Global Parameters
1. Global Parameters Overview
Global parameters refer to the flexible use of parameters in multiple aspects of data integration and data analysis in Guandata, such as in cards, dataset calculated fields, view datasets, and SQL of direct connection datasets. Through the use of parameters, you can achieve complex chart dynamic analysis, such as switching analysis dimensions, switching analysis indicators, dynamic data classification, cross-table dynamic queries, etc.
2. Global Parameters Usage Guide
2.1 Creating Parameters
You can set global parameters that users need in "Management Center > Enterprise Configuration > Global Parameters". Click the "Add Parameter" button in the upper right corner to configure new parameters.
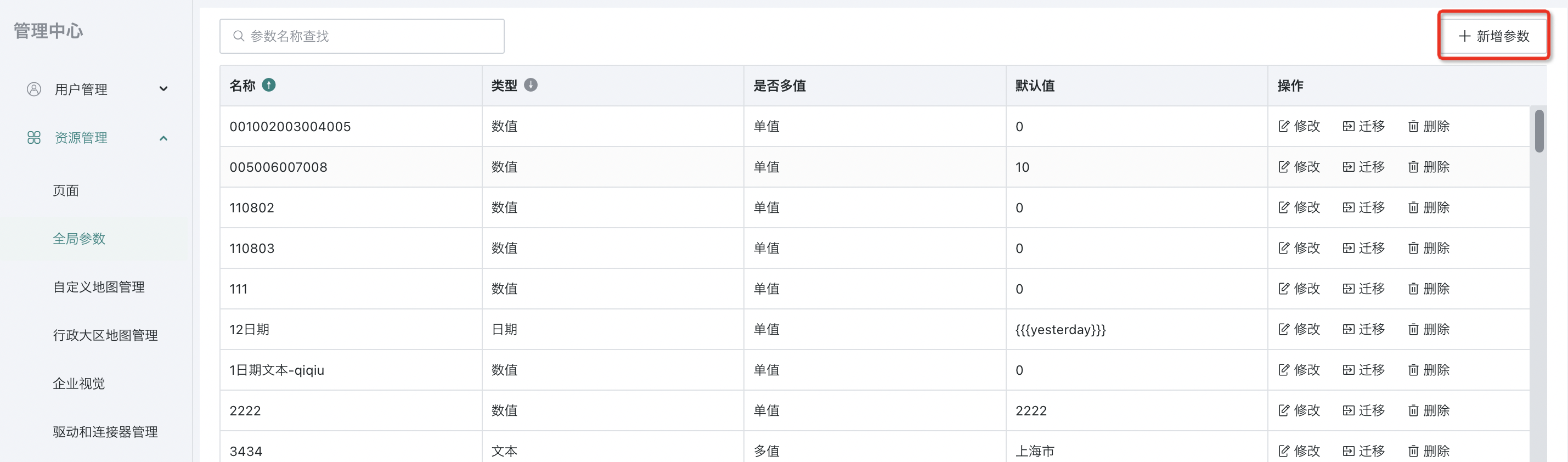
Each parameter must contain parameter name, parameter type, and default value. You can choose to add some description information to assist in parameter management. If it is a text type parameter, you can also set custom text or select from predefined dropdown lists.
.png)
2.2 Using Parameters in Card Calculated Fields
After parameters are created, they can be used in card calculated fields. The figure below shows how to achieve card analysis dimension switching through the use of parameters in calculated fields. Among them, the expression of the calculated field is:
case when [DYNAMIC_PARAMS.维度钻取示例]="城市" then [城市] else [门店] end
.png)
Of course, you can also achieve analysis indicator switching by using parameters in measure fields:
case [DYNAMIC_PARAMS.显示指标] when '销量' then [Quantity] when '销售额' then [Sales] when '利润' then [Profit] end
Using parameters in measure fields can also achieve dynamic classification calculations. For example, if we want to calculate the sales volume of high-priced products, and the threshold for judging whether it is a high-priced product is an external input parameter, we can define the following calculated field [高单价商品销量]: if([Price]>[DYNAMIC_PARAMS.数值参数],[Sales],0)
2.3 Using Parameters in Direct Connection Datasets
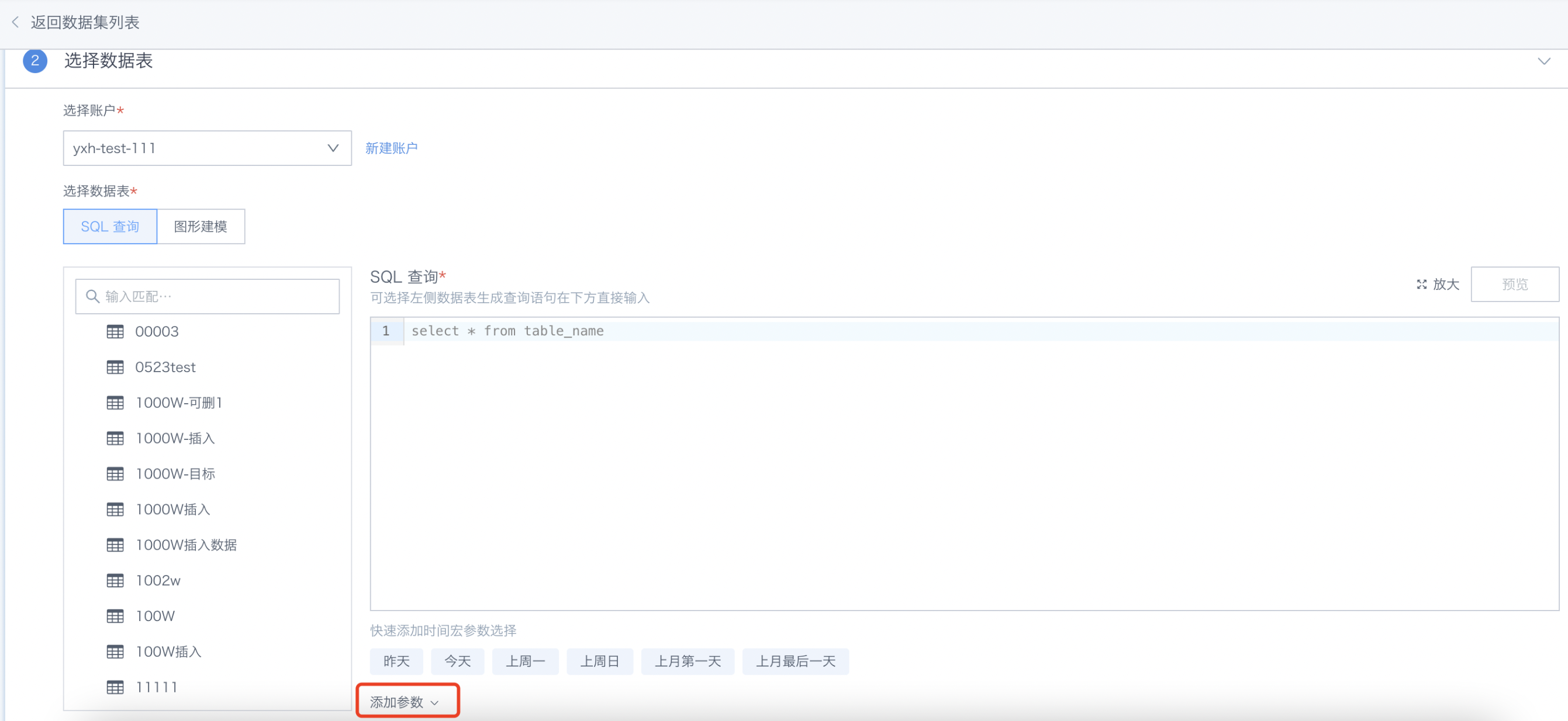
In the method of accessing data from databases, you can use parameters in SQL when creating datasets (also called direct connection datasets). Click the "Add Parameter" button to use parameters to achieve data analysis dimension switching.
.jpeg)
Note: After referencing parameters, when data preview and update are performed at the dataset, the platform will obtain the default values of the corresponding global parameters in real time and replace them in the query SQL to achieve dynamic query effects.
For example, we use the following SQL to create a dataset, and by passing date parameters in cards or pages, we can achieve dynamic analysis of customer order information within a specified time interval.
select * from order_items where customer_id in (select customer_id from customers where create_date >= [DYNAMIC_PARAMS.日期参数] )
2.4 Using Parameters in Extracted Datasets
Database extracted datasets, Web Service extracted datasets, and remote file extracted datasets support using global parameters.
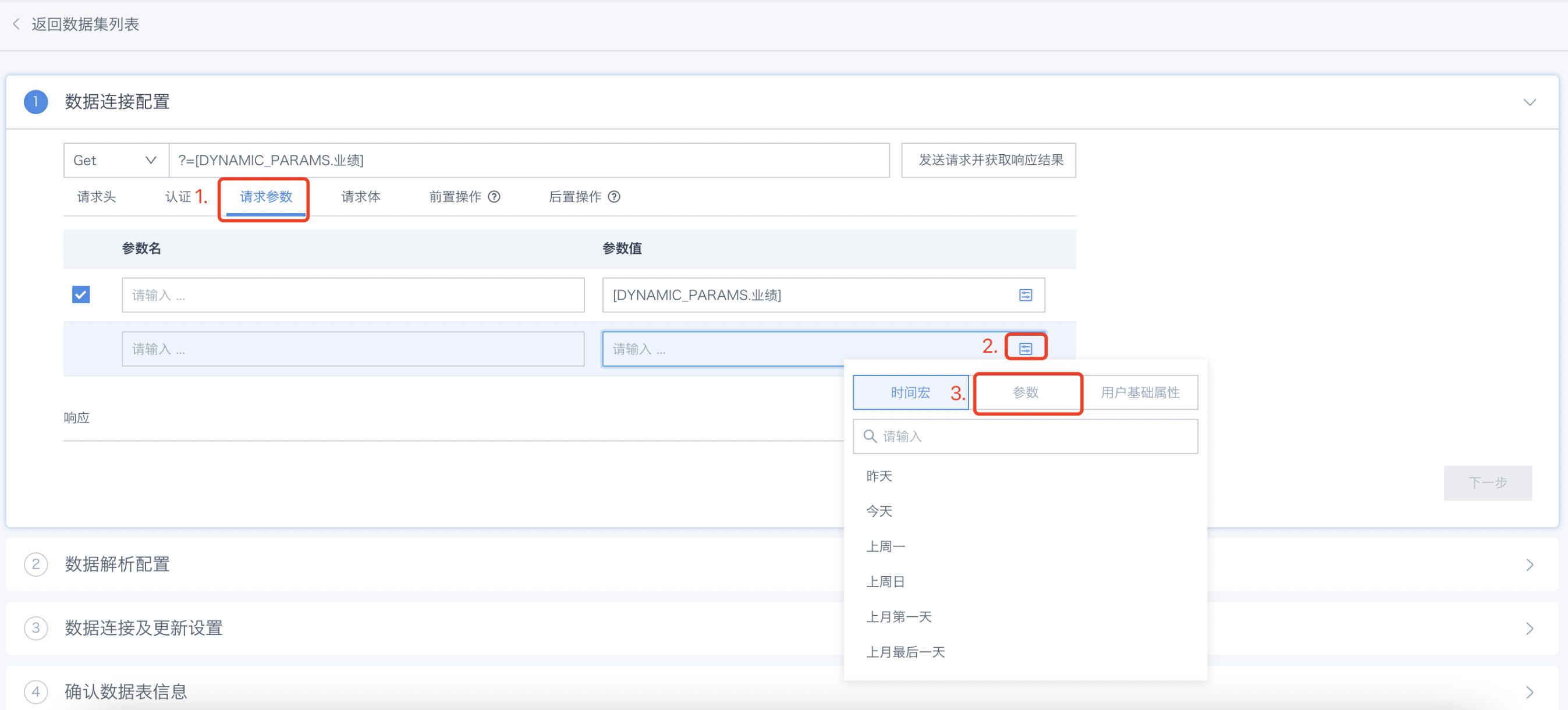
- When creating/modifying model structure/configuring incremental updates for database type extracted datasets, the example is shown in the figure below:
- When creating/modifying model structure/configuring incremental updates for Web Service type extracted datasets, the example is shown in the figure below:
- When configuring incremental updates for remote file type extracted datasets, the example is shown in the figure below:
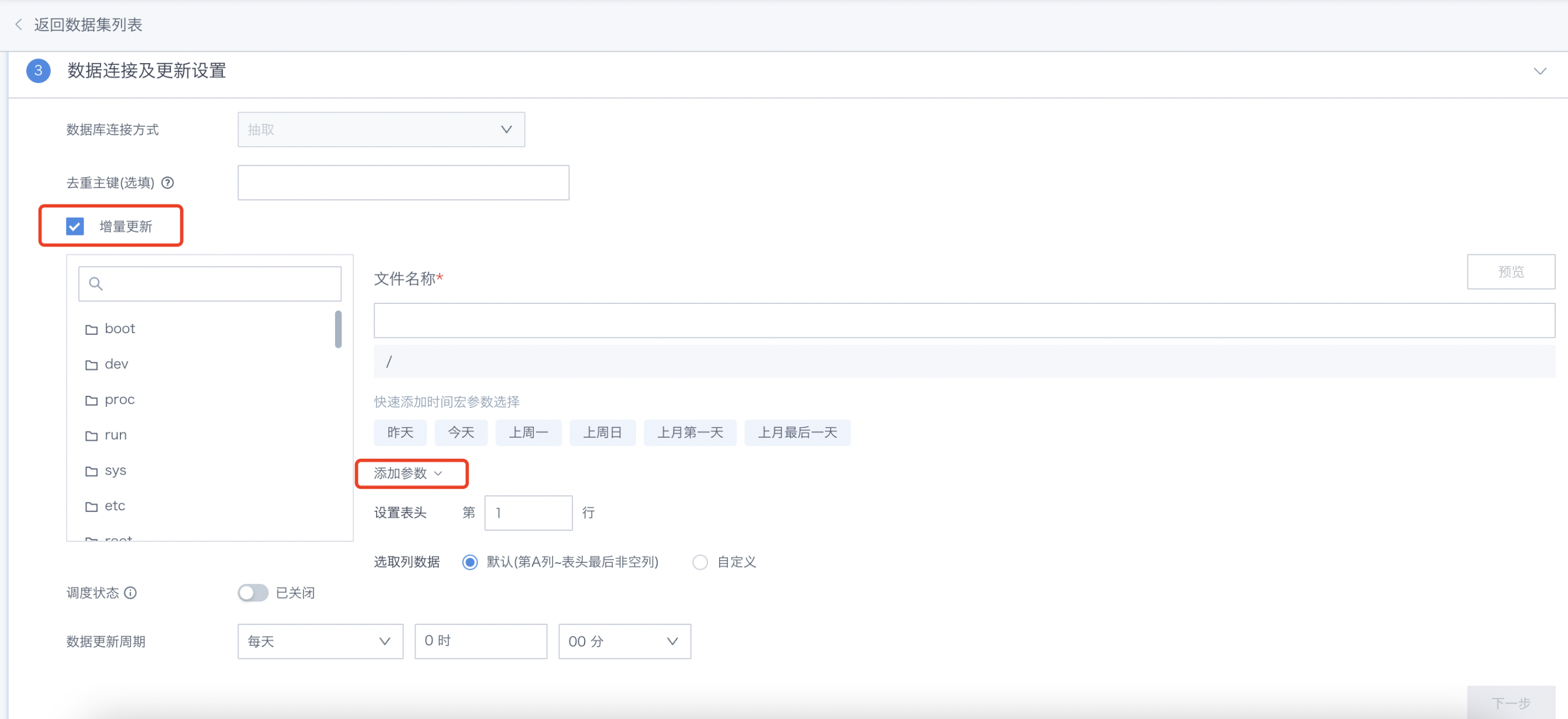
Basic usage: Consistent with the method of using global parameters in direct connection datasets, after creating a Guan-Index type dataset, when updating the dataset, it will query the default values of the global parameters used in real time and replace them in the query SQL for data extraction.
Applicable update scenarios are as follows:
-
Manual update;
-
Scheduled update;
-
URL triggered update;
-
Other Public APIs that trigger data updates.
Applicable update methods are as follows:
-
Overwrite old data;
-
Add new data.
Note:
If you use Guan-Index datasets to create cards, and parameters are only used in model structure and data update definitions, these parameters will not be passed to the cards and do not support linking parameter filters for dynamic queries.
2.5 Using Parameters in View Datasets
When creating view datasets, use parameters in SQL:
.jpeg)
2.6 Using Parameters in Stored Procedure Datasets
When creating stored procedure datasets, parameters can be used.
.jpeg)
2.7 Using Parameters for Dynamic Analysis
When there are cards in the page that use parameters (whether from calculated fields or datasets), you can open the parameter display window by creating new filter cards. After opening, you can adjust parameter values on the page to perform dynamic analysis on the corresponding cards. When global parameters take effect on card data through filters, they can only filter data rows.
When the filter conditions are cleared, the parameter default values set by the card will be taken.
When using global parameters at the dataset, the following situations need to be passed to the card:
-
All calculated fields of all datasets;
-
All parameters used by direct connection datasets, view datasets, and stored procedure datasets.
When using global parameters at the dataset, the following situations are not passed to the card:
-
FTP/SFTP/ADLS Gen2 datasets - incremental updates;
-
WebService extracted datasets/database extracted datasets - model structure SQL, incremental update SQL, pre-cleanup rules.
.png)
3. Global Parameters Macro Usage Cases
For specific usage cases of global parameters, it is recommended to visit Global Parameters Best Practices for more information.