Data Integration from Web Service
1. Overview
1.1. Function Description
Data integration from Web Service refers to Guandata's support for accessing API data through the Web Service data connector, which allows flexible configuration of parsing rules for API returned data and selection of required fields, and finally uses the connection to create Web Service datasets.
1.2. Application Scenarios
Webservice (web service) is a network-based distributed computing technology that allows different applications to interoperate over the network. Through Webservice interfaces, applications can access remote services and obtain data, extracting data to BI for further processing operations.
2. Usage Guide
2.1. Creating Data Connections
Function entry: Data Preparation > Datasets > New Dataset > Application > Web Service.
First, fill in the Web Service URL address, request method, request headers, authentication, request parameters, request body, pre-operations (optional), and post-operations (optional). Click "Send Request" to test the connection and view the response results, including status codes and response message body.
| Configuration Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Request Method | Supports GET/POST, default is GET: GET: generally used for requesting resourcesPOST: generally used for transmitting resources |
| Request Headers | Consists of key/value pairs, telling the server the type of resources needed. For specific parameter settings, see the following document: https://www.cnblogs.com/yunlongaimeng/p/10904558.html |
| Authentication | Currently only supports 2 authentication methods: API Key and Token: API Key: API key is the name given to a secret token of some form, submitted with Web service (or similar) requests to identify the source of the requestToken: Token refers to the permission to represent user roles and request interfaces within a specified valid time |
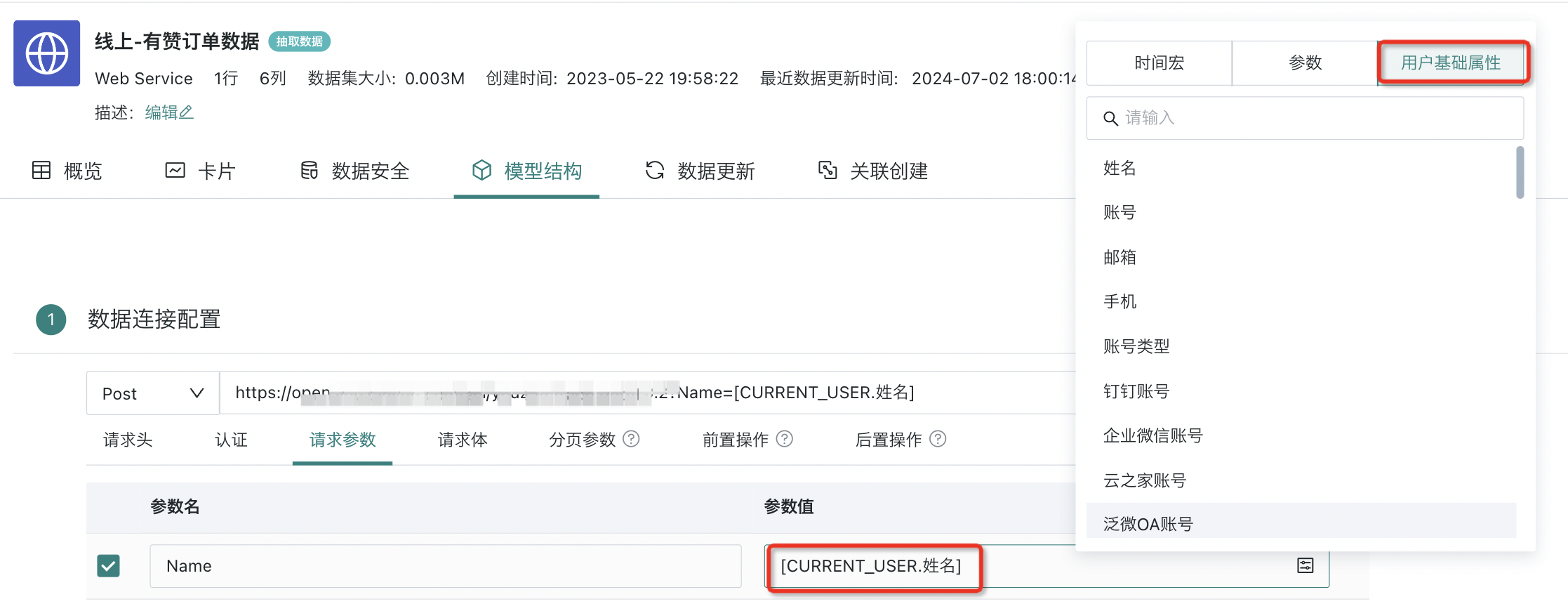
| Request Parameters | Fields and conditions that need to be obtained, and supports global parameters. See Global Parameters for details. Users can add "User Basic Properties" as parameters when creating datasets, and can also view specific parameter information in the dataset details page. After setup, when users view dashboards, the data they can see will be controlled accordingly based on parameters, ultimately making data security control more refined; at the same time, when users view data, it achieves a personalized effect. |
| Request Body | Only supports JSON format: encapsulates request parameters for POST request messages, GET has no request body |
| Pagination Parameters | When the API data source that customers need to integrate uses pagination to return data, data extraction needs to be performed through pagination parameter configuration. Currently supports two pagination methods: page number-based and offset-based. |
| Pre-operations | Each time the main API is called, "pre-operations" will be executed in advance, and supports storing partial results of pre-operations as dynamic parameters, which can be referenced in the request headers/request parameters/request body of the main API, achieving dynamic parameter acquisition |
| Post-operations | Through custom JavaScript scripts, the response of WebService requests can be intercepted, and data processing, transformation, filtering, etc. can be performed, changing it to a standard structure that conforms to the platform's JSONPath parsing method, and then data parsing configuration can be performed. See usage examples below |
- Select "Pre-operations", click "Add Pre-operation":
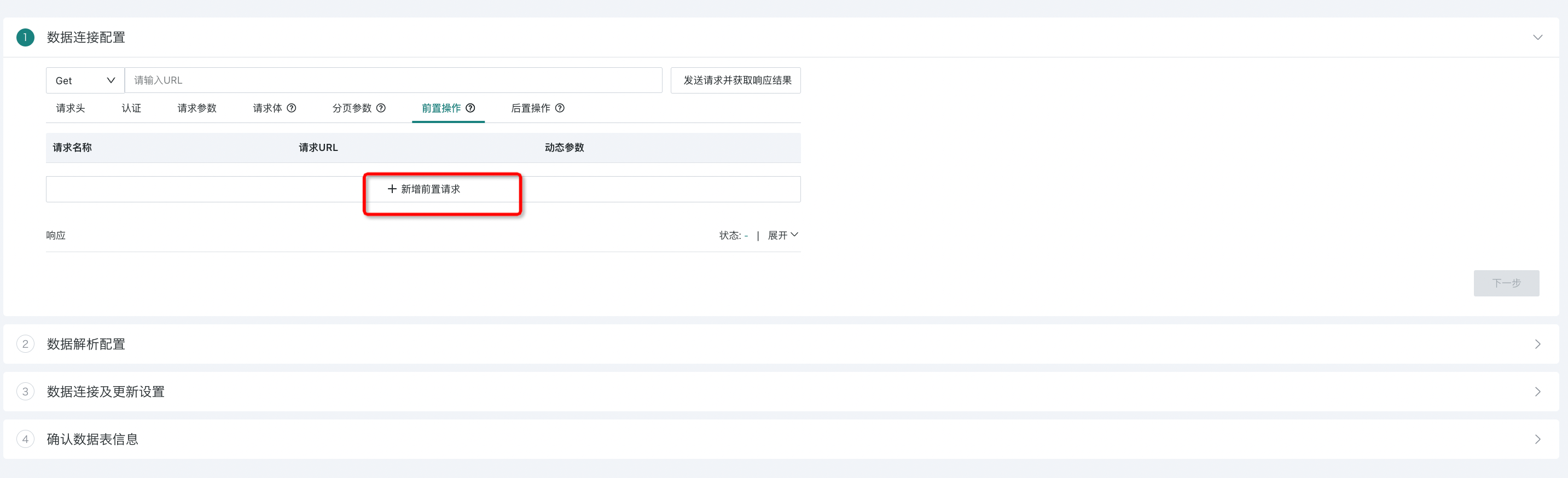
- Fill in the necessary information for the pre-execution request URL, and support adding dynamic parameters based on the response:
-
Dynamic Parameters: Parse the response content through result field paths to obtain dynamic parameter values, usually used for scenarios such as token information acquisition. Created dynamic parameters can be referenced in subsequent request parameters through ${parameter name}; *Not required, you can only execute pre-operations without passing any parameters;
-
Result Field Path: Use JSONPATH to parse the response content and obtain target parameter values.
Through the above operations, the authentication interface is used as a pre-operation, and its returned token information will be passed as dynamic parameters to the Web Service dataset configuration to be defined.
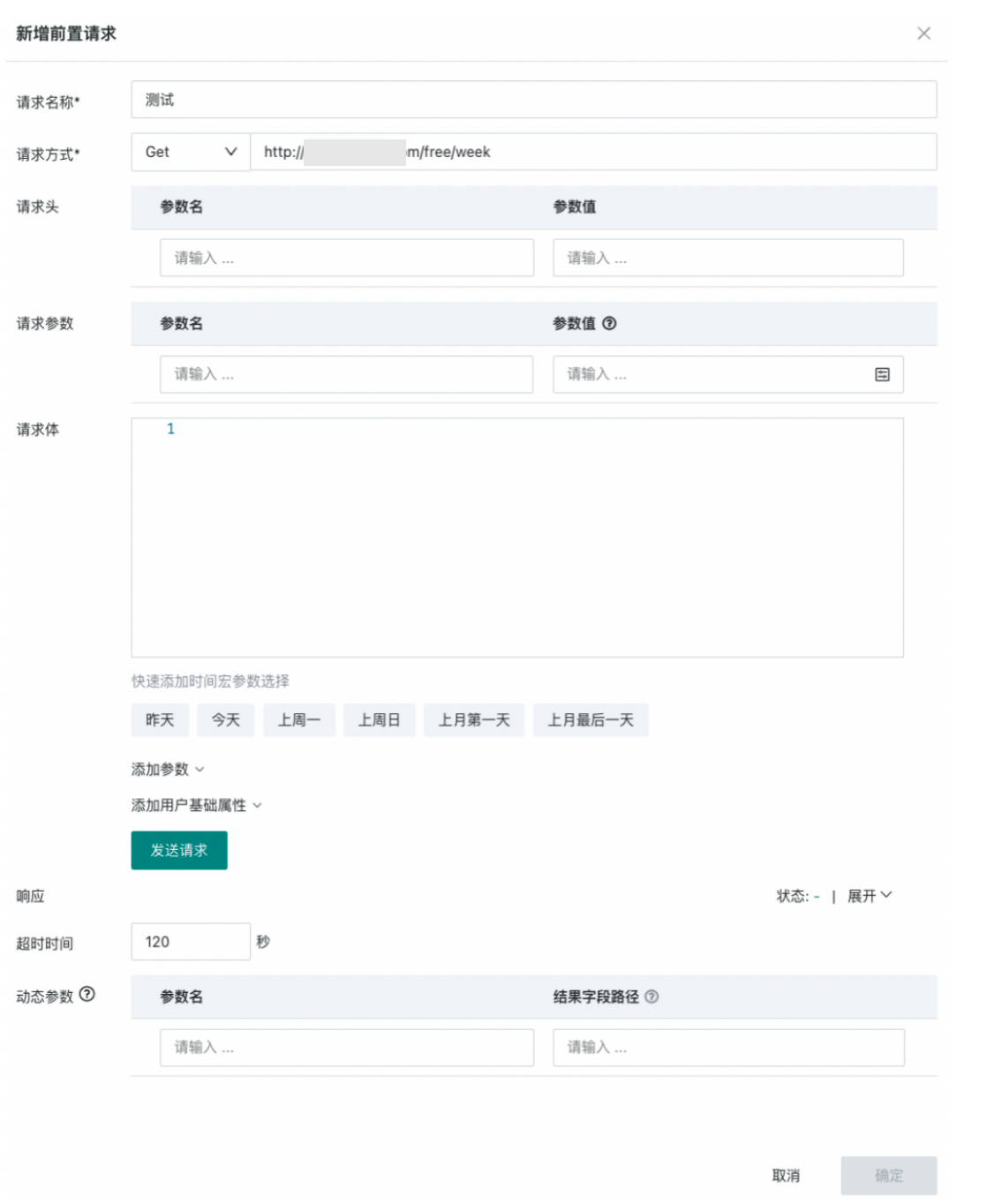
- Click OK to save the pre-operation.
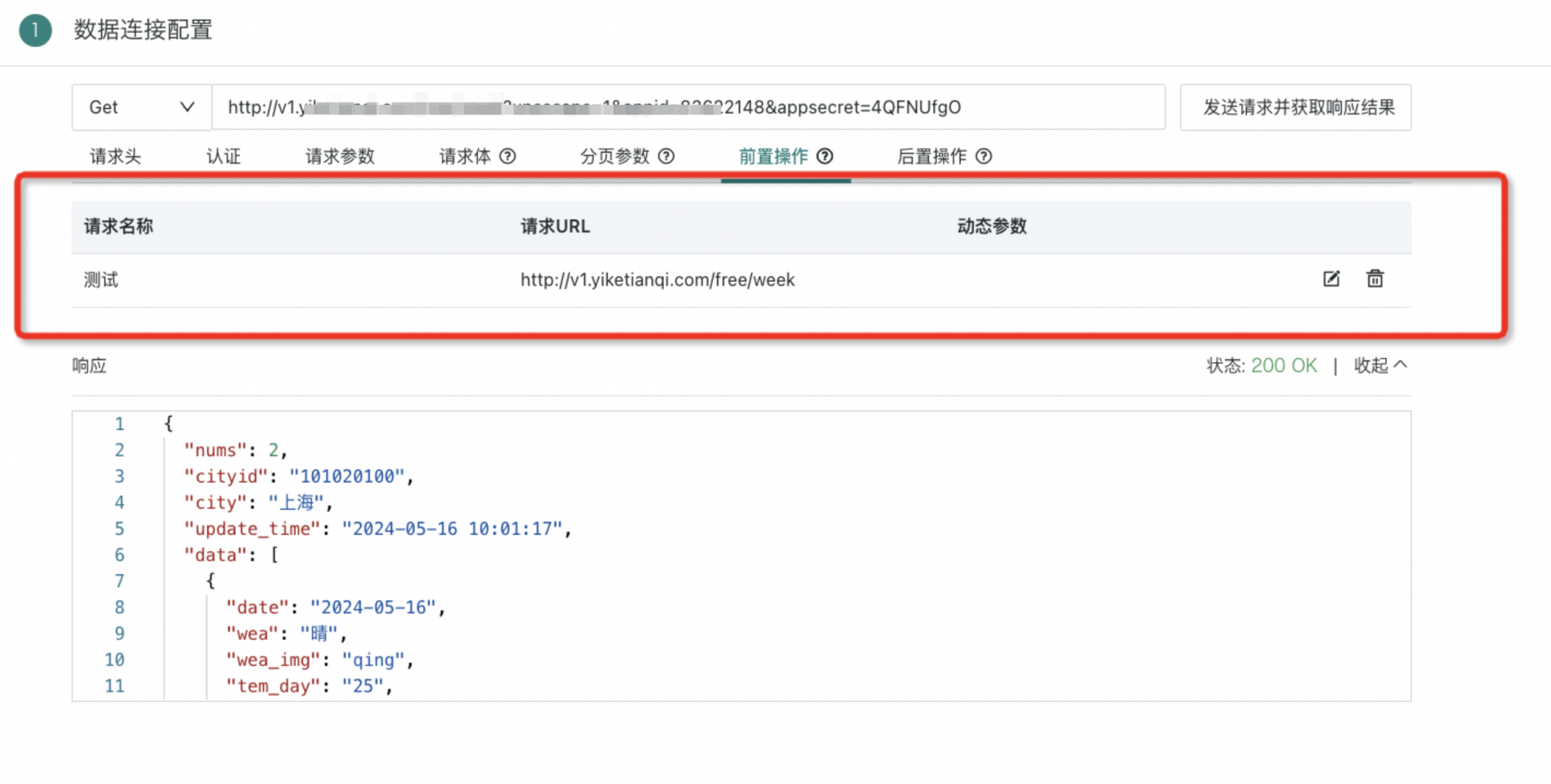
- According to the interface documentation requirements, use dynamic parameters in the Web Service dataset request headers/request body/request parameters to achieve dynamic parameter passing capabilities.
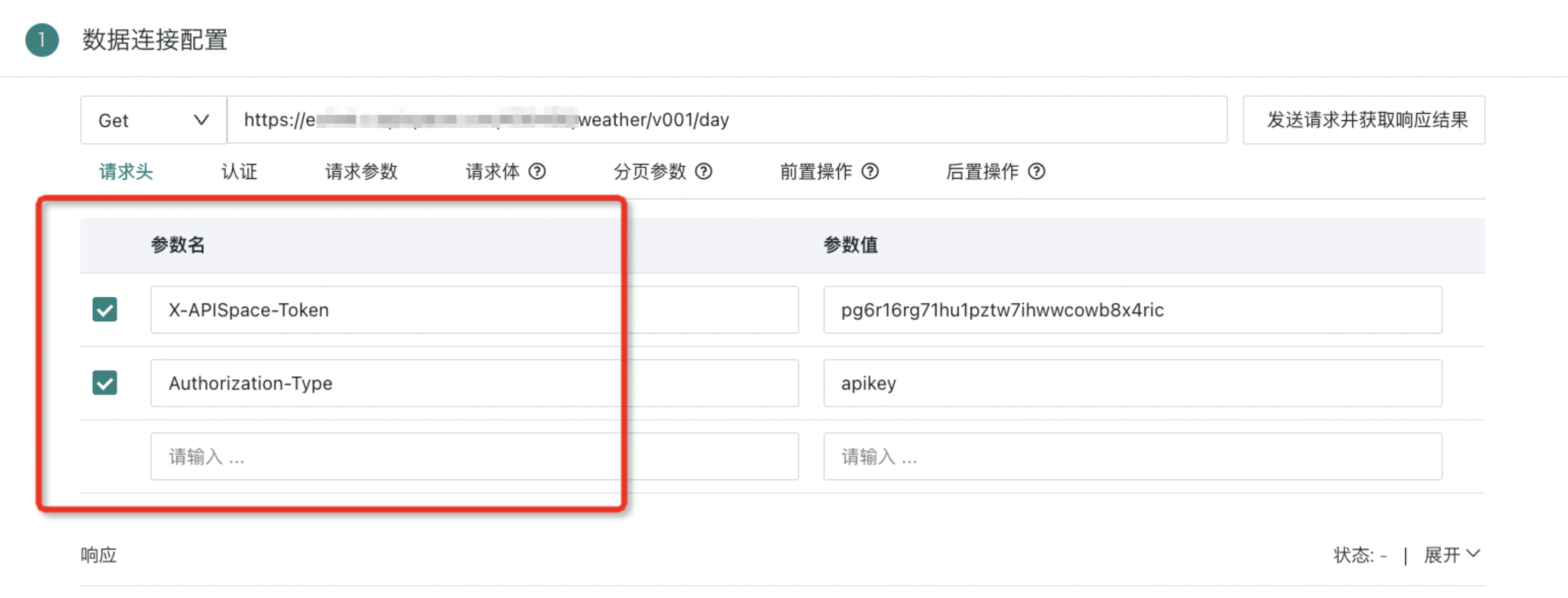
Note:
Currently, the dynamic parameter value caching mechanism is not implemented, so each time the WebService dataset is updated, pre-operations will be executed.
Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the business party's authentication API call frequency limits. If there are frequency limits, frequent calls to the authentication API may trigger its limits.
Request Parameters
When configuring request parameters, add parameter names and parameter values, where parameter values support selecting time macros, parameters, and user basic properties.
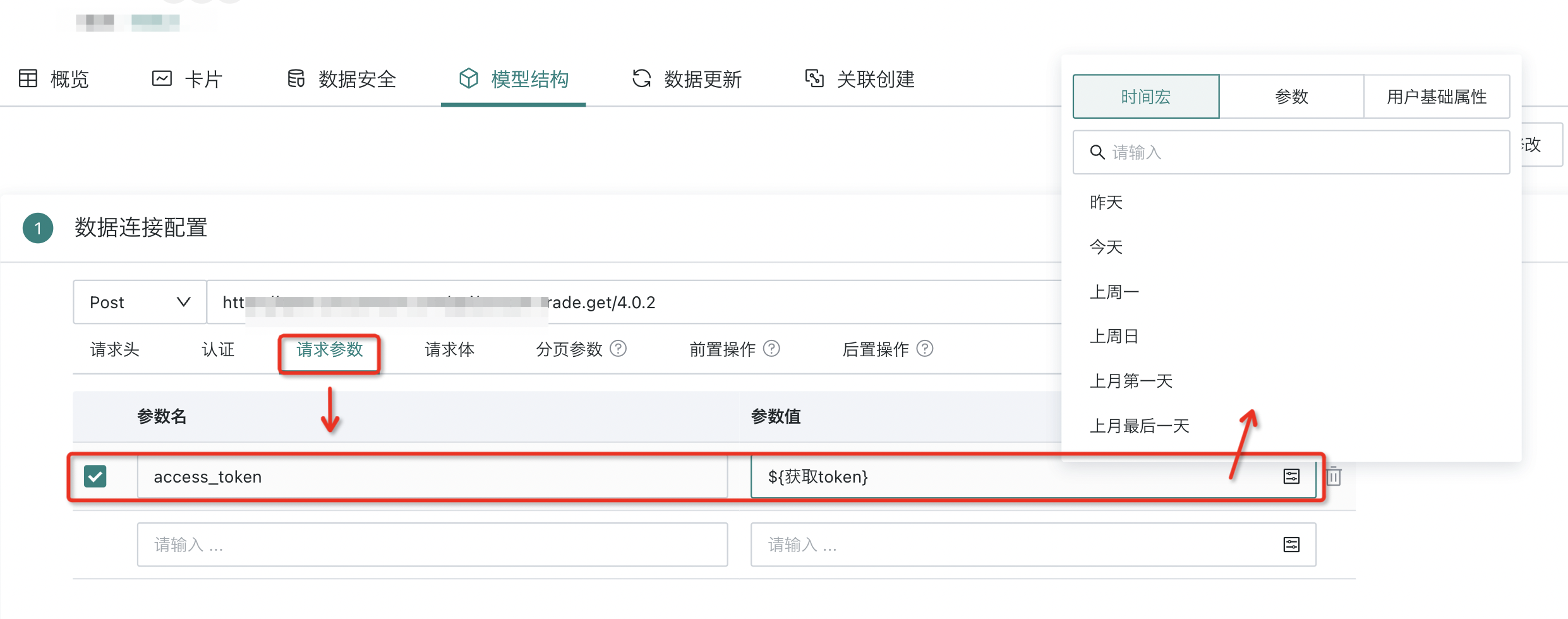
Among them, "User Basic Properties" refers to users being able to add "User Basic Properties" as parameters when creating datasets, and can also view specific parameter information in the dataset details page. After setup, when users view dashboards, the data they can see will be controlled accordingly based on parameters, ultimately making data security control more refined; at the same time, when users view data, it achieves a personalized effect.
Note: User basic properties are also supported in "Request Body" configuration.
Post-operations
Through custom JavaScript scripts, the response of WebService requests can be intercepted, and data processing, transformation, filtering, etc. can be performed, changing it to a standard structure that conforms to the platform's JSONPath parsing method, and then data parsing configuration can be performed.
Usage Example:
Define the convertJson method and return the modified response
function convertJson(response) {
//Please define the response modification logic within the method
return response;//Return the modified response to the BI platform
}
Below is a basic Response example to demonstrate the supported basic syntax:
//Original response
{
"a":1
}
Scenario 1: Adding fields
//Post-operation script
function convertJson(response) {
response["b"]=2;
return response;
}
//Modified Response
{
"a": 1,
"b": 2
}
Scenario 2: Modifying fields
//Post-operation script
function convertJson(response) {
response["a"]=2;
return response;
}
//Modified response
{
"a":2
}
Scenario 3: Deleting fields
//Post-operation script
function convertJson(response) {
delete response["a"];
return response;
}
//Modified Response
{
}
Scenario 4: Processing return content with separated structure and values into key-value pair format
//Post-operation script
function convertJson(response) {
response = response["data"];
var i_data = response["results"][0]["series"][0];
var o_data = [];
for(var i=0;i<i_data["values"].length;i++){
var temp = {}
for(var j=0;j<i_data["columns"].length;j++){
temp[i_data["columns"][j]] = i_data["values"][i][j] == null ? "null" : i_data["values"][i][j];
}
o_data.push(temp);
}
return o_data;
}
2.2. Configuring Data Parsing
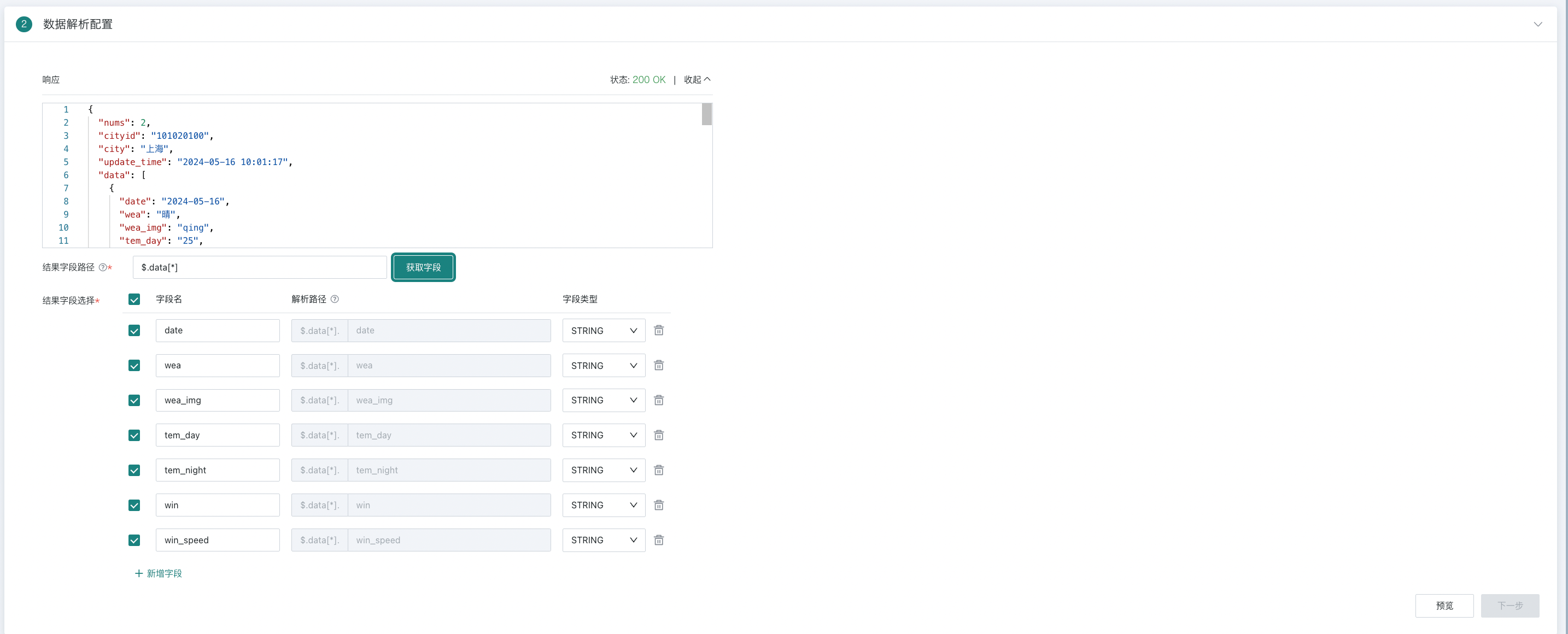
After successful connection testing, you can view the API's return structure. By using standard JSONPath rules to parse JSON, you can input result field paths (result field paths support JSON objects and arrays), and the system will automatically parse all key-value pairs (key/value) of objects under the 1-level hierarchy of the result field path and automatically display a checkbox list. If you need to further parse nested structures within them, you can refer to Using ETL to Parse JSON.
If you need to add additional key-value pairs from nested objects under the result field path, you can add them through new fields.
Finally, check the required fields, modify field names and types, and preview 30 rows of data.
2.3. Data Connection and Update Methods
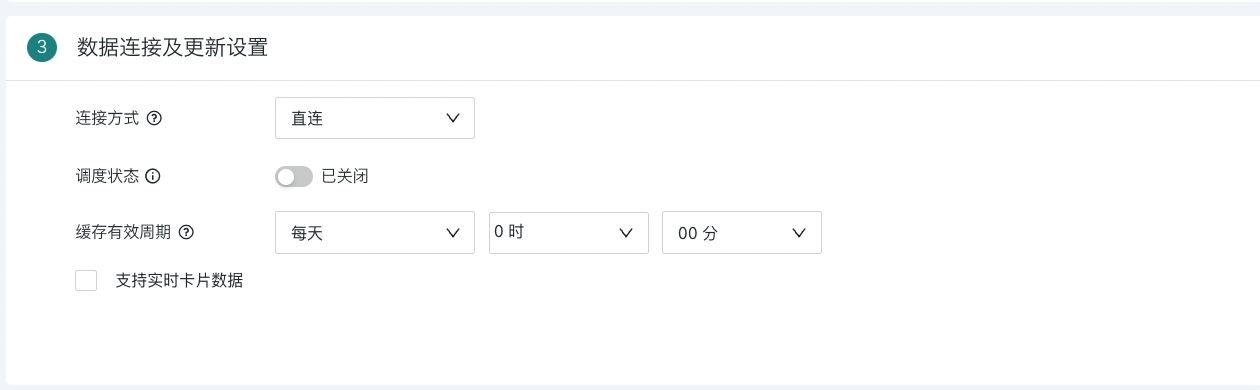
Guandata supports two data connection methods:
-
Direct Connection: Through Restful API for near real-time interface data acquisition, and visualization display through BI; at the same time, parameterized queries can be achieved through global parameters and other means. At this time, the system does not perform persistent management of extracted data, nor does it perform incremental updates. The data has real-time characteristics.
-
Extraction: Through Restful API for historical data full extraction, and configure incremental strategies to sink the obtained data as extracted datasets within the BI platform for subsequent data processing.
Direct connection/extraction and various configurations are not expanded in this article. For details, please refer to [Standard Database Connection Guide](../3-Database Data Integration/0-Database/1-Standard Database Connection Guide.md).
Note:
1. After using global parameters in interface requests, only "Direct Connection" is supported, not "Extraction".
2. When the connection method is "Direct Connection", a reasonable cache validity period can be set for the Web Service dataset, and whether to support real-time card data can be selected.
3. SOAP protocol is not supported.
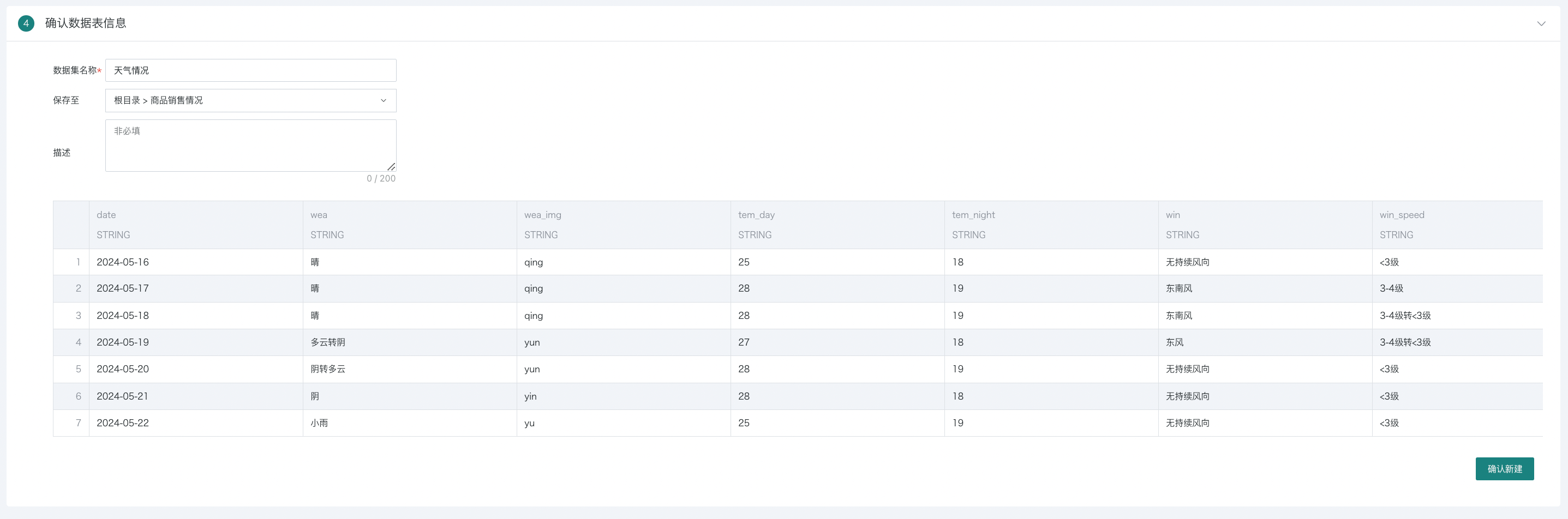
2.4. Confirming Dataset Information
Specify the dataset name and storage location, click "Confirm New" to complete dataset creation.
2.5. Dataset Model Structure Editing
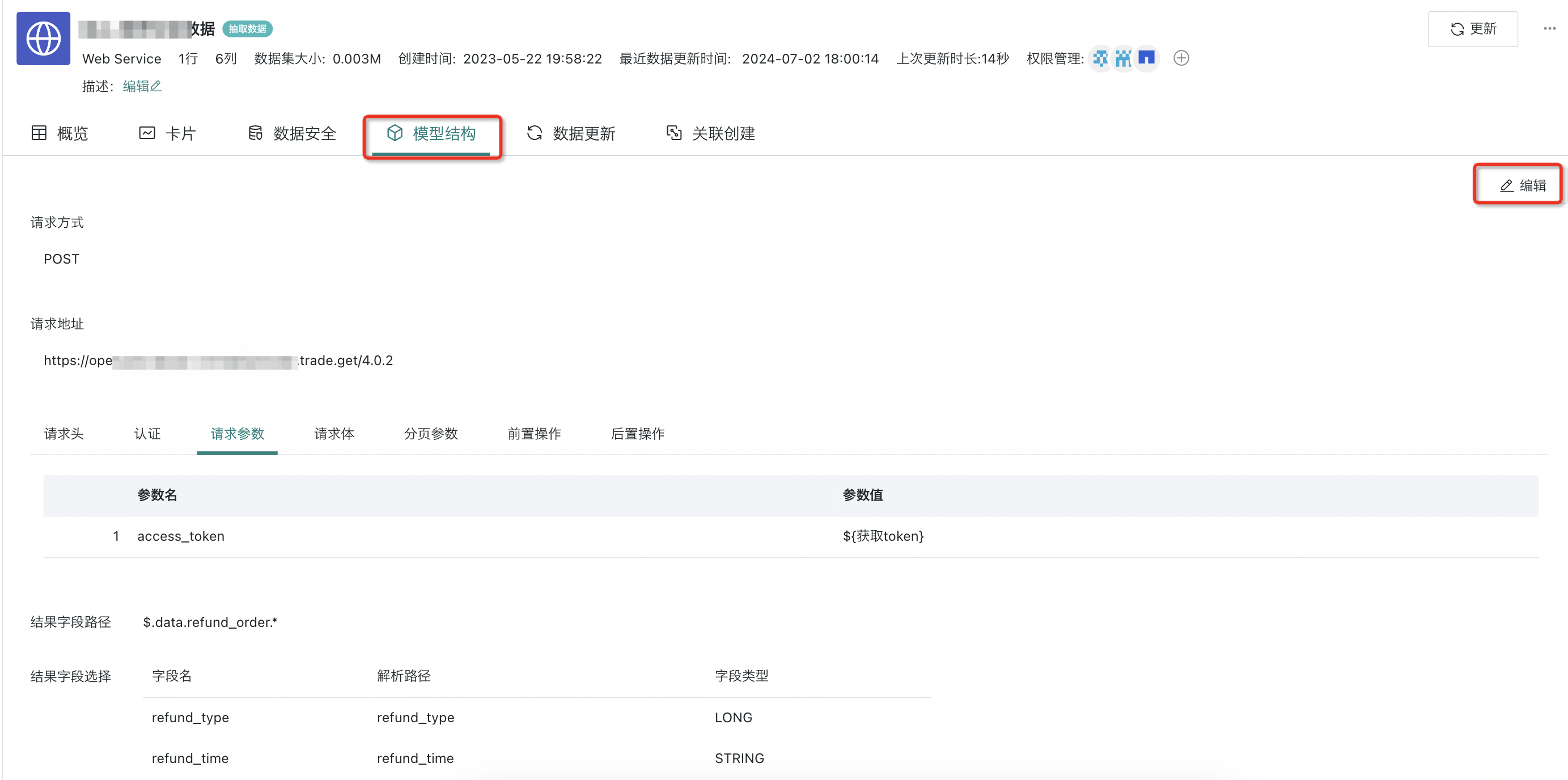
After creating the Web Service dataset, click to enter the dataset details page, where you can see the dataset overview, related cards, and data security information. On the "Model Structure" page, click Edit in the upper right corner to modify and edit the dataset model structure. The content that can be modified includes:
-
Request method
-
Request address
-
Request headers/authentication/request parameters/request body
-
Result field path
Note: For "Extracted Data" type (when creating a dataset, select "Extraction" connection method) Web Service datasets, using parameters/user basic properties as parameter values is not supported.
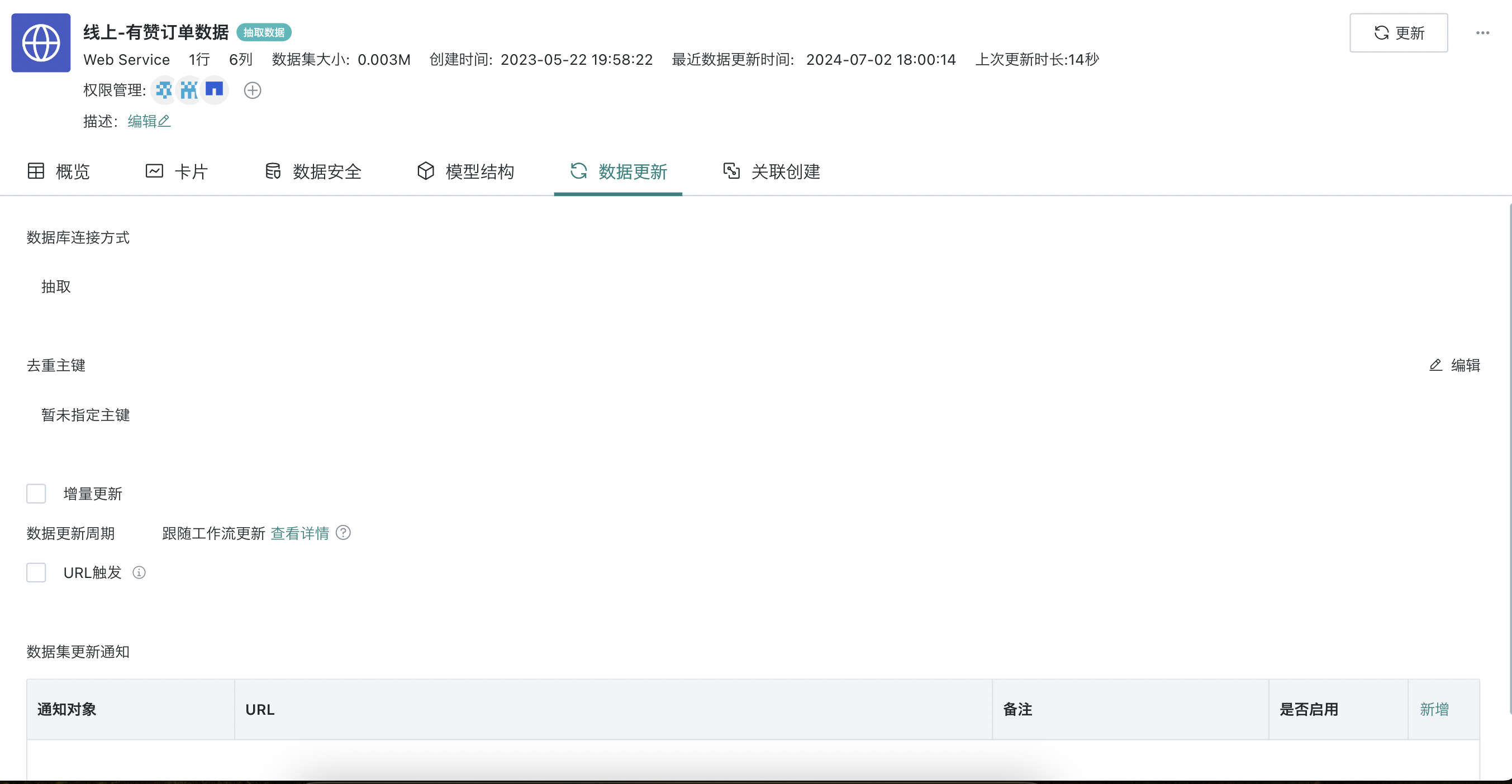
2.6. Dataset Update Settings
On the dataset details page, click "Data Update" to modify incremental update related configurations; at the same time, you can manually trigger dataset updates, including two methods: overwriting old data and appending new data. In addition, request parameters and request body also support custom modifications, and dynamic time macros are also supported.
(For more content about time macros and parameters, see Dynamic Time Macros, Global Parameters).
Note: Incremental updates can only be configured for datasets in extraction mode (when creating a dataset, select "Extraction" connection method).
For error details, see Data Volume Exceeds Allowed Threshold
3. Parameter Filling Instructions
Web Service supports supplementing global parameters, time macro parameters, user basic parameters, and tokens in request parameters, request body, and pre-operations. The filling instructions for related parameters are now introduced to help users get started quickly.
| Category | Involved Entries |
|---|---|
| Global Parameters | Request parameters Request body Pre-operations |
| Time Macros | Request parameters - Parameter value popup Request body - Quick add time macro parameter selection Pre-operations - Add/edit pre-operations |
| User Basic Property Parameters | Request body - Add user basic properties Pre-operations - Add pre-parameters - Add user basic properties |
4. Common Questions
Q: How to test when integrating API data through Web Service?
A: Free APIs available for testing can be registered by yourself. After registration, you will have free calling qualifications. The details are as follows:
-
Weather interface (Get request): https://www.kancloud.cn/ccjin/yingq/603579
-
24 Solar Terms (Post request): https://www.apishop.net/#/api/detail/?productID=88
-
Other API recommendations: https://www.zhihu.com/question/32225726