datasets from different data sources. For example, supermarkets have multiple payment methods: cash, UnionPay, mobile payment, etc., resulting in a variety of datasets for decision-makers and IT departments. Row concatenation allows you to combine data from different sources for the same business.
In practice, first use the "Select Columns" operator in column editing to standardize a batch of data and use it as the standardized dataset. Other business data can be integrated into a more standardized and comprehensive dataset through the "Row Concatenation" operator.
Example:
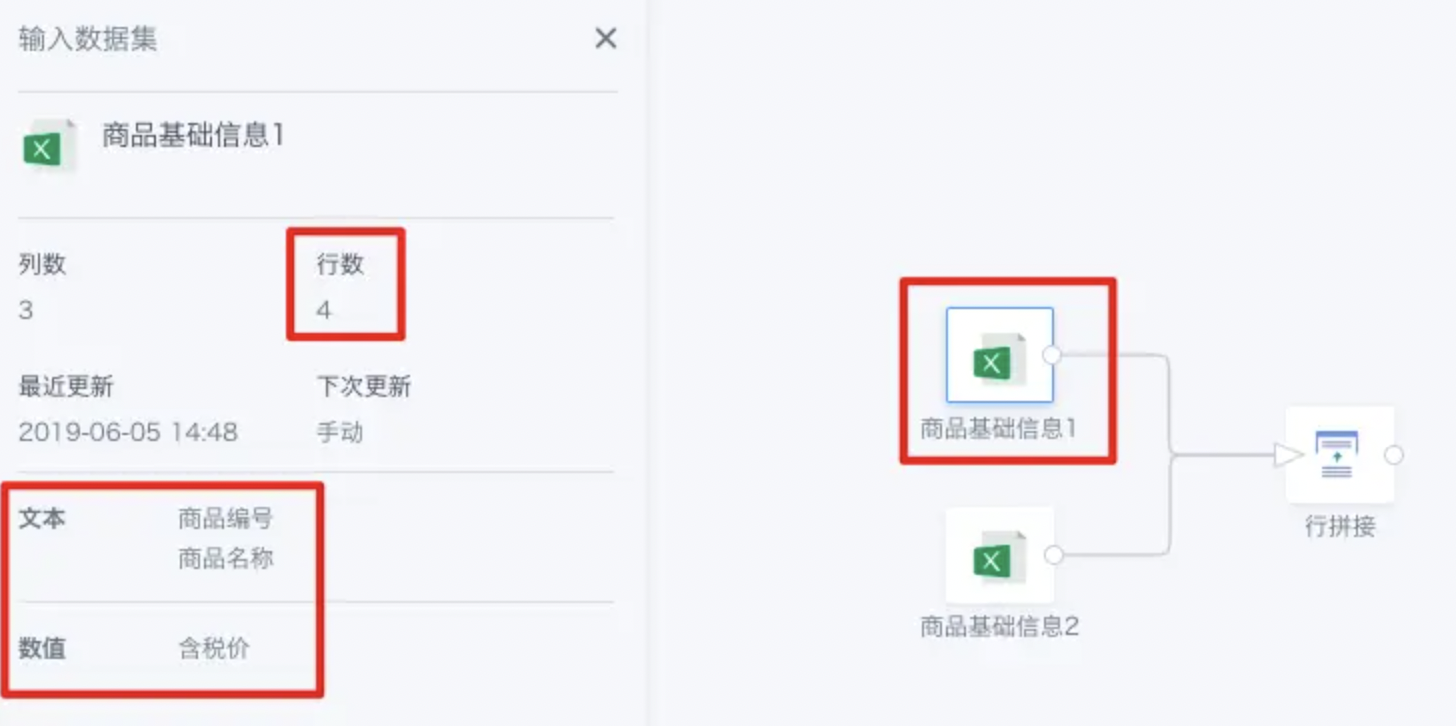
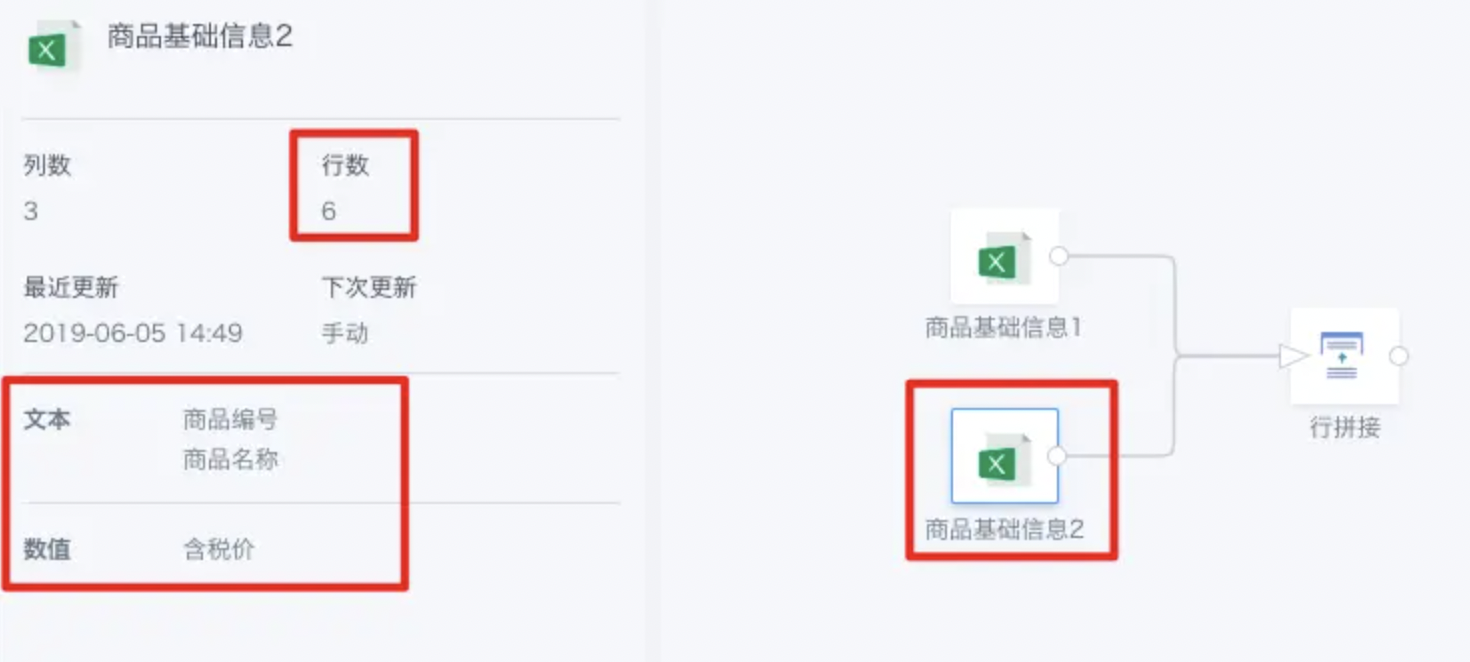
As shown above, there are two datasets from different sources, but the fields are exactly the same.
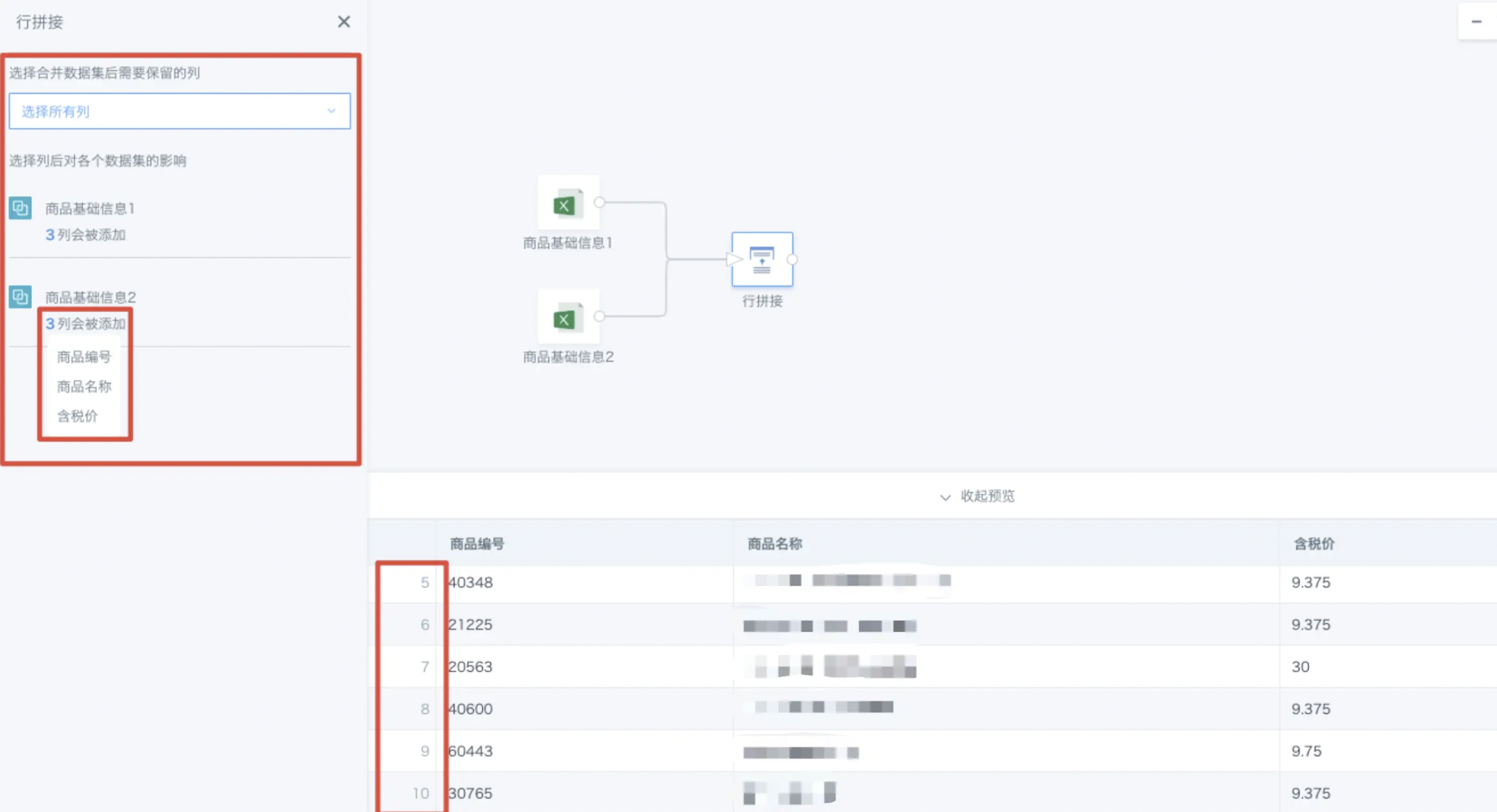
When performing row concatenation, you can choose which columns to keep, such as keeping all columns, only common columns, or all columns from any dataset.
After obtaining the concatenation result, you can click the number under a dataset in the upper left area to see which fields are retained for that dataset.
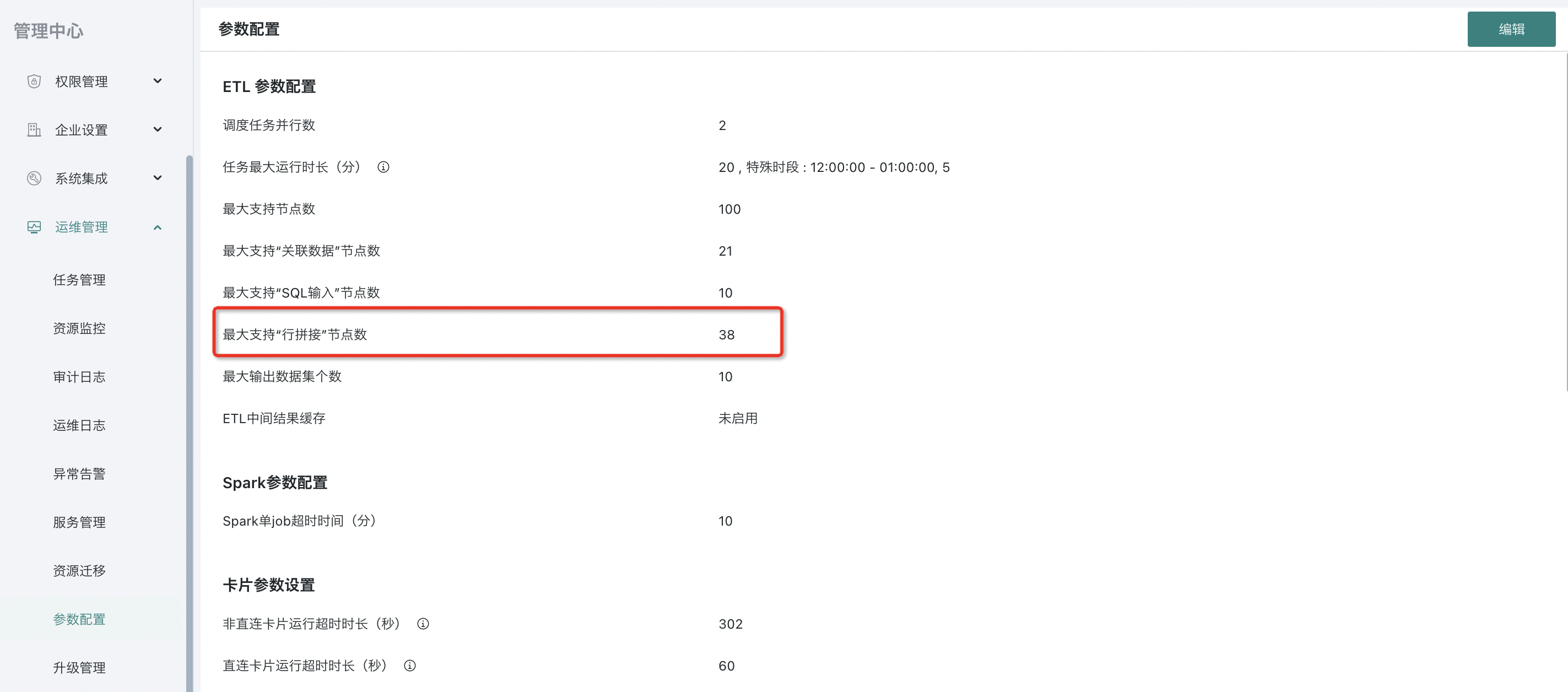
1.2. Node Number Setting
In ETL creation, a node number configuration function is provided for Row Concatenation. Standardizing ETL creation can avoid system operation exceptions caused by improper operations.
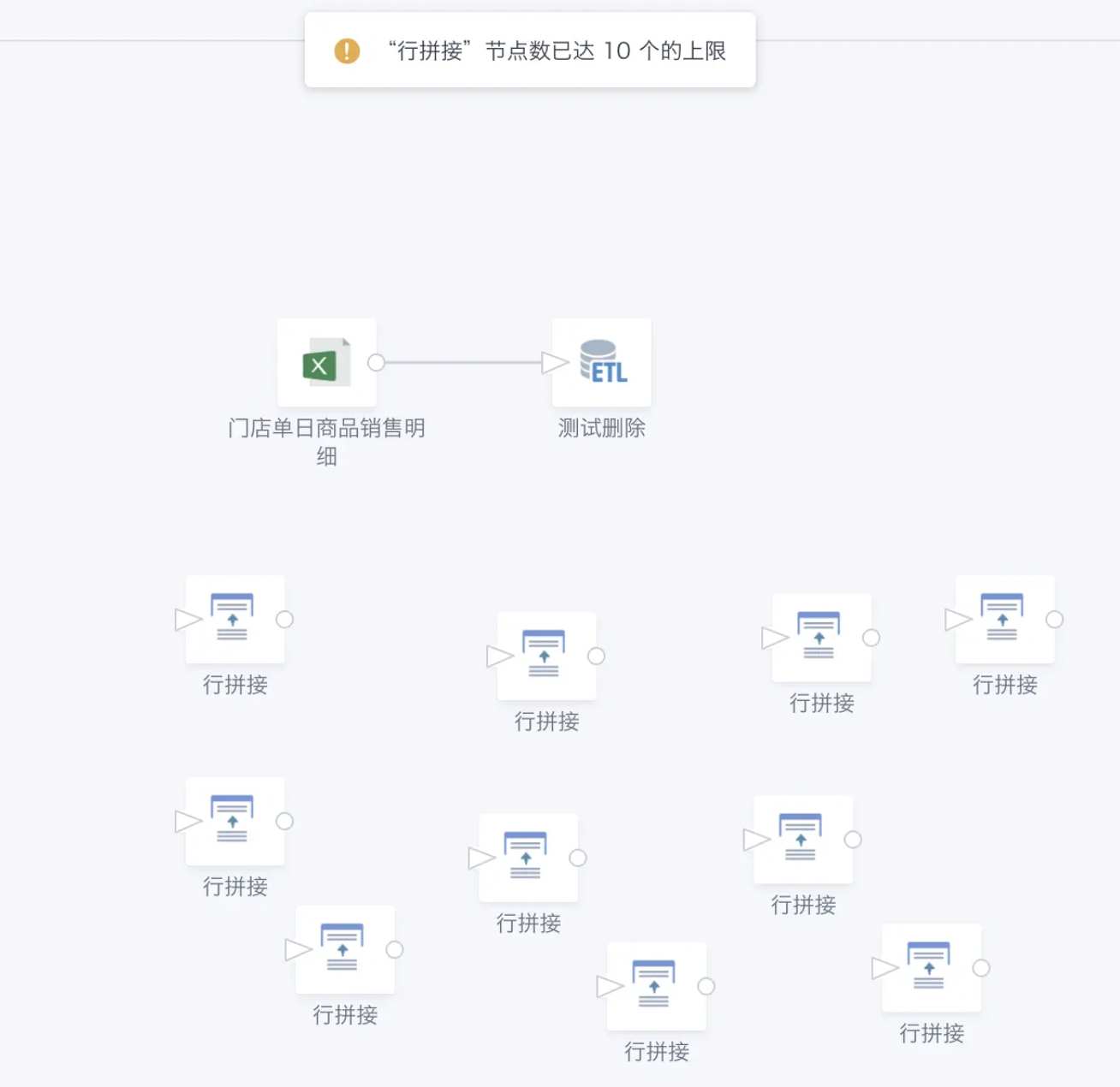
Specific operation: Management Center > Operations Management > Parameter Configuration, ETL Parameter Configuration > Maximum Supported "Row Concatenation" Node Number. (Configurable range: 1-50. New customers: default 10, existing customers: default unlimited). If the limit is exceeded during creation, a prompt will appear.
2. Data Join
Functional Description: Data Join can be understood as "column join". The difference is that data join requires finding the same join column in both datasets; the join forms are also diverse, and the final dataset can have custom columns, as follows:
| Join Type | Description |
| Inner Join | Only connects the intersection of join columns |
| Left Join | Outputs all rows from the left table by default and joins matching columns from the right table |
| Full Join | Connects the union of join columns |
Example:
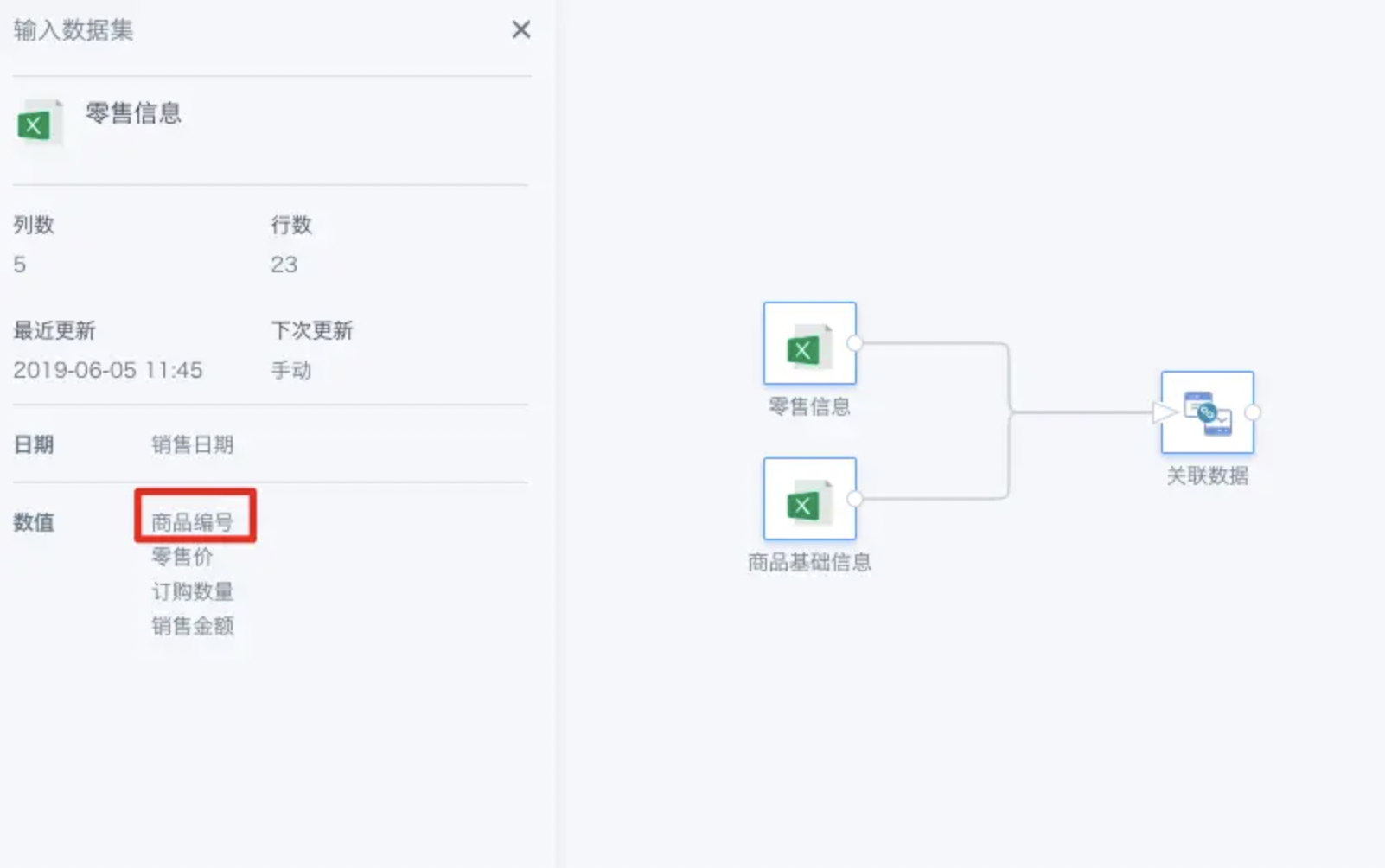
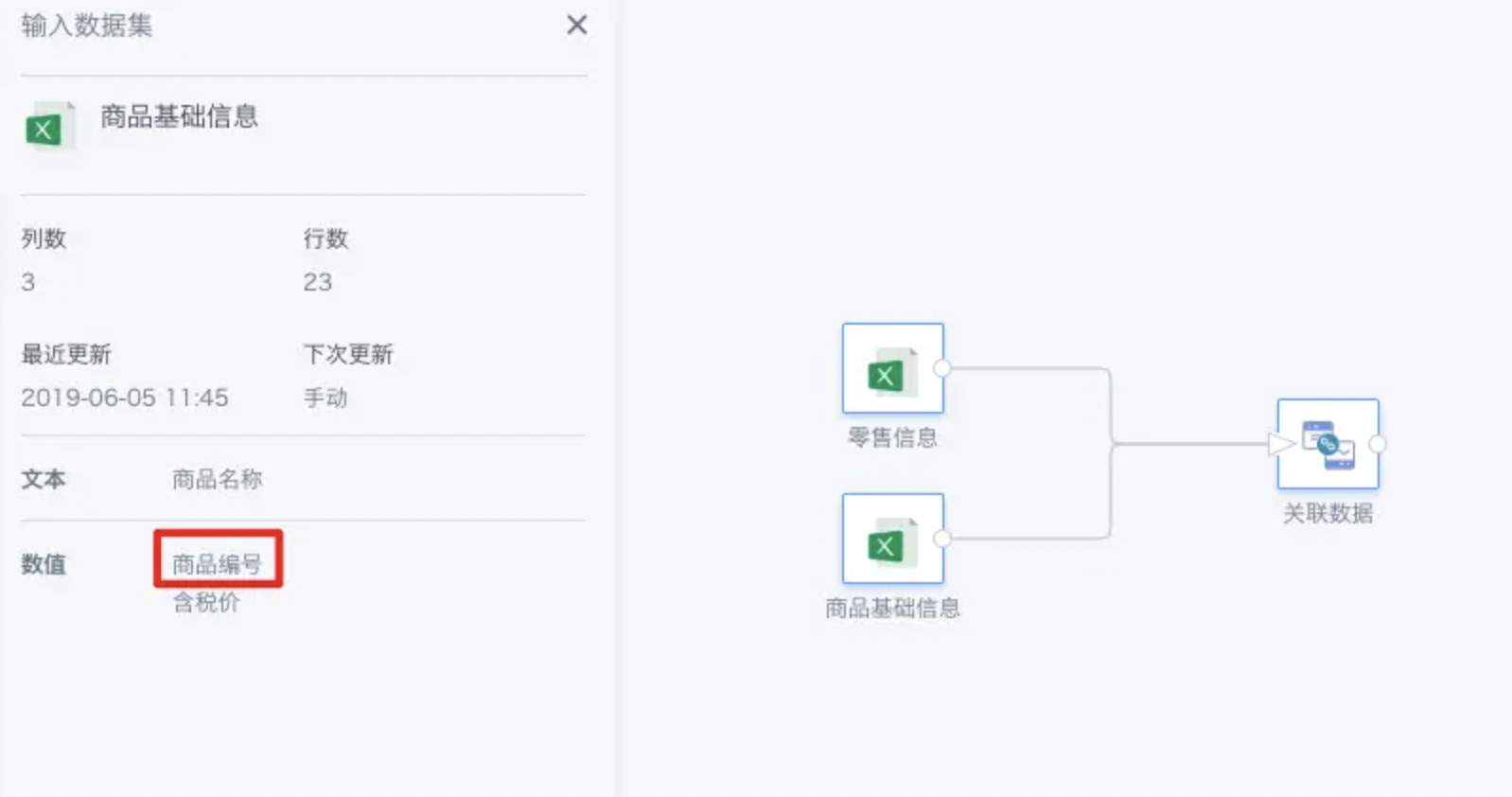
As shown, the two datasets are retail information and product basic information. For product basic information, the product number is the unique key.
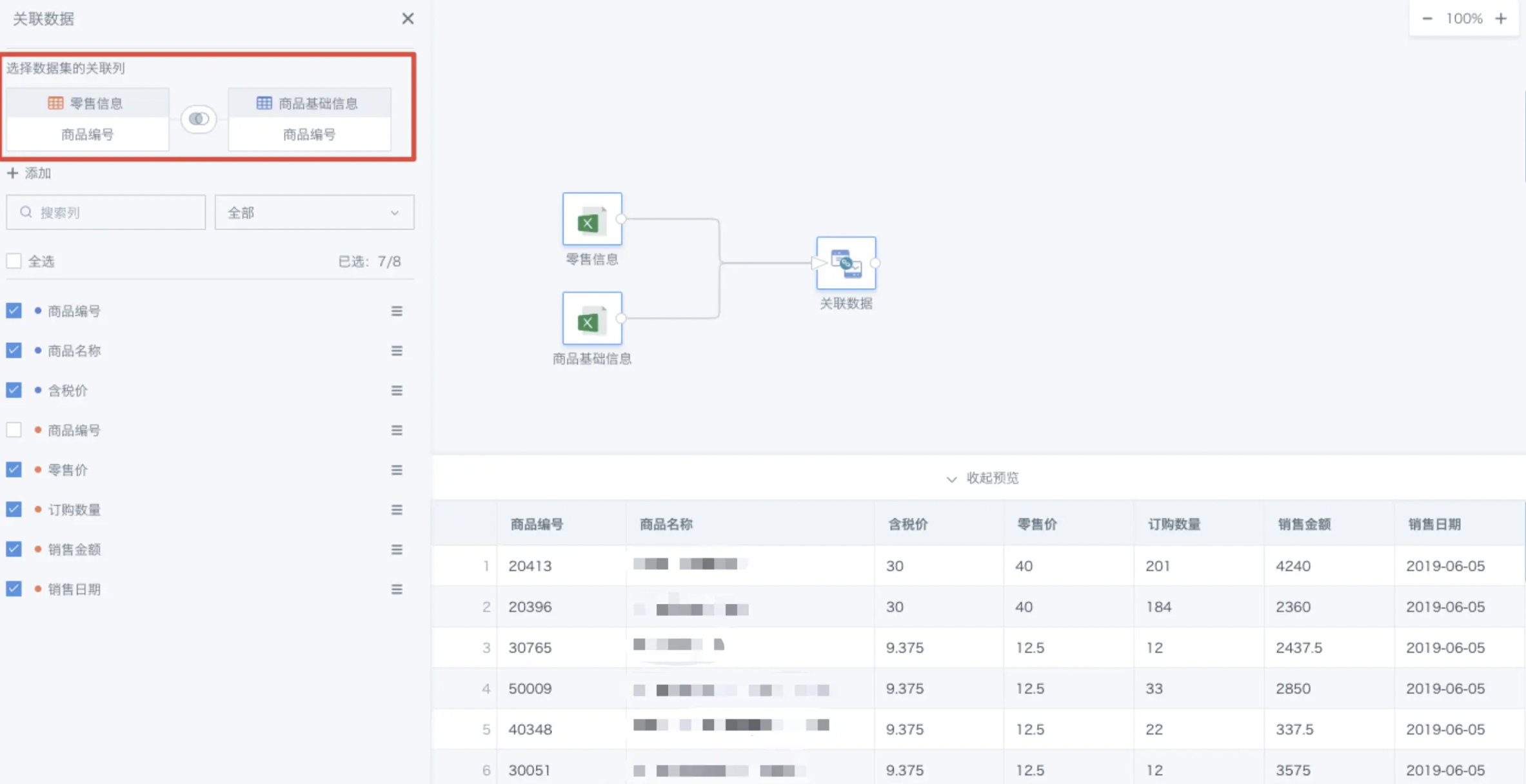
We want to supplement the products in the retail information with information from the product basic information, so we choose Product Number as the join field for a left join.
Error details: [Reference 'id_1666072244947.truck_id' is ambiguous, could be id_1666072244947.truck_id, id_1666072244947.truck_id.; line 1 pos 0](../../../../12-Error Description.md#message--reference-id_1666072244947truck_id-is-ambiguous-could-be-id_1666072244947truck_id-id_1666072244947truck_id-line-1-pos-0)
3. Batch Replace ETL Datasets
During data development, when you need to replace a dataset with a new one, ETL supports batch replacement of datasets in ETL, just like batch operations on dataset cards, greatly improving efficiency.
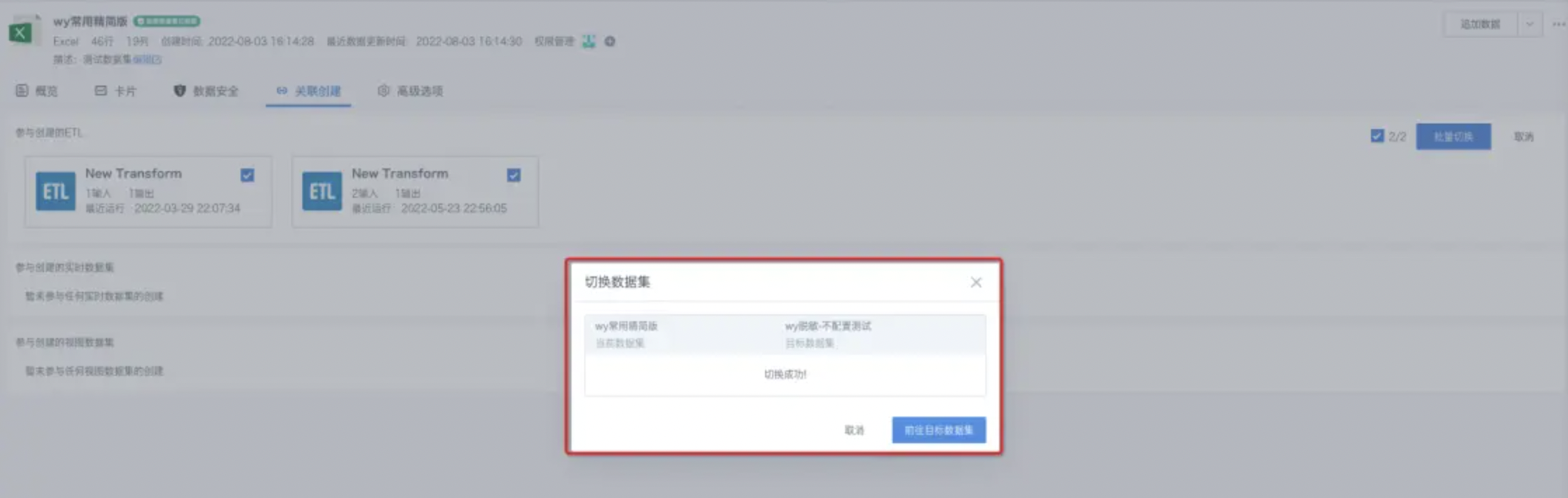
- In the details page of a non-direct connection dataset, find the Associated Creation tab, select Switch Dataset on the right, and you can select multiple ETLs to switch (up to 200 at a time);
- After selecting the dataset to switch, you still need to check the consistency of ETL node field names after switching, and you can manually correct them;
- After switching, a success or failure notification will be returned, and you can jump to the details page of the switched dataset to view it.
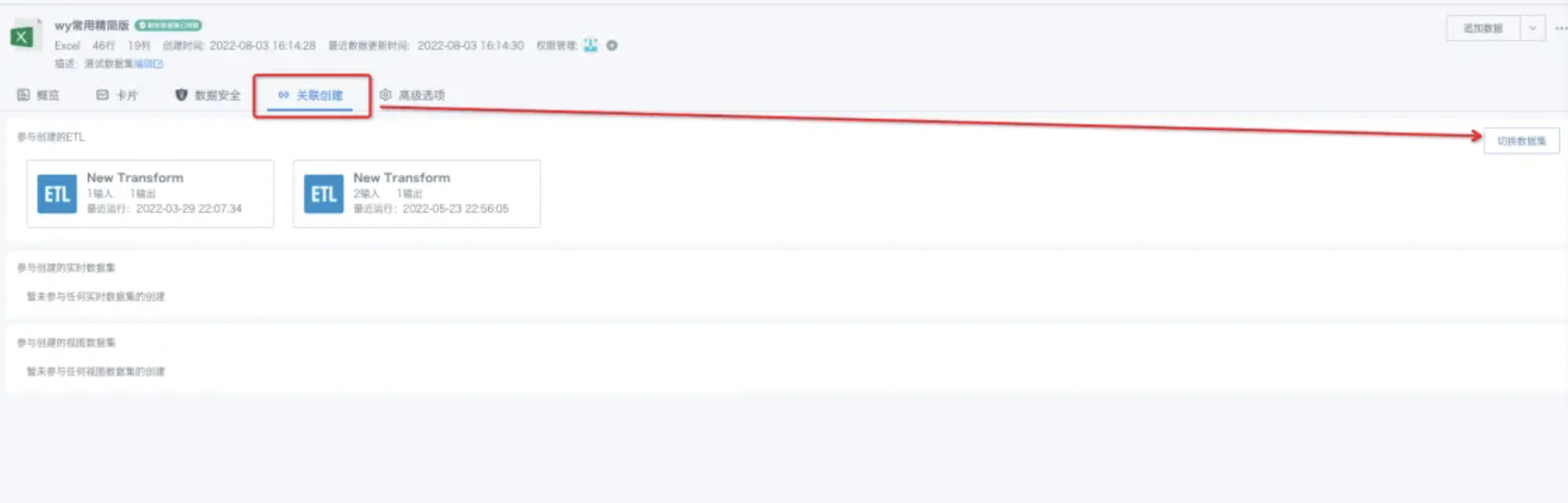
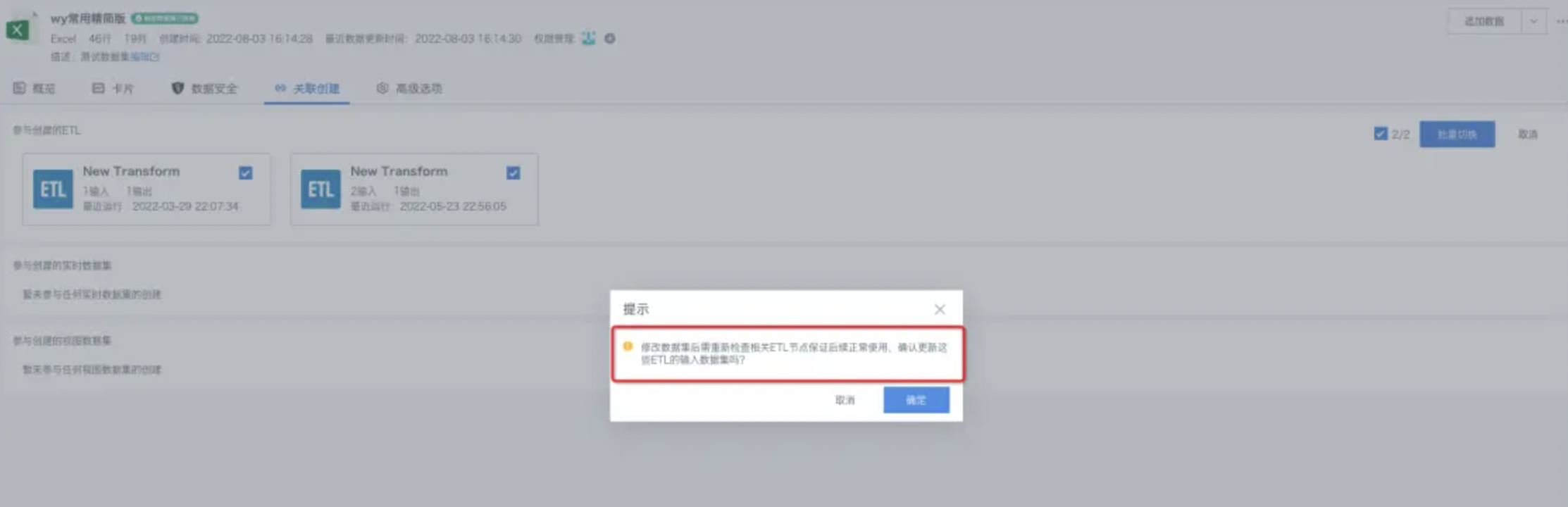
For subsequent use of other data processing operators, see Getting Started.