Data Masking
Note: This product module is a value-added module. If you need a trial, please contact Guanyuan Data business personnel or your Customer Success Manager (usually your company's current service contact).
1. Product Overview
Data masking means Guanyuan Data can transform certain sensitive information through masking rules to protect sensitive and private data. For example, in cases involving customer security data or some business-sensitive data, such as ID numbers, mobile numbers, card numbers, customer numbers, etc., data masking can be applied to solve the problem of using such data in untrusted environments and improve compliance.
Note: This product module is a value-added module. If you need a trial, please contact Guanyuan Data business personnel or your Customer Success Manager (usually your company's current service contact).
2. Product Features
| Description | User Role | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Masking Tag Settings | Configure data masking tags in System Management - Advanced Settings - Data Masking Tag Settings. Tags bridge detection rules and masking rules. | Administrator |
| Masking Configuration | When creating a new dataset, configure dataset sensitivity, field masking rules, and associated users in the dataset details - Data Security, Model Structure page. | Administrator, Dataset Owner |
| Data Masking Template | Configure masking rule templates and associated users on the Data Security Template - Data Masking Template page. | Administrator, Security Template Editor |
| Detection Rules | Configure detection rules for intelligent detection on the Data Security Template - Detection Rules page, including field name detection, content detection, and hybrid detection. Supports "equals", "contains", and "regex". | Administrator |
| Intelligent Detection | When creating a new dataset, you can perform manual detection on the dataset details - Data Security, Model Structure page. If forced detection is enabled, it will be executed. | Administrator, Dataset Owner |
3. Product Advantages
3.1 Product Value
- Reduce the risk of sensitive data leakage
Data containing sensitive information such as name, age, mobile number, bank account, etc., can be transformed into non-sensitive data suitable for business scenarios through masking, keeping sensitive information within controllable business systems and significantly reducing leakage risk.
- Comply with regulatory requirements
Whether it is the highest-level law, government regulations, or industry standards and guidelines, all require security for sensitive data including personal information. Data masking helps organizations improve data security and ensure compliance.
- Improve analysis efficiency
Compared to traditional masking at the database level, dynamic masking greatly reduces the time required, improving data delivery efficiency. It enables quick response to masking needs, so data masking is no longer a bottleneck in analytics projects, shortening project cycles and improving satisfaction.
- Detect sensitive data, use data securely
Unified data security management, with pre-configured detection and masking rules, allows data handlers, analysts, and viewers to use data within the enterprise's information security control scope, maximizing data value while ensuring security compliance.
3.2 Product Advantages
From a product usage perspective, Guanyuan Data's data masking achieves dynamic masking, with high compatibility, flexibility, and usability.
| Advantage | Description |
| More Compatible | Balances data security and usability; masked data can still be used for analysis and testing |
| More Flexible | Can configure different permissions for each user |
| More Usable | Intelligent detection: detects data by matching field names, previewing identified sensitive fields |
| Masking template: provides high replicability and better control effect reports |
4. Usage Steps
4.1 Feature Enablement
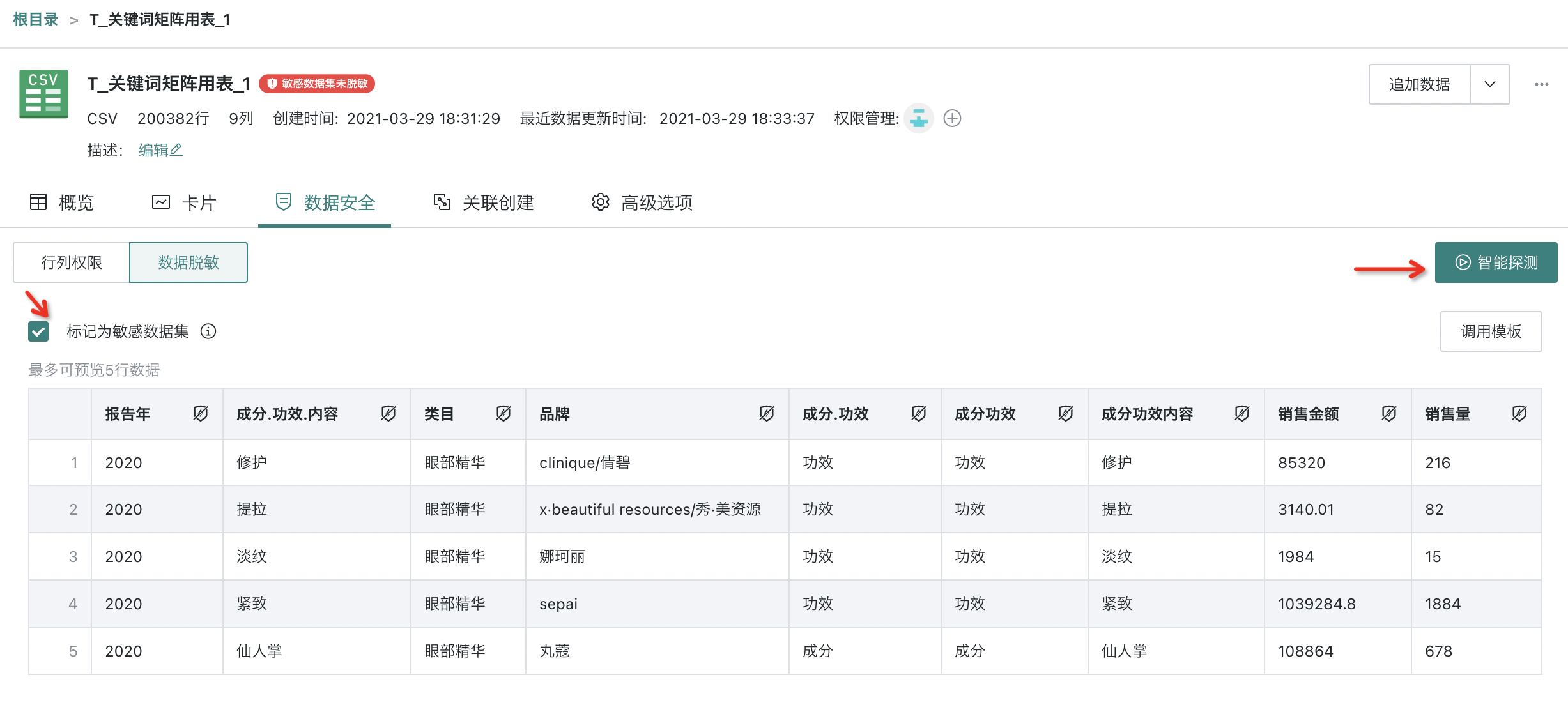
(1) "Intelligent Detection" and "Mark as Sensitive Dataset" features
- Manual mode
Users can enable or disable related switches on the operation page.
2. Forced mode
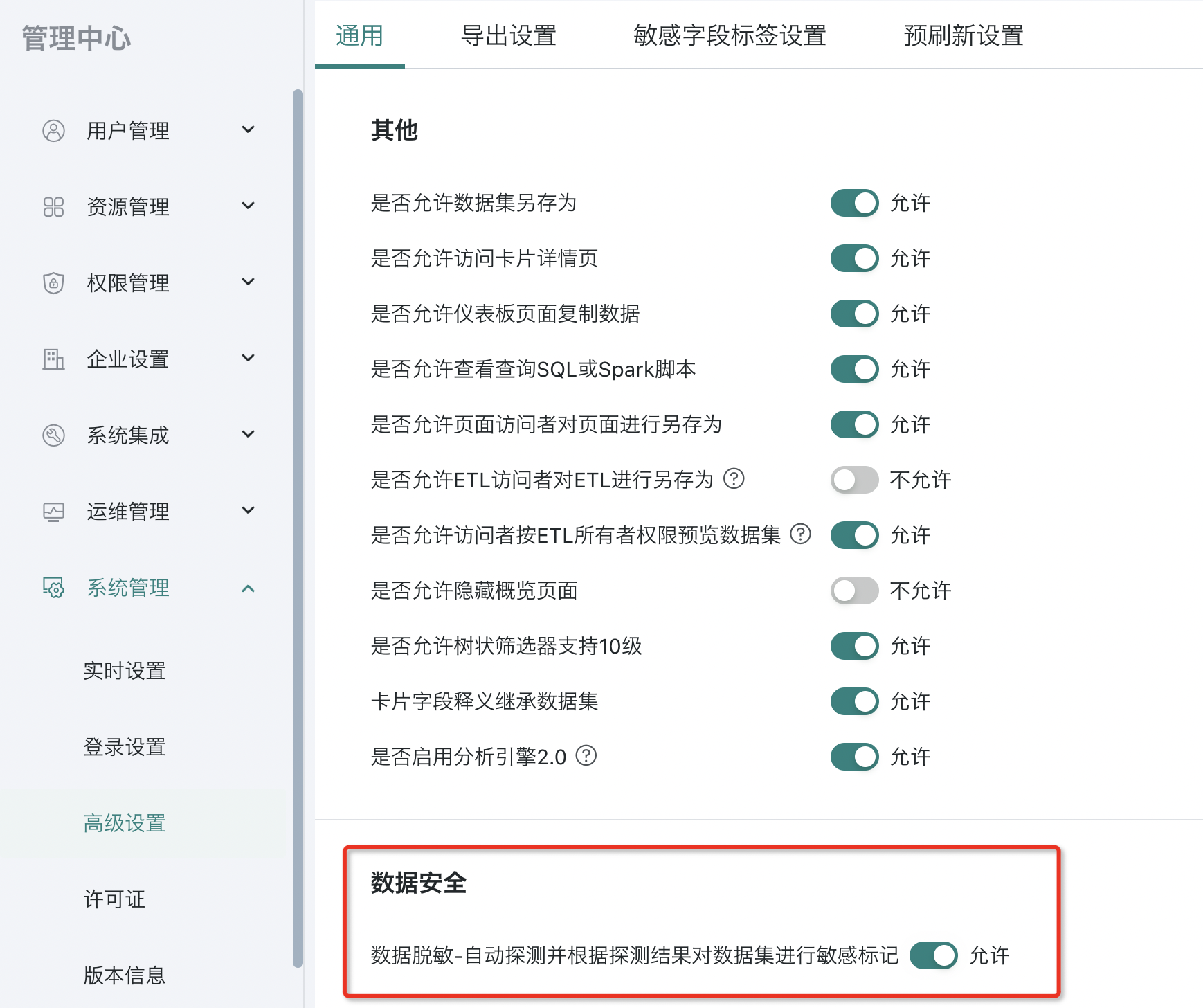
Users can enable the button for "allow automatic detection and marking when creating a new dataset" in the Data Security section of System Management - Advanced Settings. After enabling, all new datasets and model structure modifications will be forcibly detected and marked as sensitive based on the results.
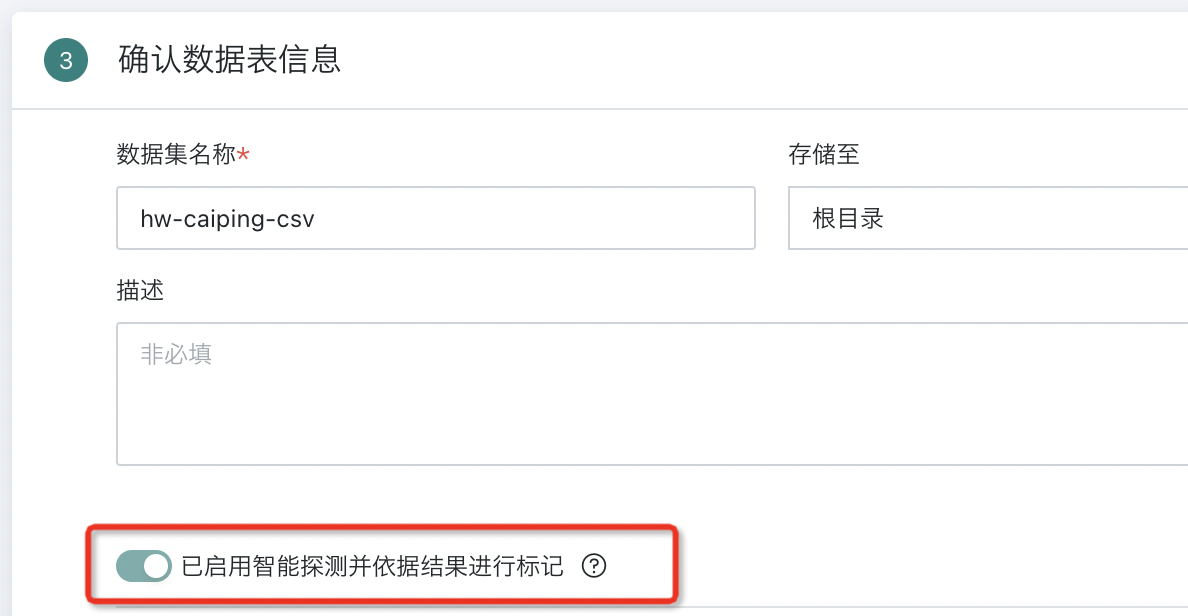
After enabling, when creating a new dataset, the system will prompt that "intelligent detection" is enabled for all new datasets and will mark them as sensitive based on the results.
(2) "Data Masking" feature
The data masking feature can be enabled or disabled via a backend switch (e.g., k8s), allowing selective use. In emergencies, this feature can be turned off.
- When enabled, all masking-related features are available.
- When disabled, the system will not perform masking permission checks or sensitivity identification, but existing configurations are retained and can be used again after re-enabling.
4.2 Data Masking Triggers
4.2.1 Creating a New Dataset
(1) Operation
Step 1: Create a new dataset
On the "Data Preparation - Dataset" page, perform the "Create Dataset" operation.
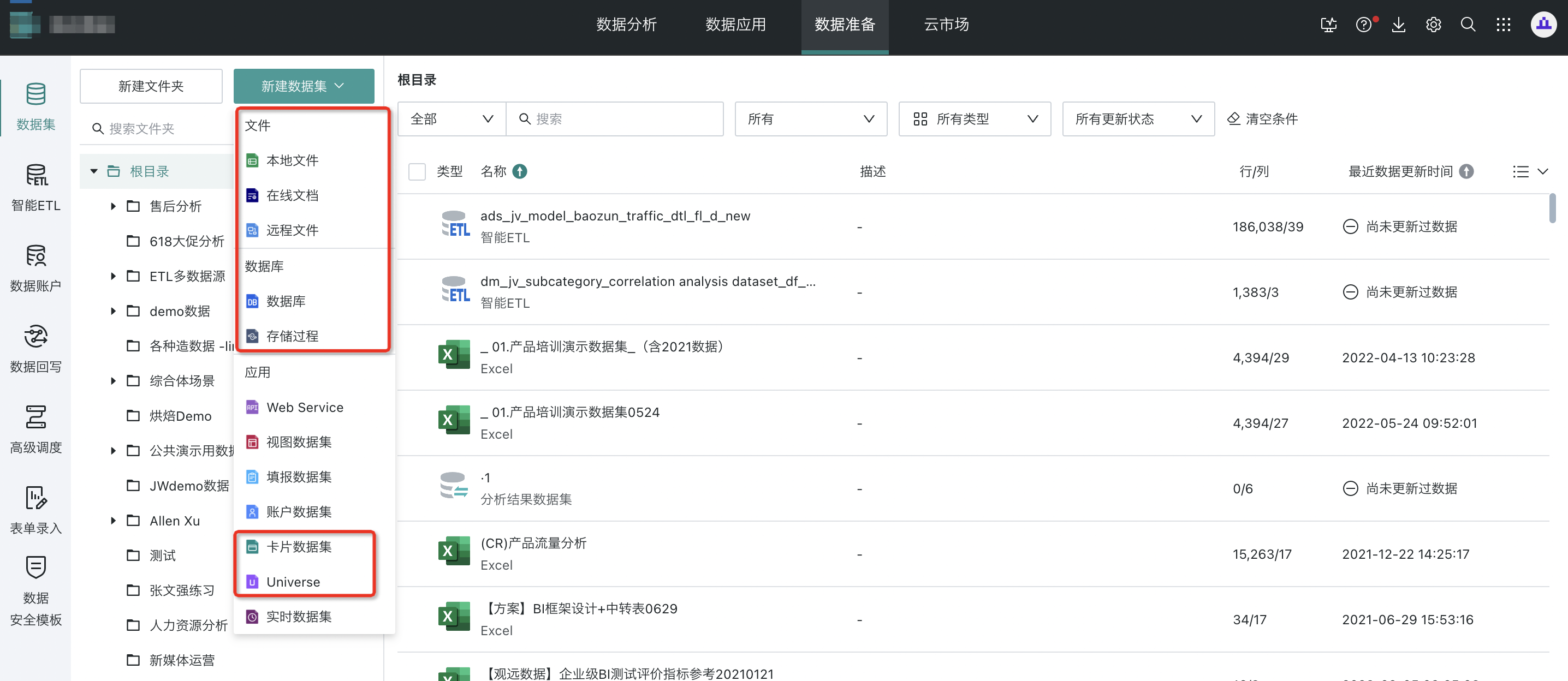
Supported types: file dataset, database dataset, card dataset, Universe dataset, ETL output dataset.
Step 2: Intelligent detection and mark as sensitive dataset
Manual mode
- Click the "Intelligent Detection" button to identify whether the dataset contains sensitive fields. After completion, a window will pop up in the upper right corner.
.png)
- Check the "Mark as Sensitive Dataset" button to complete the marking.
.png)
- Forced mode
In forced mode, new datasets are automatically detected and marked as sensitive based on the results. The sensitivity type cannot be modified.
.png)
4.2.2 Modifying Model Structure
(1) Manual mode
In manual mode, when modifying the dataset model structure, you can re-detect or change the sensitivity type.
.png)
(2) Forced mode
In forced mode, model structure modifications are automatically detected and cannot be changed or canceled.
.png)
4.2.3 Data Security Details Page
(1) Operation
Step 1: Detect sensitive fields in the dataset
- Open the "Data Security - Data Masking" page and check the "Mark as Sensitive Dataset" button.
.png)
- Click the "Intelligent Detection" button to start detection.
.png)
- After detection, sensitive fields are marked with a yellow exclamation mark and moved to the front.
.png)
Step 2: Change the sensitivity type
- Click the shield button next to the field title and set "Masking" or "Hash Masking" in the popup (see 4.3.1 Field Masking Rule Configuration for details).
.png)
(2) Sensitive Dataset Tags
- Sensitive dataset not masked
When a dataset is marked as sensitive but not masked, a red tag is attached, and it cannot be used to create cards directly.
.png)
.png)
- Sensitive dataset masked
When any field in a dataset is masked, it is automatically marked as a masked sensitive dataset.
.png)
.png)
(3) Other Notes
- Datasets saved as new support carrying sensitivity tags.
- ETL output datasets inherit sensitivity tags from input datasets and are automatically tagged on first run.
4.3 Data Masking Rule Configuration
4.3.1 Field Masking Rule Configuration
During operation, users can set different masking rules for sensitive fields to achieve different masking effects.
(1) Operation
Step 1: Click the shield button next to the table header field and select "No Masking", "Masking", or "Hash Masking" in the popup.
.png)
Step 2: If "Masking" is selected, set the replacement symbol, masked/retained part, and field masking position.
.png)
- Masking effect
.png)
.png)
- Retain effect
.png)
.png)
Step 3: Click the "Apply" button to complete masking.
.png)
(2) Effect Display
- Masking
.png)
.png)
- Hash Masking
.png)
.png)
4.3.2 Associated User Permission Configuration
During operation, users can configure the application scope of masked fields.
Scope settings include: user/user group, enabled/disabled, effective for view/export or only export, etc.
(1) Operation
Step 1: On the "Data Security - Data Masking" page, configure associated users/user groups and click "Add".
.png)
Step 2: Configure in the associated user editor and click "OK" to set the application scope.
.png)
Note: If not configured, all users will be masked for view/export by default.
.png)
(2) Other Notes
When saving a dataset as new, configured sensitive fields are retained.
4.4 Data Masking Template
4.4.1 Template Configuration
(1) Operation
Step 1: Add a new masking template
Open the "Data Preparation - Data Security Template - Data Masking Template" page and click "Add Masking Template".
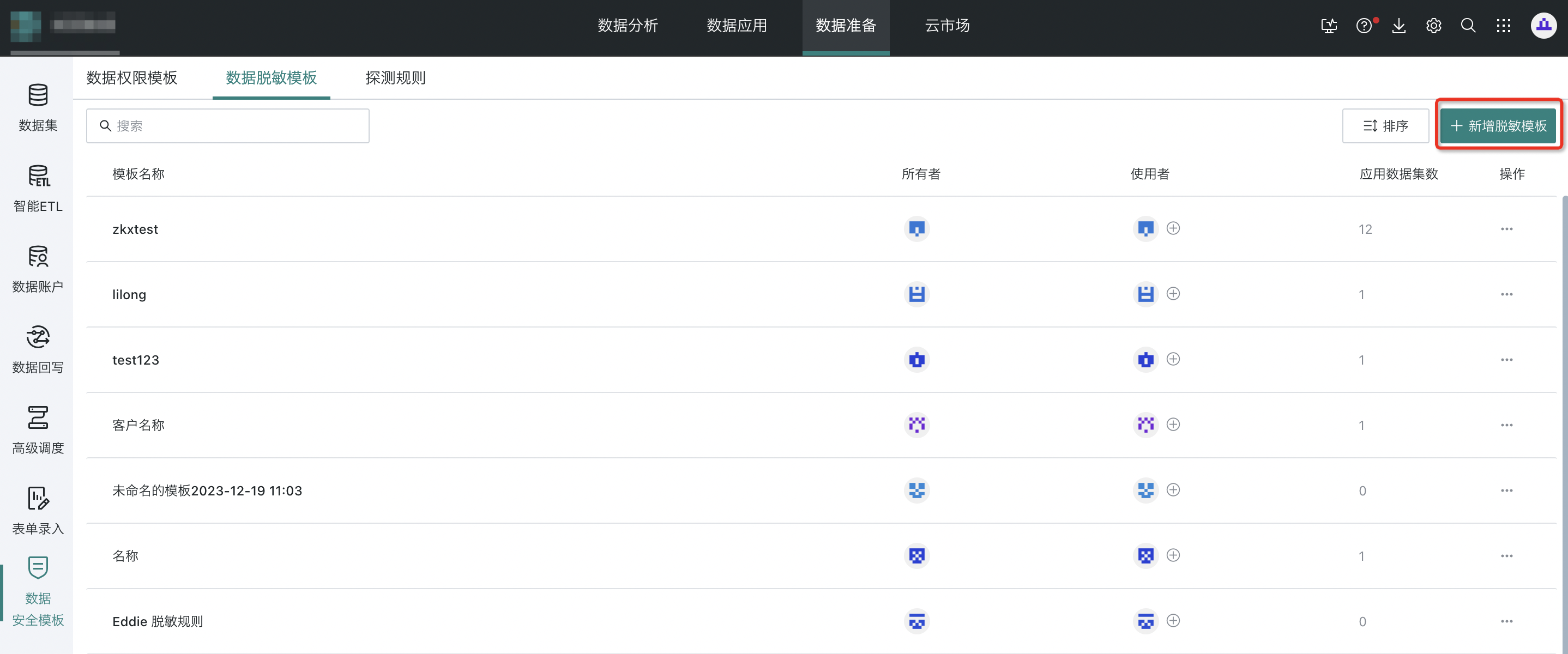
Step 2: Configure content
- New template includes template name, content, and associated users/user groups.
.png)
- Click "Add" in the template content to configure in the masking editor window, then click "OK".
.png)
- Enter field name
- Select sensitive field tag (optional)
- Select rule: "Masking", "Hash Masking (SHA1)"
- Select replacement symbol for masked part
- Select "Retain" or "Mask" and specify from/to positions
- Click "Add" in associated users/user groups to configure in the editor (same as 4.3.2).
.png)
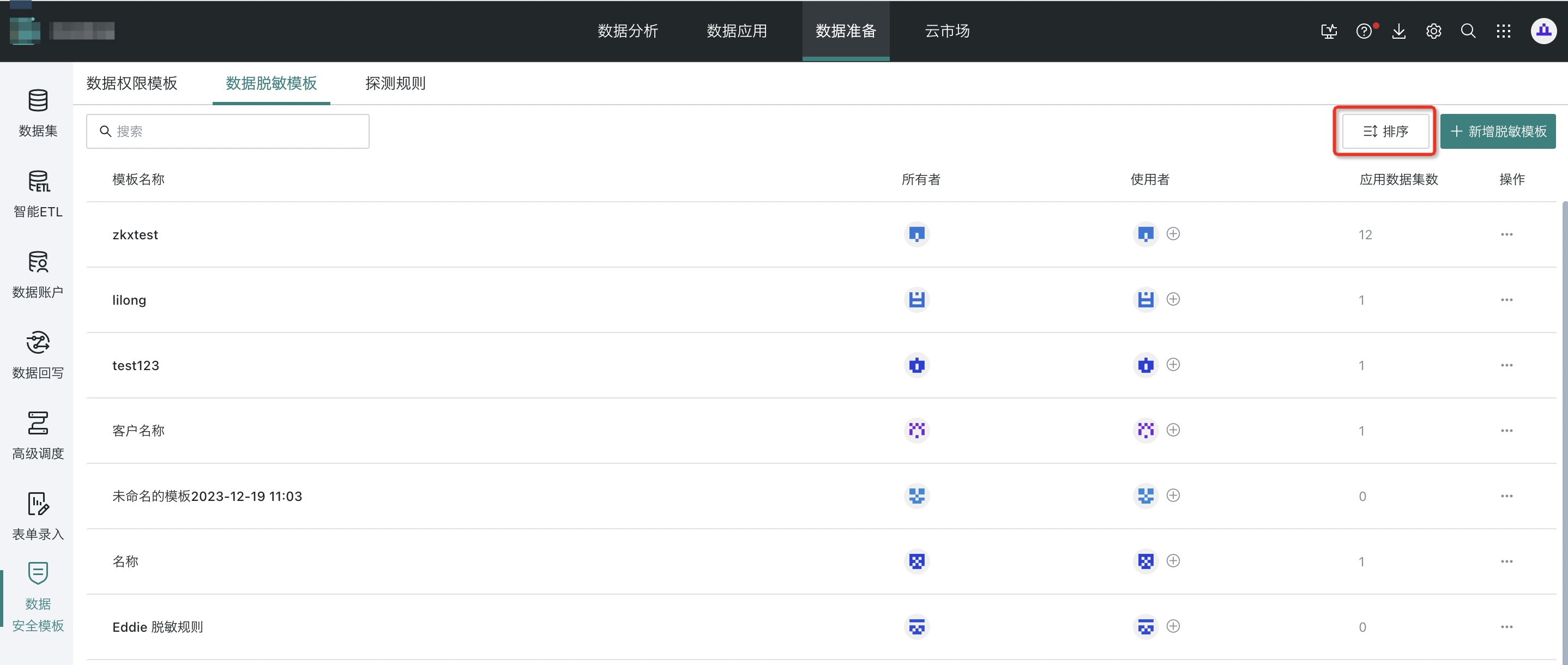
(2) Masking Template Sorting
Step 1: Click the "Sort" button in the upper right to enter the sorting page.
Step 2: Hover over the button to drag and sort. The order will be reflected when calling the template.
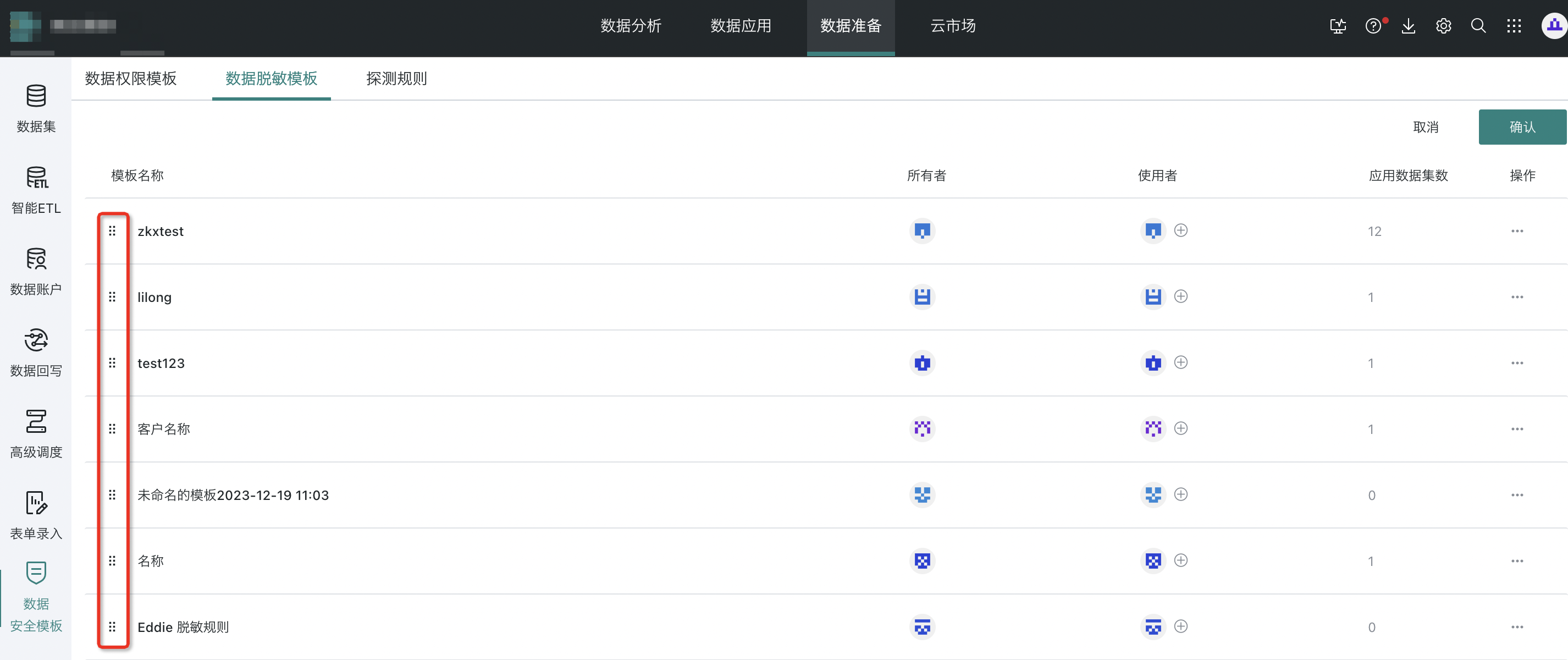
4.4.2 Template Usage
(1) Operation
Step 1: On the "Data Security - Data Masking" page, click "Use Template".
.png)
Step 2: Select the template and click "OK".
.png)
After applying a data masking template, the dataset can no longer configure field masking rules individually; it will follow the template.
(2) Other Notes
- If you want to customize based on the template, enable custom editing. This will copy the template rules to the current dataset for further editing.
.png)
- You can batch apply or remove templates on the template application page.
.png)
4.5 Data Masking Tag Configuration
(1) Background
When data quality is average, e.g., the same field has different names in different datasets, you can tag sensitive fields to associate detection rules with masking rules in templates, reducing configuration complexity.
For example, if the "ID number" field has different names ("ID", "identity card", "ID card num", "证件号", etc.), you can set a tag for it.
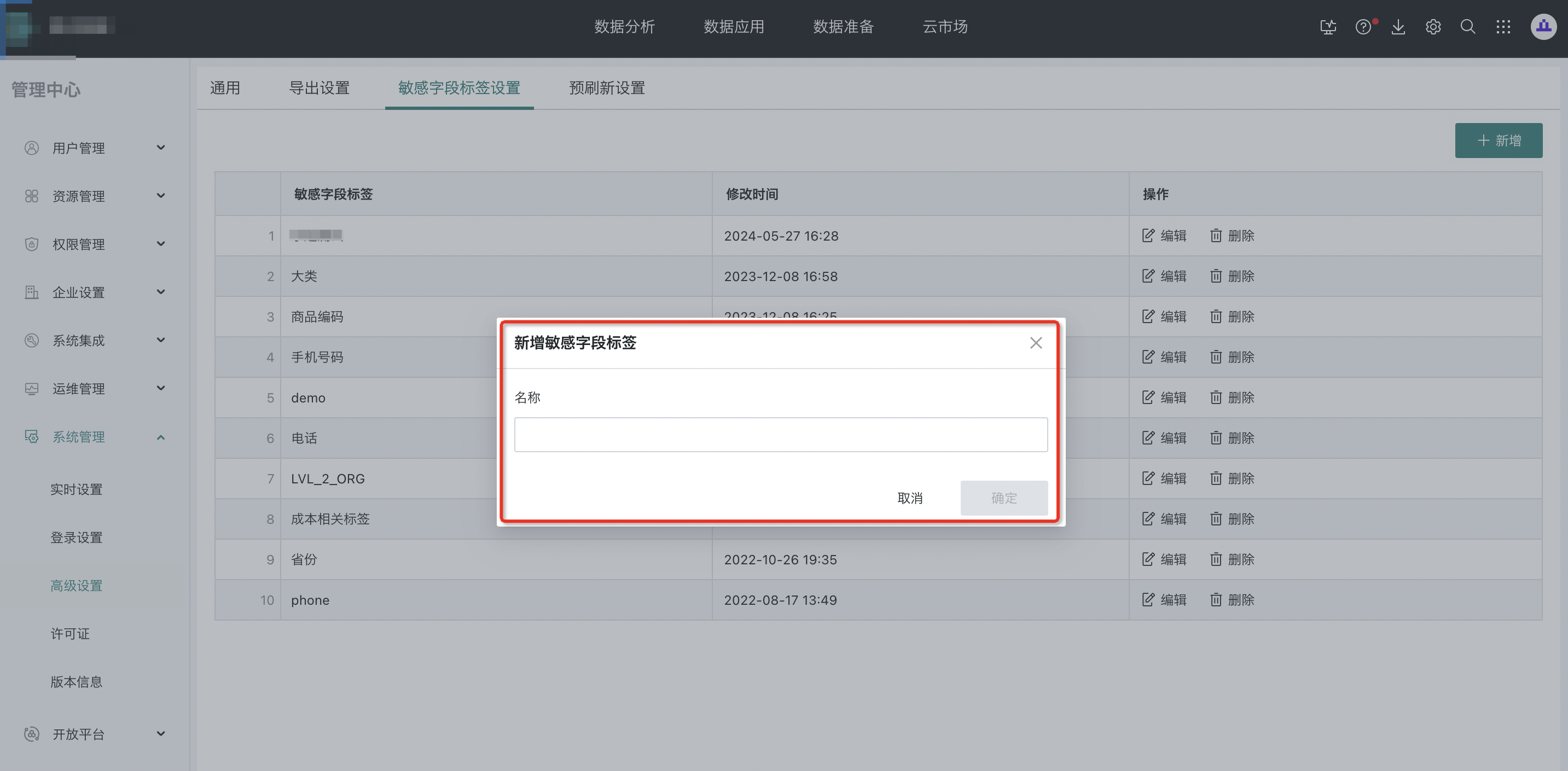
(2) Operation
Step 1: Open "Management Center - System Management - Advanced Settings - Sensitive Field Tag Settings" and click "Add".
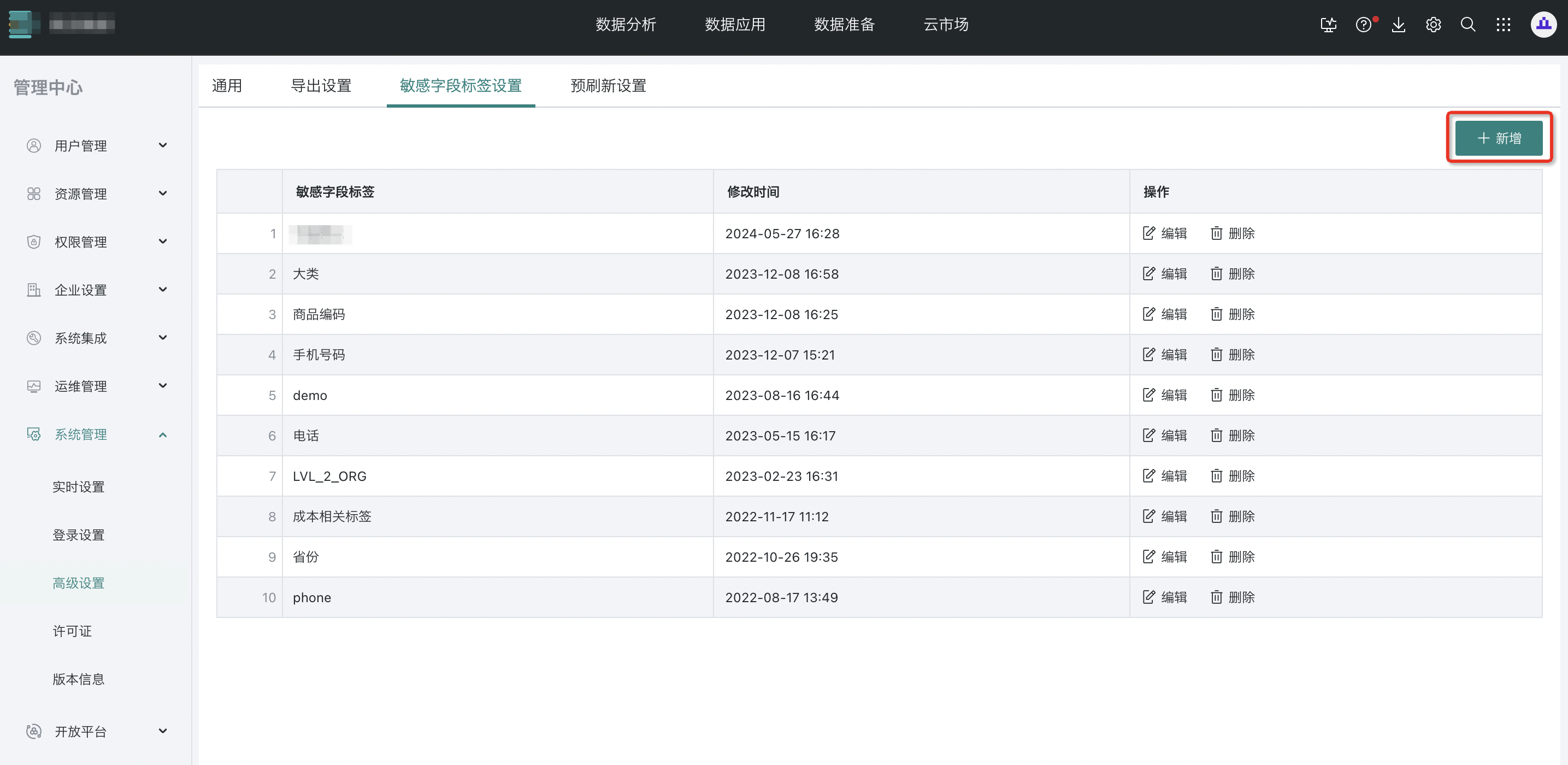
Step 2: Enter the tag and click "OK".
4.6 Detection Rule Configuration
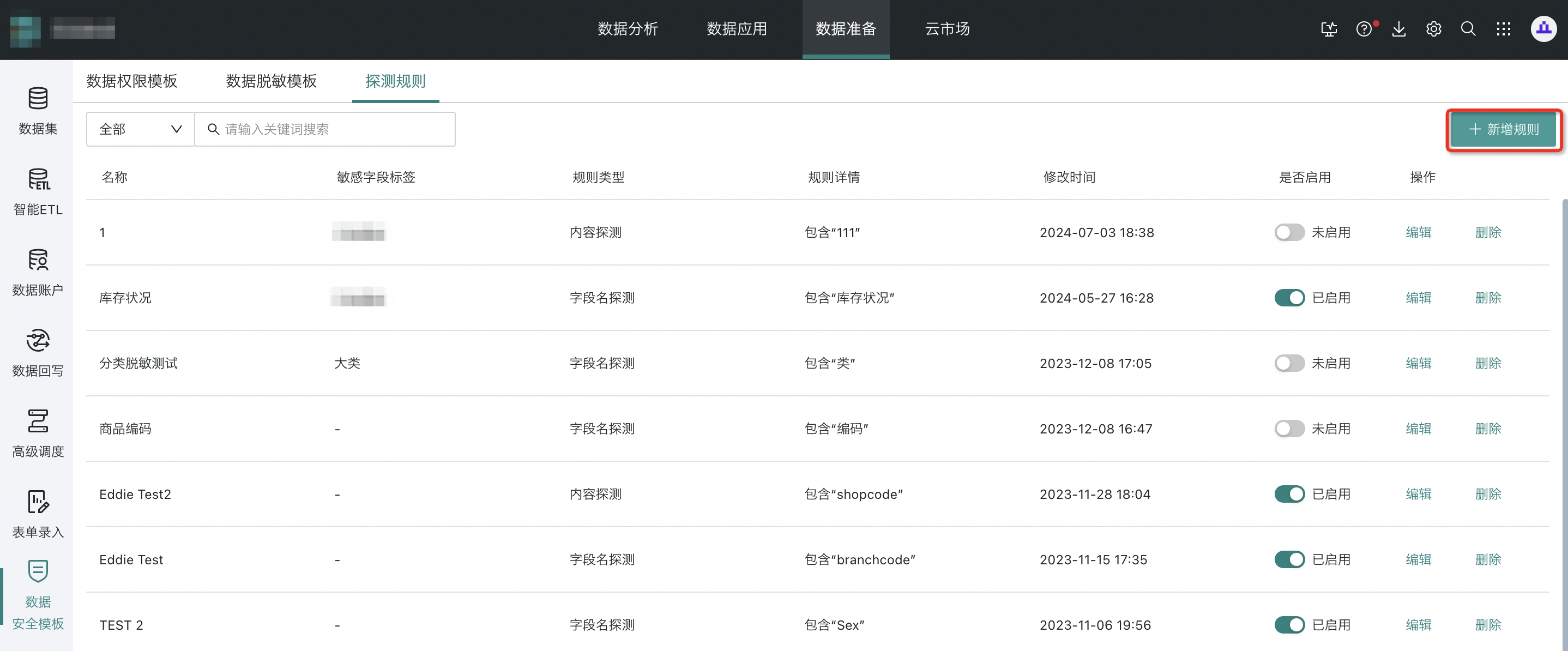
(1) Operation
Step 1: Open "Data Preparation - Data Security Template - Detection Rules" and click "Add Rule".
Step 2: Configure the rule and click "Confirm".
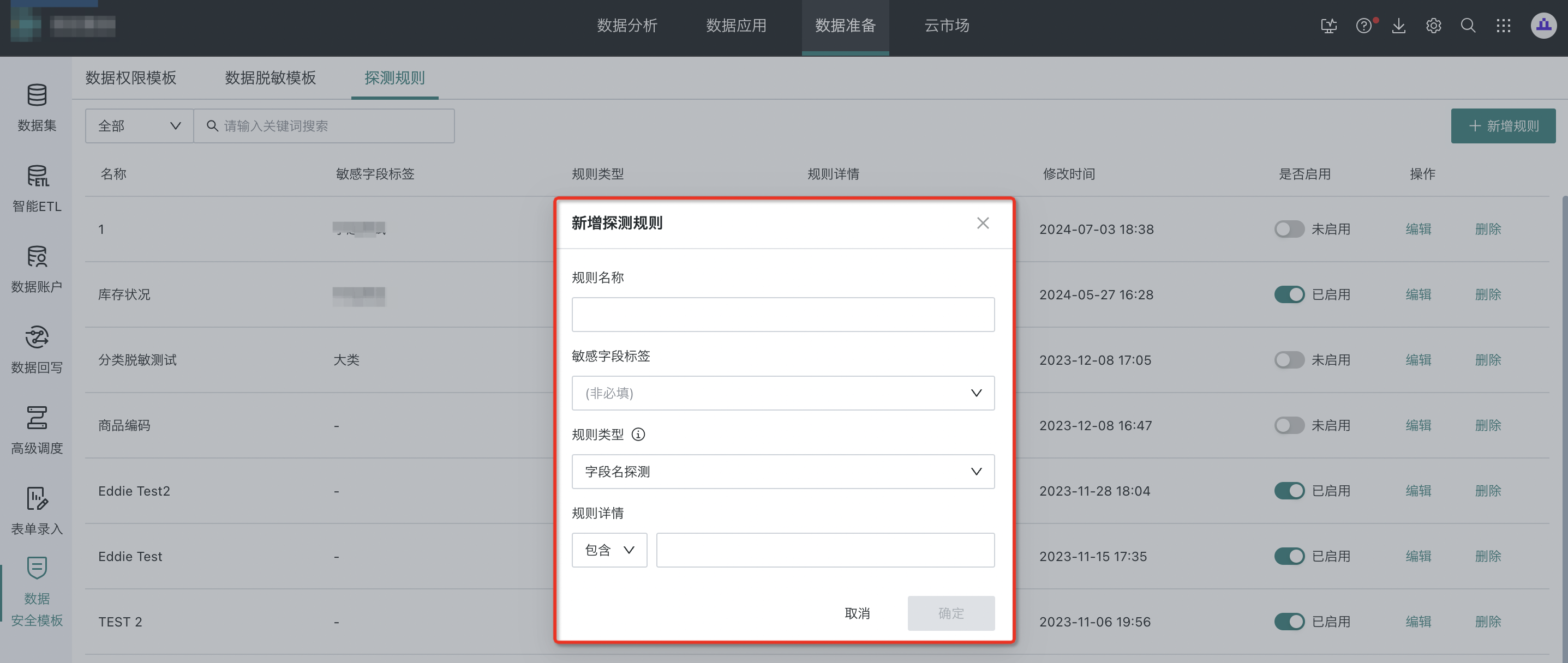
(2) Configuration Notes
Supports three types: field name detection, content detection, and hybrid detection.
- "Field name detection" and "hybrid detection" can be set to "equals" or "contains" a string.
- "Content detection" supports "equals", "contains", and "regex".
.png)
- Supports editing, enabling/disabling, and deleting detection rules.
- Supports configuring data masking tags to match masking rules in templates after detection.
(3) Detection Rule Application
- When creating a dataset, modifying model structure, generating ETL output, or on the dataset details page, enabled detection rules are applied during intelligent detection.
- Detection supports exact field name matching and content matching (if 80% of the first 100 rows match, the field is considered sensitive).
5. Glossary
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Sensitive Field | A field identified by the system as containing sensitive information, not yet masked |
| Masked Field | A field that has been masked |
| Masking Rule | The rule applied to mask a field; currently supports masking and hash masking |
| Masking Template | A set of masking rules organized as a template, improving efficiency and enabling unified changes according to company policy |
| Dataset Sensitivity Tag | After intelligent detection, the system tags the dataset as masked sensitive, unmasked sensitive, or non-sensitive based on the result |
| ETL First Run Sensitivity Inheritance | On first run, ETL output datasets inherit sensitivity tags from input datasets |
| Intelligent Detection | The process of manually or forcibly detecting sensitive data using built-in rules, which can occur when creating a dataset, generating ETL, or opening the details page |
| Forced Detection | For strict enterprise control, intelligent detection can be configured as mandatory |
| Data Masking Tag | The rule for identifying sensitive data, used to determine which data needs masking. In some sense, it is a tag for the field |
| Hash Algorithm | A basic technique for information storage and retrieval, mapping any length of key to a fixed-length hash value. Used for authentication, encryption, indexing, etc. Advantages: simple operation, short preprocessing time, low memory usage, fast matching, easy maintenance, supports many rules, etc. |
| Static Masking | Masking sensitive data and storing the masked data in a specified database location |
| Dynamic Masking | Masking data dynamically when users query sensitive data, usually by calling masking rules via API |
| k8s | Kubernetes, an open-source system for managing containerized applications across multiple hosts, providing mechanisms for deployment, planning, updating, and maintenance |
Note: This module is a value-added feature. For a trial, please contact Guanyuan Data business personnel.