Custom Filter
1. Overview
Custom filters are functional modules that allow users to develop custom solutions based on business requirements, used to filter content that meets conditions from datasets, and can adapt to complex scenarios and changing data processing needs.
Currently, Guandata BI's built-in page filters have deficiencies in type richness and style flexibility, making it difficult to adapt to personalized analysis needs in complex business scenarios. They rely on custom development and continuous maintenance, with problems such as long development cycles, high technical barriers, and high iteration costs.
To address this, Guandata BI has launched the custom filter feature, based on a plugin development model, providing a visual configuration interface that supports enterprises to quickly build filter components that fit business characteristics, flexibly extend filter logic and interaction styles, significantly improving business agility and analysis experience.
2. Applicable Scenarios
Custom filters can be flexibly configured and are widely used in data analysis, content management, e-commerce platforms, financial industries, and other fields. They support the following common scenarios:
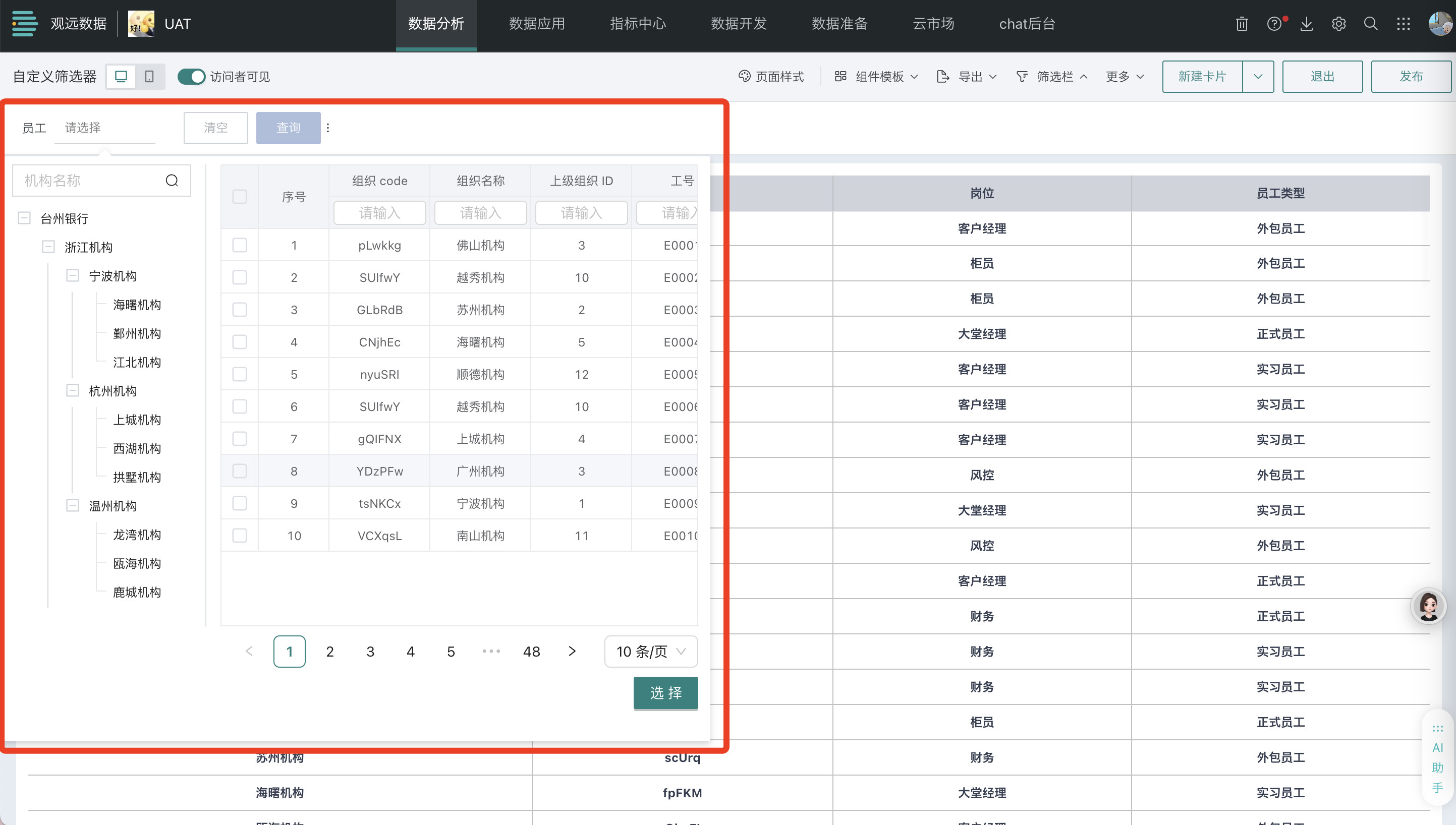
Scenario 1: General Organizational Structure Filtering
Based on organizational structure, job types, and other multi-dimensional tags, quickly locate target employee groups, monitor real-time attendance rates, sales achievement, and performance indicators, providing precise data support for talent management decisions.
Scenario 2: Product Management
Based on multi-level category systems, product attribute tags, and price ranges, intelligently filter product data, track inventory dynamics, delivery cycles, and sales conversion rates in real-time, providing full-chain data support for product operation decisions.
Scenario 3: Financial Deposit and Loan Business
Based on company entities, business types, and user classification multi-dimensional attribute tags, precisely filter financial business data, dynamically monitor total deposits and loans, repayment cycles, and non-performing rates, providing real-time data insights for risk control and business decisions.
Scenario 4: Internet User Behavior Analysis
Based on channel sources, marketing activities, and user segmentation tags, precisely filter target customer groups, deeply analyze user behavior trajectories, retention rate trends, and sales conversion funnels, providing quantifiable decision-making basis for precise marketing strategy optimization and user lifecycle management.
3. Usage Guide
3.1. Configure Plugin
Entry: Management Center > Open Platform > Plugin Management
- Click "New Plugin" in the upper right corner, configure the basic plugin information, then click "Confirm" to complete plugin creation.
- Click "Edit Code" to the right of the plugin created in the previous step, input the filter plugin code, then click "Confirm". For custom filter plugin code writing, refer to [Custom Filter Plugin Development Guide](1-Custom Filter Plugin Development Guide.md).
- Turn on the enable switch to enable this custom filter plugin.
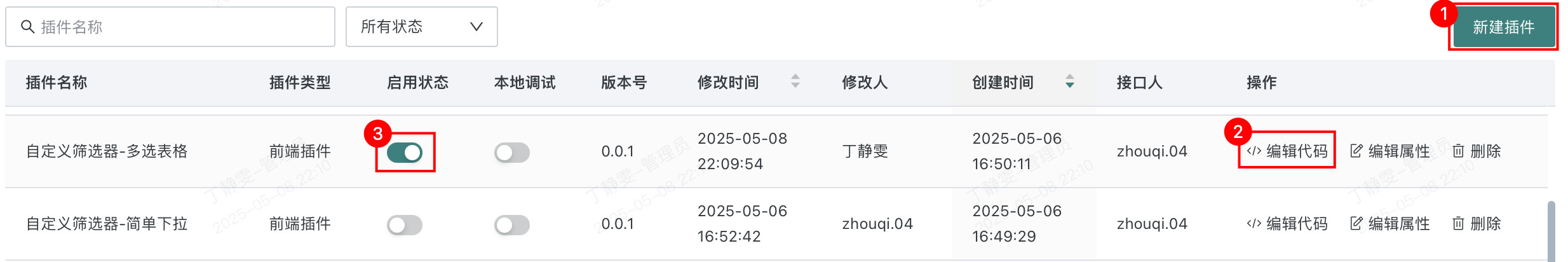
For more plugin management operations, refer to Plugin Management.
3.2. Configure Filter
3.2.1. Create Filter
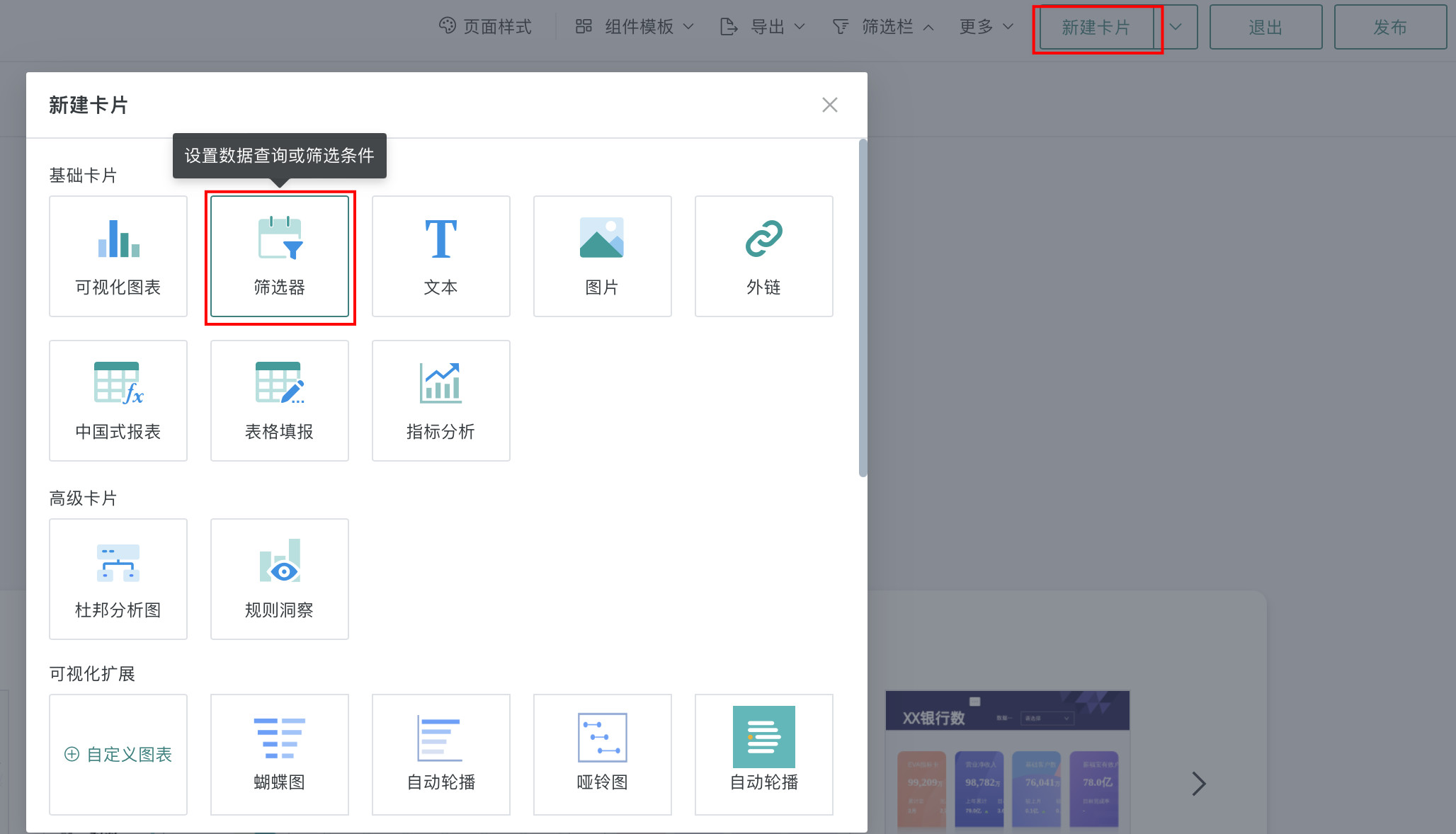
In the data analysis page, there are two entry points to create a custom filter: creating a new filter in the page's filter bar, and creating a new card on the page - selecting the card type as filter.
- Filter bar - New filter - Custom
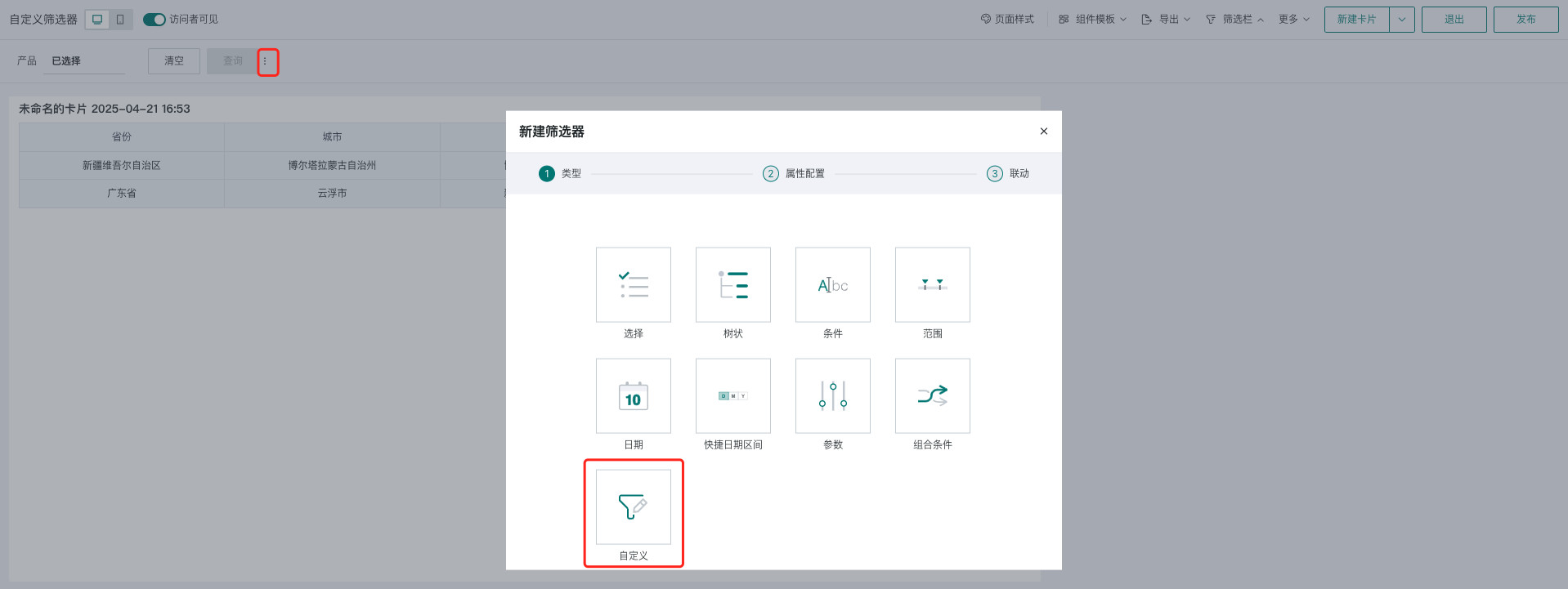
- Page - New card - Select filter: Select type as "Custom" to enter the new filter popup.
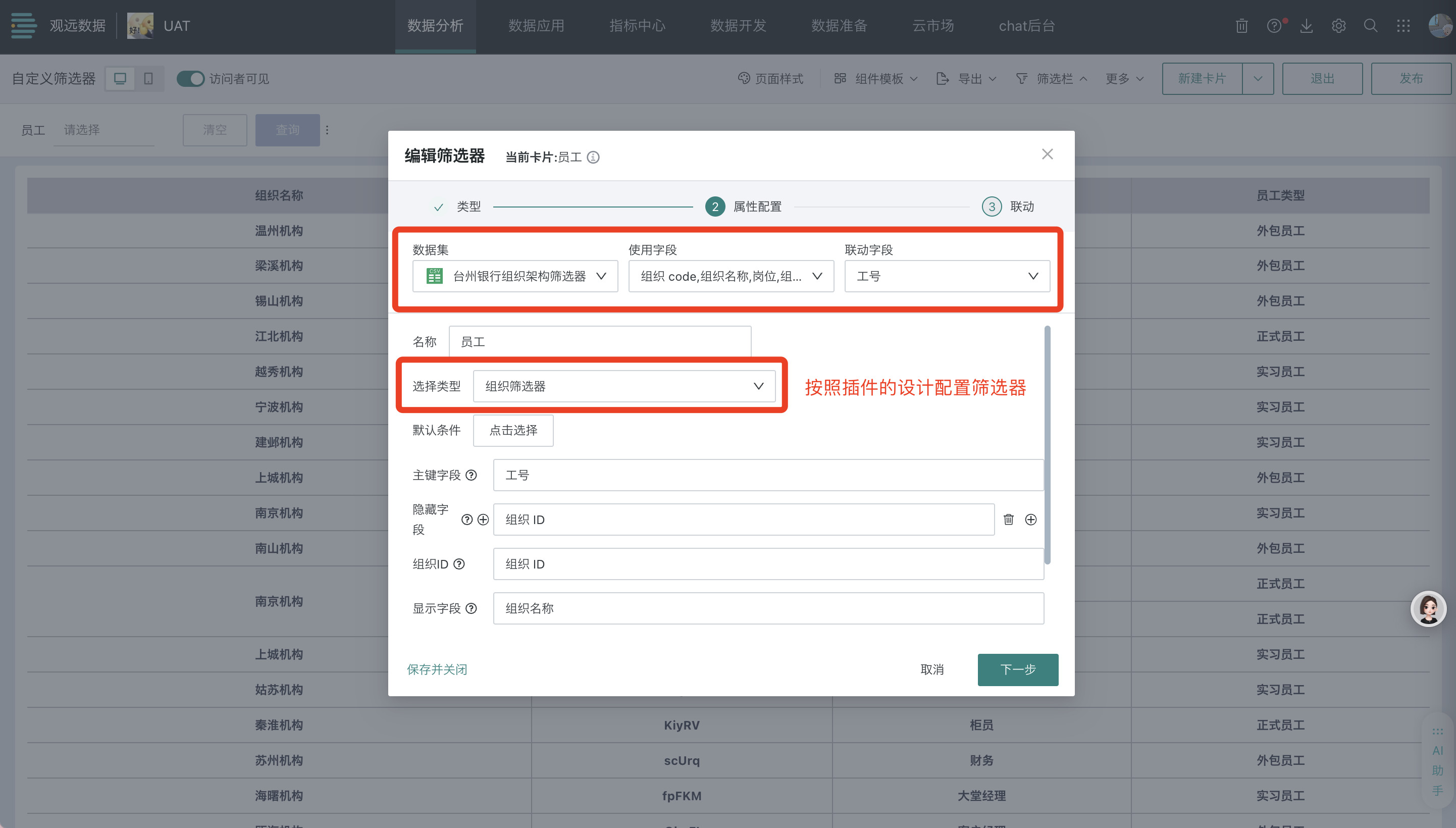
3.2.2. Filter Attribute Configuration
When setting up a custom filter, you need to select the dataset, fields to be used in the filter plugin, and the final linkage field.
- Dataset: You can quickly select the current page's dataset or search for a new dataset
- Usage fields: You can select all fields of the selected dataset, and the selected fields can be used for interactive filtering in the filter
- Linkage field: Regardless of what fields are used during the process, only the set linkage field will ultimately produce linkage, and only one linkage field can be set
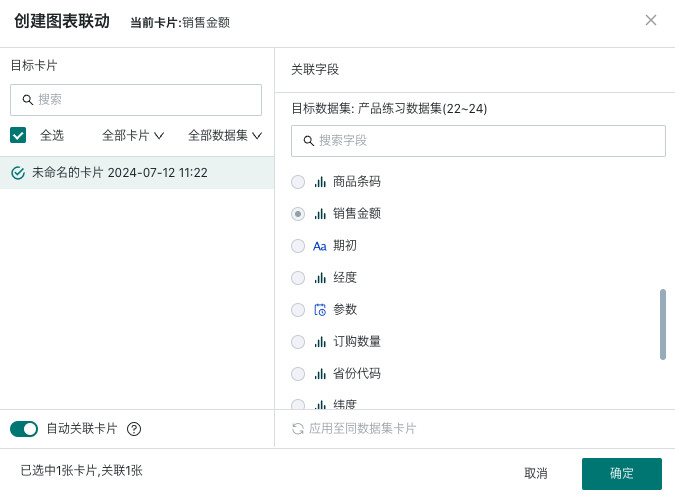
3.2.3. Set Linkage Target Card
When linking, you need to select the target card and the corresponding filter field. The linkage field needs to be consistent with the linkage field selected in the previous step; after the linkage field is set, changes in the filter will link and change the data presented by the associated card.
- Auto-link card: After the filter enables auto-link, it will automatically link visualization cards with the same field name; auto-linked cards can be manually unlinked;
- Apply to cards with the same dataset: Click to apply to cards with the same dataset, and it will automatically link other cards under the same dataset with the corresponding field. Cards applied to the same dataset can be manually unlinked.
3.3. View Filter Usage Effect